Vaginal discharge is a topic that women are embarrassed to talk about openly. Many of them resort to the Internet to find out how to treat discharge and itching at home. However, such tactics are not always justified: true information is posted only on medical websites (not on forms!), the knowledge gained will help to figure out whether everything is okay with the female body and suggest the cause of painful symptoms. In any case, a reliable diagnosis can only be made by a qualified gynecologist after conducting a series of examinations.
White discharge in women
White discharge in women and girls who have reached puberty is considered normal. Often bad thoughts arise because of this. White discharge may be accompanied by itching and an unpleasant odor, and vice versa.
First of all, they mean that the vagina displaces dead cells, blood, mucus and other waste products. In other cases, leucorrhoea portends the development of pathologies or diseases.
You need to know that girls have more discharge than women. This happens due to unformed hormonal levels.
Important Tips
Normally, intermenstrual discharge is transparent and does not have an unpleasant odor. In the middle of the menstrual cycle, their number increases slightly. To maintain freshness and cleanliness in this case, it is recommended to use daily napkins or pads, which, in addition to additional comfort, keep your underwear clean. An unpleasant smell of discharge in women may indicate abnormalities in the functioning of the genitourinary organs and reproductive system. In this case, you should not delay going to the doctor. The specialist will prescribe an examination, determine the causes of the disorders and draw up a course of treatment.
Causes of vaginal leukorrhea
A woman cannot independently determine the reasons for the formation of white discharge. The occurrence of pain in the vagina becomes a dangerous sign for the female body.
The following reasons for this discomfort are noted:
- Infection.
- During menstruation.
- Feeling pain during menopause.
- Pain before, after and during sexual intercourse.
- Psychological or psycho-emotional factors.
- Dryness of the vaginal mucosa.
Possible complications
Only timely, high-quality treatment can eliminate unpleasant consequences. Neglect of clearly alarming symptoms often leads to serious consequences and infertility.
It is important to know! Vaginal candidiasis is not a dangerous disease only if measures are taken in a timely manner.
Pregnant women should take special care of their health. Advanced forms of the disease often provoke miscarriage and infection of the fetus.
The doctor will talk about the causes of candidiasis in women in the video:
Discharge without odor
White, odorless discharge becomes more abundant during ovulation. They become thin, more watery than after menstruation.
When leucorrhoea has a thick consistency, this discharge usually accompanies sexual intercourse. The vagina is capable of producing natural lubrication so that a man's penis can easily enter.
Non-dangerous leucorrhoea may increase in the amount of secretion released in the early stages of pregnancy. The body thus creates protection for the fetus to prevent pathogenic bacteria and infections from entering. The use of intrauterine devices and special creams can cause odorless white discharge.
If leucorrhoea does not go away
Girls may experience constant white spotting due to:
- the onset of inflammation due to improper intimate hygiene;
- presence of problems with heart function;
- the occurrence of an imbalance of metabolic processes in the body;
- designations of the initial stage of sexually transmitted diseases;
- development of cervicitis (endocervicitis);
- presence of cervical ectopia;
- foreign objects entering the vagina;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- formation of genital fistulas (fistulas);
- the occurrence of cancerous tumors in the organs of the reproductive system;
- manifestations of an allergic reaction to underwear or condoms;
- violations of the vaginal microflora;
- development of diabetes mellitus.
If white discharge appears, you need to contact a gynecologist to establish an accurate diagnosis and select effective treatment.
Discharge with odor
The appearance of leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor may indicate the presence of infections and bacteria in the vagina.
The following factors are considered to be the causes of this secretion:
- Thrush or candida fungus infection. Symptoms of thrush include copious, curd-like discharge. Along with this, itching and burning occurs in the vagina. Leucorrhoea has a sharp, sour odor.
- If bacterial vaginosis occurs , then the connections between microbes in the acidic environment of the vagina are disrupted. The leucorrhoea released is gray in color and quite abundant. In some cases they are foamy. This disease is characterized by an unpleasant fishy odor.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Trichomonas colpitis disease. It is difficult to distinguish due to the variety of features that are similar to other factors. The discharge is usually purulent, profuse, and may be foamy and thick. The color is greenish. You should pay attention to at least one of the signs so that it does not turn into a serious disease.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules . A common cause of profuse leucorrhoea with an unpleasant odor is considered to be poor hygiene of intimate areas. If you don't take care of yourself, bacteria can multiply quickly. Against this background, diseases of the genital organs arise.
Prevention
The occurrence of white cheesy discharge can be avoided. To do this, it is necessary to follow preventive measures.
They include the following rules:
- take care of intimate hygiene - and a woman should not overdo it, it is enough to wash herself once a day, and during menstruation the figure increases up to 2 times;
- take medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- avoid frequent douching with antiseptic solutions;
- use toilet paper without dyes;
- eliminate stress;
- purchase underwear made from natural fabrics, choose clothes according to size;
- dress according to the weather;
- purchase housing in ecologically clean areas of the city;
- timely treat various diseases;
- eliminate bad habits;
- use contraception when in contact with a partner;
- refuse rough contacts with a sexual partner;
- be examined by a therapist once every 6 months;
- sign up for a body examination once every 12 months;
- As a preventive measure, take antifungal medications with your partner.
Why does white discharge appear?
Leucorrhoea means a normal state of the body if it is odorless. White discharge that causes discomfort and has negative deviations from the norm requires consultation with a specialist. The characteristic symptoms of the disease must be treated in the early stages. In the future, they can turn into pathology.
Discharge before menstruation
Throughout the menstrual cycle, leucorrhoea can change.
This happens due to hormonal instability of the body. A few days before and after ovulation, the secretion becomes thick. Before menstruation they turn white. The consistency is more like creamy. Not many women can celebrate the end of the luteal phase. The secreted secretion changes and becomes thick, even viscous.
White discharge means a natural reaction of the body. They moisturize the vaginal mucosa and prevent infections and harmful bacteria from appearing. Another function of leucorrhoea is the removal of dead cells from the body.
If they are spotting, then these discharges indicate the presence of pathology. Some symptoms may be accompanied by a delay in menstruation. They can be stringy and cheesy. It is necessary to consult a gynecologist if unusual formations begin to appear from the vagina.
During pregnancy
- When a woman carries a child, an increase in hormones occurs in her body . Also due to pregnancy, there is increased blood circulation in the genital area. The resulting discharge means a normal reaction.
- If profuse leucorrhoea occurs, the cause is considered to be synthetic or tight clothing . During pregnancy, it is necessary to take care of personal hygiene. White vaginal discharge does not affect the course of labor and the condition of the fetus.
- In the early stages of pregnancy, yellowish discharge may occur. They talk about the presence of diseases or pathologies. Usually in pregnant women this is associated with fungal infections or sexually transmitted diseases. In some cases, sexual activity should be reduced.
- Brown vaginal secretion during pregnancy is considered a negative sign . If they look like bloody discharge, then this threatens the health of the unborn baby. For a woman, this implies the threat of miscarriage.
- Curdled leucorrhoea during pregnancy means candidiasis. They may be abundant, but do not change in color. Then the resulting secretion may contain E. coli. During pregnancy, a woman may experience bacterial vaginitis.
In the later stages, women experience discharge that is confused with leucorrhoea. The mucus plug may liquefy during this period. Afterwards it flows out, and this process gradually becomes abundant.
During and after sexual intercourse
The amount of leucorrhoea before and after intimacy increases. Vaginal discharge helps avoid discomfort when a man's penis enters. The formation of secretion during excitement, which changes in color, consistency and produces an unpleasant odor, requires consultation with a gynecologist.
These signs can be the beginning of sexually transmitted diseases.
These include:
- trichomoniasis;
- thrush;
Older women have a lack of leucorrhoea during sexual intercourse. If this happens in young girls, then you need to consult a specialist. It depends on the tolerable state of arousal. Lubrication will not come out of nowhere if the woman does not have the desire.
Itching and burning in the intimate area without discharge
The reasons that can lead to itching and burning in the genital area in the absence of discharge may be the following:
- Violation of the rules of intimate hygiene (affects contact with urine, activity of the sweat glands, folded structure of the external genitalia, etc.);
- Illiterate depilation and use of a razor to remove hair (scratches and other microtraumas appear, ingrown hairs can also irritate the skin);
- Impact of temperature changes on the genitals;
- Wearing tight-fitting underwear (size mismatch, rough seams, poor quality materials);
- Received injuries to the genital organs;
- Using soap for intimate hygiene (using it too often), which leads to drying of the skin in the intimate area and itching;
- The use of low-quality pads and tampons, which can cause an allergic reaction;
- Tendency to allergic reactions;
- Diabetes;
- Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism;
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder (itching is caused by the accumulation of bile acids in the body and can occur on any part of the body, including in the perineum);
- Genital herpes;
- Pediculosis pubis.
Some gynecological diseases, with certain characteristics of their course, may not be accompanied by discharge, but cause a sensation of itching and burning, for example, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis and others. Therefore, if discomfort of unknown etiology occurs, you should consult a doctor.
What discharge is considered normal?
At a young age, girls experience more leucorrhoea than middle-aged women.
This occurs due to the formation of hormonal levels. The environment in the vagina is slightly acidic. It is formed with the help of lactobacilli and is considered destructive to microbes, infections and organisms from the outside world. Vaginal discharge is considered normal if:
- moderate amount of leucorrhoea;
- transparent or white secretion formed;
- discharge that is odorless or has a specific aroma that is unique to women;
- does not irritate the vaginal mucosa;
- do not create discomfort.
The formation of vaginal secretion per day should not exceed a teaspoon. An increase in the amount of leucorrhoea occurs before menstruation, during arousal, during intimacy and after. These factors mean normal discharge formation.
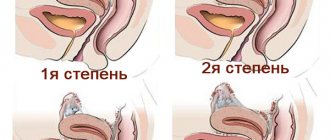
Types of discharge for existing disorders
Depending on the location of the pathology, white discharge, accompanied by itching and burning, is divided into several types:
Pipe
They appear due to a tumor, inflammatory process occurring in the tissues of the fallopian tubes.
Uterine
They arise due to the growth of fibroids, polyps, endometriosis, and sometimes also serve as a sign of a cancerous tumor.
Cervical
As the name suggests, the problem of secretion is observed in the cervix. Mucus may not be produced properly due to endocrine disorders, the presence of postoperative scars on the neck, erosion, or traces of ruptures.
Vaginal
They are fixed when the epithelium is damaged by careless douching, rough intimate intercourse, or when the normal microbial flora is disrupted.
Vestibular
Appear in patients with diabetes due to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, as a result of inflammation and ignorance of hygiene rules.
Only a doctor can determine why white mucus is released from the genital tract, accompanied by burning, discomfort and a changed odor.
What diseases does white discharge indicate?
Normal secretions do not differ in color or smell. Sometimes the consistency of the formations changes, but this does not indicate illness.
Thick
Vaginal secretion may have a thick consistency. This signals the presence of infections and microbes in a woman’s body. If you detect the signs accompanying the disease, this will help prevent further development of the virus.
The occurrence of strong discharge is associated with fungal diseases, viruses, and dysbacteriosis. Very rarely they can occur due to serious pathologies.
A common disease with such symptoms is considered candidiasis or thrush. In other cases, cystitis and other infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Liquid
Discharge of secretion of a liquid consistency means the norm only during ovulation or during the luteal period. Frequent formations from the vagina with white streaks foreshadow inflammatory processes in the cervical canal.
Discharge accompanied by an unpleasant odor and a yellowish or greenish tint indicates diseases of trichomoniasis, chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Mucous
A situation arises when leucorrhoea forms throughout the entire menstrual cycle. The secretion has a dense, cloudy and sticky consistency and can be stretchy. It may be accompanied by an unpleasant aroma. Mucous leucorrhoea in this case causes itching.
These signs symbolize the presence of chlamydia, trichomoniasis, vaginosis, candidiasis and gonorrhea.
There are factors that form mucous leucorrhoea; they are not classified as infections:
- Vulvar dermatitis.
- Benign formations, polyps on the cervix.
- Objects in the genital tract.
- Malignant tumors.
Rich and cheesy
Curdled, opaque and abundant formations in the form of flakes from the vagina are not considered normal. They warn about problems with women's health. They vary in color or smell. The aroma of sour milk indicates the presence of candida fungus. It creates an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the genital tract.
A yellow tint during curd secretion warns of inflammatory processes in the ovaries, fallopian tubes or appendages. This occurs due to a bacterial infection.
Abundant discharge of this consistency warns of acute diseases. For example, the diseases of adnexitis, salpengitis and oophritis. Their chronic stages pass with a small amount of secretion.
Green shades of leucorrhoea are considered a sign of diseases of the urinary system and infectious diseases.
Pathology according to the type of leucorrhoea
Secretion can be released from various parts of the reproductive system. The origin of leucorrhoea or white discharge in women may be as follows:
- Pipe. Whitish secretion occurs due to an inflammatory process in the uterine tubes. First, the fluid accumulates, gradually entering the uterus, and only then ends up in the vagina.
- Vaginal. Vaginal diseases cause microflora disruption. This could be thrush, dysbiosis or infection of the reproductive system.
- Cervical. The appearance of leucorrhoea is most often caused by cervicitis. Inflammation is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms against the background of gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis and chlamydia.
- Uterine. White secretion from the uterus is released due to endometritis (acute, chronic, specific). Fluid from the cervix enters the vagina, where it mixes with normal clear discharge.
A woman is unable to independently determine the area of the reproductive system where exactly a significant strange secretion could originate. The cause of white discharge in women should be determined by a doctor, and priority in treatment should be given to traditional medicine. In gynecology, there are several diagnostic methods. The specialist will evaluate the symptoms, check the smear material and only then prescribe appropriate therapy. Incorrectly selected therapy is not only useless, but also extremely dangerous to health.
When should you see a doctor?
Abundant secretion from the vagina exceeds the norm, is accompanied by discomfort, a cheesy consistency, foamy or other abnormalities are considered a reason to consult a gynecologist.
First of all, he diagnoses the woman. The doctor monitors the color of the discharge and its abundance. He asks questions that clarify the detection of a symptom of the disease. From this the duration of the disease is traced.
The specialist prescribes general tests and conducts an examination. He palpates the inner thighs, lymph nodes and perineum.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to pay attention to the urethra. A careful examination can reveal the presence of swelling or inflammation.
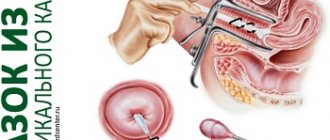
Specialists refer patients for a bimanual vaginal examination. Sometimes a rectal examination helps in establishing an accurate diagnosis of diseases or in detecting pregnancy.
Other tests and examination methods to establish a diagnosis may include the following:
- Bacterioscopic examination with taking a smear of secretion;
- Referral for a blood test that identifies enzyme-linked immunosorbent components;
- The use of PCR diagnostics helps to accurately determine where and how the infection originated;
In some cases, ultrasound hardware examinations are used. This method helps by examining the organs of the genitourinary system. The use of calposcopy helps in identifying the diseases of cervical dysplasia and its erosion.
Diagnostics
In order to eliminate unpleasant symptoms, a woman must first undergo a comprehensive examination. Only after making a diagnosis, the gynecologist selects a course of treatment. In order to identify the problem, a number of activities are carried out:
- anamnesis collection. The doctor clarifies what exactly worries the woman: only itching or the appearance of a burning sensation, pain and other symptoms;
- conducting an examination and taking a smear;
- taking blood tests;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound.
Having received the examination results, the doctor selects medications and prescribes an adequate course of treatment.
Possible gynecological diseases
The appearance of white vaginal formations with an unpleasant aroma implies the presence of pathologies:
- Salpingitis is considered one of the common diseases. Inflammation of the appendages occurs.
- This symptomatology is similar to the disease of oophoritis. Negative processes disrupt the functioning of the ovaries. There is a generalized disease if both pathologies occur in a woman’s body. It is called salpingophritis.
- Another reason is hypothermia.
- Another common disease of the genital organs is infection with candida fungus or thrush. Along with the formation of a cheesy secretion, an unpleasant odor may occur. During the discharge process, burning and itching is felt. Candidiasis should be treated immediately after the first symptoms, unusual discharge and associated odor occur. Treatment with medications occurs as prescribed by the attending physician. If reduced immunity remains in this state for a long time, then this provides a positive environment for the proliferation of viruses and fungi. This process leads to the progression of inflammation. The reasons why fungus develops include the following: changes or disturbances in hormonal levels;
- reduced immunity during pregnancy;
- stress and depression;
- physical and mental fatigue;
- failure to maintain intimate hygiene;
- trauma to the vaginal mucosa after sexual intercourse;
Vaginal itching after intercourse
Vaginal itching can also bother a woman after anal sex if her partner has an infection in the vagina - bacteria found in the intestines, such as E. coli. Such infections cause severe inflammation of the appendages, but it all starts with itching.
If you feel itching in your intimate area, do not waste time, contact a gynecologist. In addition to infections, itching is a symptom of incipient genital cancer. The doctor will conduct an examination and take swabs for infections and oncology - all together this will not take more than 15 minutes, but will allow you to identify the cause in time and quickly recover. Advanced gynecological diseases are treated long and difficult, and sometimes end in complete removal of organs. So is it worth bringing the situation to such an outcome?
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Features of treatment
A gynecologist or venereologist helps in the treatment of infectious, fungal and viral diseases of the female genital organs. Drug treatment and prescription of therapy occurs after a complete examination with an accurate diagnosis.
Antibiotics are prescribed to destroy viruses. To suppress burning sensation with heavy discharge, vaginal suppositories and tablets are used.
At the end of the therapeutic course, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes as preventative medications.
After using antibiotics, therapy is prescribed to improve the bacterial status of the intestines. In some cases, baths are used to restore vaginal microflora.
After and during hospital treatment, traditional medicine methods can be used.
Women do not always take antibiotics well because of their consequences. They make decoctions from the following herbs:
- Gravilata urban;
- Nettle;
- The cuff is ordinary;
- Horsetail;
- Mistletoe leaves.
To create a decoction, take 2 teaspoons from each plant. They are crushed and mixed well. The infusion is made using 2 tablespoons of herbs and brewed with half a liter of hot water. It is infused overnight and consumed 3 times a day, half a glass.
It is recommended to wash yourself with decoctions of oak bark, St. John's wort and lungwort. Chamomile helps well with douching. To prepare, use 2 tablespoons of flowers and pour 100 milliliters of hot boiling water.
Eucalyptus leaves can be a universal anti-inflammatory agent. The solution is prepared in the following proportions:
- 40 grams of eucalyptus leaves;
- 200 milliliters of hot water.
This solution is used not only for washing the vagina. They can soak a tampon with it and insert it into the vagina for a few hours, no more.
There are several more recipes:
- Some people take an infusion of wormwood internally. It is made from 30 grams of the plant, brewed with 200 milliliters of hot boiling water. The resulting decoction is infused for several hours. Use a tablespoon orally 3 times a day.
- Vaginal rinsing using the herbs yarrow, rosemary and sage. The method of preparing a decoction based on these plants is simple. They are mixed in equal proportions and crushed. Next, infuse in boiling water. Afterwards you can use it for douching 3 times a day.
- Calendula and celandine flowers are used to wash the vagina. In addition, baths based on pine needles are used. This extract can be purchased at the pharmacy. Baths have always been considered an effective method of traditional medicine. Even for eliminating leucorrhoea, this method will be useful and healing. The main thing is to regularly visit the bathhouse and not shy away from your doctor’s prescriptions. If all conditions are met, the results will show themselves immediately.
Methods for treating and preventing vaginal itching
To protect yourself from irritation, vaginal itching and other unpleasant symptoms:
- do not forget about regular hygiene,
- wear comfortable underwear made from natural fabrics,
- stop using pads every day,
- in the cold season, avoid hypothermia,
- take vitamins,
- visit a gynecologist once every six months.
Sources:
- Acute vulvovaginal candidiasis. A modern view of the problem, innovations in treatment. Serova O.F., Zarochentseva N.V., Menshikova N.S., Zlotnikova Yu.P. // Ross. Vestn. Akush-gin. - 2008. - 1. P. 68–71.
- Treatment options for acute and chronic recurrent vulvovaginitis. Tikhomirov A.L. // Gynecology. - 2005. - 3. P. 166–169.
- Local therapy of vulvovaginal candida. Sergeev Yu.V., Romanovskaya T.A., Sergeev A.Yu. // Venereologist. - 2004. - 7. pp. 57–59.
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/aktualnaya-problema-zhenschin-v-postmenopauze-urogenitalnye-rasstr…
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/rol-infektsiy-v-geneze-zabolevaniy-vulvy
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/bakterialnyy-vaginoz-sostoyanie-izuchennosti-problemy
Treatment for bacterial vaginosis
You cannot use the same drugs to eliminate bacterial vaginosis as for thrush.
Treatment of the disease is carried out in two stages:
- Conducting an examination. The doctor does a smear analysis and determines the type of bacteria that caused the disease. The patient is prescribed the most appropriate antimicrobial drugs.
- The use of products to restore vaginal microflora.
It is strictly prohibited to use any medicines without a preliminary medical examination. This can only make your condition worse. Only a gynecologist will tell you how to treat this disease.