Lichen planus - a non-infectious, chronic disease of the mucous membrane or skin. If color or spotted lichen is of a fungal nature, the causes of this disease are unknown, and its symptoms are completely different. Among all patients with dermatoses, 1-2.5% are affected by this disease, and as for pathologies of the mucous membrane - 10%.
The disease is characterized by the formation of various papules. They can be solitary or grouped in groups of different sizes.
Varieties and atypical forms
There are several types of the disease, which differ in their symptoms:
- typical shape
- ring-shaped,
- erythematous,
- warty (sometimes called verrucous),
- pemphigoid,
- atrophic,
- erosive-ulcerative.
There are also very rare types - obtuse, serpiginous, erythematous.
Lichen planus is changing, and now the pathology has characteristics that did not exist several decades ago. This is due to environmental changes, frequent use of antibiotics and other factors.
The disease today has the following features:
- relapses occur faster;
- Atypical variants of the disease occur more often;
- cases of malignant transformation of affected cells have become more frequent (up to 10-12%).
Reasons for appearance
The disease was first identified in 1860, but since then doctors have not been able to determine exactly what the prerequisites for its appearance are.
Today, doctors do not have a common opinion about the origin of lichen. This is partly why there are no therapeutic agents that eliminate the cause of this disease and cure it completely. Scientists can identify only a certain group of factors that contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- Genetic predisposition (genetically predetermined characteristics of immunity).
- Internal disorders (immune problems, neurological problems).
- External influences (the influence of viruses, allergens, side effects of using certain drugs).
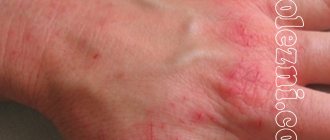
On the surface of the body there are characteristic places that are most susceptible to lichen planus - the joint area of the wrist, forearm, lower leg, sacrum, skin of the penis. Speaking of mucous membranes, plaques appear in the mouth and genitals.
How to cure
Treatment depends on the severity of the process, the cause of its occurrence and concomitant diseases.
How to get rid of the disease for adults
Severe itching:
- antihistamines (Clemastine, Tavegil);
- sleeping pills (Medazepam);
- sedatives (Chloropyramine, Cetirizine).
Foci of chronic infection - antibiotics: Penicillin, Erythromycin, Doxycycline (medium doses).
For extensive lesions - drugs of the aminoquinolone group: Plaquenil, Delagil. Course 3 weeks, 1 tablet 2 times a day.
In the acute phase - systemic corticosteroid therapy. Prednisolone tablets. Diprospan IM 1-2 ml once a week. Course 2-3 weeks.
Immunomodulators: Ridostin, Neovir.
Peripheral vasodilators: Nicotinic acid.
Vitamin complexes containing vitamin A.
Physiotherapy:
- PUVA therapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Laser therapy.
Some doctors recommend: electrosleep, acupuncture, sanitary-epidemiological treatment.
Treatment with ointments:
- Corticosteroids: Advantan, Elokom, Celestoderm.
- Inducing agents in the composition with salicylic acid, tar, naphthalan, ichthyol.
- Antiallergic: Gistan, Fenistil.
Any complex of treatment should be selected only by the attending physician, taking into account an individual approach.
How to cure a child
Children are rarely diagnosed with LP.
This is usually a bullous form (atypical). It is complicated and difficult to treat. In many cases, symptomatic treatment is used, as in adults. The treatment methods used make it possible to suppress the symptoms of the disease and increase the period of remission.
It is impossible to completely cure LP in children. Such patients are registered at a dispensary at their place of residence.
Symptoms
The main manifestations are monomorphic body rashes of the type of nodules or papules. Their hue varies between red and purple, and their size ranges from 2 to 5 mm. The papules have a retracted middle, and their entire surface seems to be covered with wax. Usually there is no or slight peeling. If the psoriasiform type of lichen develops, the peeling is similar to psoriatic separation of scales.
Ringworm rashes cluster in specific areas of the skin, resembling rings or garlands. Then small elements merge into plaques and grow. When they resolve, the skin remains hyperpigmented for a long time afterwards. Often the patient suffers from severe itching, causing discomfort and problems sleeping.
The usual location of such lichen is the bends of the arms and legs, thighs, groin area, and armpits. Also, elements of the rash cover the torso. But the most popular location for the rash is the oral cavity.
The disease most rarely grows on the nails. Then, longitudinal striations, clouding, destruction of the nail fold, and ridges are characteristic. Feet, palms, head, face are unpopular locations for ringworm.
25% of patients with this pathology report wounds exclusively in the mouth, without any skin pathologies.
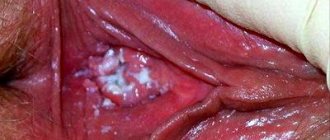
Favorite places for rashes are the oral cavity and genitals. The rashes are usually grouped into rings, laces, or can be isolated. The formations in the mouth have a grayish-opal color; on the tongue they may have a whitish tint. Small purple plaques form on the lips, which peel off a little.
The classic form of the disease has some characteristic symptoms. In particular, the so-called Wickham pattern, when the surface of the largest formations is covered with a grid-type pattern, which is especially pronounced after smearing the rashes with oil. The disease is also characterized by the Koebner phenomenon, when new rashes form on injured skin.
Hypertrophic (or verrucous) lichen. This form is characterized by multiple warty layers on the papules due to hyperkeratosis. In addition, many individual nodules are localized near the plaques. With this form of the disease, rashes usually form on the legs; they are extremely rarely observed on the arms and face. Some symptoms of the disease are very similar to senile keratosis and basal cell carcinoma.
Atrophic form. The disease is characterized by modifications of the rash - sclerosis and atrophy. Sometimes a rash appears in the hair, stimulating the process of baldness.
Pemphigoid form. The disease resolves with the formation of many blisters with clear or bloody fluid. Bubbles can be on the site of papules or on healthy skin. Next to them is the usual lichen rash. The most common localization of the pemphigoid form is the feet and legs. If the blisters reach a large size, the lichen becomes bullous.
Lichen moniliformis. The disease is characterized by the formation of round rashes with a waxy surface. Together they form the so-called necklace. Usually the rash is localized on the neck, forehead, hands, behind the ears, buttocks, abdomen, elbows, etc.
Pigment form. In this case, not only regular rashes form on the surface of the skin, but also brown spots and nodules. Most often they appear before the classic rash.
Pointed shape. The main locations of the rash are the neck, legs, and back in the area of the shoulder blades. The predominant elements of the rash are pointed papules, the central part of each of which has hyperkeratosis in the form of a horny spike.
Ring shape. This type of disease is characterized by the growth of the peripheral zone of the plaque, followed by a transition to the central part. As a result, the rash becomes ring-shaped. This type usually occurs in men, in whom it affects the genitals and the inside of the legs.
Erosive-ulcerative form. It usually appears in the mouth, where ulcers and erosions form, accompanied by redness and swelling. The healing stage of erosions is very long, up to several years. During this time, several relapses of the disease may occur in the same place or nearby.
Symptoms
In the early stages of development, the disease manifests itself in weakness, irritability, and possibly general malaise. Often these signs are not recorded by patients.
Subsequently, the symptoms of lichen ruber become more pronounced:
- the appearance of smooth-shaped papules, grouped together in rings, stripes or a mesh, as a result of which a red spot is identified;
- plaques acquire a glossy appearance;
- the appearance of a red, purple, crimson rash;
- formation of scales and peeling of the skin;
- itching in the area where the papules are located;
- the appearance of distinct pigmentation.
Lichen is localized on the wrists, in the forearms, sacral area, on the legs, under the knee, on the inside of the thigh. Men suffer from rashes on the genitals. In some cases, plaques may appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth or lips.
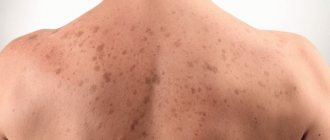
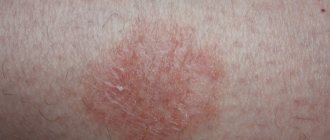
Photo of lichen planus: what it looks like
Below are some photographs from which you can understand approximately what characteristic skin rashes look like. So, the first two photos show the general appearance of plaques in a typical type of disease, and the last two show generalized skin lesions in large areas.
Content may be difficult to view
Diagnostics
Diagnostic procedures to determine the disease are carried out by dermatologists. To do this, they evaluate the patient's symptoms and compare them with those of lichen. If it is difficult to make a specific diagnosis, a histological examination is prescribed. In addition, symptoms of similar dermatoses, in particular psoriasis, syphilis, and other pathologies, are excluded.
When the skin is covered with a characteristic rash, this symptom is sufficient to make a diagnosis. If the patient has some kind of atypical or rare form of the disease, it will be much more difficult to differentiate this type of lichen from others. The problem is also that conventional laboratory tests do not simplify the task, since with this lichen there are practically no deviations in blood counts. And only occasionally eosinophilia, leukocytosis, and a slightly increased ESR are observed.
In some cases, a biopsy is performed to determine the disease. The method involves examining skin tissue for hyperkeratosis, the presence of inflammation, hypergranulosis, hydropic degeneration of the basal part of the epidermis, stripe-like infiltration of the upper part of the dermis, and the presence of colloidal Sevatt bodies between the epidermis and dermis.
Treatment of lichen planus
Most approaches to the treatment of lichen planus consist of eliminating the symptoms of the disease, that is, most of its external manifestations. This means that in each specific case the treatment will be different, since everyone’s disease manifests itself individually.
So, if the main symptom of lichen planus is severe itching, then doctors prescribe the patient antihistamines, sedatives to calm the nervous system, local glucocorticosteroids, and sleeping pills.
If a secondary bacterial infection appears in the area of the rash, it is necessary to start using antibiotics in an average dosage. This must be done, since a protracted fight against microbes leads to a significant weakening of the immune system, which further contributes to the development of skin disease.
Further, the lichen can spread to large areas of the skin or mucous membrane. In this case, its successful treatment is possible only with the use of strong quinolone immunosuppressants, in particular Delagil, Plaquenil and others.
If the disease progresses, glucocorticosteroids, which have an immunosuppressive effect, are also prescribed. They give very quick results regardless of the dosage form.
There are other types of therapeutic effects, in particular, the administration of vitamins, electrosleep, acupuncture, etc. In combination with classical methods of treatment, they give a stable result, which can improve the prognosis of the disease.
Ointments
Typically, topical medications are not used. But there are situations in which inflammation or its individual manifestations (for example, severe itching) manifest themselves clearly, therefore the use of steroid ointments (prednisolone, hydrocortisone ointment), vegetable oils, and products with phytoextracts is indicated. Their use is effective only to suppress itching; in other cases, internal remedies are used, since the cause of the disease lies inside the body.
Pills
The main treatment for lichen are 4-aminoquinoline derivatives (Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine) and hormonal therapy. Antidepressants and sedatives are prescribed as auxiliary agents to combat itching. Doctors often prescribe antihistamines if there is a suspicion that an allergen caused the reaction.
These are the following drugs:
- Claritin,
- Tavegil,
- Telfast et al.
To normalize the body's metabolism and quickly restore the healthy appearance of the skin, certain vitamins are prescribed, in particular, vitamin A (it is responsible for the division of skin cells), carotenoids, vitamin E (increases the effectiveness of hormonal therapy). If the disease is accompanied by frequent relapses, it is possible to use tablets that increase oxygen supply to tissues - Actovegin, Cyto-Mac.
Diet
If there is lichen planus on the oral mucosa, it is necessary to avoid the use of too hot, spicy and irritating foods. It is also prohibited to eat food that can cause allergic reactions (for example, bee products, citrus fruits).
To create a diet, it is recommended to consult a doctor. He will indicate which foods should not be consumed due to their irritating effect on the mucous membrane.
In general, the recommendations are as follows:
- eat as many pureed foods as possible;
- refuse to eat rich foods;
- reduce sugar and salt intake;
- take soups and jellies warm;
- Avoid eating smoked, spicy and salty foods;
- stop eating ice cream, sour foods, and sweet carbonated drinks;
- Avoid taking coffee, alcohol, hot tea.
After each meal, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a decoction of calendula or chamomile. This is necessary to disinfect the mouth and reduce the likelihood of rotting of the remaining pieces of food in it.
Folk remedies
There are several folk recipes for eliminating lichen planus:
- Herbal collection. Mix chamomile, string and sage (1:1:1) and brew 1 tbsp. l. per glass of boiling water. The product is taken three times a day, it relieves inflammation, calms the nervous system, and strengthens the body.
- To strengthen the fight against skin irritation, prepare cold lotions from a decoction of the string (20 g of herb per 1 cup of boiling water).
- To treat plaques directly, crush 50 g of garlic cloves and infuse in a glass of vodka. Wipe the affected areas of the skin with the product.
- A cabbage leaf has a good effect, the surface of which is smeared with sour cream, after which it is applied to the rash. It alleviates the symptoms of the disease and accelerates skin healing.
Traditional methods of treatment cannot be considered as the main ones. They only complement drug therapy prescribed by a doctor, but on their own cannot effectively cope with the disease. Moreover, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist about the self-treatment methods you choose to make sure that they will not harm the body.
General recommendations
Experts highlight several recommendations for patients prone to relapses of lichen planus in order to combat the disease as successfully as possible:
- eliminate all carious cavities in the mouth using filling;
- visit your dentist regularly;
- find out if you are allergic to something and avoid contact with allergens;
- do not allow the exacerbation of chronic internal diseases, especially those of an infectious nature;
- practice regular rest, eliminate stress at work.
Prevention of pilaris
All diseases are easier to prevent, but following simple rules of prevention can contribute to a speedy recovery:
- Do not neglect the rules of personal hygiene, take a shower in a timely manner, do not use other people’s personal hygiene products such as a comb, towel, slippers;
- Do not use detergents with aggressive components that can disrupt the body's barrier functions;
- Avoid frequent injuries, and if there are wounds, treat them with antiseptic drugs;
- Use clothes made from natural fabrics;
- If you have an allergy, try to remove or replace the provoking factor;
- Increase immunity and maintain its functions;
- If there are acute or chronic diseases, treat them completely;
- Do not abuse the solarium;
The duration of the disease varies from two months to a year; timely treatment and strict adherence to the doctor’s instructions will speed up recovery. To prevent a relapse, it is advisable to retake tests a couple of months after recovery and repeat the course of vitamin therapy.
Complications and consequences
In most cases, the disease does not pose a life-threatening danger. The patient may experience discomfort from severe itching, which will increase without medical attention. This can significantly affect the human psyche, and also cause some problems in communicating with society.
In addition, recent studies suggest that it is extremely rare (in 1 case out of 100) that seemingly harmless rashes of pityriasis rubra may degenerate into malignant neoplasms. This once again confirms the need to see doctors to receive quality medical care.
During pregnancy
Pregnancy is stressful for the female body, so this condition can cause a recurrence of lichen ruber. This especially happens during a sharp release of certain hormones that undergo changes, including the immune system.
There is no danger to the woman herself or her unborn child from this disease. But there are a number of symptoms that will cause certain difficulties, in particular, severe itching.
Therefore, it is necessary to follow preventive measures to avoid the occurrence of lichen:
- if possible, avoid contact with heavy chemicals;
- treat any infectious diseases, in particular skin diseases, in a timely manner;
- worry as little as possible, eliminate stress and strong feelings;
- monitor the correctness of your diet;
- lead a healthy lifestyle.
Types of pityriasis pilaris
In addition to the main type, there are other lichens that can affect areas of the skin with hair, these include - red lichen, pink lichen (Zhibera), ringworm.
- Ringworm is often an autoimmune reaction of the body, due to the use of medications, or due to the presence of diseases such as hepatitis C.
- Pityriasis rosea is one of the manifestations of an allergic reaction of the body; this type is not contagious, but cases of zoster affecting the whole family have been recorded.
- Ringworm is an infectious disease caused by fungi. The disease is contagious.