Definition
Cardiopathy is a disease in which metabolic processes in cardiomyocytes (heart cells) are disrupted. The gradual failure leads to disruption of myocardial contraction and signal conduction due to the replacement of muscle tissue with connective tissue, which does not transmit electrical impulses. The genesis (origin of the pathology) is not fully understood. It is generally accepted that it occurs due to heredity, infections, hormonal surges, alcohol and other reasons. Sometimes, instead of the diagnosis “cardiopathy,” the doctor writes “cardiomyopathy” in his report. It has an identical development mechanism and forms of manifestation.
Danger of illness
For a long time, the pathology does not manifest itself particularly. Initially, the patient experiences only general symptoms (irregular heart rhythm, chest pain, weakness). If treatment is not started as early as possible, cardiomyocytes will gradually begin to degenerate. Muscle tissue becomes connective. Over time, cardiac hypertrophy appears, the left ventricle suffers especially severely. In the pulmonary and systemic circulation, blood stagnation occurs, heart failure and arrhythmia develop. In fact, in 70% of cases, an advanced form of cardiopathy leads to blockage of blood vessels with blood clots and a significant decrease in performance.
A favorable prognosis depends on the cause of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. Due to mild symptoms, it is sometimes not possible to identify the pathology initially. In more rare cases, the diagnosis remains unspecified, since there is no way to find out the factor that influenced the development of the failure. The patient will have to be registered with a cardiologist for life, lead a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular examinations.
Causes and types
Cardiopathy can be primary or secondary. You can familiarize yourself with the features of these types of disease below:
- The primary form of cardiopathy is considered idiopathic, that is, arising for unknown reasons. It can be mixed, congenital or acquired over time. The disease is characterized by various changes in the structure of the heart muscle and an extensive clinical picture.
- The secondary form of failure is a complication of various pathological processes that are characterized by metabolic failure. The prognosis in this case depends on the severity of the underlying disease.
According to the mechanism of development, cardiopathy is divided into several types of damage to the heart muscle:
- The dilated form is considered the most dangerous. It is characterized by the proliferation of the walls of the ventricles. Pathology is caused by enteroviruses and alcoholic beverages.
- The restrictive type of cardiopathy is the least common. It is manifested by impaired filling of the left ventricle with blood against the background of thickening of the endocardium. The myocardium remains intact for a long time.
- Hypertrophic cardiopathy often occurs in athletes and is one of the leading causes of sudden death due to cardiac arrest. It is characterized by significant thickening of the myocardium, as a result of which signal conduction is disrupted. The symptoms are mild and do not appear for a long time. The main reason for the failure is genetic predisposition.
- The ischemic form of the disease develops due to insufficient nutrition of the heart muscle. It is characterized by myocardial hypertrophy, death of cardiomyocytes, and the appearance of scar tissue.
According to the causative factor, cardiopathy is divided into the following forms:
- The dishormonal type of the disease occurs under the influence of disruptions in the endocrine system. It is not an inflammatory disease and is common in older people and adolescents. Sometimes it is provoked by taking hormonal medications.
- Alcoholic cardiopathy occurs in people who abuse alcohol. Ethanol has a detrimental effect on cardiomyocytes. They malfunction due to the onset of intoxication. Gradually, the heart cells die and the myocardium loosens. The pathological process manifests itself as shortness of breath, arrhythmia (extrasystole, tachycardia) and swelling of the legs.
- Dysmetabolic (metabolic) type of disease occurs due to metabolic failures. The problem is often diagnosed in diabetes mellitus and thyroid dysfunction. Inflammatory changes are not typical for this form of cardiopathy.
- Climacteric (disovarial) cardiopathy occurs in women during menopause.
- The post-infectious (infectious-toxic) form occurs due to the development of otitis, appendicitis, sore throat, pneumonia and other diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. It often manifests itself in the form of myocarditis (an inflammatory disease), which leads to the death of heart cells and the replacement of muscle tissue with connective tissue.
- The dysplastic type of failure often has a primary nature of occurrence. It is manifested by the destruction of heart tissue and its replacement with connective tissue, which over time leads to acute heart failure. The disease can develop due to heredity, rheumatism, autoimmune disorders, fibrosis and other factors.
- The posthypoxic appearance occurs under the influence of ischemic disease. Cardimyocytes begin to lack nutrition, which causes irreversible disruptions in the metabolic processes of the heart.
- The autoimmune type of disease occurs due to failures in the human immune defense. Because of them, antibodies are synthesized that attack the cells of the heart, which affects its contractility and conductivity.
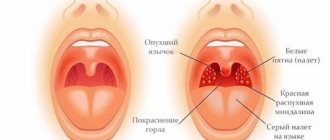
- Tonsillogenic cardiopathy is a type of autoimmune form of the disease. It occurs under the influence of an infection that causes tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils). The body's natural defenses weaken and begin to synthesize antibodies that mistake the cardiomyocytes for intruders and attack them.
- The functional form occurs in people who are often exposed to physical and psycho-emotional overload. In most cases, it is diagnosed in children and adolescents. Typically, this type of disease does not cause much harm and the changes are reversible in the early stages.
Diagnostics
Functional cardiopathy, its alcoholic, infectious-toxic and other forms can be diagnosed by the attending physician in the following ways:
- examination and interview of the patient, where the doctor will be able to form preliminary conclusions about his condition;
- ECG. There you can see changes in the myocardium, rhythm problems and changes in ventricular segments;
- X-rays of light. It identifies congestion, dilatation and other problems that may indicate an infectious-toxic type of disease;
- Ventriculography. Is an invasive study of the cardiac ventricles;
- MRI of the heart muscle. Involves scanning an organ with radio waves;
- MSCT. It scans all cardiac tissues layer by layer and is used to reconstruct a three-dimensional model of the heart;
- probing. Involves taking tissue from the heart cavity for research.
Based on the results of the research, drug treatment is prescribed.
Clinical picture
With cardiopathy, symptoms appear depending on the factor that influenced its development. The dilated form is characterized by the following clinical picture:
- chest pain not relieved by Nitroglycerin;
- dyspnea;
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle (cyanosis);
- changes in the structure of the chest due to cardiac hypertrophy.
The restrictive form of the disease is most often found in people living in the tropics. It manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- pain in the heart;
- constant shortness of breath;
- irregular heartbeat;
- swelling of the face;
- increase in belly size.
With hypertrophic cardiopathy, the patient may suddenly die due to physical overload due to the development of acute heart failure.
Her symptoms are pronounced. You can find them below:
- compression in the chest area;
- attacks of dizziness;
- heartbeat disturbance;
- dyspnea;
- loss of consciousness;
The ischemic type of pathology is characterized by the rapid development of heart failure and a high risk of thromboembolism. It can be detected by the following symptoms:
- chest pain;
- loss of consciousness;
- abnormal heart rhythm;
- shortness of breath with any physical activity;
- increasing weakness;
- lack of air;
- increased sweating;
- pale skin.
Symptoms of cardiopathy: how to suspect pathology and what are the first signs?
Often patients do not immediately notice the symptoms of the disease, attributing them to fatigue, stress, and poor nutrition.
Unfortunately, many people turn to the doctor when complications have already appeared. Despite the large number of varieties of the disease, the symptoms will be almost the same. The main complaints for any cardiopathy are:
- pain or heaviness in the heart area;
- severe weakness, dizziness;
- lack of air or shortness of breath during moderate physical activity;
- swelling in the lower extremities;
- cyanosis;
- sleep disturbances, presyncope;
- visible enlargement of the chest.
Cardiopathy with rhythm disturbances
With cardiopathy, the organization of the muscle tissue of the left ventricle changes and impulse transmission is disrupted. Rhythm disturbances appear in 85% of patients, regardless of the type of disease. There are atrial and ventricular forms of arrhythmia, which are paroxysmal in nature. During an attack, in addition to the main symptoms of cardiopathy, palpitations, increased fatigue, cold sweat, and a feeling of fear are possible.
The danger of arrhythmias lies in the formation of blood clots and the likelihood of complications: stroke, infarction of internal organs, pulmonary embolism.
It is important to suspect heart problems in time and consult a doctor. In addition to preventive annual examinations with a therapist, you should not self-medicate if the above symptoms appear, especially if there are risk factors (viral infection, endocrinological, immune diseases, connective tissue pathology, toxic effects).
Course of therapy
The treatment regimen for cardiopathy depends on its form. It may include medications, traditional medicine recipes, lifestyle changes and surgery. The basis of treatment is the fight against the causative factor. If it cannot be eliminated, then supportive medications are prescribed to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
For dilated cardiopathy, the doctor will recommend the following medications:
- ACE inhibitors (Spirapril, Ramipril) must be taken to stabilize blood pressure and stop the growth of the heart muscle.
- Beta-blockers (Nipradilol, Alprenolol) reduce myocardial oxygen demand and stop arrhythmia.
- Diuretics (Indapamide, Furosemide) are used to remove excess moisture from the body, especially if there is stagnation in the pulmonary or systemic circulation.
- Blood thinners (Curantil, Phenilin) prevent the development of blood clots.
To eliminate the hypertrophic form of cardiopathy, medications are used to reduce the myocardial oxygen demand and improve its contractility. The treatment regimen includes beta-blockers and blood thinners. Only calcium antagonists (Verapamil, Diltiazem) can be added to it. They stabilize the heart rhythm and reduce the automaticity of the sinus node. In severe cases, it is necessary to perform surgical intervention, the purpose of which is to install a pacemaker or remove a hypertrophied section of the septum.
The restrictive type of the disease is the most difficult to treat, especially its primary form. The course of therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms and underlying pathologies, for example, hemochromatosis is treated with bleeding, and sarcoidosis is treated with corticosteroids. To slow the development of heart failure, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and diuretics are prescribed. Heart transplantation was previously popular, but its effect was only temporary. Gradually, pathology developed in the new organ.
Ischemic cardiopathy is treated by slowing the development of the underlying pathological process. In severe cases, surgery is prescribed to improve coronary blood flow or a heart transplant.
Among the general drugs suitable for any form of the disease are the following:
- "Riboxin" activates metabolic processes in the heart muscle, reduces platelet aggregation and eliminates areas of ischemia.
- "Metonate" improves oxygen transport, normalizes nerve conduction and eliminates areas of ischemia.
- "Carnivit" is used to enrich heart tissue with levocarnitine. The substance will improve myocardial metabolism and slow down the development of structural changes.
ethnoscience
As a complement to the treatment regimen for cardiopathy, the use of folk remedies is allowed. They virtually have no contraindications or side effects, which is a clear advantage, especially with long-term use. The following recipes are most relevant:
- Flax seed contains a high concentration of organic acids, which can stabilize metabolic processes in cardiomyocytes. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour 40 g of the main ingredient into 1 liter of boiling water. Next, the container is placed in a water bath. After 50 minutes, you need to remove it from the stove and remove the raw materials. Drink the prepared medicine during the day, half a glass at a time.
- Viburnum is rich in essential oils, vitamins and microelements that are vital for normal heart function. Every day it is enough to take 100 g of its fruits. Making a decoction is not recommended, as the beneficial substances are partially destroyed during heat treatment. Berries are contraindicated for angina pectoris and varicose veins.
- An infusion of hare cabbage is especially useful for the dilated form of cardiopathy. It tones the body, improves tissue regeneration, relieves inflammation and strengthens the immune system. To prepare, you will need to pour 50 g of cabbage leaves into 250 ml of boiling water. Then close for 4 hours. Before use, remove the raw materials. Drink 50 ml 4 times a day.
Composition and release form
The Optisalt complex of drugs for cardiopathy and cardiomyopathy includes dietary supplements:
- Maxifam plus (1 can, 60 tablets of 500 mg). Contains essential microelements. The composition of two tablets: silicon - 20 mg, iodine - 100 mcg, chromium - 40 mcg, manganese - 1.6 mg, zinc - 9.6 mg, selenium - 60 mcg.
- Fomidan plus (1 package, 60 capsules, 420 mg each). Neutralizes free radicals, reduces the risk of developing diseases of the reproductive system, heart attack, hypertension, atherosclerosis, stroke, helps normalize blood circulation, improve the condition of blood vessels, rejuvenate the skin, prevent the appearance of cysts and neoplasms. Contains omega-3, raspberry leaf extracts, green tea, red wine, rosemary.
- Methosept plus (1 jar, 60 capsules, 300 mg each). Helps neutralize parasitic pathogens and remove toxins from the body. Ingredients: tansy, horsetail, lingonberry, cloves, yarrow, dandelion.
- Vitanorm plus (1 can, 60 capsules, 400 mg each). It is a phytosorbent that promotes the removal of toxins and products of parasitic decay from the body. Includes burdock, dandelion, alfalfa, ginger.
- Regesol (1 can, 60 tablets of 400 mg). Improves the condition of mucous membranes and skin, produces a wound-healing, anti-ulcer, anti-erosion, protective effect. Ingredients: sea buckthorn, large plantain, marsh cudweed, stinging nettle, peppermint, medicinal calendula, naked licorice, agrimony, marigold flowers.
- Bactrum (1 jar, 60 tablets of 650 mg). Biosorbent that normalizes microflora and activates detoxification. Ingredients: Jerusalem artichoke tubers of the “Extra” variety (inulin), dietary fiber (calcium alginate), vitamin E.
Release form: set of five jars and one package.
Prevention rules
To alleviate the condition, you will need to change your lifestyle. The following recommendations will help with this:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- get enough sleep (at least 7-8 hours a day);
- engage in physical therapy (without overexerting);
- follow the doctor's recommendations;
- be examined annually;
- adjust your diet.
Cardiopathy in adults occurs due to various failures and diseases that disrupt metabolic processes in the heart. If no action is taken, myocardial degeneration will begin and impulse conduction will deteriorate, which will lead to the development of arrhythmia and other complications. Gradually the changes will become irreversible. To select effective treatment methods, it is necessary to be examined and find the cause of the disease. The basis of therapy will be methods for its elimination. Additionally, you will have to use antiarrhythmic and maintenance drugs that will alleviate the condition and reduce the load on the heart. Sometimes it is necessary to perform surgery to correct congenital defects, eliminate sources of false signals, or restore conductivity.
How to deal with the manifestations of pathology?
Cardiopathy is treated by a cardiologist. To make a diagnosis, electrocardiography, echocardiography, blood tests, magnetic resonance or computed tomography, and hormone level studies are performed.
Treatment methods:
medicinal. Drugs are used to lower blood pressure, eliminate arrhythmia and tachycardia, reduce the load on the heart, and slow the progression of heart failure. Beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, antiplatelet agents, cardiac glycosides are used;- surgical – valve replacement for defects, implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator, heart transplantation;
- modification of lifestyle in the absence of specific therapy.
Features of treatment in adults
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type and causes. In case of secondary cardiopathy, the previous disease is eliminated, for example, antibiotics are prescribed for the post-infectious variant, hormonal imbalance is corrected, and metabolic processes are improved. In the primary form, therapy is aimed at compensating for heart failure, eliminating complications, and restoring myocardial function. Diet therapy and regulation of physical activity are carried out.
The prognosis is usually unfavorable: heart failure progresses, and severe, painful complications appear. The average five-year survival rate is 30%.
Correction of the condition in children and adolescents
Cardiopathy in children can be congenital (defects) or acquired (secondary and functional). Newborns are also sometimes diagnosed with this disease; the disease appears due to hypoxia.
Treatment for children and adolescents is quite effective. Drug therapy may be prescribed to prevent complications; for serious congenital defects, surgical intervention is necessary.
Functional cardiopathy, which is characterized by the appearance of complaints during physical activity, does not require specific treatment. Physiotherapy, spa treatment, and optimization of daily routine can be used.