Symptoms of foot fungus
Symptoms of foot fungus will depend on the type of pathogen and the degree of involvement of the skin and nails in the pathological process.
- Symptoms of foot fungus when affected by Trichophyton red:
- The disease manifests itself by damage to the interdigital folds. Moreover, the initial location of rubrophytosis is the closest folds of the feet - between the third and fourth toes. After which the soles, lateral and dorsal surfaces of the feet are successively involved in the pathological process, the infection may spread to the palms and nails;
- The skin becomes dry and thickens. The formation of furrows is characteristic. As the disease progresses, the stratum corneum thickens into rough calluses, the cracks become deeper, and painful sensations develop;
- Peeling of the skin is mealy or lamellar;
- Most patients complain of itching that bothers them;
- An erased clinical picture is possible with exudative variants of rubrophytosis, including intertriginous (proceeding like diaper rash), dyshidrotic (with the appearance of blisters) and mixed interginous-dyshidrotic lesions. Cracks between the fingers are barely noticeable, the peeling is superficial, the itching is mild. In this form, the disease can last for a long time, so a person often does not seek medical help;
- Leukonychia is sometimes observed - the appearance of white stripes and spots on the nails;
- In addition to the feet, large skin folds, for example, buttocks, groins, and under the mammary glands, can be susceptible to fungus;
- Foot fungus occurs with multiple lesions of the nail plates.
- Symptoms of foot fungus when affected by Trichophyton interdigitalis:
- Most often, the third and fourth interdigital folds are affected, as well as the sole of the foot, its lateral surface, toes and arch;
- The inflammatory process is pronounced, has similarities with the foot fungus described above, but never occurs hidden;
- Peeling is often accompanied by exudative phenomena;
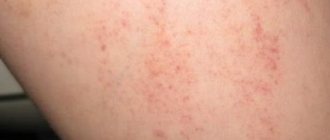
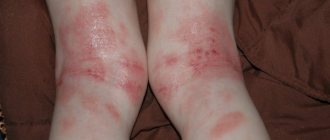
- It is possible to develop allergic reactions with rashes on the torso, face and limbs;
- Damage to the nails is sporadic, most often observed on the first and fifth toes.
- Symptoms of foot fungus depending on the clinical form of the disease:
- With the erased form of the fungus, the peeling is slight, often it occurs only in one interdigital fold. The cracks are small, invisible, superficial. The patient does not experience discomfort and does not consult a doctor;
- With the squamous form, the lateral surface of the feet and the folds between the toes peel off. Inflammation is not observed, sometimes hyperemia of the skin is possible, which is accompanied by itching. On the soles, the skin is lichenized; due to the thickening of the stratum corneum, the effect of its varnish shine is created. In the area of natural skin furrows, lamellar peeling is observed, and a noticeable increase in the skin pattern is observed. However, the patient does not experience any concern about the condition of the skin of the legs, except, perhaps, an aesthetic defect;
- With the hyperkeratotic form of foot fungus, dry and flat papules with bluish plaques form on the arches of the foot. In the center of these rashes, scaly layers with a grayish-white tint are formed, and along their periphery there are borders with exfoliating epidermis. Upon closer inspection, bubbles can be visualized. Existing rashes tend to merge with the formation of large lesions and gradual coverage of the entire sole. The clinical picture may resemble psoriasis.
Trichophyton red rarely affects children, which scientists associate with the high rate of regeneration of the skin and nail plates. In adolescence, the disease is diagnosed in 17% of cases, and boys are more often affected.
Features of the disease
Statistics say that about a third of the world's population suffers from foot fungus. Among all mycoses of the skin, this form of the disease is the most common. You can become infected with fungus at any age. About 20% of patients are children and adolescents, about 40% are elderly people and patients with diabetes.
A fungal infection provokes the development of erysipelas on the feet. This reduces local cellular immunity and complicates treatment. A fungal disease detected in a timely manner is quite treatable, but therapy for an advanced form of the fungus can take many months.
Timely treatment is often difficult due to the lack of clear symptoms. At the initial stage, the fungus manifests itself as slight dryness and flaking, which many do not pay due attention to, expecting the discomfort to go away on its own. As a result, the fungus is not treated, the disease progresses and after some time causes a number of specific symptoms.
The initial signs of fungus can easily be confused with normal dry skin.
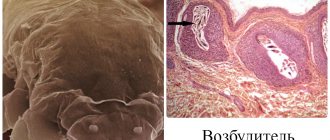
Pathogens:
- Trichophyton rubrum;
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes;
- Epidermophyton floccosum;
- yeast fungi.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the causative agent of the disease. When infected with the fungus Trichophyton rubrum, treatment takes many months. Unfortunately, this form of fungal infection is the most common, as this type of fungus is very contagious.
The second most common infection is Trichophyton mentagrophytes. This mycosis is characterized by severe symptoms, but can be treated quickly enough with the right choice of therapy.
The rarest forms of mycosis are caused by Epidermophyton floccosum and yeast-like (yeast) fungi. Treatment in these cases depends on the stage of the disease. Infection of the feet with yeast-like fungi rarely acts as an independent disease; usually this form of infection is generalized, that is, various areas of the epidermis are affected, including the feet and nails.
Causes of foot fungus
Foot fungus is an infectious disease. More often than others, fungal infections of the feet are caused by fungi belonging to the group of dermatophytosis. These are ascomycete molds, 30 species of which can cause the disease - rubrophytosis or rubromycosis. They account for more than 70% of cases of foot fungus.
Approximately 10% of the world's population suffers from athlete's foot, which is caused by the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes. It is possible that the skin of the feet may be affected by mold and yeast-like fungi, but this occurs much less frequently - in approximately 1.5% of cases.
The following are possible causes of foot fungus:
- Most healthy people (up to 28%) become infected with foot fungus while visiting public places. These can be not only saunas, swimming pools, baths, but also sports clubs, fitness centers;
- Intrafamily infection with foot fungus is possible if there is a sick relative who evades treatment. Most often these are elderly and older relatives. The use of shared towels, slippers, personal hygiene products, baths, showers, foot mats - all this increases the risk of intra-family infection;
- Decreased immunity leads to an increase in the number of patients with mycosis among older people. Moreover, men are most often affected, and their foot fungus is combined with onychomycosis.
Where and why does infection occur?
Mycosis of the feet is a contagious disease that is easily transmitted through direct contact with a carrier of the fungus or through household items. For example, through shoes, socks, towels, manicure supplies, rubber shower mats. In 70–95% of cases, the causative agent of mycosis of the feet is Trichophyton red (Tr. rubrum).
Typically, infection occurs in public places with high humidity, where there are favorable conditions for the reproduction and spread of the pathogen. Such places include swimming pools, public showers, saunas, water parks, and gym locker rooms. If a person infected with fungus walks barefoot on the shower floor or rugs, they will leave behind infectious particles. And if a healthy person then steps on this place with bare feet, the pathogen will get on his skin. However, the fungus does not always immediately manifest itself and cause characteristic symptoms of the disease. With strong immunity and no health problems, a person remains simply a carrier of the infection, but does not get sick himself.
The risks of getting fungus and developing mycosis of the feet increase:
- damage to the integrity of the skin;
- disruption of the blood supply to the extremities, in which the supply of oxygen and nutrients to tissues deteriorates, regeneration processes slow down, and local immunity is weakened;
- diabetes mellitus, high levels of glucose in the blood create favorable conditions for the proliferation of the fungus and the progression of the infection;
- increased sweating;
- dry skin, which leads to microcracks;
- elderly age;
- blood diseases;
- long-term use of antibiotics, drugs that suppress the immune system;
- vitamin deficiency;
- wearing shoes that do not allow air to pass through and create a “greenhouse effect.”
Why is foot fungus dangerous?
If foot fungus is not treated for a long time, it is dangerous for the development of serious consequences.
First of all, as a result of exposure to mycotic organisms and the influence of their metabolic products (pigments, toxins, enzymes, antibiotics), polyvalent sensitization develops. As a result, the number of allergic manifestations from the skin, blood vessels and mucous membranes increases. Complications from such allergic reactions increase significantly and become more frequent. Drug resistance and intolerance to antibacterial drugs, especially the penicillin series, are developing.
Existing hay fever becomes more pronounced, the same applies to vasculitis. Mycogenic sensitization can aggravate the course of various forms of dermatitis (atopic and seborrheic), as well as other skin pathologies: hemoderma, psoriasis, dermatoses.
In addition, pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate through cracks and erosions formed on the skin. Patients with foot fungus are three times more likely to suffer from pyoderma and erysipelas, accompanied by lymphostasis and elephantiasis. An additional danger of such bacterial complications lies in the fact that they are extremely difficult to treat with antibacterial drugs. This is due to acquired resistance, which has arisen as a result of prolonged exposure of bacteria to antibiotic substances produced by fungi.
Another danger posed by untreated foot fungus is an increased risk of developing plantar warts. They very often form in places where calluses and hyperkeratosis are present. This is due to a decrease in local immunity, which is unable to control the growth and development of papillomaviruses.
Types of mycosis
Mycosis appears due to strong pathogens - saprophyte, moldy fungus, candida and other complex microorganisms.
- Interdigital mycosis is the most popular type, which can infect the entire surface of the lower leg.
- Foot, or moccasin-like - spreads to the soles of the feet, severely injuring the skin and causing moderate pain.
- Ulcerative – accompanied by severe discomfort, itching, burning and peeling of the skin.
Any of these forms of fungus can cause severe complications, so it is important to start treatment as soon as possible.
Treatment of foot fungus
The following drugs are used to treat foot fungus:
Griseofulvin
The main effect that allows you to get rid of foot fungus is the fungistatic effect. That is, as a result of the use of this drug, mycotic organisms stop reproducing
Release form:
- In tablets of 0.125 mg;
- As part of a combination ointment called Grimelan;
- In the form of an oral suspension (100 ml);
- In the form of an ointment.
Regimen for taking the tablet form: For the first 30 days of treatment, take once a day at the rate of 16 mg per kilogram of body weight. For the next 30 days, the dosage does not change, but is taken every other day. The treatment regimen for the third month is similar to the second, ending as healthy nails grow.
Scheme for using the ointment: Apply to the affected areas for 14 days. The effect of therapy is absent with candidiasis.
Possible contraindications:
- Liver pathologies;
- Kidney pathologies;
- Oncological processes in the body;
- The period of bearing a child and breastfeeding;
- Leukocyte deficiency.
Terbinafine
Other names of the drug: Lamisil, Binafin, Thermikon, Terbinox.
Has pronounced antifungal activity. The drug has a detrimental effect on all groups of mycotic organisms, including fungi of the genus Candida.
Release form:
- In tablet form (0.25 g or 0.125 g);
- In cream form;
- In the form of a spray for topical application;
- In the form of an oral solution.
- Regimen for taking the tablet form: Adults take the drug up to 2 times a day for 14 – 45 days (dosage 0.25 g). For children up to 40 kg, a dosage of 0.125 g is indicated, for children up to 20 kg, a dosage of -.0625 g
Scheme for using the ointment: Local application involves rubbing the composition into damaged areas up to 2 times a day. Treatment can last from 7 days to 6 weeks.
Possible contraindications:
- Severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
- Hematological diseases;
- Malignant tumors;
- Angiopathy of leg vessels, obliterating endarteritis;
- The period of lactation and gestation.
Fluconazole
Other names of the drug: Diflazon, Medoflucon, Mikosist, Diflucan, Flukoral, Mikomax, Flucostat, Flukorik, Flumed, Flumicon, Flusenil, Florcan.
It has high activity against fungi of the genus Candida.
Release form:
- In the form of tablets of 0.2;
- In the form of capsules of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 1.5 g;
- In syrup form;
- In the form of a solution for intravenous administration.
Regimen for taking the tablet form: Take once every seven days at a dosage of 150 mg, or once a day at a dosage of 50 mg. The course of treatment is 1.5 months.
Possible contraindications:
- Age up to 4 years;
- Combined use with astemizole and terfenadine;
- Severe kidney and liver pathologies;
- The period of gestation.
Sertaconazole
Other names of the drug: Sertamicol, Zilain.
It has broad antimycotic activity against yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and against gram-positive streptococci and staphylococci. Capable of having fungistatic and fungicidal effects.
Release form:
- In the form of candles;
- In the form of a solution;
- In the form of a cream.
Scheme for using the ointment: The cream is applied up to 2 times a day in a thin layer. The course of treatment is one month.
Possible contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- During lactation, applying cream to the mammary glands is prohibited.
Itraconazole
Other names of the drug: Irunin, Kanazol, Canditral, Orgunal, Sporanox.
Allows you to fight dermatophytes, yeast and mold fungi. Some strains of fungi show resistance to the main active ingredient.
Release form: Available in the form of capsules of 0.1 g and in the form of a solution for oral administration.
Regimen for taking the tablet form: Take after meals, up to 2 times a day for 14 days (the treatment period may be extended). For onychomycosis, treatment is a course.
Possible contraindications:
- Heart failure;
- Breastfeeding period;
- The period of bearing a child;
- Pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
- Peripheral neuropathy;
- Severe pulmonary pathologies;
- Elderly and children's age.
Econazole
Other names of the drug: Ifenek, Ekalin, Gino-Pevaril, Ecodax.
It has a wide antimycotic spectrum of action and is capable of providing bactericidal and fungicidal effects. Active against mold and yeast fungi, as well as against dermatophytes. Recommended for use when fungi are resistant to other drugs.
Release form:
- In cream form;
- In lotion form;
- In the form of a solution for topical use;
- In aerosol form.
Scheme for using the ointment: The drug is applied to dry skin of the feet up to 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days; with high keratinization of the surface of the feet, it can be extended to 6 weeks.
Possible contraindications:
- Age up to 18 years;
- Individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- The period of bearing a child.
Natamycin
Other names of the drug: Pimafucin, Pimafucort.
It is active against all groups of mycotic organisms that can provoke foot fungus.
Release form:
- In cream form;
- In the form of a suspension for topical application;
- Pimafucin is available in suppositories and tablets, but is used to treat fungal infections of the intestines and female genital organs.
Scheme for using the ointment: The drug is applied to damaged areas of the skin once a day or more. The course of therapy can be extended up to a month.
Possible contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Clotrimazole
Other names of the drug: Vicaderm, Candide B, Antifungin, Imidil, Lotrimin, Candibene, Yenamazol, Kandil, Kanizol, Kanesten, Clomazol, Lotrimin, Clofan, Faktodin, Funginal, Fungizid, Fungitsip.
A broad-spectrum drug that is the basis for many antimycotic drugs. Only local use is possible.
Release form:
- In ointment form;
- In cream form;
- In lotion form;
- In aerosol form.
Scheme for using the ointment: The drug is applied to clean, dry soles up to 3 times a day. The maximum course of treatment is a month or plus 3 weeks after the disappearance of all symptoms of the disease.
Contraindications: First trimester of pregnancy.
Naftifine Hydrochloride
Other names of the drug: Fetimin, Exoderil.
The drug is effective against all groups of mycotic organisms that cause fungal infections of the feet. In addition, it has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect.
Release form:
- In cream form;
- In the form of a solution for external application.
Scheme for using the ointment: The drug is applied to clean skin of the feet up to 2 times a day. The course of treatment is up to 2 months. If onychomycosis is detected in parallel, then therapy can be extended to 8 months.
Possible contraindications:
- Childhood;
- The period of bearing a child;
- Breastfeeding period.
Treatment of foot fungus with folk remedies
Effective treatment of foot fungus is only possible with the use of medications. Folk remedies are applicable only after consultation with a doctor and act as auxiliaries.
Read more: Folk remedies for toenail fungus
Precautionary measures
By following simple precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of fungal infection.
- Do not walk barefoot where there is a risk of infection. When using a shower in a hotel, hostel, swimming pool, or at work, be sure to wear rubber slippers.
- If you have damaged your skin or nails, do not visit baths and swimming pools until they are completely healed. If you do happen to come into contact with “questionable” surfaces, after which itching appears in the wound area and redness intensifies, use Fungoterbin NEO.
- Never lend someone else and, of course, do not wear someone else’s slippers, stockings, or socks. Do not use other people's towels, pedicure or manicure tools.
- In a pedicure salon, insistently require the technician to wash their hands and disinfect instruments after the previous client.
- Wash your feet twice a day (morning and evening). And after that, wipe them thoroughly, especially between your fingers. If you cannot dry the narrow spaces between your fingers with a towel, use cotton swabs or even a hair dryer. For prevention, treat the interdigital area with talcum powder.
- Change your socks, stockings, and tights daily. All such products must be cotton or other natural materials.
- Give preference to shoes only made of genuine leather or fabric. In addition, in no case should it be too narrow, much less tight.
Inexpensive but effective drugs for the treatment of foot fungus
Inexpensive but effective drugs for the treatment of foot fungus include:
- Sangviritrin tablets (price no more than 100 rubles);
- Nogtevit and Nogtimycin are drugs that help get rid of onychomycosis, which in 77% of cases accompanies foot fungus. The price of these funds does not exceed 120 rubles;
- Fluconazole tablets for 140 rubles;
- Fungavis tablets with the main active ingredient ketoconazole (120 rubles);
- Mycozoral ointment based on ketoconazole – up to 180 rubles;
- Fundizol ointment – 100 rubles;
- Terbinafine cream and ointment, Atifin cream, Exifin cream, Termicon cream. All these drugs are made on the basis of terbinafine and cost no more than 200 rubles;
- Bifosin cream based on bifonazole – up to 40 rubles;
- Creolin ointment for the treatment of onychomycosis – 160 rubles.
Useful tips
To quickly cure foot fungus, you need to carefully monitor your feet. Foot hygiene comes first. It is necessary to wash your feet several times and always dry them. It is important to remember: a humid environment promotes the spread of fungal infection. To wash your feet, it is better to use laundry or tar soap.
Any products for external use are applied only to clean and dry skin. In order for the components of the ointment to better penetrate the epidermis, it is recommended to steam your feet before the procedure by making a bath.
To avoid re-infection, you must carefully monitor the cleanliness of your socks and shoes. It is recommended to boil socks with laundry soap, and treat shoes with special solutions. To treat shoes, you can use antiseptics or a special Stop Fungus spray.
After a shower, it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect the bath. It is recommended to avoid carpets for a while, as they can accumulate fungal spores.
Alternative treatment for foot fungus
Hydrogen peroxide has many medicinal properties, including antiseptic and antibacterial effects. It has no contraindications, as proven by Professor Neumyvakin, who in his book “Hydrogen Peroxide. Myths and Reality” described in detail and clearly for the reader the effects and mechanism of action of this remedy.
To treat nail fungus, the professor also recommends using hydrogen peroxide. To get the maximum effect, you need to soften your nails in a soda solution (take a teaspoon of soda per liter of hot water). When the nails become soft, apply a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide to the diseased plate. First, the disc must be shaped into the shape of the diseased nail. If possible, peroxide should be instilled into the nail cavity up to 3 times a day.
The soaking time for a cotton swab is up to 1 hour for feet and up to 15 minutes for hands. Two procedures per day are enough. In order for the tampon to remain soaked in peroxide throughout the entire time, the finger must be wrapped in cellophane or put on a finger cap.
After the tampon is removed, you may experience a burning sensation and discomfort. To eliminate these symptoms, you just need to rinse your finger with water.
Compresses with peroxide can be replaced with foot baths. To do this, a small amount of the product is diluted in water (two tablespoons of peroxide at a 3% concentration per liter). Then the feet or hands affected by the fungus are lowered into the bath for 15 minutes. The effect of treatment with peroxide can be detected after 4 days.
Read more: How does hydrogen peroxide help quickly cure toenail fungus?
Prevention
To recognize the problem in time, you should know what the fungus looks like. To do this, it is better to inquire about this issue in advance by looking at photos on the Internet. Then you need to listen to the advice of dermatologists on what to do to avoid getting infected with foot fungus:
- after visiting the beach, swimming pool and other public places, you should thoroughly wash your feet;
- when your feet sweat, there is a risk of becoming infected with mold, so you should avoid wearing socks and closed shoes for long periods of time;
- in order to avoid becoming infected with pathogenic microflora, you should not give personal hygiene items, clothing or shoes to others;
- You should regularly care for your toes: get a pedicure, trim overgrown nails.
How to treat onychomycosis with varnishes
Anti-fungal nail polish is the most common product that can be used under cosmetic coatings. The advantage is concealment of the defect with simultaneous treatment, no negative impact on the body. In this way it is recommended to get rid of the initial stages of the disease. Well-known brands of varnish medicinal products are:
- Loceryl, with the active ingredient amorolfine. The principle of healing is to destroy the membrane of fungal cells. Apply twice a week.
- Oflomil has a fungistatic and fungicidal effect, returning nails to a healthy appearance within six months of use, if the disease is not advanced.
- Analogues of Oflomil - Batrafen, Cyclopiroxolomine give the same effect, but are cheaper. Batrafen must be used according to a special regimen, so you need to carefully study the instructions.
- Mikozan - in the form of a serum, perfectly saturates the diseased tissue of the plate to the very bed. You can use it more often than varnish and do the procedures on a daily basis, which speeds up the healing process.
- Onychoplast - applied to the nail in a softened form after steaming.
The duration of varnish therapy is up to a year. Then you can use the products as a preventive measure.
Good to know! External medications and varnishes will not help with complicated forms of mycosis. A comprehensive treatment algorithm is effective against advanced fungus.
Diagnostics
For fungal treatment to be successful, consultation with a dermatologist is necessary. The specialist will conduct a visual inspection, carefully examining the lesions.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is important to tell the doctor about all alarming symptoms and report previously suffered mycoses and other diseases.
To accurately determine the presence of infection and the type of pathogen, the doctor must take blood, a nail or skin scraping for analysis. Laboratory tests must be carried out without fail. There are more than 500 species of fungi that have different thresholds for drug resistance and require different treatment tactics.
- Microscopic examination reveals the presence of fungi. The sample is treated with special preparations and examined under a microscope, trying to find spores. This test allows you to determine the presence of fungus and its concentration.
- More accurate results are provided by bacterial culture. Biological material is placed in a nutrient medium. If pathogenic cells are present in the scraping, fungal colonies begin to grow from them, which are subject to careful examination. The analysis takes from 2 days to 4 weeks. The time depends on the type of infection.
- PCR - polymerase chain reaction - is necessary to establish the specific type of fungus by identifying the DNA of the pathogen. This requires scraping from the affected area. The test performance is about 100%.
- An enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA) is taken from a vein and allows you to identify the titer of antibodies to a specific pathogen and find out the exact cause of the disease.
You should go to the hospital if there are any changes in your skin condition. Even minor flaking and itching between the fingers cannot be ignored. Otherwise, the disease will affect the foot and nails, and it will be more difficult to cure.
About the types of antifungal drugs
Pharmacy has developed categories of drugs for topical use, which are sold in pharmacies and are available to customers without prescriptions. These include:
- creams, ointments, gels;
- solutions, serums;
- sprays, varnishes;
- plasters.
They have a general effect, have a minimum of side effects, and can be used by adults and children. The key to a successful fight against mycosis is regular use and adherence to the procedure. After a visit to the doctor, you will know the procedure, how many times to apply the medicine, in what quantity, and you will achieve recovery from the disease. Typically, healing occurs with local remedies within 4-6 months.
If the infection is advanced, then local treatment of the fungus on the nail plates is irrelevant. A combination is required - external medications plus tablets. It is carried out under the supervision of a doctor, as it has significant side effects.