Pregnancy changes the activity of the immune system. These changes can lead to an increased incidence of colds, especially during cold weather. The good news is that symptoms of a respiratory infection do not affect the baby in any trimester of pregnancy. But any respiratory disease can become more complicated if it is treated. That is why it is so important to take the necessary measures at the initial stage of a cold. To do this, you should choose effective cough tablets during pregnancy and know how to take them.
Safe herbs for coughs during pregnancy
Cough can be successfully treated with medicinal herbs, but not all. It is important to know the list of permitted herbs and strictly follow the dosage when preparing decoctions. Safe to take:
- Ginger root;
- Linden blossom decoction;
- Raspberry leaves;
- Sage;
- Chamomile;
- Marshmallow root (part of the Mukaltin tablets).
Taking even the safest cough medicines during pregnancy requires the approval of the supervising physician.
Forbidden herbs
List of medicinal herbs prohibited for use during pregnancy:
1. Eleutherococcus and ginseng increase overall tone, but cause overexcitation;
2. Coltsfoot and comfrey can cause fetal growth retardation;
3. Ginkgo biloba thins the blood, can promote uterine bleeding if there is a tendency;
4. St. John's wort - helps to increase pigmentation on the face, reduces the effectiveness of analgesics and anesthesia (if childbirth is resolved by cesarean section).
Echinacea is used to strengthen the immune system - as a preventive measure, and not as a remedy. You should not use alcoholic herbal tinctures or pharmaceutical cough medicines during pregnancy.
In folk medicine, herbs with abortifacient properties are often used, which relax the uterine muscles and cervix, causing premature birth. Medicinal herbs with weak effects are also unsafe for pregnant women.
Each woman has an individual body reaction to herbs. Some plants are prohibited in the form of tinctures and syrups or in herbal tea or as a primary medicine:
- Oregano (motherboard);
- Pine buds;
- Tansy;
- Elecampane;
- Barberry root;
- Plantain;
- Thyme;
- Yarrow;
- Violet dioecious.
Medicines for dry, wet, severe cough - list
Often pregnant women buy “harmless” children’s medications as an additional remedy. They contain not only mint and eucalyptus extract, but also some chemical components. You can take tinctures and cough tablets during pregnancy only in accordance with the dosage. Extracts in the form of:
- Chewing marmalade and lozenges;
- Lollipops that dissolve under the tongue;
- Potions and syrups.
Treatment of wet cough - list of drugs
- Chest collection;
- Bromhexine;
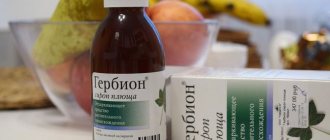
- Gerbion;
- Doctor Mom;
- Tussin";
- Flavamed;
- Ambroxol;
- Bronchipred;
- Licorice or marshmallow root syrup.
Purchasing medications through a trusted network of pharmacies does not exclude the purchase of counterfeits and drugs with unproven effectiveness. There are also insufficiently studied cough remedies that affect the fetus. Dietary supplements are classified as auxiliary products and are not a medicine; their effectiveness has not been proven.
Treatment of dry cough - list of medications
- Coldrex;
- Stoptussin;
- Bronchicum;
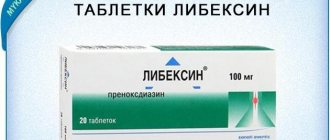
- Libexin;
- Travisil;
- Falimint.
Warm milk and honey softens a dry cough.
It is important to use all medications under medical supervision. If the cough is severe, in the second half of the term you can ask the pharmacy which cough medicine is safe during pregnancy. This is permissible only as a last resort, when it is not possible to quickly get an appointment with a doctor from remote and rural areas.
Surely, the pregnant woman will be offered a “hot” drug at the pharmacy, but it is important to go to the antenatal clinic and clarify the recommendations. Unknowingly, it is easy to buy analogue drugs, unwittingly doubling the dosage!
Hot baths are not recommended, and steaming your feet is prohibited. Even with a strong dry cough at any stage, it is not advisable to use antibiotics and the following cough medications for pregnant women:
- Codterpine (and analogues);
- Bronholitin;
- Stoptussin and Tussin plus;
- Glycodin;
- ACC and ACC Long;
- Influenza;
- Codelac;
- Pertussin;
- Ascoril;
- Alex plus;
- Joset."
Drinking against cough
Tea, tea and more tea. Black, green, herbal, most importantly – not strong and not very hot. You should always add a slice of lemon and a small amount of honey to tea for treatment: vitamins and warming are provided in this case. In addition, to warm up and strengthen the immune system, you can put ginger in tea: dry ground or in the form of fresh grated ginger.
Warm milk also relieves coughs well: according to one recipe, the drink is prepared by adding honey and soda to milk, another recipe suggests combining milk with sage. The first recipe involves adding 1 teaspoon of honey, a third of a teaspoon of butter and soda in the amount at the tip of a knife to heated milk. The drink should be drunk before going to bed and immediately go to bed. According to another recipe, put 1 tbsp in a glass of milk. spoon of sage herb, boil it all over low heat and let the drink brew for 3-4 hours. The infusion, again, is drunk in the evening, in anticipation of going to bed.
A tasty and healthy drink for a coughing pregnant woman would be a decoction of figs in milk. The healing drink is prepared as follows: 4 pieces of dried figs are poured with 500 ml of milk, and the whole thing is simmered over low heat until the milk acquires a brownish tint. The finished drink is taken 50 ml three times a day.
Another effective “anti-cough” product for pregnant women is onion. Take ½ kg of onion, 2 tbsp. spoons of honey and 400 g of granulated sugar. Pour the mixture into 1 liter of water. Place on the stove, on the burner over low heat. Keep on low heat for 30 minutes. Cool, cool. Let's strain it. We take 1 tbsp. spoon 4-6 times a day for severe cough.
Additional permitted funds
1. Topical antiseptics are used to gargle, especially after visiting places with infected people. Dissolve a few drops of eucalyptus tincture or furatsilin tablet in a glass of warm water and gargle - and that’s enough.
2. Inhalations are the most gentle method for mitigating coughing attacks, especially before bedtime. Breathe in the steam - what could be easier? Steam from potato broth or boiled alkaline mineral water are considered harmless. Drops of eucalyptus and mint are added to hot water; for other ingredients, consult a doctor.
3. Natural expectorants, such as Mucaltin, are considered relatively safe if there is no individual intolerance. It is not recommended for ulcer sufferers and diabetics.
4. Effective cough tablets: Ambroxol, indicated in the 2nd half of pregnancy. It is justified in case of complicated symptoms, with strict adherence to the dosage.
5. Syrups and mixtures are popular remedies; they are used when they don’t know what to take when coughing during pregnancy:
- Doctor MOM";
- Gedelix";
- Bronchicum";
6. Aromatherapy is used if nothing else is at hand, and also as an additional remedy. Heated essential oils will fill the room with fragrance, irrigate the upper respiratory tract, your choice of oil:
- Fir and eucalyptus;
- Lemon and orange;
- Cardamom and tea tree.
7. Herbal preparations – multicomponent herbal mixtures, extracts and tablets based on herbs. Linden and raspberry, ginger and lemon, chamomile and plantain are the most harmless medicinal plants.
8. Antibiotics. Not recommended. They are prescribed by a doctor for bronchitis, ENT diseases and pneumonia, and this is only within his competence.
Cough medications by trimester
Cough is not a disease, but its manifestation. As a rule, it occurs with the following diseases:
- Flu or acute respiratory infections;
- Pharyngitis or bronchitis;
- Laryngitis or tracheitis;
- Pneumonia or bronchial asthma.
If a woman is diagnosed with bronchitis or pneumonia, the attending physician has the right to prescribe antibiotics and strong drugs that relieve attacks. Doctors may suggest bed rest or hospitalization to monitor the patient's condition.
If taking pills is unavoidable, then it is important to know which cough medications during pregnancy are allowed to be taken in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester. Take tablets and liquid medications most carefully in the first 3 months of pregnancy, when the placental barrier is not fully formed and the formation of fetal organs is underway.
Treatment of cough in the 1st trimester
The first months are the most difficult, the body is being rebuilt, immunity is reduced, hormonal levels and blood pressure “jump”, chronic diseases make themselves felt. New sensations appear, pay maximum attention to your health.
In the first trimester the following will be useful:
- Inhalations and rubbing;
- Honey and raspberry jam;
- Natural based cough syrups.
The list of approved drugs can be found above in the text in the corresponding section.
It is important to treat any infections immediately with cough medications approved during pregnancy. You cannot relieve symptoms of diseases with analgesics and antipyretics. Under stress, a “nervous” cough also occurs. You should not “bring down” the temperature; it is important to undergo thorough treatment, as well as:
- Switch to a healthy diet of natural products as much as possible;
- Eliminate the influence of allergens;
- Do not use synthetic substances, review your first aid kit;
- Take more walks in warm clothes and shoes, improving blood circulation and oxygen supply to tissues;
- Avoid crowded places where infections are possible;
- Exercise moderately, reducing strength loads;
- Strengthen your immune system and register for pregnancy.
Attacks of prolonged coughing during pregnancy in the 1st trimester increase the tone of the uterus, blood supply complicates the nutrition of the embryo and frequent coughing, which provokes fetal hypoxia. The doctor will recommend the main cough medications that pregnant women can take, comparing the test results and the patient’s chronic diseases. Treatment is carried out comprehensively, with gentle medications, avoiding antibiotics and “chemicals”.
How to treat cough in pregnant women in the 2nd trimester
From the 12th to the 24th week, the immune barrier strengthens. Cough medications that enter the bloodstream are retained by the placenta and cause less harm to the embryo. A cold cough is not as harmful as before if there is no threat of miscarriage.
The future baby's skeleton, central and autonomic nervous systems are actively developing, so peace and positive emotions are important. But only the doctor has the right to decide what the expectant mother can take for a cough. Self-medication with tablets and mixtures and drugs containing alcohol is still undesirable. If there is no fever or coughing attacks, then at the pharmacy you can buy herbal medicines, which indicate all contraindications and doses.
During pregnancy, women do not always attend antenatal clinics, but actively use herbal (folk) cough medicines. This is a dangerous mistake. If you have any symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis. Chronic bronchitis and severe pneumonia begin with a slight cough!
How to treat cough in the 3rd trimester
A woman prepares for childbirth, filling her free time with pleasant anticipation and preparing the house for the arrival of the baby. It is important not to get carried away with work, take breaks more often and fully rest, change body position, and not sit too long in one position.
Infections can harm the fetus and the expectant mother; it is important to get tested and examined on time. The placenta “ages” and becomes permeable to certain viruses. What cough medicines to take during pregnancy in the last trimester and before childbirth can only be advised by an observing doctor. Complications are likely - breaking of water, hypoxia, placental abruption.
Therapy methods
Depending on the specific trimester, the nuances of the recovery course may vary. For example, something that can be used by a woman from the third to the sixth month of pregnancy should under no circumstances be used at first. That is why cough treatment must be considered separately.
1st trimester
It is recommended to avoid the use of mucolytics, expectorants and other drugs. In this case, it is recommended to treat a pregnant woman’s cough through inhalation or heating, and the use of vitamins. Additionally, other physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
The decision to implement drug therapy is made as a last resort - if the course of the disease turns out to be more threatening than the effect of drugs. Experts insist on the use of syrups or herbal tablets, as well as medications in which Interferon is the main component. It helps boost immunity.
2nd trimester
Treating cough during pregnancy at this stage is a little easier. This is due to the fact that the formation of the child’s internal organs and systems is complete. In this regard, infections that provoke a dry cough will not cause as much harm as in the first trimester. Given the relatively large maturity of the fetus, the range of medications is expanding.
At high temperatures, Coldrex Knight is used.
Bronchicum, Falimint and Gedelix are prescribed with caution for treatment.
3rd trimester
Perhaps the most unfortunate period for the appearance of a cold and, in particular, a cough. This can be fraught with undesirable consequences, including premature birth.
In this regard, treatment of cough during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester should be carried out as follows:
- allowed to take Bronchipret, Mucaltin, Doctor Mom lozenges;
- in the most difficult cases, synthetic compounds are used, for example, Ambrobene or Stoptussin;
- Certain medications should never be taken - ACC (tablets), Codelac, thermopsis herb.
It is unacceptable to use Ascoril (in the form), Travisil, Bronholitin. Self-treatment at any time can cause much more harm than good.
Why is coughing dangerous during pregnancy?
- Treatment of cough with safe medications during pregnancy should begin immediately at the first symptoms. Severe, prolonged attacks strain the abdominal muscles, which is extremely undesirable.
- There is also a possibility of complications and premature birth.
- Untreated viruses lead to chronic lesions in the respiratory tract. Patients often complain of loss of strength.
- Severe attacks create excessive shock to the abdominal cavity, deteriorate fetal nutrition and hypoxia.
- Pregnant women may vomit due to muscle strain.
Severe coughing attacks are dangerous, even if the pregnant woman thinks that everything is fine and she does not attach much importance to them. Conversely, some suspicious patients abuse medications, even knowing about their predisposition to miscarriages.
Causes and signs of nonproductive cough in pregnant women
A dry, or non-productive, cough accompanies many acute respiratory diseases. The causative agents of acute respiratory infections are pneumotropic viruses and bacteria, which are infected by airborne droplets.
Viral diseases are detected in 85% of women during gestation, and bacterial diseases in 15%.
The most common cold pathogens:
- enteroviruses;
- staphylococci;
- reoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- streptococci;
- coronaviruses;
- rhinoviruses, etc.
With a dry cough, sputum is not produced. When coughing, a burning sensation occurs in the throat. I am concerned about chest pain, dry mucous membranes and soreness.
A decrease in general immunity and hyperventilation of the lungs are factors that provoke acute respiratory infections in pregnant women.
Preventive measures
Avoid:
- Visiting crowded places during influenza epidemics;
- Long-distance travel and relocations;
- Changes in climate zones;
- Overheating and hypothermia;
- Overstrain and overwork.
Coughing, as a reflex clearing of the respiratory tract from mucous foci of a cold infection, is not so harmful. But, as a concomitant symptom of a virus or cold, provoking spasms of the abdominal muscles, it is undesirable during pregnancy. The fewer chemical components and medications enter the bloodstream, the better for the unborn baby.
How to protect yourself from infections and viruses
A pregnant woman in the 2nd trimester needs to avoid crowded places, ventilate the room more often, and take a daily walk in the fresh air. There is no need to treat a cough if you adhere to basic rules of personal hygiene and eat a healthy, balanced diet. During seasonal epidemics of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, you can lubricate the nasal passages with oxolinic ointment and periodically gargle with herbal decoctions.
Kovalchuk Irina Timofeevna
37 years of experience
Pulmonologist of the highest category. Engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory tract pathologies. Accepts patients with chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchial asthma, and occupational respiratory diseases.