These pathologies include:
- endometritis (inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus);
- salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes);
- oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries);
- tubo-ovarian abscess (enclosed focus of pus in the fallopian tube);
- pelvioperitonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum);
- possible combinations of these diseases.
According to Russian statistics, patients with these diseases make up 60-65% of those attending outpatient clinics and about 30% of those admitted to gynecological hospitals.
Causes of development of female diseases
Women's gynecological diseases can be provoked by both external factors and internal pathological processes. Women's bodies are very sensitive and can become upset due to hypothermia or overheating, stress, or climate change.
External reasons also include:
- chronic fatigue;
- excessive physical activity and overwork;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- lack of personal and intimate hygiene;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
Common internal causes include:
- inflammation in the uterus or its abnormal development;
- problems with appendages;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- endometriosis;
- sexually acquired infections.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a type of pregnancy that is classified as complicated. With it, the fertilized egg attaches outside the uterus. In almost all cases of ectopic pregnancy, the child cannot grow and develop. In addition, such a pregnancy poses a great threat to the woman’s life, as internal bleeding occurs. Immediately after a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is made, a woman requires urgent qualified medical care, otherwise she may simply die.
When pregnancy occurs without abnormalities, the egg with which the sperm has united passes into the fallopian tube and is fertilized there. After this, the zygote moves to the uterus, where ideal conditions are created for the development of the unborn baby. But in cases where the pregnancy is ectopic, the zygote does not move to the uterus, but connects to the tube or returns back to the ovary. The chorionic villi get into the tissues, they are damaged because of this, and the woman experiences internal bleeding.
Main symptoms of genital diseases
Female gynecological diseases, regardless of type and course, have a number of similar symptoms.
The following is most often observed:
- Menstrual irregularities. Many diseases of an endocrine or tumor nature manifest themselves as such a disorder. You should pay attention not only to the prolonged absence of menstruation, but also to the nature of the bleeding, which can become heavy or barely noticeable. You should definitely contact a gynecologist if a woman uses products with a high level of absorption, changing them very often for 2-3 months or more.
- Pain syndrome. Sometimes very severe pain indicates that a woman has a life-threatening condition. For example, a cyst may rupture or ovarian apoplexy may occur. All this is an indication for immediate hospitalization.
- It's a dull pain. It may bother you before or after menstruation, sometimes it accompanies sexual intercourse. Typically, such pain indicates inflammatory processes in the uterus and appendages. It is important to remember: you can only tolerate minor discomfort, and if it occurs in the first few days of the cycle, in all other cases, and especially if the pain is so severe that you have to take pills, you should definitely consult a gynecologist.
- Vaginal discharge. Any uncharacteristic discharge noticed on your underwear should be a cause not only for concern, but also for a visit to the doctor. Deviations from the norm are those that have an unpleasant odor, purulent or foamy, yellowish, milky-white or bloody. At the same time, the absence of any discharge, with the exception of menstrual blood, is also abnormal for the female body. Dry vagina syndrome is a reason to visit a gynecologist.
- Itching of the perineum. If it occurs at the same time as heavy discharge, it may be thrush.
Multifollicular ovaries, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
This diagnosis is made to perhaps every fourth woman when visiting a gynecologist. According to statistics, this disease affects from 2.5 to 8% of women, mainly aged 25-30 years. Polycystic ovary syndrome is a disease in which the maturation of follicles is disrupted, ovulation does not occur, and the eggs that remain in them turn into numerous cysts.
Often the disease develops spontaneously, but the main cause is still considered to be a hereditary factor, in which there is an increased production of androgens (male sex hormones) with a decrease in the formation of progesterone. A predisposing factor is excess weight, so the most effective way of prevention is to normalize body weight.
The main and only symptom of this female disease is an irregular menstrual cycle. Several months may pass between periods. Recently, in the West, there has been a tendency that doctors regard this condition as a variant of the norm and are in no hurry for a woman to restore her menstrual cycle. Recent studies have concluded that PCOS is not a clear cause of infertility, as previously thought.
Polycystic ovary syndrome: symptoms and main causes of the disease.
Groups of women's diseases
Women's gynecological diseases are divided into the following types:
STIs are female gynecological diseases that are sexually transmitted
| Group | Description |
| Infectious diseases | Infectious diseases cause disruption of the normal functioning of the reproductive system. These include candidiasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis. In most cases, these diseases occur hidden. Therefore, if you have an active sex life, or if you have unprotected sex with a new partner, you should definitely go to a gynecologist and have a smear test for common types of diseases. Even better is to visit a doctor and have appropriate tests done on a regular basis. |
| Endocrine diseases | Such diseases are associated with impaired functioning of the endocrine glands - adrenal glands, pituitary gland, ovaries. Their course can negatively affect both a woman’s sex life and her ability to bear and give birth to a child, as well as her appearance. Diseases of this kind are sometimes hereditary, as in the case of congenital androgenital syndrome, or acquired during life, such as polycystic ovary syndrome. Doctors also include obesity in this group, which leads to menstrual irregularities and serious problems with reproductive function. |
| Tumor formations | They can be either benign or malignant. In women they are diagnosed at any age. Various modifications of the cervix, including ectopia, also belong to this category of diseases. It is important to understand: a malignant tumor is not always a death sentence. If you don't miss the early stage, it can be cured. Those patients who know about their heredity should be especially careful about their health. |
Chlamydia
Every year, chlamydia is diagnosed in more than 100 million people in the world. The World Health Organization (WHO) lists it as one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases
From 5% to 15% of sexually active young people aged 20 to 40 years are already infected with chlamydia infection and this percentage is only increasing every year
Causes of chlamydia
The reasons for infection and rapid spread of chlamydia in women are the structural features of the bacterium itself
Chlamydia attaches to sperm and spreads to all organs of the reproductive system. One sexual act without contraception is enough to get an unpleasant infection
The main reasons for the presence of chlamydia in women are:
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- promiscuity, without the use of protective contraceptives;
- numerous abortions and other genitourinary operations;
Reasons for women becoming infected with chlamydia include reduced immunity.
Factors leading to a decrease in immunity include:
- constant stress;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
Main symptoms
In the female body, chlamydia shows its symptoms differently than in the male, so they can easily be confused with other possible pathologies
The first signs of infection can appear two to three weeks after infection, sometimes much later
They are expressed by the following symptoms:
- itching;
- burning;
- discomfort in the genitals;
- pain when urinating;
When the disease is long enough, a yellow or whitish discharge with an unpleasant odor begins to appear from the vagina.
In the future, the pain will be localized in the area of the uterine appendages, on one or both sides at once, and can often radiate to the lower back. It is also typical for the temperature to rise to 38 degrees, and for no apparent reason.
During a routine examination by a gynecologist, swelling of the cervix is clearly visible, erosion and discharge mixed with blood are possible
Every day, the woman’s condition changes for the worse. Lethargy of the whole body appears, gradually turning into chronic fatigue and loss of appetite. All chronic diseases begin to worsen
Possible complications
As a rule, during the initial infection with chlamydia, the disease does not have any pronounced symptoms
Women who have an infection do not feel any pain or discomfort, so they do not consult a doctor in a timely manner
Pain comes over time when the organ becomes severely damaged and is unable to fully cope with its work. The pathological process takes over the entire body.
Against the background of chronic chlamydia infection, the following complications may develop:
- cystitis;
- infertility;
- pneumonia;
- pyelonephritis;
- decreased erectile dysfunction;
How gynecological diseases are treated
Modern medicine has many possibilities in the treatment of female genital diseases. In addition to prescribing medications, a physiotherapeutic approach is used. In some cases, the patient is prescribed surgery as a necessary procedure.
Female gynecological diseases may be subject to the following therapy:
| Treatment with medications | |
| Purpose | Description |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | These drugs are necessary to relieve inflammation that occurs in infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract and to make life easier for the patient during painful menstruation. |
| Antibiotics, antifungals and antivirals | These drugs are used when the doctor is dealing with infectious diseases of the genital area and the consequences that they entail, in particular. For example, if genital warts appear in a patient’s vagina, it is not enough to just get rid of them: if the human papillomavirus that caused them is not treated, the removed warts will return. |
| Hormonal agents | With their help, they cope with endocrine disorders, but if we are talking about steroid hormones, then they act as powerful anti-inflammatory drugs. Hormonal oral contraceptives help in the treatment of infertility. |
| Vitamins | They are necessary for a woman’s body to recover faster from various gynecological diseases. After chronic blood loss and even after heavy menstruation, doctors often prescribe additional medications to patients that help normalize iron levels. |
| Physiotherapy | |
| Purpose | Description |
| Cryodestruction | This procedure affects living tissue using a very low temperature and allows you to freeze the pathological focus using liquid nitrogen. The method has proven to be very effective in the fight against cervical cysts and ectopia, as well as chronic cervicitis and condylomas. |
| Chemical destruction | It has a similar effect to cryodestruction, but differs in that most drugs are completely harmless for nulliparous patients. The method is especially effective in combating cervical erosion. |
| Radio wave therapy | It is used as an alternative to surgery and is considered a gentle option. Radio waves heat tissue, destroying pathological areas, but without harming healthy tissue. There is also no risk of bleeding or inflammation. This method is especially often used if a woman suffers from erosion and plans to become pregnant. |
| Laser therapy | It is considered the most promising procedure in the gynecological field. She showed herself at the highest level in the field of intimate plastic surgery, when the vagina, stretched after childbirth, needed to regain its elasticity. |
| Surgical intervention | |
| Modern gynecological surgery operates unnoticed, through fairly small punctures. Thanks to this, no rough scars remain on the woman’s body, and the procedure goes quite quickly. | |
Endometritis
In this disease, the cells of the inner layer of the uterus (the so-called endometrium) grow beyond its boundaries. They undergo the same processes as in normal endometrium, but due to their atypical location this leads to various disorders.
Endometritis can be either genital (in this case it develops within the genital organs) and extragenital (localized in the navel or intestines). Typically, genital endometritis causes heavy and prolonged bleeding, and pelvic pain also manifests itself during menstruation and during sexual intercourse.
Due to the fact that endometrial cells differ in their ability to metastasize, the number of lesions may increase. Timely help from a gynecologist will save you from this.
In therapy, specialists most often prescribe antibiotics (Ciprofloxacin, Roxithromycin) and physiotherapy to restore the uterine lining and normalize the cycle. Medicinal plants help relieve symptoms and alleviate physical condition.
For example, you can prepare a decoction from St. John's wort, for this:
- 1 tbsp. l. herbs should be poured with 1 cup of boiling water.
- Place on the stove and boil for 15 minutes.
- Strain.
Take a decoction of 50 ml 3 times a day.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is traditional therapy that is widely used to cure diseases of the genital organs:
- Chamomile decoction, which is prepared both from a pharmaceutical mixture and from ready-made bags, is very popular. Preparation is not difficult, so you can use it without violating the selection of conditions. The course of therapy lasts on average 7 - 14 days, and is often selected in combination with etiotropic therapy. Can be prescribed for inflammation in both adults and children. Chamomile has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
- Calendula solution has a similar effect. This plant has a great advantage due to its anti-allergic components in people prone to such manifestations.
- Also, for fungal inflammation at home, a soda solution is used , which is capable of breaking down the mycellium.
- The boron uterus effectively copes with inflammation of the upper genital tract. It is prescribed in the form of a decoction or infusion. At the same time, the course of therapy is long, in some cases it may be a course of prophylactic administration during periods of remission.
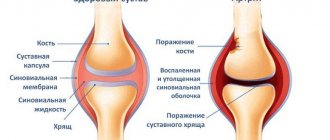
Adnexit
This disease is also called salpingoophoritis. It is an inflammation of the uterine appendages, which develops not due to one factor, but due to their combination: an infectious pathogen and predisposing factors such as hypothermia, stress, abortion or poor hygiene. Salpingo-oophoritis can occur acutely or chronically.
The acute form is accompanied by signs:
- lower abdominal pain;
- deterioration of health;
- temperature increase;
- purulent discharge.
The chronic form of adnexitis is characterized by disturbances in the menstrual cycle and periodic pain in the lower abdomen.
Regardless of the form, this gynecological disease is treated exclusively in a hospital.
If the course is not carried out on time, it will cause obstruction of the fallopian tubes with subsequent formation of adhesions, which in a neglected state can lead to infertility.
Before treatment for acute adnexitis begins, ice is placed on the patient’s lower abdomen. The right- and left-sided forms of the disease require therapy with antibiotics, antispasmodics and desensitizers. Electrophoresis, ultrasound, and paraffin baths may also be prescribed.
For a speedy recovery, it is recommended to combine traditional and folk methods of treatment.
This is facilitated by:
- infusions;
- douching with chamomile decoction;
- cabbage leaf baths;
- decoctions of dried viburnum flowers.
To prepare the herbal infusion, you need to take leaves of nettle, St. John's wort, yarrow, sage and calendula flowers, 3 tbsp each. l. After infusing in a thermos for 2 hours, drink 3 times a day.
Colpitis
This is an inflammatory process that is caused by pathogens. The disease is less common than thrush, but belongs to the category of quite common.
For colpitis to develop, it requires a provocation in the form of a somatic disease, which reduces the body's defenses. Typically, such a provocateur is an endocrine pathology, such as obesity or diabetes mellitus. Also, damage to the vagina and poor hygiene can serve as an impetus for the development of colpitis.
The main manifestations of the disease are vaginal itching and discharge, which look unusual and smell unpleasant.
Colpitis is treated with the following groups of drugs:
- antibiotics (Tiflor, Ampicillin, Cephalexin);
- antifungal agents (Diflucan, Flucanazole);
- antiherpetic drugs (Valtrex, Acyclovir).
In addition to tablets, local therapy can also be prescribed - creams, ointments, solutions.
To strengthen the immune system and support microflora and liver cells, the following is prescribed:
- probiotics;
- enterosorbents;
- vitamins;
- immunomodulators.
For douching use:
- boric acid;
- zinc sulfate;
- chlorophyllipt.
Before taking folk remedies for the treatment of colpitis, you should consult a specialist. A product based on chamomile and calendula is considered a good antiseptic.
It is prepared as follows:
- You need to boil 1 liter of water.
- Add 15 g of chamomile and calendula flowers to it.
- Cook for 15 minutes.
- Cover the container with a lid and let the broth cool.
- Strain the liquid.
This product is used for washing and douching.
Treatment
Vulvitis
It is recommended to treat inflammation of the vulva mainly with local remedies. The choice of drugs will depend on the etiological factor.
- In girls, as well as in case of nonspecific lesions, you can use the appointment of washings. These include good solutions with an anti-inflammatory effect, such as Furacilin, Chlorhexidine and chamomile or calendula decoction.
- In case of severe inflammation, antibacterial or antiviral, as well as antifungal agents in the form of creams and gels can be used.
Cervicitis
This type of inflammation usually requires complex treatment.
- In the development of the process, it is necessary to exclude viral infection of the cervix. Tablets and local forms of medications are used.
- When the cause of inflammation is precisely clarified, remedies are selected taking into account sensitivity, and in the case of a nonspecific process, this inflammation is usually eliminated with properly selected treatment without problems.
- The woman does not require hospitalization in a hospital, or interruption of the work process.
Endometritis and adnexitis
These inflammations require mandatory and timely treatment due to the high risk of complications.
The mode will be selected based on the stage of the process:
- In severe conditions, hospitalization in a hospital is required. Antibacterial or antiviral treatment is considered etiopathogenetic therapy. The route of administration is selected exclusively parenteral; only after completion of treatment can you choose medications in tablet form.
- In addition, detoxification therapy must be carried out. For this purpose, blood replacement and isotonic solutions are used in combination with vitamins.
- After the main course, anti-relapse courses are required , aimed at preventing the development of complications or recurrent inflammation.
- When a mass formation forms or inflammation spreads to other organs with the development of a purulent process, surgical intervention is required with possible washing, removal of formations and drainage with the introduction of antibacterial agents.
Bartholinitis
Tactics in this case will depend on the stage of the inflammatory process:
- At the initial stages, this may include the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, as well as local antiseptics.
- With the development of a purulent process and the development of a limited formation or transition to an abscess, surgical intervention is necessary, followed by drainage of the inflamed cavity.
- Prescribing thermal or physiotherapy procedures before opening the cavity is strictly contraindicated, as this can lead to generalization of the process.
Candidiasis
Inflammation of the genital organs requires etiotropic therapy, these are antifungal agents. The form of drugs is selected based on the level of damage:
- For vulvitis, these can be creams or solutions that have antifungal activity. These include a solution of baking soda, which is applied to the skin and relieves inflammation.
- For inflammation of the vaginal cavity, you can use not only the form of cream and ointment, but the most effective and common are vaginal suppositories or tablets. These can be drugs with only an antifungal mechanism or with a complex effect (inexpensive Fluconazole or Flucostat ). In addition, systemic tablet forms are prescribed in combination with local therapy.
Very often, candidiasis tends to recur. In this case, even in the absence of signs of inflammation, systematic prescription of drugs is required.
Other diseases
- Treatment of inflammation caused by sexually transmitted infections is required after precise confirmation of the cause. To do this, it is necessary to select funds after determining sensitivity. After treatment, additional monitoring of treatment is necessary.
- Cervical erosion. This is a special group of diseases of the female genital organs. When combined with a viral infection, mandatory treatment of inflammation with the prescription of antiviral drugs is required. Surgical treatment of the inflammatory process is very popular. Among them is diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction.
Uterine fibroids
It is otherwise called fibromyoma. This benign tumor develops in the muscular layer of the uterus - the myometrium, hence the name. Myoma can be either millimeter-sized or grow to 10 cm or more.
The most important symptoms of such a tumor are two – excessive menstruation and unpleasant pressure in the lower abdomen. Sometimes, if fibroids grow, the functions of the rectum and urethra are disrupted. This happens because the tumor presses on neighboring areas.
For the conservative treatment of uterine fibroids, the following drugs are prescribed:
- oral contraceptives (Novinet, Marvelon);
- antiprogestogens (Mifepristone);
- antigonadotropins (Danoval, Danogen);
- hormonal drugs.
One of the most common folk remedies is the use of flax seeds. The main thing is to consult a specialist before using them.
To prepare a decoction according to Vanga’s recipe you need:
- 4 tsp. seeds pour 0.5 liters of boiling water.
- Cook the mixture over low heat, stirring constantly and occasionally.
Take it half a glass 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals. The course of therapy is 15 days.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
A gynecological disease characterized by hormonal imbalance, in which women develop cysts outside or inside the ovarian capsule.
Arise due to:
- emotional shocks and stress;
- frequent acute respiratory viral infections and recurring sore throats;
- disorders in the functioning of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland and pituitary gland;
- chronic infectious diseases.
Main signs of the disease:
- menstrual irregularities, delays may exceed 2-3 months;
- infertility, due to the rarity and unpredictability of the time of ovulation;
- hirsutism (excessive hair growth according to the “male pattern”);
- body weight gain;
- dysfunction in the endocrine system, most often the thyroid gland suffers.
It is impossible to cure polycystic disease, you can only temporarily restore functions and reduce the risks of developing other diseases.
The following drugs are used in therapy:
- antiandrogens (Dimia, Jess);
- metabolic drugs (Metamorphine).
The following recipes can be used from folk remedies:
- based on nettle. 10 g of dry leaves pour 1 tbsp. boiling water and let it brew for 20-30 minutes. The decoction should be drunk 2 times;
- from mumiyo. It must be diluted in warm water to a paste consistency. Apply a little product to gauze and make a tampon, which should be placed overnight. Course – 1-2 weeks;
- from dandelion root. It should be crushed to a powder, divided into portions of 2-3 g. Use instead of tea.
Ovarian cyst
This is a special hollow formation that is filled with liquid or semi-liquid content. If the cyst is formed from the natural structures of the ovary, for example, a follicle, then such a formation is called functional. As a rule, it resolves without outside intervention in just a couple of months.
Endometrial and dermatoid cysts can be dangerous for the female body. The most dangerous thing is that the formation of a cyst is difficult to notice, since the disease is asymptomatic. The maximum they manifest themselves with is pain in the lower abdomen and minor menstrual irregularities.
Cysts are treated either conservatively (using hormonal contraceptives) or surgically (laparoscopy is performed). Among the folk remedies for the treatment of ovarian cysts, you can take a decoction of dandelion root.
For this:
- You should chop 2 roots of the plant with a knife.
- Pour 0.5 liters of water and place in a water bath.
- Simmer the broth for 3 hours.
- Strain, cool and pour into a jar with an airtight lid.
- Place in the refrigerator.
The decoction should be taken three times a day, 3 tbsp. l. 1 hour before meals. Course – 5 days before menstruation.
Cervical erosion
With this disease, small ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the cervix. Most often, erosion does not manifest itself at the initial stage; pathology can only be detected upon examination.
Subsequently, it will be characterized by symptoms such as:
- infertility:
- bleeding during sexual intercourse;
- discharge from the genital tract with a strong unpleasant odor.
Drug therapy includes the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs and agents that act on the cause of erosion and promote tissue restoration.
In addition, the following methods are possible:
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- the use of ultrasound;
- radio wave therapy;
- the use of chemicals with cauterizing properties.
From folk remedies, you can use sea buckthorn oil as follows: put a tampon soaked in oil every night. The course of such treatment is 1-2 months.
Infectious inflammations
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an inflammatory lesion that belongs to the specific class. It is caused by a specific microorganism belonging to the gram-negative group.
Characteristics of the disease:
- This pathogen is specific and primarily affects the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract. The result is an inflammatory process that can affect all parts of the reproductive system.
- The pathogen is sensitive, so it quickly dies in the environment.
Inflammation is caused to a greater extent among females.
Symptoms:
- It manifests itself as a purulent inflammatory process. The woman notes symptoms such as itching and burning in the external genital area.
- The discharge is purulent in nature, quite abundant with a yellow-green tint and an unpleasant odor.
- When the process moves to the upper parts of the genitourinary tract, the general condition is disturbed, the body temperature rises to febrile levels, less often it is subfebrile.
- Pain appears in the lower abdomen and can become intense. If the process is not treated in a timely manner, the gonococcal infection moves to other areas, which leads to the development of peritonitis or space-occupying formation.
Chlamydia
This is one of the specific inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract. Currently, this pathology is very common. This is due to the fact that the causative agent is chlamydia - an intracellular microorganism that is tropic to the organs of the genitourinary system.
It is resistant to environmental factors, easily transmitted by contact, and is also slightly susceptible to drugs. That is why this inflammatory disease leads to the development of complications in many women. Among them, the most common are infertility and adhesions.
Chlamydia is most often detected in women aged 25 - 40 years. Moreover, these characteristics are associated with the fact that women are at risk for inflammatory diseases due to high sexual activity, planning pregnancy, and frequent visits to specialists for possible diagnostic testing.
Symptoms:
- Very often, chlamydia does not manifest itself at all or the symptoms are mild. In most cases, this inflammation is detected only during a random examination for periodic pelvic pain or infertility.
- Sometimes a woman is bothered by itching and discharge from the genital tract. A discharge of a pathological nature appears, it becomes liquid, almost transparent, sometimes accompanied by itching. Separation usually occurs in the morning, 20 - 30 minutes after waking up.
- With a long course, a pain syndrome is detected , which has a mild course and intensifies with physical activity or sexual intercourse. Subsequently leads to complications such as ectopic pregnancy or infertility associated with chronic inflammation in the uterine cavity.
Herpes
This is a viral infection of the reproductive system.
The disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus. There are several varieties of it, each of which causes damage to one or another part of the body.
In this case, there is a predominant damage to the organs of the reproductive system, in particular the external parts.
At the same time, herpes occurs in both men and women, but representatives of the fair sex are more susceptible to this pathology.
The age groups that have inflammation of the genital organs caused by herpes are also different, but most are 20 - 40 years old. This corridor is due to the fact that it is during this period that a person can have the largest number of partners and sexual life is very diverse.
Symptoms:
- The disease is characterized by the involvement of the mucous membranes of the genital organs, as well as the skin, in the pathological process.
- In this case, the appearance of bubbles is noted, which are filled with liquid contents and have a slightly yellowish color. The sizes of these formations vary, from several millimeters to centimeters, this is due to the fact that they can merge. In this case, severe pain, constant itching, and, if the integrity is violated, a burning sensation is manifested.
- Subsequently, elements deprived of a protective film are covered with crusts and a bacterial process can join them. The general condition changes, body temperature may rise and intoxication may increase.
Leukoplakia of the cervix
The disease is a dystrophic change in the squamous epithelium - the mucosa, during which the horny and granular layers are formed.
Among the symptoms, one can note a change in the color of the mucous membrane from pink to white, which can only be seen by a gynecologist during examination. Women in therapy can be prescribed the following groups of drugs - antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiviral.
For the healing of leukoplakia lesions, the following is used:
- laser coagulation;
- cryogenic exposure;
- radio wave destruction;
- chemical exposure.
The patient’s diet is also important, which should be provided with foods high in vitamin A and beta-carotene. During the period of treatment, the woman should completely exclude sexual activity.
From folk remedies, you can use the following recipe for douching or washing:
- It is necessary to combine St. John's wort, calendula, yarrow, knotweed, chamomile, horsetail and eucalyptus in equal parts;
- 2 tbsp. l. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over this collection and place in a water bath.
- After 15 minutes, remove and keep covered for 30 minutes.
- Strain.
It is recommended to use daily.
Candidacamicosis
Thrush is considered the most common female disease on the planet. The disease is called so because of the fungus that causes it. Candida is normally present in the vagina of most women, but is activated only under the influence of certain factors.
Candidiasis: that is, the period when the fungus is dangerous, can be provoked by:
- taking antibiotics;
- weak immunity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- venereal diseases.
Signs of vaginal candidiasis are as follows:
- burning and itching;
- characteristic discharge with a cheesy consistency;
- pain not only during sexual intercourse, but also during normal urination.
If any of these symptoms appear, it makes sense to immediately consult a gynecologist.
In the treatment of thrush using traditional methods:
- tampons soaked in plant solutions;
- douching and vaginal baths;
- decoctions and infusions;
- adjustments to diet and lifestyle.
The simplest and most effective remedy is considered to be regular douching with chamomile infusion. To prepare it you need 3 tbsp. l. pour 1 liter of boiling water over the flowers of the plant and let it brew for at least 2 hours.
How often should you visit a gynecologist?
In order to avoid the development of complications and maintain health, a woman should visit a gynecologist 2 times a year. Even in cases where she has no worries. When visiting a specialist, it is recommended to undergo tests (bacterioscopy of a smear, culture of vaginal discharge, etc.) even if the doctor did not reveal any abnormalities during the examination.
Such tests will help to timely identify whether or not the causative agents of the most common infectious gynecological diseases are present in a woman’s body. You will have peace of mind about your health, knowing that everything is fine. Remember about the complications that cause female diseases that are not treated in a timely manner, and at the slightest suspicion of any problem, consult a doctor!
Cervical dysplasia
With this disease, atypical cells form on the cervix.
The potential danger of the disease (usually provoked by the papilloma virus) is that, despite its asymptomatic course, at some point it can develop into oncology.
By regularly taking smears, dysplasia can be detected at an early stage, which means that the chance of getting rid of the problem will be as high as possible.
Therapy uses immunostimulants or surgical removal of the dysplasia area. Depending on the severity of the disease, this can be either amputation of the cervix or a method of laser, radio wave therapy, or electrocoagulation.
You can also regularly make tampons from celandine or douche with it. For cooking you need 1 tbsp. l. pour dry raw materials with a glass of boiling water and leave for 1 hour.
Mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland).
Inflammation of the mammary gland, or mastitis, occurs mainly during breastfeeding; at other times it is extremely rare. In most cases, women of reproductive age - 30-50 years are affected. The incidence is 1-16% depending on the region, of which 85% are primiparous women.
The reasons for the development of the inflammatory process in the mammary gland in nursing mothers is lactostasis (milk stagnation), which creates ideal conditions for the proliferation of bacteria. In other cases, the cause is also a bacterial infection, most often staphylococcus.
Mastitis is characterized by redness, swelling and a feeling of tension in the mammary gland on the affected side, an increase in body temperature up to 39C. At the same time, there is a risk of developing an abscess or fistula in the affected area. As a rule, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, treatment brings quick results.
Mastitis: what it is, the main causes and symptoms of the disease.
Endometrial hyperplasia
The disease is characterized by tissue growth beyond normal and thinning.
This is possible due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance;
- abortions;
- infections;
- inflammation of the genital area;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs.
Usually, in the early stages, hyperplasia does not manifest itself in any way; when it develops, there is first a slight spotting, which, if left untreated, can turn into prolonged bleeding. Due to hyperplasia, endometrial carcinoma can develop, and it can also cause infertility.
Traditional treatment may be as follows:
- taking hormonal medications;
- surgical removal of the endometrium;
- laser cauterization;
- uterus removal;
From folk recipes, you can take a mixture based on peony extract, which is available in pharmacies. Take the product 2 ml 3 times a day, diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2.
Bacterial vaginosis
This disease is a pathology of the vagina, provoked by the growth of bacteria such as mycoplasma, gardnerella, peptococcus, in which there is no inflammation.
There are also practically no symptoms, the only thing that may indicate bacterial vaginosis is copious vaginal discharge, which has a characteristic unpleasant odor of rotten fish. At first, this discharge is white or gray, later it acquires a yellow-green tint and becomes thick.
Complex therapy consists of 2 stages:
- The use of antibacterial drugs, for example, Metronidazole (in the vagina), Clindamycin (orally and in the vagina).
- Use of eubiotics (Lactobacterin, Bifidumbacterin).
For douching, you can make a solution from bird cherry fruits. The berries should be boiled over low heat for 20-25 minutes, then cooled and strained.
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix. It can be provoked by strepto- and staphylococci, chlamydia and trichomonas, E. coli, as well as viruses and parasites. The acute course of the pathology is characterized by strong mucous discharge (sometimes purulent) and dull pain in the lower abdomen.
When examined on a gynecological chair, swelling and hemorrhage, hyperemia and protrusion of the mucous membrane are detected. Treatment of cervicitis includes taking antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
For douching at home, you can prepare a decoction, which will require the following medicinal plants:
- flowers of calendula and wild mallow;
- birch leaves;
- motherwort grass;
- liquorice root;
- dandelion;
- caraway berries.
Preparation:
- All ingredients should be crushed and mixed, select 10 g.
- Pour 0.5 liters of warm boiled water.
- Simmer in a water bath for 15 minutes.
- Leave in a warm place for 2 hours.
- Strain.
The decoction should be used three times a day, 1 tbsp.
Consequences of inflammatory diseases
- One of the most common complications is the transition of inflammation to a chronic course.
- In addition, relapses of the process may develop.
- With inflammation of the cervix, a chronic process can develop with the further formation of a malignant process.
- The upper genital organs are prone to the development of infertility in women of reproductive age, as well as miscarriage and spontaneous miscarriages.
- In women, against the background of inflammatory processes, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted and menstruation becomes more painful and prolonged.
- With massive inflammation, a purulent focus may occur, which requires surgical treatment.
- When inflammation spreads to neighboring organs, there is a risk of life threatening.
Cervical cancer
This is a malignant tumor that develops from the mucous epithelium in the area of the transition of the cervix to the vagina.
In the early stages there are no symptoms of cancer, but in the later stages they appear:
- severe leucorrhoea and spotting;
- bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle and contact discharge during sexual intercourse;
- bladder and bowel dysfunction;
- anemia.
Treatment most often includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. The appointment is individual and depends on the stage, condition of the patient and the presence of inflammation.
Folk remedies for therapy can be:
- Eating wolf berries. You should take no more than 1 berry per day.
- Sea kale powder, which should be consumed 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day, with plenty of warm water or tea.
- Drinking an infusion of shepherd's purse herb. To prepare, take 1 tbsp. l. herbs and pour cold boiled water over it.
- After steeping for 8 hours, strain and take.
Diagnostic methods
To identify the cause of vaginal and genital problems, a number of studies are carried out:
- Visual examination and palpation.
- Taking a smear from the vagina and cervix. It will help determine the microflora and the presence of atypical cells.
- Bacteriological culture. Identifies the causative agent of the disease and determines the body's sensitivity to antiseptics.
- Blood test for hormones.
- Ultrasound and mammography. Helps determine the presence or absence of neoplasms.
- Computer infrared diagnostics. Determines the boundaries of the tumor and the presence of metastases.
- Radiography. Used to detect tumors and tubal patency.
In controversial cases, material is taken for a biopsy.
Mammography helps to determine the condition of the mammary glands
Complications of female diseases
The most important danger of diseases of the female genital area lies in their possible complications - untreated or lately detected diseases lead to more serious pathologies - increased inflammation and the development of their chronic form, infertility and oncology.
Considering that most diseases are practically asymptomatic, regular visits to the gynecologist are necessary. Examinations by a gynecologist once every six months are the best preventive measure in preventing the development of gynecological diseases.
Article design: Mila Friedan
How to identify hidden diseases?
The smears that we are used to taking in clinics are not very informative. The maximum that they will show is the presence of an inflammatory process.
To see serious diseases, it is worth doing a more complete examination, which is usually carried out only for a fee: this is PCR, cultures, blood from a vein, femoflor screen - this is an examination of the urogenital tract and other gynecological examinations.
The number of necessary examinations is prescribed by the doctor who is observing the patient.