From this article you will learn:
- causes of rosacea on the face,
- what role does the solarium play here?
- symptoms, effective medications,
- reviews of rosacea treatment with laser and IPL.
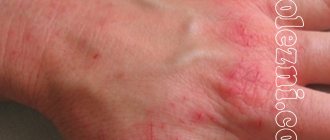
Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that manifests itself in the form of erythema (redness) of the skin, telangiectasia, as well as papules and pustules resembling regular acne. Due to the latter, this disease is also called “acne rosacea”. Rosacea occurs mainly in the middle third of the face, as well as in the forehead, nose and chin. In rare cases, it can occur outside the face - mainly on the neck, chest, scalp or ears.
Typical locations of Rosacea are:
A predisposing factor to the appearance of rosacea is considered, for example, to be exposure to solar UV radiation, which stimulates the production of vascular endothelial growth factor and leads to the appearance of networks of small capillaries, i.e. telangiectasia. Accordingly, rosacea can easily appear after tanning. Another factor is genetic predisposition (associated with the lability of the walls of blood vessels), as well as a person’s individual tendency to redness of the skin, which is also associated with the superficial location of the vessels.
In addition to these factors, the influence may be exerted by: 1) parasitic skin disease caused by Demodex folliculorum mites, as well as the bacteria Staphylococcus epidermidis, 2) gastrointestinal diseases associated with infection of the intestines by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Studies have found that in the presence of intestinal inflammation and Helicobacter pylori, hypersensitization of sensory neurons in the facial area occurs (through the synthesis of bradykinin, which is a powerful vascular dilator).
Most often, the disease is detected in patients 30-50 years old, and according to statistics it occurs in 10% of the population. It has been noted that rosacea occurs more often in people with fair skin who blush easily. Most often these are women with fair skin, blond hair and blue eyes. In men, the disease develops less frequently, but phymatous changes develop more often. Depending on the clinical manifestations, rosacea is usually divided into 4 types, which we will discuss below.
Causes and mechanism of development
Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that manifests itself as persistent redness of the skin of the cheeks, nose, forehead, which manifests itself in the form of bright pink rashes, spider veins, pustules and skin atrophy.
Even today, unfortunately, it is impossible to say with complete confidence about the causes and mechanisms of rosacea. There are two assumptions: on the one hand, it is believed that the basis of the disease is the high sensitivity of blood vessels to various physical influences of the environment (cold, heat, dry air, or sudden changes in temperature), and on the other hand, it is believed that the disease is hereditary in nature . That is, the fragility and fragility of blood vessels is a genetic predisposition, since the majority of people do not have any reactions to such irritants.
There was an assumption that the disease is caused by a mite called demodex (Demodex folliculorum), which parasitizes the skin of the face and the sebaceous glands of the hair follicles. It was also believed that this mite causes the disease demodicosis, which contributes to the occurrence of rosacea. However, modern research has established that demodex is found on the skin of absolutely healthy people and does not need to be treated.
There is also an assumption that the occurrence of rosacea is closely related to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The appearance of rosacea is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which is responsible for the development of gastritis and gastric ulcers. Thus, people with gastritis and peptic ulcers are more susceptible to rosacea than those in whom this bacterium is not detected.
There is an opinion that medications can also cause rosacea. And this is partly true. Thus, corticosteroid ointments that cannot be used on the face can cause “steroid rosacea.”
Thus, rosacea is more likely to develop in the following cases:
- in women during menopause, puberty or pregnancy, since during this period hormonal levels change, which affects the condition of blood vessels;
- in people with very fair skin, the “Celtic” phenotype. It’s not for nothing that the British called rosacea “the curse of the Celts”;
- in people with sensitive skin and fragile blood vessels;
- in persons suffering from chronic forms of allergic and contact dermatitis;
- in case of disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- in persons suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia, with damage to the vascular network of the face;
- in persons with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- when drinking alcohol, hot or spicy foods;
- with a sharp change in temperature outside, indoors, in saunas and baths.
Rosacea occurs in both sexes, but women are more likely to suffer from this condition. From a genetic point of view, northern peoples living in a sharply continental climate are more predisposed to the appearance of rosacea than people living in warm countries.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that tends to affect a highly visible area of the skin such as the face. The cosmetic symptoms of rosacea can be significant and can significantly reduce a patient's quality of life. Although there is no definitive cure for rosacea, effectively treating symptoms can reduce the harmful effects of the condition and improve your quality of life. In this article, we will review existing and new cosmetic treatments for rosacea, including topicals, systemic pharmacological treatments, light therapy techniques, and other modalities, and evaluate their ability to improve the cosmetic symptoms of rosacea. Since there is no definitive cure for rosacea, effective treatment is aimed at improving cosmetic symptoms. The choice of therapy should be determined on an individual basis, taking into account the clinical features of greatest concern to the patient. A combination of techniques and/or graded therapy is often required to achieve optimal cosmetic results. Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects approximately 16 million Americans. Dermatosis most often affects the central part of the face (forehead, cheeks, nose, chin). The pathophysiology of rosacea remains poorly understood despite the relatively high prevalence of the disease and a significant portion of current research devoted to this dermatosis. Modern theory suggests the involvement of the innate and adaptive immune system, disorders of neurovascular regulation, changes in the blood and lymphatic vessels, genetic predisposition and the reproduction of synanthropic organisms, such as Demodex, in the pathogenesis of rosacea. In addition, the clinical course can be worsened by a variety of external factors, such as UV radiation, heat exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress. The diagnosis of rosacea is usually made clinically and rarely requires histological confirmation. Although rosacea can present with a wide range of clinical features, its main feature is diffuse erythema of the central face. This centrofacial redness can intensify during periods of exacerbation and becomes persistent over a long period of time. Other signs of rosacea include telangiectasia, swelling, plaques, phymatous changes, dry skin, ocular manifestations and inflammatory lesions in the form of papules and pustules. Patients may also complain of a burning sensation in the areas of the skin lesions. Rosacea is classified into 4 subtypes: erythematotelangiectatic, papular-pustular, phymatous, ocular, and one variant, granulomatous. This division is conditional, because One patient may exhibit signs of several subtypes. Compared with the general population, patients with rosacea are more likely to have low self-esteem, embarrassment, social anxiety, and depression. However, effective treatment can improve cosmetic appearance and mitigate the negative psychological consequences of the disease. In the treatment of rosacea, topical and systemic medications, light methods, and various procedures are used. The selection of therapy should be carried out on an individual basis, taking into account clinical characteristics, using combined or sequential treatment methods.
Symptoms
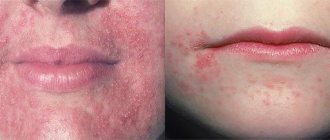
The first symptom of rosacea (see photo) is a rash of red spots on the face immediately or a few minutes after exposure to the provoking agent. The spots are mainly localized on the forehead, cheeks, bridge of the nose and chin. It is very difficult to suspect rosacea at the initial stage, since the rashes, in addition to not disappearing for a long time, do not cause any discomfort to the person. These spots can be easily hidden with regular cosmetics.
Attacks of redness become more frequent and are provoked more and more easily in the future. Constant dilation of blood vessels is accompanied by a feeling of heat on the face. Increased blood supply to the skin of the face leads to the activation of microorganisms that are constantly present on it. This leads to the formation of bumps on the skin. If left untreated, small pustules may appear at this stage.
At a later stage, skin rosacea leads to changes in the structure of the skin on the face: they become rough and dense to the touch. Chronic expansion of subcutaneous capillaries becomes noticeable to the naked eye - a vascular network appears on the face. Individual vessels with rosacea dilate especially strongly - telangiectasias appear. At this stage of the disease, redness of the skin is permanent and is no longer associated with provoking factors.
The last stage of rosacea is lupoid, manifested by numerous rashes around the eye sockets and mouth in the form of brown-red nodules and spots. With a particularly unfavorable course, there is a tendency of these rashes to merge. The stage is named so because of the similarity of the clinical picture with the manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus (from the Latin - lupus).
Common symptoms of rosacea are:
- skin itching in the area of the rash;
- burning;
- feeling of tightening skin;
- paresthesia in the form of “goosebumps” on the skin.
A typical symptom of rosacea in men is more pronounced thickening of the skin of the nose. This leads to the fact that rosacea is also complicated by rhinophyma.
Other types of rosacea
In practice, there are several types of this disease, they are classified according to the characteristics of their manifestation and other factors.
- Conglobate rosacea is a disease accompanied by the formation of spherical growths. They are huge in size and appear on skin that is reddened by lesions. The causative factor in the occurrence of the disease is the uncontrolled use of certain groups of drugs.
- Steroid rosacea begins its development path only after the patient has used a large number of hormonal ointments to eliminate skin diseases of a different nature. This form has several difficulties in treatment, but is less common, unlike the previous disease.
- Fulminant form of the disease - the development of this disease occurs due to hormonal disorders. The shape is typical for young women. The reasons are stress, pregnancy, hormonal imbalance, menopause. The problem with the course is that the disease begins to progress rapidly and greatly disfigures the appearance of individuals, causing neurosis.
- The edematous form is less common, unlike other types of the disease, and is manifested by swelling on the face, which is usually located in the central part. Over time, the swelling takes on a purple hue, and if pressure is applied to it, no pits will remain.
Many features of its manifestation, as well as the nature of the consequences, depend on the type of disease.
Classification
| Subtype | Characteristics |
| Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea | • Hot flashes last more than 10 minutes; • Possible burning and slight tingling; • Redness is limited to the midface; • Telangectasia (dilation of small vessels). |
| Papulopustular rosacea | • The appearance of small papules and pustules; • Redness and swelling of the entire face; • Enlargement of pores and superficial nodules. |
| Phymatous rosacea | • Enlargement of all skin elements; • Affects the nose (mainly), chin, forehead, eyelids. |
| Ocular rosacea (ophthalrosacea) | • Burning, tingling and itching of the eyes; • Increased sensitivity to light; • Blepharitis; • Conjunctivitis. |
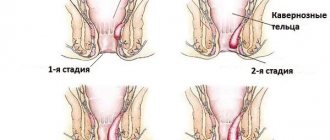
Subtypes of rosacea (from left to right): erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous (mild stage)
In addition to these four subtypes, some doctors distinguish two more types of the disease:
- Rosacea fulminans. It is characterized by the rapid appearance of many erythematous rashes, papules and pustules with purulent discharge. In some cases, it may occur in the context of hormonal changes, inflammatory bowel disease, stress and pregnancy. Rosacea fulminans is not often mentioned in the medical literature, so doctors have not come to a consensus whether to classify the symptom complexes of this condition as rosacea or related diseases.
- Granulomatous rosacea. It appears as hard red or yellow-brown papules on the cheekbones, around the mouth and eyes. It is more common in middle-aged women with weakened immune systems. Symptoms may resemble sarcoidosis or cutaneous tuberculosis.
When diagnosing, steroid or steroid-induced rosacea is distinguished separately, the cause of which is associated exclusively with the use of topical products containing corticosteroids.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Dark spots on the face in the elderly
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, a dermatologist only needs an external examination, as the clinical signs of rosacea are very specific. But laboratory diagnostics are still carried out to clarify the condition of the body and identify associated parasites (for example, demodex).
In the presence of pustular rashes, a bacterial culture is required to determine the type of pathogenic microflora and apply appropriate antibiotic therapy.
There is a certain difficulty if demodicosis is detected at the same time. Sometimes this disease is mistakenly identified as the cause of the pathological process, although with rosacea the mite is simply activated.
Complications
If you don’t try to treat rosacea at all and don’t even treat it correctly, at the last stage the pathology takes on an ocular form.
The cornea of the eye is affected, in most cases keratitis develops, which is fraught with complete blindness. In men, a complication such as rhinophyma is often diagnosed. As a result of hypertrophy of the nasal tissue, a benign change in the nasal tissue, similar to a tumor, develops.
This organ increases in size, the surface becomes lumpy, and nasal breathing becomes difficult. Rhinophyma can only be treated surgically. Often, rosacea is accompanied by the occurrence or relapse of demodicosis - the activation of a microscopic intradermal parasite.
How to treat rosacea on the face?
Rosacea can be corrected, but is not 100% curable. The key treatment goals for rosacea are:
- reducing the severity of symptoms of the disease;
- prevention of exacerbations of the disease;
- prolongation of remission periods.
Therapeutic tactics largely depend on the clinical type of the disease. However, the basis for the success of treating rosacea in adults lies in the joint efforts of the doctor and the patient to identify provoking factors, which are strictly individual. Thus, for rosacea of all degrees of severity, it is recommended:
- completely eliminate alcoholic drinks;
- avoid spicy, smoked, hot and oral irritating foods;
- exclude spices from the diet, even the most harmless ones at first glance;
- eliminate or minimize the time you wear makeup;
- wear hats that prevent direct sunlight from entering the skin of the face;
- use sunscreens (only if they do not worsen rosacea);
- dress wisely to avoid overheating or hypothermia;
- protect your facial skin from the wind;
- do not sit with your head down for a long time; instead, it is better to sit down with your back straight;
- avoid heavy physical activity, instead it is better to do the work in several approaches;
- care for the skin, nourish it, maintain its hygiene;
- if a combined pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system or pelvic organs is detected, contact an appropriate specialist and undergo a course of treatment.
The list of medications used at home may include:
- macrolide antibiotics;
- tetracycline preparations;
- 0.75% -1% gel or mash based on metronidazole;
- 15% gel based on azelaic acid;
- 10% sulfacetamide with 5% sulfur to cleanse the skin.
The combination of local agents and oral medications allows you to achieve the following results:
- reduce the first manifestations of the disease;
- prevent exacerbations when stopping oral medications;
- prevent progression of the disease over a long period of time.
Taking antibiotics is the mainstay of therapy. It is these drugs that can have an anti-inflammatory effect and prevent the development of suppuration.
For local therapy at home, additional medications in the form of ointments and creams can be used:
- Ovante cream - effectively helps fight all skin processes that lead to the formation of a rash. There are no chemicals or antibiotics in the composition, which makes the composition preferable.
- Rosamet - this natural, highly effective product helps reduce redness and eliminate acne. The product has an excellent antimicrobial effect and actively fights any problems.
- Metrogyl gel helps cope with various bacterial and parasitic infections. It is effective for children and adults.
- Rosex - has a detrimental effect on sensitive microorganisms and allows you to overcome any processes caused by the disease in question.
- Ruboril - this cream has a safe and effective composition, it compares favorably with other products because it gives results after just a few uses.
- Zinc ointment is an effective remedy designed to fight inflammation and other processes. It has an affordable price and decent quality.
- Skinoren gel is a dermatological product that has a significant effect on the pathogenetic components of the disease. The cost varies from 200 rubles.
- Demoten gel is a cosmetic and preventive treatment for combating skin ailments of any type and location.
- Erythromycin ointment contains an antibiotic, which allows it to have a quick effect and have the proper effect on the skin.
- Yam ointment helps cope with the basic symptoms of the disease and improves the condition of the skin after just a few uses.
Masks
In the fight against facial skin pathology rosacea, masks should be used. These can be antiseptic, anti-inflammatory drugs.
These substances include masks based on:
- Blue clay. The product relieves inflammation well and exhibits a good wound healing effect. You should buy blue clay powder at the pharmacy. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. powder and dilute in cool water until smooth. Apply to disease-damaged facial skin. Leave until completely dry (20-30 minutes). Then the mask should be washed off with a suitable product or antibacterial soap for your skin type.
- Green clay. The use of the product for rosacea stimulates blood circulation well and has a tonic effect. You should take 1 tbsp. l. dilute the product (you can buy it at any pharmacy) with cool water and spread it on damaged areas of the skin. Let dry. Should be washed off with an antibacterial agent for daily facial skin care.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of rosacea can be supplemented with the following physiotherapeutic techniques:
- Cryotherapy. Can be used at any stage of the disease. The affected area is exposed to low temperatures using liquid nitrogen. This technique reduces the appearance of telangiectasias and improves the appearance of the skin.
- Electrocoagulation. The affected area is exposed to electric current through a thin electrode. This method removes papules, pustules and telangiectasias, but may leave burns on healthy skin.
- Rotational massage. The affected areas are massaged with circular stroking movements twice a day. This method improves lymph flow and reduces tissue swelling.
If rosacea is complicated by abscesses and fistulas, the patient may be recommended surgical treatment aimed at excision of pathological foci and installation of drainage for better outflow of purulent discharge. After performing such interventions, the patient is prescribed dressings using antibiotics and other anti-inflammatory and disinfectants.
Nutrition and diet
It is extremely important for patients with rosacea to maintain a healthy diet. It is better to eat little by little and regularly. It is necessary to limit as much as possible the consumption of any canned foods, salt, sausages, vinegar, pepper and other spices, any fried foods, animal fats, and sweets. It is not recommended to eat fruits such as oranges, grapes, tangerines and pears. You should forget about alcoholic drinks, strong hot coffee and tea.
What is possible? Your diet should include lean meats - boiled, stewed or steamed. You can eat fish, boiled eggs, butter and vegetable oil, potatoes. Cabbage, carrots, beets and fresh cucumbers, berries, apples and plums, dill and parsley, rhubarb, beans, any fermented milk products, cereals (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal), and unleavened bread are also allowed.
In severe forms of the disease, a doctor may prescribe therapeutic fasting for 5 days:
- Day 1: in the morning, the patient drinks a 10% solution of magnesium sulfate for 30 minutes, and then during the day drinks only mineral water (Borjomi, Narzan, etc.) with a total volume of 1000-1500 ml.
- Day 2: drink up to 2 liters of mineral water.
- Day 3: consume kefir, fermented baked milk, vegetable oil, 200 g of boiled potatoes, 20-25 g of butter, stale white bread or crackers (200 g), unsweetened tea, cottage cheese, vegetable soup, apples, fresh cucumbers.
- Day 4: in addition to the products of the previous day, you can eat fish or boiled meat (100 g), as well as cereal products.
- Day 5: You can include in your diet any vegetables and berries allowed for rosacea.
Laser therapy
This type of rosacea therapy is one of the most effective. Depending on the stage of the disease and the goals set, one or another laser therapy method is selected.
There are the following types of laser therapy for rosacea:
Deep tissue reconstruction with surgical lasers
This method actually refers to the methods of plastic surgery and is used in the extreme stages of the disease - with formed phymas. Its essence is to remove all pathological growths of connective tissue under the skin, down to bone and cartilage tissue. The ultimate goal of this method is to restore the previous contours of the affected part of the body.
The use of argon and carbon dioxide lasers can reduce blood loss during surgery and lead to healing by primary intention, that is, without subsequent scar formation.
Pulsed phototherapy
Pulsed phototherapy is the most commonly used laser treatment for rosacea in medicine. Its essence lies in the effect of photons of a certain wavelength on the skin, through which the surface capillaries of the skin are heated and glued together. Destroyed erythrocytes (red blood cells) act as an adhesive agent. As a result, the root cause of rosacea is eliminated - blood stagnation in the blood vessels of the skin.
The duration of one session is from 5 to 15 minutes, depending on the area of the lesion. To achieve a satisfactory therapeutic effect, 8 to 10 procedures are usually required. The interval between procedures is one week. To reduce local discomfort, a special cooling gel is placed on the area exposed to radiation.
This method is used for all forms of rosacea and demonstrates good clinical effect. It is most noticeable in the treatment of prerosacea and first degree rosacea (telangiectasia, single papules). Contraindications to this method are low blood clotting, acute periods of inflammatory diseases, neoplasms in the area of irradiation, tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, etc.
Oils
When treating the skin pathology of rosacea, it is necessary to use not only drug therapy, masks and compresses, but also oils that have a good effect on the affected skin. You should use essential oils - meleleuca tree (is a strong antiseptic), rosemary, lavender.
The drugs have a good anti-inflammatory effect. Essential oils must be added to the base - cream for daily use in an amount of up to 10 drops per 100 ml of cream. Should be used daily.
Folk remedies
Treating rosacea at home is no less successful, starting with lotions using effective decoctions and tinctures of plants. The only condition for a positive cosmetic effect is chilled solutions:
- Cranberry. Folded gauze in 10 layers is soaked in cranberry juice and applied to the face, with a layer of cotton wool on top. Next, everything is wrapped in a bandage and they wait from half an hour to an hour. First applications (diluted in a ratio of 1:3 with water), if the skin reacts favorably, you can make the solution more concentrated the next time (gradually reaching pure cranberry juice);
- Chamomile. An infusion of flowers is used (1:15), then gauze is soaked, folded several times, wrung out and placed on the face for 3 hours. This is done once a day;
- A series. Use 1 part herb to 30 parts water, moisten a napkin with the solution and apply it to the face for about 30 minutes;
- Calendula. At the pharmacy you buy calendula tincture, dissolve 50 ml of tincture in a glass of cold water, and then do the same as with chamomile.
For stars, it is recommended to use masks from:
- Oatmeal. 2 tbsp. Grind oatmeal into powder, add 100 ml of hot water and let stand for a while. When the mixture reaches room temperature, it can be applied to the face (not thickly) for 35-40 minutes. Using a damp cloth, wet the dried parts of the mask;
- Kefir. The gauze is soaked in fresh kefir and applied to the face for 10 minutes.
Using cosmetics
How to treat rosacea has already been discussed. But proper hygiene and cosmetic care is no less important. In winter and autumn, you need to protect your facial skin from strong wind, cold, snow and rain. In summer and spring, it is recommended to protect your skin from direct sunlight: wear a wide-brimmed hat, dark glasses, or use a sun umbrella. It is also necessary to apply sunscreen with SPF 15 or higher to your face before going outside. Visiting the sauna and solarium is prohibited.
Rosacea disease requires the use of only mild cosmetics. It’s good if they contain extracts of grapefruit, blueberries, chamomile, and cucumber. All cosmetics for rosacea (lotions, tonics, creams) should not contain alcohol, and it is better to choose from those products that are marked “hypoallergenic” or “anti-rosacea”. In order for cosmetics to have healing properties, and not just mask the manifestations of the disease, you can add a solution of dimexide to them.
It is always necessary to apply a protective cream under decorative cosmetics. For rosacea in men, it is recommended to use an electric razor. Blades can only be used if they are very sharp. The application and removal of cosmetics must be extremely gentle: do not rub creams too hard or rub your face with a towel after washing.
Therapeutic measures
When diagnosing rosacea on the face, the causes and treatment are closely interrelated elements. First of all, the dermatologist will try to find out the cause and begin treatment by eliminating it.
Therapeutic tactics are selected in accordance with the stage of the disease, the gender of the patient, and the presence of underlying diseases.
At the first stage, local drugs that have a vasoconstrictor effect are prescribed. Cold lotions of resorcinol and boric acid are used. They constrict blood vessels and thereby help eliminate burning and itching.
It is imperative to carry out hygiene procedures using gels that have sebum-regulating and anti-inflammatory effects. In this situation, gels and lotions from the same series are used as for caring for problem skin with acne.
If spider veins, persistent redness, or a feeling of skin tightness appear, a cream from the pharmaceutical cosmetic line Diroseal is prescribed.
Previously, when rosacea formed on the face, treatment was carried out with local corticosteroid drugs. Long-term use of such drugs often leads to the transition of the disease to another stage, which is characterized by persistent spider veins and spider veins, tissue atrophy, the appearance of age spots and pustular rashes. Therefore, recently steroid hormones are not recommended for local therapy.
When lumpy elements in the form of papules and pustules form on the face, local antibiotics, mainly of the tetracycline series, are prescribed, since it is tetracyclines that can accumulate selectively in the area of the sebaceous glands and eliminate inflammation. Treatment with antibiotics is long-term (3 months) and very often leads to adverse reactions in the form of allergies, disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract, and reactions to the sun.
Macrolides, in particular Erythromycin, are also used among antibiotics. A five-week course of Erythromycin ointment is prescribed 2 times a day. Longer use of an antibiotic leads to microflora resistance and ineffectiveness of the drug.
A drug such as Zinerit, which contains erythromycin and a zinc compound, has proven itself well. The solution relieves inflammation and has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microflora. Treatment time is at least 3 months.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to quickly cure a boil at home: simple recipes, homemade ointments
Treatments for rosacea on the face are used, the main active ingredient of which is azelaic acid - Skinoren, Azelik, AcneStop, etc. They have an anti-inflammatory effect, are destructive to bacteria, and also soften the stratum corneum of the epidermis and promote cell renewal. The drugs are used 2 times a day. A noticeable change in skin condition is observed no earlier than after a month of regular use.
If necessary, treatment is also carried out with vitamins and antihistamines.
Products such as retinoids, synthetic derivatives of vitamin A (retinol), have found widespread use:
- Tretinoin cream - a course of therapy of 1.5 months with twice a day application.
- Adapalene - used once a day before bedtime. Improvement occurs after long-term (3 months) use. Treatment begins with the gel, but if side effects occur in the form of burning and peeling, switch to cream. Contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
- Retinoic ointment is an anti-acne, antiseborrheic and anti-inflammatory drug. It is not recommended for use during pregnancy and for girls planning to become pregnant. Before applying the product, you should take into account the fact that it cannot be combined with other retinoids and topical tetracycline-based drugs.
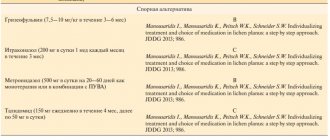
Prescribed drugs based on metronidazole (synthetic antibiotic):
- Metrogyl gel;
- Rosamet face cream for rosacea.
In any case, whether this or that medicine can be used is determined exclusively by a dermatologist and often together with a gynecologist or ophthalmologist.
When rosacea reaches a stage with the formation of pustules with purulent contents, systemic retinoids and, above all, isotretinoin (Roaccutane) are prescribed. Before treating rosacea on the face with systemic medications, it is imperative to consult a doctor due to numerous side effects and a significant list of contraindications.
The advanced stage of the disease, which is characterized by skin growths, can be treated mainly by surgical methods.
Diet
Diet for facial rosacea is one of the components of complex treatment. The daily diet menu should exclude foods that cause redness and irritate the stomach: alcoholic drinks, coffee, citrus fruits, spicy dishes with a lot of spices. It is recommended to eat food warm.
It is necessary to reduce the consumption of foods high in iodine, as this substance can trigger the reappearance of rosacea.
When rosacea is diagnosed, treatment will be more effective with proper hygienic and cosmetic facial care.
Patients with hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands, wide pores and a tendency to form comedones are recommended to use gels and lotions for washing, which have a sebum-regulating effect (normalize sebum production) and an anti-inflammatory effect. It is very important that cosmetic products do not disturb the water-lipid mantle (protection) of the skin. Therefore, their pH level should not exceed 7 units.
It is recommended to carry out hygienic facial skin care using the following gels and lotions:
- Klerasil Ultra;
- Cleanance;
- Keraknil;
- Cetaphil;
- Aven.
Caring for problematic facial skin helps soften the epidermis, open pores, remove dead cells and moisturize. Cleansing products should not be used more than 2 times a day.
During treatment, side effects such as dryness and flaking often occur. Therefore, cosmetics for rosacea on the face must include moisturizing creams:
- Klin AK;
- Aven;
- Anti-rouger;
- Rosaliak;
- Sensibio AR.
All these products moisturize well, eliminate the feeling of discomfort and improve the tolerability of medications.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is most effective at the first symptoms of rosacea. First of all, lotions from decoctions of plants such as chamomile, sage, calendula, marshmallow and tea are used. The decoctions are prepared in a water bath for a quarter of an hour, then infused for another 30-40 minutes at room temperature. A prerequisite is that the liquid must be cold. Lotions constrict blood vessels and soothe the skin.
Face masks for rosacea based on kefir and oatmeal are also effective. These two components are used to prepare monomasks. Kefir is applied to the face and left for 10-15 minutes. Oatmeal is brewed in boiling water, left for an hour and spread over the face.
Important! You cannot use self-heating masks that are commercially available in the “anti-acne” category.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used to treat dilated blood vessels, eliminate hyperpigmentation and scar changes.
The following methods are used:
- electrophoresis;
- cryomassage;
- electrosurgery;
- laser therapy.
To eliminate skin changes, dermabrasion (only in the complete absence of inflammation on the face) and various chemical peels are used. If you are prone to scarring, Contractubex gel may be prescribed.
Prevention
Neither laser therapy for rosacea nor cryotherapy guarantees that the disease will not worsen. In order to prevent relapses, you should regularly undergo preventive treatment with laser or cold.
However, the frequency of visits to a cosmetologist for this disease can be significantly reduced, you just need to follow some simple rules:
- Do not let your face sunbathe; if possible, use a protective cream.
- In winter, avoid hypothermia and exposure of the face to cold, dry air (you can use creams with a high fat content).
- Balance the diet - it must contain sufficient amounts of vitamins A, E and absent - fried, peppery, fatty foods.
- Treat all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, especially gastritis and peptic ulcers.
- Stop using hormonal ointments (unless they are prescribed for a serious illness).
At the first symptoms of rosacea, consult a dermatologist. Avoid progression of the disease and the appearance of cosmetic defects that disfigure your face.
Demodicosis in humans: photos, symptoms and treatment Wen on the face Trigeminal neuralgia Facial nerve neuritis Seborrheic dermatitis Neurodermatitis: causes, psychosomatics and treatment
When to see a doctor
A visit to a dermatologist should take place no later than 7 days after the woman begins to notice the first signs of a change in the color tone of her face, the appearance of a red spot, which is distinguished by more enlarged pores, and swelling.
Delay in examination and initiation of treatment is dangerous because the disease can quickly move to the next stage of development, watery papules will begin to form, and a pathogenic infection will develop. The latter complication will require completely different treatment approaches and the use of antibacterial agents.