Gonarthrosis is a pathological condition that is characterized by degenerative processes occurring in the knee joint.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint is characterized by destruction of cartilage, as well as deformation of the joint, accompanied by disruption of its functions. Most often, this disease affects older women.
You can undergo a course of treatment for gonarthrosis at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic! Anyone can become our patient—metropolitan registration is not required.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a traumatologist-orthopedic specialist.
- Initial consultation – 2,700
- Repeated consultation – 1,800
Make an appointment
Current gonarthrosis
Gonarthrosis is a concept that covers a large group of diseases. Scientists have conducted studies that have shown the connection of the disease with errors in the coding of many genes. The reasons for the development of this disease cover many factors that a person cannot influence.
The disease "Gonarthrosis" is characterized by:
- Damage to the articular surface of the knee joint.
- Inflammation of the subchondral area of the bone.
- Inflammation of the synovium of the joint.
- Inflammation of the ligaments, capsule and periarticular muscles.
In English-language sources, gonarthrosis is a degenerative disease of the joint.
The spread of the disease is very wide. About 10-12% of the population has signs of knee joint destruction. This may be due to an increase in average life expectancy, since there has been a clear trend of increasing incidence with increasing age of the population.
It is believed that gonarthrosis of the knee joint occurs equally in both men and women. The only thing that should be noted is that in men the maximum number of cases occurs after 45 years, and in women - after 55 years.
What is the essence of the disease
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is destruction, dystrophic damage to the connective tissue of the cartilaginous cells of the femoral-knee joint. More often, women suffer from it, especially those who have crossed the 40-year mark and are overweight. The disease can be unilateral, arthrosis of the right or left knee joint, or bilateral, affecting one or both legs at once.
Without proper treatment, the disease progresses, affecting muscles, fibrous compounds (ligaments), and bones. Because of it, you can completely lose the ability to move: with the final destruction of the cartilage, the bone will be exposed.
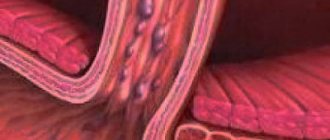
The photo shows the differences between healthy and damaged cartilage
The concepts of gonarthrosis, osteoarthritis, and deforming arthrosis are identical and are characterized by identical morphological and biological characteristics. This disease is typical for older people, but there are more and more cases when symptoms of abnormalities are diagnosed in children.
Causes of degenerative inflammation in the knee joint
Gonarthrosis is divided not only according to the intensity of clinical manifestations into 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees, but also due to the cause of occurrence:
- Primary or idiopathic is that gonarthrosis that occurs in a clinically healthy joint.
- Secondary – inflammation that occurs in the joint, in which there are signs of changes in the cartilaginous surfaces. The cause of newly emerging inflammatory processes can be a congenital pathology, trauma, or constant increased load, which provokes the occurrence of microtraumas.
Most doctors talk about the great importance of the hereditary factor, but given the multifactorial causes that influence the development of the disease, one can argue with this theory.
Important! The main pathogenetic and pathophysiological cause of gonarthrosis is the discrepancy between the mechanical load to which the joint is exposed and the ability of cartilage tissue to absorb force. Due to constant microtraumas, a large-scale inflammatory process develops, affecting all tissues that surround the joint space.
Factors that most likely lead to gonarthrosis:
- Congenital dysplastic changes in cartilage tissue (cartilage failure).
- Poor posture, which leads to a change in the axial load on the bone and joint structures of the human body.
- Constant physical stress on the joint (heavy weight, hard work).
- Vascular pathology of the lower extremities, which leads to malnutrition and circulatory failure.
- Metabolic disorders (gout or chondrocalcinosis).
- Impairment of the nervous sensitivity of the joint, which leads to pathology of the blood supply.
- Hormonal pathology, which leads to a general dysfunction of all body systems.
- A hereditary factor that has been proven only in the case of two types of gonarthrosis (primary generalized Kellgren's osteoarthritis and isolated damage to the distal interphalangeal joints or Heberden's nodes).
Therapeutic exercises for arthrosis
Considering the cause of the development of the disease (wear and tear of cartilage), many people wonder what is better: doing exercises or resting more without putting stress on the joints? There is a one-word answer to this question: exercises are extremely useful both for those suffering from gonarthrosis and for the prevention of this disease! Usually, when pain occurs, people try to give their joints rest, but this is the wrong way. Lack of mobility is the main risk factor for arthrosis in general and gonarthrosis in particular.
Performing special exercises can increase muscle strength and improve coordination. In addition, joint movement promotes the formation of synovial fluid, which acts as a lubricant and reduces friction between the joint surfaces.
Sports and gonarthrosis
What really helps? Does exercise help or is it better to rest? One thing is for sure: sports and exercise are invaluable both for those who already suffer from gonarthrosis and for those who want to prevent it! When people experience pain, they try to move the affected knee as little as possible. This is a fundamentally wrong approach, since insufficient physical activity is one of the main factors in the development of arthrosis.
Targeted training of joints affected by arthrosis helps strengthen muscles and improve coordination. When you move, more synovial fluid is produced, which contributes to less wear and tear on the articular cartilage.
The most preferred sports for patients with osteoarthritis
Preferred sports that are gentle on joints:
- Swimming
- Water aerobics
- Cycling
- Golf
- Skiing
- Walking
Undesirable “contact” sports:
- Football
- Skiing
- Tennis
- Volleyball
Determine the type of sports activity that suits you best. Avoid strenuous exercise associated with sports. If you are unsure whether you can participate in any sport, seek advice from your doctor.
Histological structure of the knee joint cartilage
In order to understand the entire process of development of the disease of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, you need to know the features of its anatomical and histological structure.
Some data on the histological structure of the knee joint:
- Cartilage consists of chondrocytes, collagen fibers and ground substance.
- The main substance contains highly polymerized proteoglycans and chondroitin sulfate, which ensures the firmness and elasticity of cartilage tissue.
- Cartilage tissue does not have blood vessels or nerve endings, so it is nourished by the diffusion of nutrients from the joint fluid, which envelops the cartilage tissue on all sides.
Histological aspects of the occurrence of gonarthrosis:
- Metabolism and sequential regeneration of chondrocytes.
- Change in the chemical composition of the main substance.
- Reduction in the amount of highly polymerized proteoglycans, which leads to an unstable collagen network.
- The cartilage loses its ability to retain water, which leads to a decrease in the cartilage's resistance to stress.
Reasons for transition of knee arthrosis to degree 2
Reasons for the transition of 1st degree to 2nd degree arthrosis:
- Late diagnosis. In the initial stages, the disease occurs almost without symptoms, so it is rarely diagnosed and most often by chance.
- Insufficiently serious attitude towards pathology, lack of systematic prevention and treatment. Patients rarely seek recommendations for the prevention of arthrosis in the early stages and even less often comply with them until the pathology worsens their quality of life.
- Provoking factors that cannot be eliminated at stage 1. These include incurable diseases that lead to weakening of cartilage (systemic, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders), age (the process goes faster against the background of natural aging of tissues), congenital defects in joint development (dysplasia), excess weight, repeated injuries, stress.
The development of stage 2 arthrosis is facilitated by a poor diet that is not rich enough in substances beneficial for cartilage, a sedentary lifestyle and heavy physical labor.
Factors for the progression of coxarthrosis: 1 – obesity; 2 – physical inactivity; 3 – hard physical labor; 4 – poor nutrition
Clinical manifestations of gonarthrosis
Clinical manifestations of gonarthrosis are manifested by disease of one or two joints. Rarely does joint damage occur above or below the pathological inflammation.
Clinical signs of gonarthrosis:
- The first symptom of the disease is the creaking of the joint when moving - not to be confused with a crunching sound (grade 1 gonarthrosis).
- After some time, irregular pain in the cartilage appears.
- The pain becomes more constant, often manifesting itself with minor physical activity. Discomfort or pain disappears at rest when the pressure on the articular surfaces disappears (grade 2-3 gonarthrosis).
- The longer a person does not seek medical help, the more intense the clinical symptoms of the disease appear.
- The pathogenetic symptom of the disease is “starting pain” - this is a special sign of gonarthrosis, which is manifested by increased pain in the knee joint at the beginning of walking (grade 4 gonarthrosis).
Important. At the diagnostic stage, it should be noted that with gonarthrosis, pain appears only when moving the joint or loading it. While rheumatoid arthritis manifests itself as pain even at rest.
Types of gonarthrosis
Based on the pathogenesis of the disease, primary and secondary gonarthrosis are distinguished. The first appears in people due to old age. While the second type of disease becomes a consequence of various mechanical injuries of the knee joint. No one is immune from the second type of disease; it can occur at both 25 and 60.
There are three stages of the disease.
First stage. At this time, the patient notes periodic pain in the knee. Pain appears when walking in the morning; as a result of movement, the joints warm up and the pain goes away. Often, dull pain occurs as a result of excessive load on the joint, goes away on its own and does not require the use of medications.
Often the patient notices a painful sensation when getting up from a chair and taking the first steps; this pain is called starting pain. As a result of warming up the ligaments, the pain goes away, but if there is excessive stress, it returns again. Over time, the pain becomes more severe, most often the source of pain is on the inside of the knee.
A crunch in the knee appears periodically, most often as a result of an awkward movement. At this stage, rapid fatigue in the knee joint is noted. Sometimes there is slight swelling of the joint, and some limitation in movement is felt.
The blood supply is also impaired, the upper part of the cartilage is dry and small cracks are already beginning to appear on it. Bone formations have not yet appeared at this stage. Meanwhile, the x-ray shows a narrowing of the interarticular space.
Externally, the knee has not yet undergone transformation and remains in its original form. Sometimes in the first stage of the disease, fluid begins to accumulate in the kneecap. Due to excessive accumulation of fluid, the joint can take on a spherical shape, movement is difficult and constrained.
Often the patient ignores the first symptoms of the disease, attributing them to overwork. As a result, the disease smoothly flows into the second stage.
Second stage. At this stage, the symptoms of the disease become more pronounced, the pain lasts longer and becomes more intense even with minor exertion. With prolonged walking, the pain intensifies. The pain goes away after rest, but reappears when moving. As the disease progresses, it becomes increasingly difficult to bend the knee.
There is stiffness in movements and some deformation of the joints is already becoming noticeable. The interarticular space becomes minimal and the bone tissue tries to adapt to the new situation, reacting with growths. They are clearly visible on x-rays.
The fluid filling the interarticular space gradually thickens. The cartilage becomes thinner and thinner. It becomes difficult to stand and walk for long periods of time. Problems arise due to flexion and extension of the knee joint; the angle of flexion becomes significantly greater. At this stage of the disease, atrophy of the quadriceps femoris muscle is often noted.
Third stage. At this stage, the clinical picture of the disease unfolds in its entirety. Persistent pain, even at rest, gait is impaired, and movements are limited. The deformation of the joints reaches such a state that they are literally pressed into each other. There is no interarticular ligament - it is completely destroyed.
Features of pain in the knee joint with gonarthrosis
Pain in the knee joints is caused by certain factors that are caused by pathogenetic processes in cartilage tissue.
Pathogenetic and pathophysiological factors of knee pain:
- The pain occurs due to reactive synovitis. Inflammation of the synovium can be caused by a large intense load or an infectious agent. Interestingly, infectious agents are often the most likely cause of the development of primary or idiopathic gonarthrosis. The infectious agent usually becomes gonococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus and other pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria.
- Friction in the joints causes “starting pains”, which are provoked by irritation of pain receptors.
- In response to pain, the muscles surrounding the joint tighten, causing a more intense pain response.
- The inflamed joint increases in size, which irritates the periarticular capsule and causes pain.
- In later stages, pain is caused by areas of ossification that occur when cartilage tissue is replaced by bone.
In any case, the fight against pain due to gonarthrosis is a powerful anti-inflammatory therapy in combination with treatment aimed at restoring cartilage tissue and combating the cause of the disease.
Reasons for the problem
The risk of arthrosis increases with age. The main reasons for modification of the knee joint are metabolic disorders in hard connective tissue and daily excessive loads.
The development of the disease is influenced by the following factors:
- Biological processes of aging. After 40, structural and functional changes and cell degeneration occur. Cartilage tissue loses its ability to regenerate.
- Problems with excess weight. The deposition of adipose tissue in organs creates additional stress on the entire body and the musculoskeletal system. People with a high body mass index are more likely to suffer from knee arthrosis.
- Poor circulation in the extremities. This leads to slow metabolism and artificial depletion of cells.
- Passive lifestyle. Physical activity should be within your capabilities, but regular.
- Diabetes. Pathology of the endocrine system is associated with insufficient production of insulin, which is involved in metabolism. In the fight against energy exhaustion, the body becomes vulnerable, blockage of blood vessels occurs, and a decrease in the elasticity of cartilage.
- Pregnancy. It may cause changes in hormonal levels and additional weight gain, which can cause problems with the knee joints.
- Dysplasia. Pathology contributes to premature wear of the cartilage cover, which threatens joint deformation.
- Injuries, especially in children: dislocations, sprains, bruises.
The risk group is headed by overweight women.
Diagnostic measures
In order to make a correct diagnosis, you need to find diagnostic criteria in a person that allow you to suspect the disease.
Pathogenetic (obligatory) symptoms of gonarthrosis:
- Knee pain lasting longer than 1 month.
- A crunching sensation when moving (put your palm on your knee and ask the patient to straighten and bend the leg at the joint).
- Morning stiffness in the affected joint for about 30 minutes (the patient often says the phrase “while I’m getting better”).
- Age over 37 years.
- X-ray confirmation of the growth of bone tissue in cartilage.
To make a diagnosis, points 1, 2, 3, 4 must be present in the patient.
Instrumental and clinical methods for diagnosing gonarthrosis:
- The synovial fluid of the diseased joint is light, viscous, cell number is less than 2000/ml.
- X-ray examination or ultrasound is better to look at in dynamics, since each patient has his own characteristics.
Read also: Medicine for coxarthrosis of the hip joint
Only the above symptoms make it possible to diagnose gonarthrosis. In the case of an atypical course, consultation with a hematologist, infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist and traumatologist is necessary.
Treatment methods
Goals of treatment of gonarthrosis:
- Reduce pain intensity.
- Improve the functional ability of the joint.
- Slow down the destruction of cartilage.
The main stages of treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
- Lifestyle changes - don’t carry heavy objects, lose weight, don’t walk for long periods of time, use a cane to reduce the load on the joint.
- Physical activity – physical therapy, massage, electrical stimulation and other methods of physiotherapy.
- Analgesic therapy - Acetaminophen 0.5-1 g 4 times a day (or another anti-inflammatory drug with an analgesic effect). You can replace Ibuprofen 400 mg 4 times a day or Zinaxin, Lycophelon, Diacerein.
- Intra-articular injections of glucocorticoids, which relieve pain very quickly.
Important! Some scientists believe that intra-articular injections of glucocorticoids lead to even greater destruction of the cartilage surface, so you should not get carried away with this procedure - no more than 3 times a year.
- Chondroprotectors are any medications containing glucosamine and chondroitin. Of course, the drugs need to be taken for a long time, and their cost is expensive. Considering the low effectiveness of drugs in this group, you can replace expensive drugs with gelatin products (jelly, jelly, marmalade).
- Detoxification therapy – taking vitamins D, C and E.
- Drugs that improve blood circulation in small vessels - Ascorutin 1 tablet 2 times a day or Pentoxifylline 100 mg 3 times a day.
Bubnovsky S.M.
For the treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, the Bubonovsky technique is used. For example, the professor’s kinesitherapy technique is widely used.
This method returns lost joint mobility by restoring normal microcirculation in the knee joint without surgical intervention.
Before using the technique and exercises, you should consult your doctor.
Physiotherapy
If grade 2 gonarthrosis of the knee joint is diagnosed, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed in addition to drug therapy. Unilateral or bilateral gonarthrosis is treated using various methods:
In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- pulse therapy;
- ultrasound;
- microwave therapy;
- hydrogen sulfide or radon baths;
- mud therapy;
- local barotherapy;
- warming applications;
- physical therapy.
The most common treatment for the knee joint is using electrophoresis. Various medications are used to eliminate the symptoms of gonarthrosis. Electrophoresis with Dimexide can reduce the intensity of joint pain. To improve metabolic processes in joints and speed up recovery, sulfur, calcium, magnesium, and zinc are used.
- Grade 2 gonarthrosis is effectively treated using ultrasound therapy. In case of cardiac dysfunction, this method is contraindicated; it is replaced by microwave therapy.
- Warming procedures help accelerate metabolic processes, which improves the regeneration of damaged tissues. Compresses based on ozokerite and paraffin therapy can eliminate the symptoms of arthrosis.
- Typical symptoms of gonarthrosis - pain, inflammation and swelling of the knee joints - can be eliminated using magnetic therapy. A low-frequency magnetic field affects the affected area, transmitting magnetic properties. As a result, joint mobility improves and their destruction is stopped.
The main thing you need to know about gonarthrosis
Compared to damage to the hip joints, gonarthrosis is less intense. The main manifestations of the disease are pain during physical activity, that is, mechanical friction in the joint.
When examining the limb, creaking (crepitus) is detected when the joint is flexed and extended.
Periodically, difficulty in flexion and extension functions occurs, which is called joint stiffness.
External signs of the disease:
- Waddle gait.
- Enlarged joint.
- Starting pain (before moving from a place, a person freezes for a moment and then just walks).
- The pain disappears when there is no movement in the knee joint.
The degree of manifestation of the disease is diagnosed according to complaints, objective examination data and the results of instrumental studies. Only after a complete assessment of all aspects of the disease can the disease be graded 1, 2, 3 or 4.
Subtleties of treating the disease at different stages
Treatment usually depends on the stage of the disease. At stages 1 and 3 it is very different, but at stage 4 it is practically not amenable to conservative methods of correction:
- Gonarthrosis 1st degree . If the disease can be detected so early, the effectiveness of treatment will be very high. Here you can perform special physical therapy exercises, go for massage and physiotherapy, and engage in treatment using folk remedies. If the patient is overweight, then he is prescribed a balanced diet for weight loss.
- Gonarthrosis 2nd degree . When this pathology is identified, it is important to reduce the load on the joints by tightening the diet and reducing the duration of walking. Be sure to perform gymnastics to strengthen the joints, and also take medications to relieve pain, chondroprotectors based on glucosamine, and intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid.
- Gonarthrosis 3 degrees . The disease is treated in the same way as at stage 2, but if the methods still do not give an effect, the pathology slowly progresses, then surgery is prescribed (damaged cartilage and growths are removed, or a joint is replaced).
- Gonarthrosis 4 degrees . This form is characterized by a complete absence of joint space. Treatment is only possible with complete joint replacement through surgery. After surgery, hard knee pads are worn to reduce the load.
Knee braces can be used from stage 2 of the disease, but they have a different design and are aimed at normalizing the position of the joint and relieving pain.
If you are lucky and the disease was found at stages 1-2, then you should immediately discuss with your doctor the possibility of using special foods and folk remedies in your diet for treatment.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint
Bilateral gonarthrosis
Bilateral gonarthrosis of the knee joint is much less common than unilateral gonarthrosis. The disease is characterized by changes typical of arthrosis, but they are localized in the knee of both the right and left legs. With this disease, patients face much more severe complications, because with bilateral damage, patients may completely lose the ability to move, and serious deformities develop in the knees of both legs. The best option is early diagnosis of arthrosis and treatment of the disease in the initial stage.
The occurrence of gonarthrosis begins with primary pathological changes that are noted in the knee joints. Primary changes in gonarthrosis occur at the molecular level.
Pathology of cartilage tissue becomes a trigger for the development of gonarthrosis in both knees. The cartilage becomes thin, capable of delamination and cracking in different places.
As the disease progresses, when the cartilage is destroyed and no longer covers the surface of the bones of both legs, the bone tissue in these places actively reacts to increased pressure: protective growths appear on it - osteophytes. However, despite this reaction, osteophytes cannot fully protect the bone surface from missing cartilage tissue, but osteophytes can cause pain and discomfort. In this case, the limbs become deformed and a visual curvature appears. If depreciation is impaired, patients begin to limp.
Gonarthrosis can be of two types, depending on the mechanism of occurrence of pathological changes. Primary bilateral gonarthrosis appears if the causes are directly related to qualitative changes in cartilage tissue. Secondary gonarthrosis is a consequence of a previously suffered disease, for example, arthritis or bursitis, after which arthrosis is their complication.
The causes of bilateral gonarthrosis of the knee joints are the following pathologies:
- metabolic disorders, as a result of which the nutrition of cartilage tissue significantly suffers, a deficiency in the supply of important components, minerals and nutrients;
- excess body weight, which increases pressure on the surface of the knee joints, causing the joints to “sag”, the intra-articular gap decreases, and gonarthrosis develops;
- vascular pathologies, in which small capillaries are prone to damage, and problems with valves arise. Gonarthrosis often appears in those patients who suffer from varicose veins;
- traumatic injuries of the knee joint - damage to the meniscus, rupture or sprain of ligaments, bruise;
- congenital defects of the knee joint, as well as foot pathologies that provoke uneven distribution of the load on the knee. For example, left-sided gonarthrosis can be a consequence of congenital pathologies of the right limb;
- previously suffered inflammatory diseases of the joints, as a result of which the quality of cartilage tissue changes, which after inflammatory processes is not fully restored, especially in older people. The most dangerous diseases are rheumatoid and infectious arthritis.
In addition to the causes, predisposing factors can also be identified that increase the likelihood of arthrosis. These include hormonal imbalances in the body, metabolic diseases, and the onset of menopause in women.
Gonarthrosis also occurs due to the body’s predisposition to pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, which can be traced hereditarily. Arthrosis can also be caused by a diet depleted in nutrients, if a person receives too few essential substances for cartilage tissue.
Types and forms of the disease
There are:
- Primary. It develops as an independent disease. More often, such knee gonarthrosis is associated with age-related changes and heredity.
- Secondary. Occurs against the background of certain diseases or injuries, for example post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
Depending on the causes, the following types of arthrosis are distinguished:
- Ischemic, associated with problems with blood supply to tissues and vascular disorders;
- Post-infectious is caused by infections, viruses, autoimmune processes;
- The idiopathic nature of the development of the pathology remains unclear;
- Metabolic is associated with metabolic disorders - gout, hemochromatosis, chondrocalcinosis;
- Involutional, as a result of age-related changes in the body;
- Post-traumatic, history of trauma;
- Dishormonal is a consequence of hormonal imbalances in the body.
Stages and symptoms
In medicine, there are three stages of gonarthrosis, but some doctors point to the fourth stage, when patients develop ankylosis, i.e. complete fusion of the knee joints and the inability to make active movements of the lower extremities.
Bilateral gonarthrosis of the 1st degree is characterized by minor manifestations, but they already worry patients. People experience pain in both knees, which is dull or aching.
It feels like the discomfort comes from the very depths of the knees. Typically, pain occurs when standing for a long time or after a long walk. In some cases, swelling of the knees can be noticed, but usually it quickly disappears, and other deformities in the knee joints have not yet appeared.
Bilateral gonarthrosis of the 2nd degree is marked by increased symptoms, which are already present in patients in the first stage of development of the pathology. The pain becomes longer lasting and may not go away on its own, but only after taking a painkiller. If you move your knees, you can hear a crunching sound in the knee joints.
Read also: Arthrosis of the feet
Patients complain of morning stiffness, which is relieved only by walking. The joints become slightly swollen, increased in size, and when moving, patients experience restrictions - the joint does not bend completely.
The image clearly shows a narrowing of the joint space
At the third stage of the pathology, all the signs that appeared earlier, at the first and second stages, reach their greatest development. Knee pain persists both at rest and with movement, and may intensify depending on meteorological conditions. Patients' gait changes, joints are limited in movement, and deformity appears: both knees either point inward or are turned outward. A diagnosis of deforming osteoarthritis is made.
Thus, if we talk about the occurrence of signs of gonarthrosis, we can summarize the following symptoms of the pathology:
- stiffness in the knees in the morning and after a long period of immobility;
- pain that occurs day or night, has a different intensity of sensation, but always manifests itself and intensifies when going up or down the stairs;
- difficulty bending and straightening your knees;
- limping gait;
- weakness in the legs due to muscle atrophy;
- crunching when cartilage breaks down and joint surfaces rub against each other.
These are typical symptoms that take on individual characteristics for each person. At the same time, at each stage there is a tendency for symptoms to intensify and the patient’s condition to worsen.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Stage 1 osteoarthritis of the knee has very mild symptoms that need to be treated very carefully.
- Inconvenience when moving, especially if the discomfort occurs in one joint.
- After physical activity, mild pain and even barely noticeable swelling appear. It is important to understand that this is not pain in the literal sense, but simply some inconvenience.
- Sometimes a slight crunch in the knee is added to the uncomfortable movements.
- Fatigue sets in faster than before.
People with similar symptoms are patients of a rheumatologist. To diagnose grade 1 osteoarthritis, he uses x-rays. The photographs show a slight narrowing of the joint plane and swelling of the joint capsule. After diagnosis, the doctor selects treatment in accordance with the severity of the disease.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, doctors first examine the patient’s knees and find out the patient’s complaints. As a standard, a blood test will be prescribed for erythrocyte sedimentation rate, rheumatoid factor, and a complete blood count.
X-ray examination of the knee joints is carried out in two projections - front and side. In the presence of arthrosis of the first or second degree, the following signs of pathology are observed:
- deformation of the bone in close proximity to the cruciate ligament;
- slight narrowing of the joint space;
- sharpening of the condyles of the femur and tibia.
The third and fourth stages of gonarthrosis are characterized by a significantly greater narrowing of the joint space. The development of osteosclerotic changes on the surface of the joint, in the place where the greatest pressure is exerted on it. Also, already at grade 3, osteophytes are clearly visible, and there may be cysts. Quite often, patients suffer from Baker's cyst and the development of synovitis. In the fourth degree, which is sometimes registered as the third, the joint space may completely disappear, which provokes ankylosis. This diagnosis is the most severe for arthrosis.
Treatment of bilateral gonarthrosis can be conservative and surgical. The choice of approach to therapy depends on the degree of the patient’s disease, because often in the later stages of gonarthrosis, surgery is the only way to help patients.
Drug therapy
In the initial stages of the disease, it is possible to stop destructive processes and relieve symptoms using a number of medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the “gold standard” in the treatment of such pathologies. Preparations are produced in various forms, but ointments and gels are mainly used to treat the surface of the diseased joint. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe intra-articular injections. The most famous representatives of this group are Diclofenac and Ibuprofen;
- hormonal drugs - supplied to the diseased joint mainly by injection, are able to perfectly relieve pain that accompanies patients with gonarthrosis of the knee joints, and also relieves inflammation if such a process has developed in the articular joint. In practice, Kenalog, Hydrocortisone, Diprospan are used;
- chondroprotectors are necessary drugs for the restoration of cartilage tissue. They contain chondroitin and glucosamine and can be either monocomponent or multicomponent. Doctors advise patients to purchase Rumalon, Structum, Artra, Dona, Alflutop. Such drugs help only in the initial stage of the disease;
- ointments that warm the joint - such drugs include Fastum-gel or Dolobene. They relieve pain due to arthrosis, warm the joint and activate blood circulation and the metabolic process;
- Vasodilators are necessary drugs that increase blood flow to damaged joints. They help effectively deliver both medications and nutrients, remove decay and waste products from the joint, and are also distinguished by their ability to relieve muscle spasms. Among the effective medicines we can recall Trental and Actovegin;
- antispasmodics – a group of drugs aimed at relieving pain that annoys patients. For this purpose, doctors recommend Mydocalm or No-Shpu.
Treatment
It is currently impossible to completely cure gonarthrosis, but the development of the disease can be significantly slowed down. This is exactly what the orthopedists at the CELT clinic focus all their efforts on. The earlier the course of treatment is started, the longer the development of pathological processes is delayed. Drug treatment consists of taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which can not only minimize pain, but also relieve inflammation. In addition, physiotherapeutic treatment and exercise therapy are used.
As for surgical treatment at the CELT clinic, it allows one to achieve positive results and is carried out only if there are indications. One of the low-traumatic but effective methods of surgical intervention is arthroscopy. It is an intra-articular procedure aimed at eliminating mechanical problems in affected joints in elderly patients.
Do you want to lead a normal lifestyle and not limit yourself to anything? Contact CELT - and we will make every effort to restore your health.
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee joint grades 1, 2, 3
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint is a fairly common disease, the leader of all arthrosis. Physicians from different countries began actively studying it more than a century ago, which has led to significant progress in the fight against the disease. At the everyday level, this pathology is persistently called salt deposition, although the calcification process does not play a priority role. The disease is dangerous in its development and can lead to limited mobility and disability.
Gonarthrosis of the knee joint requires long-term treatment, which is not always able to help without surgery. In order to avoid ending up on the surgical table, it is very important to promptly identify pathological changes and begin treatment at an early stage. Like most joint diseases, this type of osteoarthritis is easier to prevent by taking preventive measures than to treat after debilitating pain.
medi products
Orthoses that correct the position of the knee joint can be an effective alternative to endoprosthetics and pain medications.
Knee braces and orthoses: Genumedi, Collamed OA, M.3s OA and M.4s OA can be used to treat gonarthrosis at different stages.
What happens with this disease?
Gonarthrosis, or osteoarthritis of the knee joint, is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the joint caused by degeneration of cartilage, up to its complete destruction, and leading to joint deformation; at the same time, less pronounced inflammatory reactions are secondary phenomena and are also generated by degeneration processes.
The onset of pathology is usually associated with structural changes in cartilage tissue at the molecular level, including as a result of circulatory disorders in small vessels. Then hyaline cartilage is involved in the process, which becomes cloudy, decreases in thickness, exfoliates and becomes covered with multidirectional microscopic cracks. The pathological process ends with the complete destruction of the small and large cartilage, and at the same time the bone joint is exposed.
The body instinctively reacts to the disappearance of cartilage with bone growth in the peripheral zones, which is expressed in the growth of osteophytes. As a result of abnormal changes, the joint is deformed and the lower limb is bent. This result provided the name for the destructive pathology - deforming arthrosis.
Bones hurt: causes of pain and methods of treatment.
In what cases is a tubular bandage used?
How to remove plastic plaster at home - read here.
Do you have arthrosis?
- Have you tried all the remedies and nothing helped?
- Are you in constant pain?
- And now you are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that will give you the long-awaited well-being!
An effective remedy exists. Doctors recommend >>
!
Gonarthrosis often occurs after 40-45 years in women; men suffer from it a little less often.
This disease is one of the subtypes of arthrosis or osteoarthritis of the knee joint, which is otherwise called deforming arthrosis. Against the background of the disease, severe pain occurs, as a degenerative change in the cartilage occurs.
The destruction process usually begins with poor blood circulation, gradually the cartilage tissue is completely destroyed and dies, and the bones are exposed.
When walking, the bones rub against each other, which leads to very unpleasant sensations. At grade 4, severe curvature of the entire leg is possible as a result of the disease, which is why gonarthrosis of the knee joint grades 1, 2 and 3 requires treatment, including folk remedies.
Disorders with gonarthrosis
The development of the disease occurs with an increase in the following pathological disorders in the joint:
- Disturbance of the metabolic process in cartilage tissue: constant nutrition of the cartilage occurs due to the release and absorption of lubricant during joint movement, but the disease leads to changes in osmotic pressure and disruption of replenishment; In areas of high pressure, thinning of the cartilage occurs.
- Structural changes in collagen fibers: softening of the patellar cartilage begins, the shock-absorbing function of the cartilage and the metabolic abilities of chondrocytes are disrupted - the cartilage loses its elasticity and its instability appears.
- Violation of articular congruence: the synthesis of bone substance is activated, leading to the growth of osteophytes. As a result, the synovial membrane is irritated, which gives rise to an inflammatory process in it, and loss of joint mobility begins.
- The most active destructive process occurs in the inner region of the joint and in the space between the kneecap and the femur.
Read also: Arthrosis of the lower extremities
Using a knee brace
This orthopedic accessory is prescribed to prevent complications of the disease and restore the position of the joint.
The knee brace secures the joint and also helps relieve pain . Additionally, the accessory helps blood circulation and stimulates the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
The knee brace helps:
- relieve inflammation and swelling;
- limits abnormal joint movements;
- restores proper blood flow.
You need to wear it for 2-3 hours on the advice of your doctor . It should be used during movement, for example, combined with physical activity.
The product should sit comfortably on the leg and not put too much pressure on the knee. You need to select strictly according to size, measuring the circumference of your leg above and below the knee by 15 cm.
Classification of pathology
Classification of gonarthrosis is carried out in accordance with the international system ICD 10 according to code 17.0 - 17.9. Based on the etiology, there are 2 main types: primary and secondary osteoarthritis.
The primary (genuine) type is the development of a degenerative process on healthy cartilage that has not previously been exposed to pathological influences. The process becomes the result of mechanical and physiological overload. The secondary form of the disease develops on a joint that has previously been subjected to pathological effects (trauma, disease), and the onset of the process is due to a decrease in the resistance of cartilage tissue to normal loads. The most common type is post-traumatic gonarthrosis.
Taking into account the localization of the lesions, unilateral and bilateral gonarthrosis is distinguished. In turn, the unilateral form is characterized by joint damage on only one limb: right-sided and left-sided gonarthrosis. The most complex and dangerous is the bilateral type, when the knee joints of both legs are destroyed. The main reason for the appearance of this form is the age factor.
Therapeutic exercise to eliminate the disease
During an acute period of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, you cannot do gymnastics; complete rest is necessary . Exercises are introduced into the regime gradually, starting with the simplest ones.
The first sessions should be carried out with the patient lying on his back. They usually look like simply raising your straightened legs up and holding them in that position.
All exercises must be performed very smoothly and carefully. The first lesson time is no more than 10 minutes. Every day, add 2 minutes to the main time, gradually increasing the range of movements.
All exercises are shown by a rehabilitation specialist and exercise therapy trainer, only after which you can perform them yourself at home.
For gonarthrosis of the knee joint, exercises such as squats, bending and straightening the knees, long walking, and any movements that provoke pain are contraindicated.
At stages 3 and 4 of the disease, you cannot do exercise therapy and yoga. Many doctors generally prohibit the use of eastern yoga practices for joint destruction.
Exercises for grade 1 and 2 gonarthrosis
For the first degree of gonarthrosis of the knee, exercises aimed at improving blood circulation are most effective:
- sitting on a chair, straighten your leg, hold it in weight and slowly lower it. Repeat 3-4 times, alternating legs;
- lean on the edge of the chair and stand on tiptoes, fix it, hold it for a minute. Now you need to move up and down 10-20 times;
- lie on your stomach, bend one leg, lift your foot up, lift your knee off the floor and lower it smoothly, repeat with 2 legs;
- You need to complete the session with self-massage with vigorous rubbing of the inner and front part of the thigh. You need to rise from your knees to your pelvis.
For grade 2 gonarthrosis, this complex can also be used . Ideally, any physical therapy exercises should be prescribed by the doctor who is treating you.
Causes and stages of the disease
In order to start the degenerative-dystrophic process of destruction of cartilage tissue, provoking factors are needed.
The following causes of the disease are identified:
- metabolic disorders, especially hormonal imbalance;
- circulatory disorders and capillary fragility;
- excessive body weight;
- knee injuries (fracture, bone cracks, torn ligaments or meniscus);
- inflammatory diseases (rheumatism, arthritis);
- frequent and prolonged physical overload (especially among athletes - gymnasts, football players, track and field athletes, tennis players);
- endocrine system disorders;
- genetic abnormalities of tissue structure;
- hereditary predisposition, disturbance of body statics;
- age factor.
The severity of gonarthrosis is determined by the type of lesion and complications.
It is divided into 3 stages and, accordingly, 4 degrees of development:
- Stage 1 (1st degree): the initial phase, characterized by a slight narrowing of the joint space, noticeable on an x-ray. There is a feeling of discomfort in the joint, fatigue in the evening, and a slight limitation of joint mobility.
- Stage 2 (degree 2): the x-ray shows a significant narrowing of the gap and the appearance of osteophytes and bone growths. There is the appearance of a pain syndrome that intensifies with prolonged standing or walking, crunching in the joint, complicated flexion and extension of the leg at the knee, the angle of extension of the leg is limited, and signs of atrophy of the quadriceps femoris muscle appear.
- Stage 3 (degree 3): joint deformation with disruption of the leg axis, joint instability. There is a sharp increase in pain even at rest, swelling, local temperature, impaired joint mobility.
- Stage 3 with 4 degrees of severity: severe deformation of the joints, complete disappearance of cartilage, impaired mobility of the limb, pain is constant.
Diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
In order to determine the severity of the disease, X-rays of the knee joints are performed using new generation devices. Mandatory radiological signs of knee osteoarthritis include narrowing of the joint space, subchondral osteosclerosis, osteophytes at the edges of the articular surfaces, and optional ones include clearing of bone tissue.
Arthroscopy allows doctors to assess the integrity and tone of the cruciate ligaments, the severity of thickening of the synovial membrane, reveals bone growths, and the presence of fixed or loose bodies in the joint cavity. The study is carried out at an early stage of the disease, before the appearance of characteristic radiological signs. During this procedure, a targeted biopsy is performed followed by microscopy of intra-articular structures.
Using ultrasound, the pathology of soft tissues is identified, the thickness and structure of cartilage, the condition of the synovial membrane, the presence of free fluid in the joint cavity, defects of the articular surfaces and bone growths are determined. Magnetic resonance imaging is the main method for imaging hyaline cartilage. Using the study, you can obtain information about all structures of the knee joint, clarify the integrity of the ligaments, see the pathology of the tendons, and the presence of bone marrow edema as a manifestation of osteitis. There were no changes in laboratory tests specific for osteoarthritis. In some patients, C-reactive protein levels increase slightly. Sometimes rheumatoid factor is detected in a low titer, especially in elderly and senile people. Synovial fluid is sterile, viscous, transparent or slightly turbid, the number of cells does not exceed 2000 per mm3.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, the symptoms of gonarthrosis are manifested by a feeling of tightening of the muscle under the knee and a slight pain after long walks. In the mornings or after prolonged sitting, it takes time for the joint to “walk” and the discomfort in the knee to disappear. The development of pathology leads to the appearance of pain under the knee. When walking, a crunching sound is detected in the joint. Further progression of the disease limits the mobility of the joint, problems appear with squatting and straightening the legs, and lameness appears. The pain becomes stronger and longer lasting.
Visual examination of the joint in the initial stages does not reveal any changes. Gradually, articular deformation becomes noticeable, and then curvature of the lower leg. If you put your hand on your knee, you can hear a distinct crunch when you bend your leg. Palpation indicates the presence of a painful area on the inside of the knee joint.
Signs of gonarthrosis increase significantly if the disease is complicated by synovitis (inflammation of the inner lining). In this case, already at the first stage, swelling of the joint due to fluid is noticeable. At further stages, it even fills the popliteal fossa in the posterior articular region (Baker's cyst). The pain syndrome increases significantly.
The primary diagnosis is established by inspection, palpation of the joint, changes in the direction of the bones, and angularity of joint mobility. Laboratory tests are carried out using general blood and urine tests: determination of ESR, fibrinogen levels, urea and other biochemical parameters. An ultrasound of the knee joint is performed. X-ray examinations and magnetic resonance imaging are the most informative. Only after this the doctor treats the disease.
Application of traditional medicine
Recipes using specific foods and herbs can enhance drug therapy and physical therapy. In terms of effectiveness, when used regularly, they can be compared with high-quality massage for gonarthrosis of the knee joint.
It is important to follow an effective diet that will enhance the effect of the recipes: it should contain a lot of foods with calcium, as well as dishes based on decoctions of bones, jelly with animal gelatin.
However, there should not be too many protein foods; some doctors advise completely eliminating meat and milk, sour vegetables and fruits, and tomatoes. In any case, an individual diet is discussed with the doctor.
As for salt, it should be small, but there is no need to eliminate the product completely.
After normalizing your diet, you can begin to use products that help increase blood flow and have a positive effect on cartilage tissue, inhibiting degenerative processes in it.
List of the most effective recipes
Most often, treatment for gonarthrosis of the knee joint begins with both rubbing and compresses to relieve swelling, pain and inflammation. If you follow a rational diet, the following recipes will be most effective:
- Radish and honey . About 100 ml of vodka is mixed with a glass of grated black radish, honey and 15 g of table salt. Let it sit for a day and rub it into the sore knee every day.
- Provençal oil and turpentine . For rubbing and self-massage, use a mixture of 150 ml of turpentine and pure alcohol, diluted with the same amount of Provençal oil. Add 8 drops of camphor and rub in every day.
- Chestnut . An infusion with 0.5 liters of vodka is prepared from a handful of chestnut flowers placed in a glass vessel. They insist for a week.
- Burdock . Burdock leaves are soaked in water, applied to the affected knee and wrapped in cling film and a scarf.
- Natural honey . You can make compresses from honey, applying it to the knee and wrapping it with a film and a scarf.
- Ficus . Prepare a tincture from a homemade ficus leaf and 100 ml of vodka. Grind the greens in a blender and leave for 3 weeks. Rub in after a salt bath (300 g for a full bath).
- Jerusalem artichoke . The fruits of the plant in the amount of 1.5 kg are mixed with 8 liters of boiling water and kept under a lid. Immerse the sore knee in the composition for 30 minutes, repeat for 10 days.
- Dandelion . Dandelion leaves and flowers are poured into a glass vessel to the middle and filled with triple cologne. Let it sit for a month and rub it into the knee. You can eat 5 leaves of the plant every day to enhance the effect.
- Dry garlic, celery and lemons . This tincture will be very effective when taken orally. The components are mixed in a blender and placed in a 3-liter jar (take 250 g of celery root, 120 g of garlic and 3 lemons). Fill it to the top with boiling water and leave it in a warm place overnight. Treated for 3 months. Take 70 ml 30 minutes before meals in the morning. Gradually increase to 3 doses per day.
- Black beans . Black bean grass is collected, dried and ground. Infuse in a thermos like simple tea. They take it for a month and take the same break.
- Clay compress . Blue or red clay is used for it. Do not allow the product to come into contact with metal. Dilute with water to the consistency of sour cream and apply a 2 cm layer on a cloth. Press it to the knee, wrapped in a damp towel. Wrap with a bandage and a woolen scarf, remove after 2 hours.
In parallel, it is necessary to carry out drug treatment to eliminate inflammation, pain and other processes characteristic of the disease.
But is it possible to play sports? The answer will depend on the type of physical activity desired . But exercise therapy for gonarthrosis of the knee joint is indicated for almost all patients with grade 1 and 2 disease.
Tactics and methods of therapy
The question of how to treat gonarthrosis of the knee joint is decided by the doctor, taking into account the stage and severity of the disease.
In general, treatment is carried out comprehensively, but usually includes the following stages:
- Elimination of the inflammatory reaction: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - Diclofenac, Olfen, Diklak, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen, Meloxicam, Nimesulide; in the complicated stage, injections with the introduction of hormones are used - the drugs “Hydrocortisone”, “Kenalog”, “Diprospan”; To stop degenerative processes, antienzyme agents are prescribed - “Contrikal”, “Ovomin”, “Gordox”.
- Anabolic and anti-catabolic effects, restoration of cartilage tissue: chondroprotectors - “Structum”, “DONA”, “Rumalon”, “Alflutop”, “Mukosat”.
- Normalization of blood circulation, warming and calming effect: ointments, gels, creams - “Finalgon”, “Fastum Gel”, “Nicoflex”, “Apizartron”, “Feloran”.
- Improving blood circulation, strengthening vascular tissues: vasodilating drugs - Cavinton, Trental, Actovegin, Upsavit, Ascorutin.
- Reducing muscle tension: antispasmodics - “No-shpa”, “Mydocalm”, “Tizalud”.
- Restoration of synovial fluid: substitutes - “Ortovisk”, “Hialual”, “Fermatron”.
Complicated forms of the disease are treated using additional methods, such as: oxygen therapy (oxygen administration); introduction of stem cells; laser therapy; introduction of the protein drug “Orthokine” based on blood serum.
In the last stages of gonarthrosis, the only effective method is surgical treatment. Surgery is performed to replace the affected tissue. Depending on the severity of the disease, the following operations are performed:
- arthrodesis (removal of destroyed cartilage along with the joint);
- arthroscopic debridement (removal of deformed cartilage using an arthroscope);
- osteotomy (fixing bones in a different position);
- endoprosthetics.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of second-degree gonarthrosis
Physiotherapy for gonarthrosis is as important as drug intervention. To achieve maximum results, it is important to start using physical therapy as early as possible. It is most correct to do this at the very initial stages of the development of the disease. Then there is a high probability of keeping the joints in “working” condition for as long as possible.
Some physical procedures can not only significantly reduce pain and eliminate inflammation, but also increase the effectiveness of the use of medications.
Based on the intended purpose, physiotherapeutic treatment can be divided into three groups.
Pain-relieving physiotherapy. Ultraviolet irradiation copes with this task better than others. A beam is shined on the affected joint until slight redness appears on the skin. Due to this effect, a substance is synthesized in the tissues, which reduces susceptibility to pain. The number of procedures is determined by the attending physician depending on the patient’s condition. On average, one course lasts 5-7 procedures.
Magnetic therapy provides a good analgesic effect. This procedure improves blood flow, improving the endocrine system of the entire body as a whole. Magnetic therapy quickly relieves pain, relieves inflammation, and relaxes muscles, which is especially important when spasms occur. That is why this physiotherapy is often prescribed to patients with second degree gonarthrosis. The course can take from 10 to 25 procedures, depending on the severity of the disease.
Anti-inflammatory physiotherapy. This effect can be achieved by infrared laser therapy, low-intensity UHF treatment and high-intensity centimeter wave exposure.
The first procedure relieves pain and stabilizes blood flow in the tissues. Due to this process, nutrition is established in the joint tissues. As a result, swelling goes away and the inflammatory process decreases. One session should last at least 5-10 minutes. To obtain a stable result, you need at least 10 sessions.
The UHF course will not allow diseased tissues to affect healthy cells nearby. Effectively removes swelling. Timely therapy will quickly restore cartilage tissue. This procedure is especially good in combination with intra-articular injections of anti-inflammatory action. For noticeable positive dynamics, 10-12 sessions of no more than 10 minutes each are required.
The centimeter wave procedure also leads to improved blood flow, which allows you to saturate the joints with important elements. By heating diseased tissues in waves, lymph flow is improved. This therapy is most effective in the first and second stages of the disease. At later stages, it is practically useless. To achieve a therapeutic result, you need to carry out at least 15 procedures for 15-20 minutes.
Physiotherapy that improves the nutrition of joint tissues. Quite a few procedures cope with this task - ultrasound, speakers, amplipulse therapy, Darsonval apparatus, interference therapy, baths.
Ultrasound is most often used to improve the motor function of the joint by stabilizing nutrition and relieving inflammation. A full course requires at least 15 procedures.
Diadynamic therapy also improves the nutrition of the cells of the cartilage part of the joint. Atrophied muscles are stimulated. To achieve a positive result, you need at least 12-15 sessions, their duration reaches half an hour.
Amplipulse therapy is in many ways similar to the effects of speakers, but its effect is much stronger. It improves the penetration of drugs into deeper layers, improving the therapeutic effect. At the second stage of gonarthrosis, about 15 procedures of 10-15 minutes each are required.
The principle of interference therapy is based on the impact of current of different frequencies on diseased areas. It has a wide range of positive effects, improving blood flow, improving nutrition of joints, relieving pain and swelling. At the second stage of gonarthrosis, procedures should be carried out daily; in case of severe pain, they can be increased to two procedures. Session time ranges from 5 to 30 minutes.
Darsonvalization promotes the active production of ozone and nitrogen oxides, which are vital for the restoration of articular cartilage. The course requires 10-20 procedures of 15 minutes each.
Therapeutic baths. They are often prescribed as an adjuvant to relieve swelling and pain. The procedure allows you to establish nutrition for joint tissues and improves microcirculation. Baths can be not only based on herbs, but also radon, hydrogen sulfide, and bischofite.