Consultation with a proctologist – 1,750 rubles.
- Symptoms of colon polyps
- Risk factors
- Diagnosis of neoplasms
- Treatment
- Popular questions
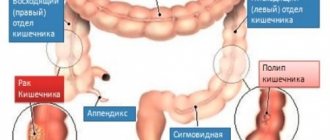
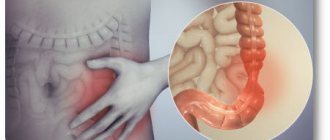
Colon polyps
- these are benign formations, which are usually asymptomatic and are most often found in patients complaining of discomfort, intestinal dysfunction, pain in the anus, pathological discharge from the anus, which also occurs in other diseases (hemorrhoids, paraproctitis, anal fissure , colitis, rectal cancer, etc.).
The prevalence of formations increases with age and ranges from 25 to 35% among the population over 50 years of age.
The clinical significance of this pathology is due to the fact that from 70 to 95% of colorectal cancer cases develop in the “polyps-cancer” sequence Source: Vladimirova A.A. The use of aquascopy in the diagnosis of colorectal polyps / A.A. Vladimirova [and others] // Bulletin of the All-Russian Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. - 2006. - No. 6 (52). — P. 32-35. .
What are intestinal polyps?
Intestinal polyps are small benign neoplasms that grow asymptomatically on the inner (mucous) lining of the intestine.
Polyps of the large intestine are the most common. This is a fairly common disease, affecting 15-20% of people. The size of polyps is usually less than 1 cm, but can reach several centimeters. They grow alone or in groups. Some look like small bumps, others have a thick or thin stalk with a seal in the shape of a mushroom or a bunch of grapes. The polyps themselves are benign formations that rarely worsen a person’s well-being. But they can transform into malignant tumors that are difficult to treat. Therefore, when polyps are identified, they are recommended to be removed.
The diagnosis of intestinal polyps can be made to people of any age, gender, or race. It is found somewhat more often in men, and the most typical age of patients is 50 years and older. People of the Negroid race are more prone to the formation of polyps and their malignant degeneration than Caucasians.
Why is polyposis dangerous?
Single polyps are not dangerous only if they do not increase in size and are under constant supervision of a specialist. Even if nothing bothers the patient for several years, this does not mean that the formation cannot degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Doctor's advice
Patients who have had surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) are at high risk of developing colorectal cancer. For them, an annual examination by a proctologist is strictly necessary.
Konstantin Tishchenko Orthopedist, Traumatologist
Most often this occurs with massive polyposis, as well as with those formations that are covered with villi (this is the most dangerous type of polyp, ending in intestinal cancer in almost half of the cases).
Another deadly danger is the development of intestinal obstruction. If there are many polyps and they are of impressive size, fecal obstruction occurs, which can lead to severe intoxication and even death of the patient if he is not provided with professional help.
Polyps only at first glance seem harmless - in fact, they require constant monitoring, as they can degenerate into malignant tumors. Removing polyps is the only way to get rid of the disease, and the best way to prevent intestinal cancer after a healthy diet and a healthy lifestyle.
For more information about the manifestations and treatment of intestinal polyps, watch the video:
Be healthy!
Useful articles on the topic: The first signs of hemorrhoids in women and treatment in the early stages What can you take for stomach pain: a review of medications What can pain under the left rib in front indicate? Pain in the right side under the ribs in front - what could it be?
This article has been verified by a current qualified doctor, Konstantin Tishchenko, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Rate how helpful this article was
5 2 people voted, average rating 5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
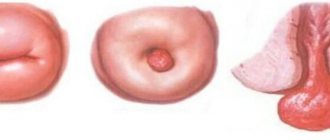
Types of polyps
- adenomatous - the most common, approximately 2/3 of all neoplasms belong to this group. In some cases, these polyps degenerate into cancerous tumors or become malignant, as doctors say. Not all of them are capable of malignancy, but if colon cancer comes from a polyp, then an adenomatous polyp is to blame in 2 out of three cases;
- serrated - depending on the size and location, they have a different likelihood of malignancy. Small polyps located in the lower part of the colon (hyperplastic polyps) rarely develop into cancer. But large, flat (sessile) ones, located in the upper part of the intestine, are most often transformed;
- inflammatory ones occur after inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease). Prone to malignant degeneration.
Causes of colon polyps formation
Why cells suddenly begin to turn into atypical ones and form tumors is still not known exactly. Analysis of incidence helped to identify factors that increase the risk of polyp growth:
- age over 50 years
- inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis)
- smoking
- alcohol consumption
- excess weight
- sedentary lifestyle
- poorly treatable type 2 diabetes
- heredity is the most significant factor.
The likelihood of the disease is higher if blood relatives (parents, children, brothers and sisters) have been diagnosed with colon polyps. The number of relatives with this disease also matters. Although sometimes multiple cases of polyposis in a family are not associated with genetic factors.
There is a whole group of genetic diseases that increase the likelihood of developing certain types of tumors (malignant and benign), including intestinal polyps:
- Lynch syndrome is the most common type of hereditary colon cancer. The disease begins with the formation of polyps, which very quickly become malignant;
- familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is a rare pathology, the formation of hundreds and sometimes thousands of polyps in adolescence. Without treatment, the probability of malignant degeneration is 100%;
- Gardner's syndrome (a special case of FAP);
- MYH polyposis is a rare cause of multiple polyps in children;
- with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, dark pigment spots first appear throughout the body, including on the lips, gums and feet; subsequently, multiple polyps grow throughout the gastrointestinal tract;
- serrated polyposis syndrome.
Will traditional medicine help?
In the treatment of intestinal polyps, folk remedies are used in several versions - decoctions for oral administration and special enemas for treatment.
| Composition of the product | Method of preparation, administration and course. |
| Horseradish and honey 1:1 | 1 tsp before meals. The course is a week, a break of 7 days and alternate so on. |
| 180g peeled pumpkin seeds, 7 yolks and 500 ml vegetable oil. | Grind the seeds and egg yolks into powder and mix everything with vegetable oil. Leave for 12 minutes. to the steam bath. The product is poured into a sterile container and stored in the refrigerator. Take 1 tsp on an empty stomach. - 5 days. Break for 5 days and repeat. Take until the product runs out. |
| Take 3 parts each of celandine and meadowsweet, 2 parts each of agrimony, St. John's wort herb, and calendula. Mix. | 1 tbsp. collection, pour 300 ml of boiling water and leave for 5 hours. Do a microenema before bed. The course of treatment is a month, a break of 2 weeks. |
| Take a glass of celandine, yarrow tops, 2 glasses each of calendula, meadowsweet. Mix. | 2 tbsp. pour boiling water, leave. Strain the cooled infusion and pour in 2 teaspoons of olive oil. Empty the intestines and make a microenema (100 ml of solution). |
Polyps in the colon, which are treated with traditional methods that allow a gentle and gentle way to reduce the risk of their further growth and reproduction.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract require specialist supervision in the selection of treatment agents. Lifestyle and diet consultations will allow for prevention and prevention of other intestinal problems. Regular physical activity reduces congestion in the lower intestines.
Symptoms
Polyps rarely signal their presence with symptoms. In most patients they are discovered incidentally during a bowel examination.
But in some people, polyps may appear:
- bleeding from the rectum (rectal bleeding);
- change in stool color (black or red-streaked);
- constipation or diarrhea lasting more than a week;
- pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting - with partial blocking of the intestinal lumen by a large polyp;
- iron deficiency anemia, which occurs due to constant intestinal bleeding.
Any of the above symptoms is a sign of a serious problem and is a reason to see a doctor immediately.
Biopsy
When a pathological structure is identified, it becomes necessary to take material for research. A biopsy of an intestinal polyp is performed using special forceps that are mounted in a colonoscope. The procedure is practically painless. It is carried out under visual control.
Tissue particles are taken from several places, including the surrounding epithelium. The laboratory evaluates the samples. They are stained with special dyes and examined under a microscope. The result of histological analysis is given on 7-10 days.
Diagnostics
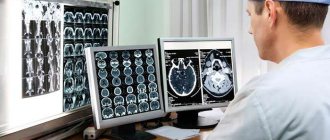
Polyps are usually detected during a routine examination of the large intestine. This is due to the fact that symptoms are not observed or are characteristic of many pathologies: hemorrhoids, inflammatory bowel diseases, peptic ulcers. A stool test may show blood; a blood test may show low red blood cell counts. But these indicators are also non-specific. Large polyps are detected by MRI or CT. Both methods are painless, convenient, but do not detect small (less than 1 cm) tumors.
Therefore, if colon polyps are suspected or during routine checks, the patient is prescribed one of two examinations:
- Colonoscopy is the most sensitive test, during which the doctor has the opportunity to examine the inner surface of the intestine using a flexible tube with a video camera at the end - an endoscope. It is inserted into the rectum through the anus, and on a large screen you can see the entire surface of the colon. In addition to the video camera, the endoscope is equipped with micro-instruments. Therefore, polyps are often removed directly during the procedure. The doctor can also select a small piece of intestine from a suspicious area and send it for histological diagnosis;
- flexible sigmoidoscopy is a shortened version of colonoscopy, during which only the rectum and partially the sigmoid colon are examined using a flexible tube 35-60 cm long with a video camera - a sigmoidoscope.
Preparation for the procedure
Before colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, it is necessary to carry out preparatory procedures. They cleanse the intestines of feces, making it accessible for thorough examination. To do this you need:
- Discuss and adjust any medications the patient usually takes with the doctor at least a week before the procedure. The doctor should be informed about existing diseases, especially diabetes, high blood pressure or heart problems.
- The day before the test, you should not eat solid food. You can drink water, tea and coffee without milk or cream, broth. You should refrain from red drinks, the remains of which may be mistaken by the doctor for bleeding. The night before the test you should neither eat nor drink.
- Taking a laxative (tablets or liquid) according to the regimen suggested by your doctor. As a rule, the medicine is taken the evening before the test, and sometimes also in the morning on the day of the procedure.
- Cleansing enemas. It is best the night before and a few hours before the procedure.
List of permitted and prohibited products
| You can eat | Can't eat | Special menu |
| Light soups | Fatty foods | Cheese is allowed, but in limited quantities |
| Milk porridge or water porridge (a small piece of butter is allowed) | Fermentable foods (kvass, milk, soybeans, peas, cabbage) | Eggs are okay, but not too many |
| Boiled meat (any) | Strong drinks | Reduce salt intake |
| Boiled or pureed vegetables | Tea or coffee | |
| Juices, compotes or jelly | Raw vegetables and fruits | |
| Crackers | Fast food products (fast food, semi-finished products) | |
| Dairy products | Sauces and spices with a strong aroma | |
| Raw smoked products | ||
| Confectionery | ||
| Bakery |
Treatment
The only effective way to get rid of polyps is their surgical removal. In the vast majority of patients, this procedure (polypectomy) is performed during an examination of the colon. It is very quick and painless. When a polyp is detected, the doctor directs an instrument to it and injects a little liquid into the intestinal wall under the polyp so that the boundaries of the neoplasm become clearly visible. Then a special loop attachment captures the polyp, tightens its leg and cuts it off from the intestinal wall, passing an electric current through the loop.
Large polyps may require surgery. Whenever possible, doctors try to use techniques with minimal intervention – microinvasive laparoscopic surgery. In this case, endoscopes equipped with all the necessary instrument attachments are inserted through small holes in the abdominal wall.
In very rare cases, when there are too many polyps, they are removed along with the affected area of the intestine. This is a complex operation that requires preparation and long recovery.
If the appearance of the polyp (size, shape) causes the doctor to suspect a possible malignant degeneration, then a small “tattoo” is made at the site of its former attachment. Such marks help during subsequent screening studies to find areas that were suspicious in the past and carefully examine them.
All removed tissues are sent for histological examination. Based on the structure of the tissue, a histologist can determine the type of polyp and identify the initial signs of malignancy. This information will allow the attending physician to determine the prognosis and schedule of preventive examinations.
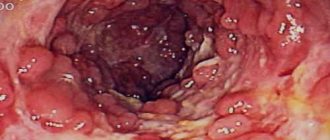
Colonoscopy
The method allows you to visualize the condition of the colon mucosa. If epithelial proliferation can be detected, its size, shape, condition of surrounding tissues, and the presence of additional structures are assessed. Colonoscopy for intestinal polyps is the standard examination. If necessary, during this procedure a biopsy or removal of the formation is performed.
The procedure is carried out using a device - a flexible endoscope. As a backlight, a special halogen lamp is built into the end of the device, giving “cold light”. This principle of operation prevents burns of the mucous membrane of internal organs. According to indications, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
How to remove polyps in the intestines
The patient is prepared before the examination. It is recommended to follow the diet for 3-5 days. They do a cleansing enema or give laxatives according to the schedule.
Complications
The most dangerous complication of polyps is malignant degeneration of the polyp cells. The likelihood of colon cancer depends on:
- size (the larger the polyp, the greater the risk);
- type of neoplasm (adenomatous and serrated polyps are more likely to degenerate);
- time of detection (the earlier polyps are detected, the less the threat).
Fortunately, polyps grow slowly. In most cases, colon cancer begins to develop 10 years after the formation of a small polyp. The exception is hereditary diseases, in which malignancy occurs much faster.
Recommendations
In advanced stages, alternative medicine will not be effective, but traditional treatment methods will help prevent the formation of new polyps. The patient is given enemas of medicinal herbs , which have an anti-inflammatory effect and improve intestinal microflora. To improve intestinal motility, it is recommended to drink a decoction of yarrow, St. John's wort, and oak bark . A decoction of viburnum is considered effective, as it has a beneficial effect on internal organs.
Sea buckthorn oil, celandine tincture , pumpkin seed infusion, and chamomile herb infusion are considered anti-inflammatory agents It is recommended to drink a mixture of butter and natural honey daily before meals. This remedy improves the digestion process, helps with constipation and makes bowel movements easier. In addition, intestinal pain and bloating disappear.
Preventive measures
Timely detection is an excellent guarantee of a favorable treatment outcome and the absence of complications in the future. Since most often there are no complaints or signs of these neoplasms, all people over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo regular examinations (every 3-5 years). Representatives of the Negroid race should begin screening a little earlier due to the greater likelihood of malignant degeneration. People with an established diagnosis of a genetic variant of polyps or suspected of having them are tested more often (every 1-2 years) and from an earlier age.
Quitting overeating, smoking, alcohol abuse, and a sedentary lifestyle is a reasonable step that somewhat reduces the likelihood of polyps. Some evidence suggests that a healthy, balanced diet rich in calcium and fiber also reduces the risk of disease.
People who have close relatives with colon polyps are advised to get tested for genetic diseases.
Table of contents
- What is a polyp in the intestine
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Can a polyp in the intestine hurt?
- Which polyps are considered large?
- Types of polyps in the intestines (classification)
- Diagnostics Differential diagnostics
- Medications
- How does the operation take place?