Impetigo (name from the Latin impetigo, which means skin disease) is a group of pustular diseases affecting the superficial layers of the skin. The disease is contagious (contagious), so it accounts for more than 15% of all skin diseases. Caused by streptococci and staphylococci.
There are many types of impetigo, but they all manifest themselves in the same way - the development of erythema (severe redness) on exposed (usually the face) areas of the skin.
Erythemas are accompanied by vesicles (from the Latin vesicula, which means bubble) with purulent contents. Attention. Skin microtraumas contribute to the disease, as well as contact with coccal bacteria strains on the skin. You should monitor your skin condition!
General information
Impetigo is a contagious skin disease, that is, it can be transmitted from sick individuals to susceptible objects (people, animals) through various transmission routes, for example, through direct contact. Refers to superficial pustular pyoderma and most often streptococci , followed by the possible addition of staphylococci .
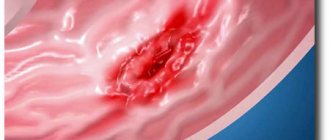
The main manifestation of the clinical picture is non-follicular conflicts - superficial pustules in the substratum of the skin, and sometimes on the mucous membranes. Outwardly, they look like flat blisters, have a flabby, easily torn tire and an inflammatory halo of hyperemia .
Impetiginization can occur against the background of various types of dermatoses , eczema or scabies . The disease is very contagious and easily spreads in families and children's institutions - kindergartens, schools, cases of mass destruction are known.
Pathohistology
Both with streptococcal and staphylococcal varieties of I. the main element is the pustule, the edges develop directly under the stratum corneum. Pustule (see) contains fibrin, neutrophilic leukocytes and a certain amount of lymphocytes. In the pustule you can find groups of cocci located extracellularly or inside neutrophils. In the spinous layer under the pustule there is spongiosis (see), many migrating neutrophils. In the upper part of the dermis there is a slight inflammatory infiltrate consisting of neutrophils and lymphocytes.
Pathogenesis
The pathology is characterized by an acute course: first, flabby, easily opened phlyctenas are formed, having a thin tire, and inside containing cloudy exudate of various origins - serous, purulent, etc. Their diameter usually ranges from 2-10 mm. After drying or resolution of the conflicts, the contents separated by them shrink with the formation of light yellow thin or purulent-hemorrhagic crusts. In their place, wet, oozing lymph, even bleeding bright pink erosions are formed, and in the slit-like type - linear cracks. Erosive areas quickly increase in size and can merge and become covered with abundant golden-yellow crusts that can be removed quite easily. What is a scab with impetigo is most clear and understandable - it is when the crusts resemble “honey crumbs” and are easily torn off.
The crusts disappear after 3-7 days, leaving behind fresh epithelialized pink areas of the skin, foci of temporary depigmentation, or, on the contrary, in a mixed infection - excessive pigmentation.
Impetigo is characterized by autoinoculation, a process that results in the transfer of infectious agents to healthy areas of the epidermis.
What other types of pyoderma are there?
Mixed impetigo - formed as a result of complications of streptococcal impetigo by staphylococcus. When conflicts appear, itching and multiple rashes appear in the neck and face.
Impetigo Bockhart - the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus. Symptoms: purulent pustules, which after a while dry out and fall off. Most often they appear on the neck, face, and thighs.
How to identify the skin disease impetigo?
Classification
Impetigo is distinguished by location and characteristics of skin lesions. The most common impetigo occurs:
- slit-shaped - localized in the folds of the skin and can spread to the mucous membranes, most often located near the lobe and behind the ears, around the wings of the nose, in the outer corners of the eye, on the eyelids, in the corners of the mouth, therefore this type of impetigo is also popularly called jam , it contributes to relapse hypovitaminosis mainly of group B , gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes mellitus , etc.;
- bullous - characterized by the presence of several tense blisters of a hemispherical shape, large size, most often located on the hands, torso, feet and legs;
- ring-shaped - characterized by the formation in the center of the skin of areas that dry out and epithelialize, which are surrounded by preserved conflicts; this is possible with centrifugal growth of the lesion;
- syphilitic - located in the genital area and buttocks, reminiscent of syphilitic papular rashes;
- vegetative - differs from the usual by the presence of erosive surfaces turning into vegetative areas, which are covered with purulent crusts, surrounded by a stratum corneum and undermined by exudate;
- superficial panaritium or in other words tourniol - damage to the posterior ridges of the nail plates by horseshoe-shaped conflicts with peripheral growth, which can cause complications - lymphangitis or lymphadenitis .
Slit impetigo
Depending on the pathogen, impetigo can be streptostaphylococcal - vulgar or streptococcal. The latter is distinguished by the presence of purulent yellowish thick contents in the conflicts.
Vulgar impetigo
Cases of mixed infection usually occur against the background of diseases such as scabies, neurodermatitis and eczema. Impetigo vulgaris is considered highly contagious, with children being most susceptible. The pathological process can begin on any part of the skin of the body and even on mucous membranes, but usually occurs on the face and hands.
The vulgar type can be distinguished by the presence of yellowish purulent exudate and the dirty gray and greenish rough lumpy crusts formed after opening, which are formed due to the constant flow and drying of exudate. The prognosis is favorable - red flaky spots remain on the skin under the crusts, which subsequently disappear without a trace.
Streptococcal impetigo
Streptococcal infection causes impetigo , cheilitis , streptococcal diaper rash, which most often affects children and young women with delicate skin. This type is also characterized by high contagiousness and a tendency to quickly spread to the skin of the face (mask-like impetigo) and open areas of the body, limbs, etc.
Streptococcal impetigo begins with minor hyperemic spots on the skin, which quickly turn into phlyctenas. After opening them, wet, bright pink erosions , which dry out and form yellowish-brown thin crusts that can fall off. As a result, after a week, bluish or pinkish spots remain with a peeling stratum corneum and a narrow border. Their subsequent separation leads to the formation of erosions.
Streptococcal impetigo
Streptococcal lesions can be located in groups or scattered, forming small vesicles with transparent and cloudy contents. They resolve spontaneously and in about a week the milky scab disappears, leaving small pink spots in its place. However, there are atypical cases when children develop a simple type of lichen on the face; its structure is scaly, and when the scabs fall off, depigmented areas remain in their place.
Staphylococcal impetigo
Usually it is ostiofolliculitis as it develops in the mouths of the pilosebaceous structures of the follicle. It is more typical for adult men who suffer from uncleanliness, excessive sweating , and constant chemical irritations of the skin during shaving. The disease can be combined with other itchy inflammations of the skin.
In children, staphylococcal skin infections are rare and occur only on the scalp. Scabs on the head look like cone-shaped yellow crusts with small pustules located on top.
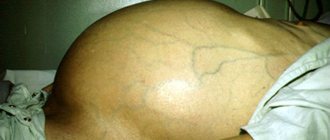
Bullous impetigo
A separate type of infectious skin disease is bullous impetigo, which is characterized by the formation of large conflicts reaching the size of a walnut. After opening them, wet areas of erosion with peripheral growth remain on the body. Most often, young children suffer from this disease due to insufficient skin care and hygiene.
Bullous impetigo
Treatment
A set of measures for the treatment of impetigo includes:
- isolation of patients in a separate box or room, strict adherence to the rules of patient care and preventive measures to prevent the spread of infection;
- taking antibiotics (tablets or injections, depending on the severity of the pathology), for which macrolides, penicillins, and cephalosporins are often used;
- local treatment with ointments, creams and gels (based on bacitracin, mupirocin, neomycin, erythromycin, tetracycline);
- symptomatic treatment with antihistamines, decongestants, painkillers and antipyretics;
- the use of anti-inflammatory herbs (sage, calendula, chamomile) during the recovery period for the preparation of baths and compresses.
A dermatologist prescribes adequate therapy in a hospital, and he also gives recommendations on how to treat impetigo at home.
This disease is characterized by rapid spread and complications, so to get rid of it you need to contact a medical facility in a timely manner. If treatment is started on time, impetigo completely disappears in 7-10 days without complications for the body.
Causes
Impetigo is caused by infectious agents such as streptococci and staphylococci. The source is skin and mucous membranes affected by impetigo, dirty objects, as well as patients with tonsillitis . Factors that increase the risk of developing impetigo include:
- microtraumas (minor abrasions, scratches, bites, hangnails, etc.);
- maceration;
- contaminated skin and warm, humid environment;
- use of shared utensils and other household items, contact (touching, kissing) with carriers of infectious agents;
- non-compliance with hygiene and skin care rules;
- hypovitaminosis;
- anemia;
- climate with high humidity;
- reduced immunity .
Important! To prevent contagious skin lesions, cuts and minor abrasions should be promptly treated with disinfectants, for example, brilliant green or Bactroban .
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on a wedge, a picture, and is confirmed by laboratory research: the pathogen is detected when the discharge from the pustules is inoculated on nutrient media. Differential diagnosis of individual forms of I. is carried out with other types of pyoderma, syphilis, fungal diseases (Candidiasis, trichophytosis). It is often necessary to conduct a general examination of the patient to identify endogenous pathogenic factors that provoke and maintain the disease, as well as to identify possible complications.
Symptoms
The main symptom is special skin rashes - phlyctenes. They are superficial pustules in the form of blisters filled with serous exudate and surrounded by a halo of hyperemic skin. They can be single, but more often they are multiple, located scattered or grouped.
Few people ask the question: impetigo, what is it? But it is important to understand that skin changes can not only cause discomfort ( skin itching , dryness, pain), but also spread to large areas of the skin, penetrate into the deeper layers of the epidermis and reach the lymph and blood flow. Pathology can cause disturbances in the general condition, and the following occurs:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- malaise;
- increased ESR;
- leukocytosis.
Traditional methods
Of course, in folk medicine there are recipes that help get rid of impetigo. But, when using additional folk methods simultaneously with traditional ones, you need to tell the doctor exactly what means you are using.
Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs are used as folk remedies for the treatment of impetigo. Herbal infusions, including St. John's wort, chamomile, and rosehip, are very useful. There are several fees that should be mentioned:
- to prepare the infusion, take string, sage, calendula - 15 g each, and St. John's wort and chamomile - 20 and 10 g, respectively. Mix and pour boiling water, the infusion should stand for half an hour. Strain and take half a glass three times a day, preferably before meals;
- for the decoction you will need rose hips, lure, rhodiola rosea - 20 g each, St. John's wort - 10 g, nettle leaves, hawthorn fruits - 15 g each. All ingredients are mixed and poured with boiling water. The infusion can be taken after half an hour, half a glass three times a day.
Decoctions of various medicinal herbs are widely used:
- a decoction of flax seeds is used both internally and in the form of lotions, which must be applied to the affected area several times a day. To prepare the decoction, take flax seeds, boil and strain;
- In a similar way, you can prepare a decoction from the roots of kirkazon. Use the resulting decoction to wash your face and apply lotions as often as possible;
- a decoction of comfrey will help relieve inflammation; to do this, pour boiling water over the herb and leave for half an hour. The decoction is used for compresses.
It is very useful to treat impetigo with fresh plant juice, such as violets, calendula, and celandine. By the way, a decoction and ointment from this plant will also be useful.
To reduce the number of foci of impetigo and their further spread, apple cider vinegar lotions are used, but the number of applications should be at least six per day.
Prevention of impetigo is quite simple - it is compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene; if you receive any abrasions, scratches or wounds, you must immediately treat the damaged areas of the skin with a disinfectant.
Impetigo in children
With insufficient child care, irritation and maceration of the skin with urine and feces, dyspepsia in a well-fed baby, syphil-like papular impetigo appears - the so-called post-erosive Sevestra-Jaquet syphiloid , which affects the buttocks and posterior femoral surfaces. Opening reveals erosive areas, which, after infiltration, turn into erosive papular rashes that can regress and form pigment spots .
Milk eschar in a baby is the presence of whitish scales on the skin of the cheeks or persistent diaper rash on the buttocks, even with proper quality care. Unfortunately, such painful conditions are very common in children under one year of age.
Prevention
If a patient with impetigo appears in a family or children's group, then it is necessary to use several simple rules aimed at preventing the spread of the disease.
- Observe personal hygiene rules, wash your hands and face thoroughly, preferably using antibacterial soap.
- Change your underwear and bed linen more often.
- Use only individual personal hygiene items, especially towels.
- Cut a sick child's nails short.
- When treating rashes, use medical gloves.
Diet for impetigo
Diet for skin diseases
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a month
- Time frame: three months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles per week
Since children and young people with weakened immune systems , in combination with treatment it is recommended to follow a special diet enriched with foods that:
- contain fish oil;
- completely replenish the body’s daily need for proteins;
- rich in vitamins and various microelements, including iron.
People with skin problems should be prohibited from eating any sweets, especially those containing white sugar and synthetic additives, wheat flour and other refined ingredients. Simple carbohydrates become the most aggravating factor for the disease, so even the consumption of honey and chocolate should be limited.
Recommendations for a quick recovery
It is not enough just to take medications and treat the skin with ointments. Precautionary measures should be taken by both the sick person and his family members. Until the rashes crust over, they should not be wetted, much less rub the skin with a washcloth, even after 5–7 days. A person’s personal belongings (dishes, clothes, bedding) must be disinfected and not used by other people. Each time you need to carry out wet cleaning, thoroughly wiping the floor and other surfaces.
The patient's diet consists of soft food. You need to avoid sweets, sour juices, solid foods, pickles and smoked foods. Any foods that can damage the mucous membranes should be avoided until complete recovery. It is better to give preference to protein foods, fresh vegetables and fruits. Instead of sweet tea, coffee, lemonade, it is recommended to drink clean water, herbal infusions and teas.
Impetigo, although considered a childhood disease, is often diagnosed in adults. An advanced stage can cause damage to internal organs and leave scars. If you suspect this pathology, it is important to contact a dermatologist in time and undergo treatment. Compliance with all recommendations will speed up the healing process and also prevent tissue scarring.
You can ask your question to our author:
How to treat the disease
No skin disease should be left unattended. Moreover, an infectious lesion of the skin, which is impetigo, caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal bacteria.
When infection occurs, a small red dot appears on the skin. After just a few hours, the point turns into a phlyctena filled with a cloudy liquid. On days 2-3, the phlyctenas open, and their contents form a yellow or brown-yellow crust over the wound surface. On day 4-5 the crusts disappear.
The main problem of such a disease is that it is acutely contagious for others and for the sick person. Self-infection often occurs, and the disease spreads over the entire surface of the skin. Therefore, differential diagnosis and proper treatment of impetigo are of great importance to prevent serious complications.
Diagnosis, in addition to visual examination and history taking, includes:
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for HIV infection;
- dermatoscopy and determination of skin pH;
- bacterial culture of scrapings from the wound surface.
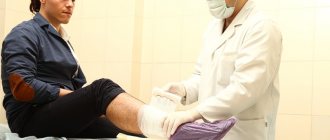
With timely initiation of treatment, when a small area of skin is affected, the following treatment procedures are sufficient:
- Treatment of the wound surface of the skin with alcohol solutions of salicylic acid and resorcinol.
- After treating the wound, applications of ointments containing antibiotics are applied - Streptocide ointment, with neomycin, oxytetracycline.
- Sometimes it is advisable to include hormonal ointments for speedy wound healing - Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Flumethasone ointment.
- Single conflicts are treated with a solution of fucorcin or a solution of brilliant green.
Treatment of impetigo in adults and children is not much different. Children, unlike adults, are covered with bandages to prevent self-infection.
Impetigo is a disease that can be treated on an outpatient basis. The attending physician determines the form of the disease, prescribes treatment and necessary medications. During treatment, the patient is isolated to avoid the spread of infection.
In severe and advanced cases, antibiotics are prescribed orally or parenterally. Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis, very rarely in an inpatient setting.
What it is
A large number of different bacteria live on human skin. The body's protective functions prevent them from multiplying and causing various diseases. But as soon as the immune system weakens, various skin injuries occur, bites, scratching with dirty hands, non-compliance with personal hygiene rules - active growth and reproduction of bacteria occurs.
All this contributes to the occurrence of infection - impetigo. The causative agents are gram-positive bacteria (staphylococci and streptococci), permanent residents of our skin.