Meniere's disease is a non-inflammatory disease that affects the structures of the internal organ of hearing. It occurs with tinnitus, hearing loss and dizziness. The set of signs of pathology and approaches to its treatment were described in the second half of the 19th century by the French physician Prosper Meniere.
What is this pathology? What symptoms does the patient experience? Which doctor treats the disease? What medications and drugs are most effective in treatment? Let's find out!
Forms of the disease
There are three main forms of Meniere's disease:
- cochlear – starting with a hearing disorder (develops in approximately half of patients);
- vestibular – manifested by vestibular disorders (occurs in every fifth patient);
- classical – with simultaneous hearing impairment and vestibular apparatus disorder (develops in 30% of cases).
In addition, the disease can be unilateral, i.e. affecting one ear, or bilateral - such patients account for no more than 15% of the total number of patients. There may be cases of transition of a unilateral disease to a bilateral form.
Classification
Depending on the development of the clinical picture, three variants of the course of Meniere’s disease are distinguished:
- the first (classic) type - there is a simultaneous development of vestibular and auditory disorders, that is, the first attack of vertigo leads to decreased hearing and tinnitus;
- the second - cochlear , is characterized by the appearance of initially auditory disorders, which are later joined by vestibular ones;
- the third most rare is vestibular , characterized by the presence at first only of attacks of dizziness, and hearing problems develop within a year after the debut of the pathology.
Symptoms
The disease is paroxysmal in nature: the symptoms of Meniere's disease periodically intensify, then after some time they disappear, only to return again after a few months, days or hours, often to a stronger degree. The main signs of the disease include:
- congestion of one or both ears, which can reach complete deafness;
- noise, ringing, or discomfort in one or both ears;
- regular attacks of dizziness, which can be so severe that a person cannot stand and falls;
- disturbance of the sense of balance;
- nausea or vomiting during attacks;
- spontaneous nystagmus - involuntary movements of the pupils during attacks;
- increased sweating;
- surges in blood pressure - usually a decrease, but in some patients the pressure may increase;
- uncoordinated muscle contractions;
- loss of coordination of movements;
- decrease in body temperature.
If left untreated, hearing loss and tinnitus worsen over time, then the disease affects both ears, which can lead a person to almost complete hearing loss. Attacks of dizziness often begin suddenly, due to which a person loses the ability to drive a car or other complex equipment - this becomes dangerous for the patient and for others. Periods of exacerbation continue for several weeks, during which attacks may recur several times during the day. Then a remission occurs, lasting several months or years, after which the disease returns. Sometimes attacks go away spontaneously after 7-10 years, but most patients require qualified treatment.
General information
Meniere's disease and syndrome is one of the rare non-purulent diseases of the inner ear, which is caused by an increase in the volume of intralabyrinthine fluid and pressure, accompanied by attacks of dizziness , deafness, and balance disorders. It was first described by Meniere P., who noted that the pathology occurs in 0.02-0.2% of the population, more often in middle-aged Caucasians (30-50 years), but can also develop in children.
Meniere's syndrome: what kind of disease?
The pathology is vestibular neuronitis and is classified as idiopathic - developing independently, and not against the background of other ailments. Should be limited only to manifestations of peripheral labyrinthine syndrome without signs of central disharmonization or dissociation of pathological reactions.
The disease that most often causes recurrent systemic vestibular vertigo, tinnitus and sensorineural hearing loss .
Causes of pathology
The causes of Meniere's disease have not yet been reliably established. There are suggestions that its development is associated with:
- the presence of vascular diseases;
- head or hearing injuries;
- an inflammatory process of an infectious or autoimmune nature occurring in the inner ear;
- increased pressure inside the skull;
- hypertension;
- dysfunction of the nerve fibers of the inner ear;
- congenital pathologies.
The main cause of Meniere's disease is a violation of the circulation of endolymph in the labyrinth of the inner ear. Liquid accumulates in the ear cavity, creating increased pressure, disrupting the conduction of sound vibrations and distorting the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. However, the factors that provoke this disorder have not yet been established with the appropriate degree of evidence.
Pathogenesis
With Meniere's disease, there is an increase in the volume of endolymph inside the membranous labyrinth and, accordingly, an increase in pressure. As a result of such endolymphatic hydrops , caused by overproduction, disturbances of circulation and resorption of endolymph, patients experience:
- recurrent attacks of unilateral deafness that progress;
- signs of tinnitus;
- cases of systemic dizziness;
- disturbances in the sense of balance;
- autonomic disorders.
Most often, endolymphatic hydrops is asymptomatic, without progressing and without causing rupture of Reisner's membrane. It is the periodic ruptures of the membrane that cause the mixing of endolymph, rich in potassium, with perilymph, and as a result, depolarization and overexcitation of the vestibular nerve.
This leads to the development of paroxysmal dizziness. While hearing impairment and the occurrence of noise may be associated with the processes of apoptosis , death of spiral ganglion neurons, difficulty in conducting sound waves in the fluids of the labyrinth, and deterioration of the trophism of labyrinthine receptors.
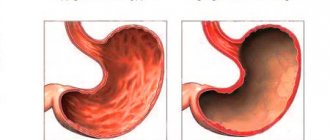
Inner ear of a healthy person and with Meniere's disease, expressed in an increase in the volume of endolymph
Important! When endolymphatic hydrops is secondary in nature, that is, the causes are directly related to another disease, then the concept of “Menière's syndrome” is distinguished.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of Meniere's disease is quite specific and begins with studies of the hearing organ and auditory function:
- otoscopy – examination of the ear canal and eardrum;
- audiometry – determination of hearing sensitivity;
- tympanometry - studies of auditory function through changes in pressure;
- acoustic reflexometry – research of auditory reactions;
- tuning fork study - studying the sensitivity of the ear to various sound frequencies;
- electrocochleography - studying the passage of impulses along auditory nerve fibers.
To exclude other diseases, the patient may be prescribed a CT or MRI, Doppleroscopy of the brain vessels. To identify a disorder of the vestibular apparatus, vestibulometry is performed - a study that must be completed during an attack and during remission.
In addition, a consultation with a neurologist and a subsequent neurological examination, which includes electroencephalography and some other studies of the nervous system, are necessary.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of Meniere's disease is established taking into account specific symptoms and the results of instrumental studies. The American Academy of Otolaryngologists, based on clinical manifestations, distinguishes three degrees of reliability of BM: possible, probable and definite BM. An important diagnostic criterion is the triad of symptoms:
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- hearing loss.
The diagnosis is confirmed by gradual deterioration of hearing and repeated episodes of vestibular attacks.
The following instrumental methods are used to diagnose Meniere's disease:
- Pure-tone threshold audiometry is the main method according to international diagnostic criteria. The result of such a study will be an audiogram, which graphically depicts the function of the hearing organ;
- Otoscopy is performed to exclude middle ear pathology;
- Extratympanic electrocochleography evaluates the performance of the auditory nerve;
- A tuning fork test determines the type of hearing loss. In this case, the hearing loss is of the conductive type.
These methods allow you to analyze the degree of hearing impairment. Audiometry is the main criterion when choosing treatment tactics. To detect endolymphatic hydrops, doctors use electrocochleography and a dehydration test.
Audiogram for Meniere's disease
An audiogram is used to determine the degree of hearing loss. Before the procedure, the doctor examines the ears; if ear plugs are found, they are removed. The patient is put on headphones, and signals of different frequencies are sent via a computer. The subject needs to press the button when he hears the signal. In the initial stages, poor perception of low frequencies is recorded.
Electrocochleography
To perform extratympanic electrocochleography, electrodes are placed on the skin of the auricle or eardrum. The electrodes determine the ability of the auditory nerve to generate nerve impulses after a signal is given.
Dehydration test
Before the test, the patient undergoes threshold pure-tone audiometry. Then osmotic diuretics (furosemide) are administered and audiometry is repeated again every 3 hours, after 24 and 48 hours. The test is positive if there is an improvement in hearing of 10 dB or more after 3-4 hours. During remission of the disease, the study is not very informative.
Multislice computed tomography of the bone labyrinth
MSCT allows you to detect the smallest changes in all organs.
The images visualize pathognomonic processes in the inner ear with BM. To assess disorders of the balance organ, the following studies are used:
- videonystagmography to detect horizontal nystagmus;
- the video impulse test displays the vestibulo-ocular reflex and the presence of asymmetry;
- stabilometry;
- bithermal bitemporal calorization is performed to assess the function of the semicircular canals;
- rotational tests.
Differential diagnosis of Meniere's disease is carried out with the following diseases:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- ischemic attacks. Such attacks last minutes and are observed in elderly people with vascular pathology;
- other vestibulopathies, they can arise as a result of purulent otitis, otosclerosis, labyrinthitis;
- tumors of the cerebellopontine fossa;
- vestibular migraine;
- otosclerosis. The disease is often bilateral, the main symptoms are cochlear;
- benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. The attack is intense and occurs in a certain position of the body;
- osteochondrosis.
To exclude brain tumors, injuries, and anomalies in the structure of the temporal bone, CT and MRI are highly informative.
To choose the right treatment tactics, timely and accurate diagnosis is necessary. At the Yusupov Hospital you can get the necessary examinations and consultation from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic has modern high-quality equipment and diagnostic laboratories.
Make an appointment
Treatment
Since the causes of the disease are currently unknown, treatment of Meniere's disease is aimed at relieving attacks, preventing dizziness and strengthening the patient's general condition. During attacks, as a rule, hospitalization is not required; the patient can be treated on an outpatient basis. The attacks are stopped by combinations of neuroleptics, vasodilators and antihistamines. If the patient develops profuse repeated vomiting, he needs hospitalization to eliminate dehydration and administer medications intramuscularly or intravenously.
In the intervals between attacks, physiotherapeutic procedures for the collar area have a good effect:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- exposure to pulsed electric currents (UHF);
- electrophoresis;
- medicinal baths;
- reflexology;
- therapeutic massage of the cervical-collar area;
- acupuncture;
- laser and magnetic therapy.
It is important that the patient maintains physical activity, for which he may be prescribed general strengthening physical therapy. There are special sets of exercises aimed at improving coordination of movements and improving the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
If careful implementation of clinical recommendations for Meniere's disease does not bring any results for a long time, the patient may undergo surgical treatment. The purpose of the operation is to remove excess endolymph. The intervention may be:
- draining;
- destructive;
- clipping nerve endings;
- forming the stirrup of the ear.
The type of operation is selected according to the indications and individual characteristics of the patient’s hearing aid.
Correctly chosen therapy slows down the development of hearing loss and deafness, reduces the intensity of attacks of dizziness, and in some cases contributes to the complete cure of the disease. The sooner treatment is started, the higher the chances of returning to a full life.
Folk remedies
Photo: mulifertility.com
Traditional medicine claims that Meniere's disease can be cured by resorting to folk remedies. This will be a longer process, but following the recommendations will ultimately give a positive result. It is important to consult your doctor first to avoid worsening the condition. The use of certain types of plants can cause individual intolerance to the body.
Traditional treatment of Meniere's disease. Peculiarities
Treatment of Meniere's disease with folk remedies consists of cleansing the body of toxins and salts, using diuretics, and using natural ingredients to improve blood flow.
Methods of cleansing the body for Meniere's disease with folk remedies
Cleansing the body of harmful salts has a positive effect on all vital systems. In the traditional treatment of Meniere's disease, the following methods of cleansing the body are the most common (which, however, are not clinically proven and are predominantly denied by representatives of official medicine):
- Tibetan - a special collection of herbs is used, which in our latitudes is most often replaced by a mixture of chamomile, St. John's wort, immortelle, strawberry leaves, birch buds. All of the above components are mixed and poured with boiling water, and then left in a thermos overnight. This decoction is usually taken in the morning after meals.
- According to Dr. Newman, it is based on taking distilled water with citrus fruits, carrot and celery juice, followed by a three-day fast. In this case, an enema is given daily (to avoid intoxication of the body).
- Russian - this method of folk treatment for Meniere's disease consists of following a salt-free diet and taking a decoction of cones in the morning and evening. The body makes up for the lack of salt from the outside by using stored salts. Treatment lasts approximately a month
- According to Dr. Walker - fasting for several days followed by cleansing the intestines through an enema. A vegetarian diet will be followed for the next few weeks.
Also, teas made from sunflower root, knotweed, bearberry leaves, watermelon peels, and horsetail are used in folk medicine to treat Meniere's disease. It is generally accepted that black radish juice effectively dissolves and removes mineral salts from the body.
Removing excess fluid in Meniere's disease with folk remedies
In the process of getting rid of excess fluid in the treatment of Meniere's disease using traditional methods, the following herbal infusions are popular:
- thyme, knotweed, burdock (infusions orally);
- birch leaves, horsetail (infusion);
- cornflower flowers, licorice root, bearberry (infusion);
- wheatgrass root, nettle, parsley;
- treatment with infusion of agave and wormwood leaves;
- pumpkin juice;
- elderberry root infusion.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of Meniere's disease in Moscow
The Clinic of Academician Roitberg JSC "Medicine" offers diagnostic services and qualified treatment of Meniere's disease. Diagnostic procedures are carried out using modern medical equipment and allow us to identify any deviations in health status. High qualifications and many years of experience of the medical staff allow us to count on the success of treatment in the most complex and advanced cases. Make an appointment online or call us to choose a convenient time to visit the clinic.
Diagnosis
For the diagnosis of M. b. It is necessary to carefully collect anamnesis and conduct a detailed otoneurological examination. If the study reveals a picture of peripheral cochleovestibular syndrome at the labyrinthine level, then a diagnosis of M. b. can be made. If the disease begins with vestibular disorders alone, then diagnosis is difficult, but the special nature of attacks of dizziness and hearing impairment, which are characteristic only of M. b., helps.
Differential diagnosis
M. b. carried out with acoustic neuroma (see vestibular-cochlear nerve), leptomeningitis (arachnoiditis) of the cerebellopontine angle, brainstem encephalitis with predominant damage to the vestibular nuclei, autonomic-vascular crises, specific labyrinthitis (see), vascular, toxic-infectious lesions and labyrinth trauma .