Diffuse toxic goiter (DTG) is considered a life-threatening disease, because it results in irreversible changes in all organs and tissues of the human body, especially in the heart, blood vessels, nervous system and skeleton of the patient.
Diffuse toxic goiter mainly affects young and middle-aged women (mainly residents of large cities), and they suffer from this disease 5-10 times more often than men. The concepts of “thyrotoxicosis” and “diffuse toxic goiter” mean the same thing for many, although this is not true. Thyrotoxicosis is a syndrome that can accompany many diseases and conditions, including diffuse toxic goiter.
Thyrotoxicosis can be caused by an overdose of L-thyroxine and taking certain medications (amiodarone, interferon). In addition, thyrotoxicosis can occur as a symptom of diseases of other organs (for example, ovarian tumors, cancer metastases).
Another concept - hyperthyroidism - differs in that it is not a pathological condition. Increased functioning of the thyroid gland can manifest itself as a physiological process during early pregnancy, stress and other short-term conditions.
In professional terms, in diffuse toxic goiter, autoimmune aggression is caused by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors located on thyrocytes - protein structures located on the surface of thyroid cells. When functioning normally, they combine with the TT hormone, which is produced and released into the blood by the pituitary gland. This tropic hormone is a signal from the central endocrine organs, causing the thyroid gland to produce more hormones, as a result of which antibodies to TSH receptors, combining with the object of their aggression (receptor), act like thyroid-stimulating hormone itself, increasing the production of thyroid hormones.
What is diffuse toxic goiter?
Diffuse toxic goiter is a pathological condition caused by increased production of thyroid hormones by diffuse thyroid tissue, and leading to poisoning of the body with these hormones - thyrotoxicosis.
Etiology and pathogenesis
This pathology belongs to autoimmune diseases. The development of the disease occurs in a polygenic, that is, multifactorial way. Among the causes of DTZ are psychological trauma, traumatic brain injury, nasopharyngeal diseases, infectious and inflammatory diseases, and heredity. In patients with diffuse toxic goiter, antibodies are produced that damage the cells of the thyroid gland. Due to disturbances, it begins to produce a large number of thyroid hormones.
In most cases, women suffer from diffuse toxic goiter. The disease affects them 8 times more often than males. The average age at which the disease peaks is from 30 to 50 years. However, it is not uncommon for goiter to develop in other age groups: in adolescents, expectant mothers and those women who have entered menopause. DTZ is a common pathology, affecting one person out of 100.
Forecast
The prognosis is favorable in most cases. In the case of long-term drug treatment, and sometimes in its absence (this is also possible), patients develop extrathyroidal complications, most often from the cardiovascular system. But thyrotoxicosis sooner or later gives way to hypothyroidism: the thyroid gland, which has been functioning intensively for a long time, is eventually depleted, and the amount of hormones it produces drops below normal.
Thus, patients, both those who received radical treatment and those who did not receive it at all, come to the same result - hypothyroidism. True, the quality of life of the latter in all the years of the existence of DTZ is low, and the former, subject to continued lifelong use of levothyroxine, live a full life.
There is a certain difference in domestic and Western terminology.
In Western literature, the concept of “hyperthyroidism” is used along with the term “thyrotoxicosis” and in a synonymous meaning. Russian endocrinologists call hyperthyroidism any increase in the functional activity of the thyroid gland, which can be not only pathological, but also physiological, for example, during pregnancy. This fact should be taken into account when reading English-language literature. 1. Fadeev V.V. Thyroidologist's Handbook, 2002 2. Bahn RS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, Garber JR, Greenlee MC, Klein I., Laurberg P., McDougall IR, Montori VM, Rivkees SA, Ross DS, Sosa JA, Stan MN Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis: Management Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. // Thyroid - 2011 - Vol. 21. 3. Muller AF, Berghout A., Wiersinga WM, Kooy A., Smit JWA, Hermus A., working group Thyroid Function Disorders of the Netherlands Association of Internal Medicine. Thyroid function disorders — Guidelines of the Netherlands Association of Internal Medicine// Neth. J. Med. 2008. V. 66. P. 134–142. Translation and comments by V.V. Fadeeva “Clinical and experimental thyroidology” 2008, volume 4, No. 2, (https://medi.ru) 4. Balabolkin M.I. Endocrinology, 1998 https://med-lib.ru 5. Petunina N.A. Conservative treatment of diffuse toxic goiter: opportunities, problems, solutions (2009) medi.ru 6. Olovyanishnikova I.V. The effectiveness of various drug therapy regimens for diffuse toxic goiter. Prognostic aspects (2005) https://www.dissercat.com
Symptoms of diffuse toxic goiter
At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. As the pathological process develops, the mass of the thyroid gland begins to increase. Instead of the required 20 g, the organ weighs 50 g. Because of this, a bulge forms on the front side of the neck. Moreover, both lobes of the thyroid gland grow evenly.
Other symptoms of diffuse toxic goiter include the following:
- The person has difficulty taking food and water;
- The patient complains of a feeling of constant pressure in the neck;
- Due to compression of the larynx, breathing becomes noisier;
- When a person lies down, shortness of breath appears;
- The patient suffers from attacks of dizziness;
- A goiter appears, which is visible to the naked eye;
- The eyeballs increase in size and protrude from their sockets. This occurs due to autoimmune inflammation, as well as swelling of the surrounding tissues. At the same time, the eyes are wide open and very shiny. It is the eye symptoms that often appear earlier than other signs of the disease and make it possible to suspect the development of diffuse toxic goiter;
- Against the background of changes in the eyeballs, the patient develops chronic conjunctivitis;
- A severe form of the disease provokes the development of fatty liver degeneration and cirrhosis;
- The heart rate increases and exceeds 120 beats per minute. Blood pressure rises, the patient complains of stabbing pain in the heart area. Among other cardiac disorders, arrhythmia, extrasystole, and heart failure may occur;
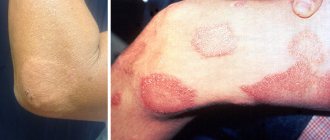
- The skin becomes swollen and crusty. It feels warm and moist to the touch;
- Vitiligo is often observed in patients with DTG;
- The patient begins to notice hair loss;
- Nails are destroyed, erythema develops, legs may swell;
- The work of the sweat glands increases, against the background of which a person suffers from excessive sweating;
- The patient’s appetite increases, but at the same time he actively loses weight, as all metabolic processes accelerate;
- Body temperature is always slightly elevated: from 37 to 37.5 °C. In this case, no accompanying inflammatory processes are observed;
- The patient suffers from multiple caries;
- The patient's hands and head tremble;
- There is a tendency to frequently recurrent pneumonia;
- The person is fussy, overly irritable, anxious;
- In men, as a result of the disease, impotence develops and attraction to the opposite sex decreases;
- Women experience deviations in the menstrual cycle, sometimes periods are delayed for a long period and may be absent for more than six months;
- Patients often suffer from diarrhea, sometimes, but rarely, from attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- Patients complain of sudden attacks of muscle weakness.
The symptoms are similar to those of a disease such as hyperthyroidism. But with diffuse toxic goiter, there are three characteristic features: a protrusion forms in the neck, pronounced exophthalmos is observed, and sometimes swelling of the skin in the area of the legs.
Prevention
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to determine the level of platelets and leukocytes once a month. To prevent severe forms of the disease, clinical observation in the clinic is recommended. If left untreated, a severe complication of Basedow's disease may develop - thyrotoxic crisis or coma . This complication can be fatal.
One of the preventive measures is to carry out general strengthening therapy and sanitation of inflammatory foci - the elimination of all possible infections. The patient should maintain a hygienic regime, combat stress and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Causes of diffuse toxic goiter
The reasons that provoke the development of diffuse toxic goiter are the following:
- Hereditary factor. The disease is often observed within the family circle;
- Insufficient iodine intake from food and drink. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. When it is low, the number of thyrocytes increases;
- Belonging to the female gender. It has been found that women suffer from diffuse goiter more often than men. This is due to hormonal changes in the body. We are talking about the period of bearing a child, breastfeeding, and entering menopause. Abortions and hormonal contraception used independently can have a negative impact on health and cause the development of the disease;
- Taking iodine preparations without medical supervision, as well as working in places where it is extracted and actively used. An excess of this element in the body is no less dangerous than its deficiency;
- Autoimmune conditions, which include scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes. Against the background of a malfunction of the immune system, the thyroid gland may suffer, its damage is included in the general immune response;
- Age under 40 is another factor that increases the risk of developing the disease. Most often it manifests itself when a person’s immune system is strong and active;
- Prolonged stressful situations and psychological shocks leading to nervous exhaustion become the causes of the development of the disease. Against this background, nervous regulation, which is important for the normal functioning of the gland, is disrupted;
- All factors influencing the decrease in immune strength: hypothermia, bad habits, increased physical activity;
- Surgical manipulation of the thyroid gland. Once removed, the node can become an impetus for the proliferation of organ tissue.
Degrees of diffuse toxic goiter
The degree of development of the disease depends on the severity of toxicosis caused by hormones produced by the thyroid gland. They are also determined by the size of the organ. There are three degrees of development of the disease, which have characteristic symptoms.
1st degree of diffuse toxic goiter
The first degree is quite easy, since this is the initial stage of the disease. At this time, the patient complains of increased nervous excitability and begins to lose weight. Body weight loss averages 15%. There is a noticeable increase in heart rate, and the first signs of tachycardia appear. A person's performance decreases. The goiter itself is not enlarged and is not visible upon examination.
Sudden changes in the skin are often the reason to consult a doctor. Pigmentation increases and sweating increases.
2nd degree of diffuse toxic goiter
Symptoms intensify as the disease progresses. This degree is characterized by pronounced nervous excitability. Loss of body weight continues, it can reach 20%. Signs of tachycardia intensify. The patient complains of a chronic feeling of fatigue, and performance decreases even more. The goiter is not yet visible, but the doctor feels an enlargement of the thyroid gland upon palpation. Circulatory failure is often observed. Visually, you can notice a small goiter when a person makes swallowing movements. Exophthalmos is already quite pronounced. Periodically, patients develop swelling in the legs, mainly in the evening.
3rd degree of diffuse toxic goiter
The last, and most severe, from the point of view of therapy and the patient’s condition, is the third degree of development of the disease. In addition to nervous excitability, a person loses the ability to work. The final stage of diffuse toxic goiter is characterized by pronounced loss of body weight and serious disorders of the cardiovascular system. Against the background of the disease, atrial fibrillation and heart failure develop.
The liver is often affected, and severe muscle weakness appears. It gets to the point where it becomes difficult for the patient to get up from a chair. Tendon reflexes increase. At this stage, the patient may lose vision.
The goiter increases in size and becomes noticeable even to a non-specialist. The neck may become deformed and swelling may appear in this area.
Complications of diffuse toxic goiter
The disease is dangerous due to the development of complications:
- Damages to the cardiovascular system are observed, in particular, the development of “thyrotoxic heart”. Symptoms of this condition: heart failure, angina, sinus tachycardia. Moreover, rapid heartbeat does not depend on physical activity and does not decrease during night rest;
- Hypertension develops, heart defects may form;
- A serious complication from the gastrointestinal tract is the occurrence of thyrotoxic hepatosis. This condition threatens to develop into cirrhosis and cause the death of the patient;
- The pathology is complicated by attacks of muscle weakness, in some cases paralysis develops;
- Thyrotoxic crisis is a serious complication of diffuse goiter that threatens the patient’s life. It occurs infrequently, in most cases with severe disease. At the same time, the production of hormones increases sharply, which causes the formation of severe thyrotoxicosis. At the same time, the person is conscious, in the initial stages of the crisis he is very fussy, often aggressive. Psychosis may give way to severe apathy, immobility, and headaches of severe intensity may appear. Then the pulse increases sharply, becomes irregular, blood pressure rises, and breathing quickens. The person sweats a lot, body temperature rises, and can reach 41 degrees. Vomiting and yellowing of the skin are often observed. The end of a thyrotoxic crisis is often loss of consciousness and the development of coma. Treatment should be carried out only in a hospital setting, assistance should be provided as quickly as possible. Death during a crisis occurs in 50% of cases.
Thyrotoxic crisis
The most dangerous complication of thyrotoxicosis is thyrotoxic crisis. This is an acutely developing clinical syndrome, which is a combination of thyrotoxicosis with thyrogenic adrenal insufficiency.
Thyrotoxic crisis develops against the background of inadequate thyreostatic therapy after surgery and in acute extrathyroidal diseases. The reasons for its occurrence are not well understood. Patients with thyrotoxic crisis are subject to observation and treatment in the intensive care unit.
Clinically, a thyrotoxic crisis is manifested by a sharp increase in the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis with progressive dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system, liver and kidneys. Hyperthermia up to 40 °C, tachycardia, depression of consciousness up to coma are noted. Thyrotoxic coma is almost always fatal. In addition, extremely difficult to correct acute cardiovascular failure often develops, which is the most severe complication of thyrotoxic crisis. Mortality during thyrotoxic crisis reaches 75% [3].
Patients with thyrotoxicosis are often very popular with people of the opposite sex, unless, of course, changes in their appearance and behavior are moderate and are not perceived by non-medics as painful. I remember how a patient, whose symptoms went away due to successful treatment, complained to me that before she had never stopped seeing fans, but now the sparkle in her eyes was gone, and with it her sexual attractiveness...
Diagnosis of diffuse toxic goiter
When the clinical manifestations of diffuse toxic goiter are pronounced, the diagnosis is not complicated. Such external manifestations as low body weight, pathological condition of the skin and nails, increased heart rate and increased blood pressure allow the doctor to make an assumption about the presence of hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. If ophthalmopathy is observed, the diagnosis is almost obvious.
To confirm it, the following types of examinations are carried out:
- Blood test for hormones. To exclude errors, laboratory tests are necessary. Test results indicate an increase in the amount of thyroid hormones in the body with a decrease in the number of TSH. To conduct the study, blood is taken to determine the level of hormones (pituitary hormone and thyroid hormones);
- Enzyme immunoassay. In order to distinguish diffuse toxic goiter from similar conditions, an enzyme immunoassay is performed, which makes it possible to determine the presence of antibodies to TSH, thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase in the blood;
- Ultrasound. The patient is also recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. It will allow you to determine the presence of diffuse enlargement of the organ, changes in its structure;
- Scintigraphy. A method such as scintigraphy makes it possible to find out the volume and shape of an organ. In addition, the method allows you to detect areas of active diffuse gland tissue;
- The doctor also studies the patient’s reflexes;
- Radiodiagnosis has been used less and less recently. This method is based on the injection of iodine isotopes into the patient’s vein and measuring their concentration a day later using a special camera;
- An X-ray examination is advisable when the goiter reaches an impressive size and puts pressure on the esophagus. The picture is taken in two projections, this demonstrates a picture of changes in the lymph nodes and makes it possible to detect narrowing of the organs of the neck;
- Biopsy. When the doctor detects lumps and secondary nodes, the patient is sent for a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. The procedure allows you to exclude or confirm thyroid cancer and enlarged lymph nodes.
An auxiliary diagnostic method is computed tomography. If the vessels and volume of the organ are enlarged, the edges are uneven, nodes and cysts are present, then the diagnosis is confirmed.
Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter
Treatment of the disease primarily aims to normalize the level of hormones produced by the gland. For this purpose, doctors have hormonal agents, as well as iodine preparations, in their arsenal. In some cases, surgery is indicated, as well as the use of radioactive iodine. The doctor determines the method of treatment. This depends on a number of factors, in particular the stage of the disease, the age of the patient, the presence of other diseases, etc.
For the treatment of DTD, drugs containing iodine are used. They make it possible to compensate for its deficiency and stop the growth of the organ. However, taking these medications should be carried out under strict medical supervision, since in case of diffuse goiter, iodine preparations can cause hardening of the gland and its increase in size!
A product such as Diiodotyrosine contains the amino acid tyrosine and iodine. Its transformation in the body helps to neutralize excess thyroxine and normalize the patient’s condition. The drug is used when there is a lack of iodine in the body, however, it is used extremely rarely as an independent therapeutic method. A course of treatment is indicated.
On the subject: Test to determine the level of iodine in the body
In order to reduce the amount of thyroid hormones produced, thyreostatic drugs are used. These drugs include Mitezol, Tyrozol, Thiamazol, Propicil. A remedy such as Mercazolil is prescribed for diarrhea three times a day; the tablet should not be chewed and should be taken with plenty of water. If the disease is severe, a gradual increase in the dose is indicated, and after normalization of the condition, the dosage is reduced every five days. A competent approach to drawing up a treatment regimen is important so as not to provoke complications of the disease.
Cancellation of antithyroid drugs occurs only when signs of toxicosis disappear, the pulse normalizes, body weight gains, and after the elimination of limb tremor. The approach to the treatment of diffuse toxic goiter should be determined individually. Therapy with Mercazolil can be started at any severity of the disease.
The total time of drug therapy for this disease ranges from one to one and a half years. If the drugs cannot be discontinued after the specified period, the patient is referred either to surgery or to radioiodine therapy. When a patient experiences frequent relapses, he cannot be constantly treated with Mercazolil. This is fraught with the formation of thyroid cancer.
If the disease is detected in a woman before 12 weeks of gestation, she will need to terminate the pregnancy. If the disease has not reached the third stage, then the patient is recommended to take antithyroid drugs. The minimum dose is selected. During breastfeeding, it is possible to take only Propicil. If the disease is severe, then surgery is indicated.
Corticosteroids are also often used to treat goiter. They influence the activity of the adrenal glands, the metabolism of hormones and in addition to this have an immunosuppressive effect.
Sedatives will help reduce anxiety and normalize sleep. The patient is prescribed Phenobarbital for this purpose, which additionally affects hormone levels.
There are clear indications for surgical intervention:
- Severe course of the disease;
- The third stage of goiter with compression of the larynx and a pronounced cosmetic defect;
- Inability to take antithyroid drugs due to an allergic reaction;
- Ineffectiveness of drug treatment for six months;
- Atrial fibrillation;
- Frequent relapses of the disease.
Surgery cannot be performed in case of kidney and liver disease, as well as in other conditions that are contraindications to general anesthesia. As a rule, almost the entire organ must be removed. The operation is called thyroidectomy. It is carried out when all indicators return to normal. Treatment of postoperative hypothyroidism is carried out using hormone replacement therapy. 5 days after surgery, the patient is allowed to go home.
It is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- In the first days, you should not eat solid food to avoid active chewing and swallowing movements. They cause pain, and swelling of the tissues of the larynx makes swallowing difficult. Therefore, food should be liquid. After a few weeks, this restriction is lifted;
- It is important to monitor your menu after organ removal. Diet is necessary to maintain a normal weight, as the likelihood of obesity increases;
- The diet should include foods rich in proteins and vitamins. The presence of seafood and sea fish is required;
- You should not take medications containing iodine without consulting a doctor;
- It is important to follow a daily routine and rest at least 8 hours a day;
- After removal of the thyroid gland, you should avoid exposure to the sun. However, the patient needs walks;
- Once a month during the first year after surgery, it is necessary to visit an endocrinologist to monitor the condition.
The scar on the neck remaining after the operation will be red at first and may increase in size. This is a normal condition and after two years it will become lighter and thinner.
Treatment of diffuse goiter with radioactive iodine
The radioactive iodine treatment method gives positive results. To do this, the patient must take capsules or liquid that contain it. Administration of the drug through a vein is practiced, but is extremely rare.
When the product enters the body, it begins to accumulate in the gland cells, causing them to die. Connective tissue forms in place of dead cells. Research shows that iodine also tends to accumulate in the mammary and salivary glands, in the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is noteworthy that the product is distributed unevenly in the organ. One, predominantly central part of the gland is destroyed, while its peripheral parts continue to function. Moreover, the tissues surrounding the organ do not suffer from the action of the isotope.
There are features of therapy:
- Before starting treatment, it is important to stop taking antithyroid drugs. This must be done several days before the start of intensive exposure to radioactive iodine. If this is not done, the effectiveness of isotope therapy will be reduced;
- Treatment should not be started during pregnancy;
- It is worth giving up some foods a few days before the start of therapy. In particular, we are talking about seafood (shrimp, mussels, crab sticks, seaweed, fish, crabs, etc.), as well as iodized salt. You should avoid foods containing such salt (sausage, cheese, canned food);
- Soy-based products should not be used in food. Sometimes their iodine content is extremely high;
- It is not recommended to eat two hours before the procedure and less than the same time after taking the capsule;
- In order to avoid aggravation of endocrine ophthalmopathy, which can be provoked by treatment with radioactive iodine, a preliminary course of glucocorticoids is advisable;
- An ultrasound of the thyroid gland is first necessary to determine its size. This must be done in order to calculate the dose of the administered drug as accurately as possible;
- It is worth giving up breastfeeding if a woman is undergoing treatment with radioactive iodine.
The effectiveness of treatment with radioactive iodine isotope is high. The data obtained indicate that more than 99% of patients are cured. However, controversy still persists over the safety of the procedure. It is known that iodine breaks down by half within a short time, which reduces its activity. This period is 8 days, which means it will not have time to harm other body systems and the environment.
The isotope is excreted mainly in urine. Therefore, if it gets on things or bedding, they need to be replaced and washed, preferably separately. If there are children under 2 years of age in your immediate environment, you should avoid contact with them for at least 9 days. If the work involves communicating with children, then you should take sick leave for one month after the therapy.
Some scientists put forward theories that those areas of the thyroid gland that are replaced by connective tissue are susceptible to the formation of cancerous tumors. Therefore, a clear contraindication to radioactive iodine therapy is the period of pregnancy, breastfeeding, childhood and adolescence and an increase in goiter in volumes of more than 40 ml.
The development of iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis is identified as possible complications after completing a therapeutic course. Moreover, if its symptoms appear immediately after the first dose of the drug, then most often they pass quickly and without a trace. When signs of pathology appear later, 5 days after the start of treatment, then the disease will be protracted.
Also, during therapy with radioactive iodine, a thyrotoxic crisis may develop, a substernal goiter may form, and it may become impossible to use drugs containing iodine. Sometimes patients complain of a sore throat, weakness, nausea and loss of appetite. There may be slight swelling in the corresponding area of the neck.
Another rule is the use of contraception after the end of isotope treatment. This must be done for 4 months to avoid the risk of fertilization and harm to the health of the unborn child. It is best to plan a pregnancy no earlier than two years after the therapy, since radioactive iodine tends to penetrate the placenta.
On the subject: Effective traditional medicine recipes for goiter
When is surgery recommended?
You should contact surgeons for resection of part of the gland in the following cases:
- If its size is too large (more than 40 cm3 according to ultrasound);
- If pharmaceuticals are ineffective;
- In case of intolerance to drugs (thyreostatics, irradiated iodine, corticosteroids and others);
- If you consciously refuse therapy with medications and radioactive iodine.
In such situations, doctors recommend a surgical method to get rid of thyrotoxicosis. During the operation, the doctor will remove a section of the organ to reduce the amount of hormones produced. After this procedure, all thyreostatic medications are discontinued and the patient’s need for L-thyroxine is determined.
It should be remembered that, despite a radical solution to the problem, relapse of Graves' disease can occur if the thyroid gland is insufficiently excised or after a long time after surgery. Therefore, you should remember the most striking manifestations of pathology and monitor your health.