The causative agent of chickenpox belongs to the ubiquitous but small family of herpes viruses. All members of the family cause skin lesions in herpes simplex and genital, cytomegalovirus infection and herpes zoster. All of them, and chicken pox is no exception, begin penetration from the mucous membranes, and then hide in the nervous tissue for the rest of a person’s life, coming to the surface in the form of herpetic eruptions.
Our expert in this field:
Nagibina Margarita Vasilievna
Infectious disease doctor, MD
Call the doctor
Causes of chickenpox in adults
Chickenpox in both children and adults develops after contact with a carrier of the herpes simplex virus type 3. This virus is the main cause of the disease.
To avoid infection and not provoke it in another person, you must:
- Cover your mouth and nose when sneezing and coughing;
- Avoid places with large crowds of people;
- Periodically ventilate and wet clean the room;
- Observe personal hygiene rules - wash your hands and face with soap after visiting public places.
The virus does not live outside the body, so you can only become infected through close and direct contact with a carrier. The source of the disease can also be a person who has had herpes zoster.
Vaccines
The chickenpox vaccines currently available on the market are produced using the so-called Oka VZV strain, which has been modified through sequential propagation in different cell cultures. Various formulations of such live, attenuated vaccines have undergone rigorous testing and have been approved for use in Japan, the Republic of Korea, the USA, and several European countries. Some vaccines are approved for use at ages 9 months and older.
From a logistical and epidemiological point of view, the optimal age for chickenpox vaccination is 12-24 months. In Japan and several other countries, one dose of vaccine is considered sufficient, regardless of age. In the United States, 2 doses of the vaccine given 4-8 weeks apart are recommended for adolescents and adults, of whom 78% seroconverted after the first dose and 99% after the second dose.
According to the current US vaccination schedule, children receive 2 doses of the vaccine (1st dose at 12 months, 2nd at 6 years).
More about vaccines
Features of the disease in adults
Chickenpox affects both men and women with equal frequency. At the same time, the nature of the course of the disease may differ significantly from what children experience.
In the process of studying chickenpox in adults, the following features of its course were identified:
- The disease is more difficult to tolerate;
- There is a well-defined intoxication of the body;
- The temperature rises to 39 degrees and above;
- The rash appears only on the 3-4th day and covers the entire skin;
- In some cases, the rash is complicated by a bacterial infection, and suppuration is observed;
- In place of the bubbles with liquid, scars (pockmarks) remain;
- Life-threatening complications develop in a third of patients;
- Exclusively airborne transmission route;
- Dangerous bodies remain in the body even after the symptoms of the disease disappear (it is better to avoid contact with recently ill people, they are carriers);
- There are no effective methods of protection.
How the disease progresses in an adult depends on the immune system. A weakened immune system will not be able to resist the virus; the risk of infection in this case is at least 90%.
It is especially dangerous for people over 50 years of age who have never had it before.
Cause of infection: how is the disease transmitted from person to person?
It is unlikely that chickenpox can be caused by contact transmission - through touching a patient. But the viral particle is perfectly transmitted by airborne droplets using an aerosol, which is formed in the air from tiny droplets of saliva when a sick person coughs and talks.
Living infectious agents float in the smallest droplets of saliva; it is believed that the infection spreads through the ventilation system in the same way, because all it takes is one sick person in an apartment building, and all the residents who do not have immunity will get sick.
If a disease occurs, you must immediately contact a specialist who can see you seven days a week and on holidays at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. Early initiation of therapy will avoid irreparable consequences.
First signs
Before the appearance of pronounced signs of chickenpox in adults, their health sharply deteriorates.
If we talk about the already known signs of this disease, then these are:
- High fever;
- Weakness;
- Lack of appetite;
- Strong headache.
- Rashes on the body;
- Temperature increase.
The appearance of such symptoms is preceded by a long incubation period, during which the patient does not suspect that he has the disease, but is an active carrier of it.
Which doctor treats chickenpox?
If your child develops symptoms of chickenpox, you should contact your pediatrician. If the disease develops in an adult, then a consultation with a therapist is required, who will refer you to an infectious disease specialist.
Author of the article:
Danilova Tatyana Vyacheslavovna |
Infectious disease specialist Education: in 2008, received a diploma in the specialty “General Medicine (Therapeutic and Preventive Care)” at the Russian Research Medical University named after N. I. Pirogov. I immediately completed an internship and received a diploma as a therapist. Our authors
Symptoms of chickenpox in an adult
There are the following stages of development of chickenpox, each of which exhibits its own symptoms:
- Incubation - the virus is localized in the cells of the nasopharynx without detecting itself;
- Prodromal - the virus enters the blood, after which the state of health noticeably worsens. Weakness, pain in muscles and head are observed. Body temperature is high, there is no appetite;
- Active - the virus infects the epidermis, causing a rash to appear on the skin. The body itches, the temperature is very high and it is difficult to bring it down. The rash covers the entire body, including the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and scalp. Small pimples are filled with fluid;
- The crust formation stage is the last stage of disease development. Pimples dry out, antibodies appear in the body and actively spread throughout it. The patient is recovering.
Stages of change in rashes
Features of a typical shape
The typical course of the disease is always accompanied by the appearance of a rash. At the initial stages, the rash appears as multiple pinpoint redness.
Over time, small bubbles filled with clear liquid form in their place. After recovery, they completely resolve and do not leave pigmentation or scars in their place.
In addition to skin manifestations, chickenpox is characterized by general symptoms. Most patients note an increase in body temperature to 38 degrees. In severe cases, this figure may be higher.
Incubation period and infectiousness in adults
During the incubation period, the chickenpox virus remains in the body from 10 to 21 days. At the same time, in adults, symptoms are absent for a longer period of time, and in children they appear faster.
On average, the incubation period for adults is 16-17 days and is divided into:
- Onset - time from infection to complete adaptation of the virus);
- Development - the virus multiplies, its pathogen accumulates in the body, which leads to the formation of a primary focus of infection;
- Completion - the virus spreads throughout the body, the production of antibodies begins to counteract it, and signs of illness appear.
The incubation period is quite long, making it almost impossible to determine the source of infection. The threat of infecting other people persists for 11-13 days, until the last trace of the rash disappears from the skin.
How does the infection usually progress?
Mild course with a few rashes, normal temperature or briefly rising to 38°C, blisters disappear within 3 days.
During a moderate infection with a temperature of up to 39°C, abundant skin formations disappear within 5 days.
Severe chickenpox is observed in patients weakened by chronic diseases; a fresh rash lasts for almost a week; the condition is severe with severe symptoms of intoxication.
If your condition worsens, you must immediately contact an infectious disease specialist, who provides consultations seven days a week and seven days a week at the Medicine 24/7 clinic. Registration is carried out 24 hours a day by telephone. Early initiation of special therapy will avoid irreparable consequences.
Immunity to chickenpox and re-infection
Despite the extreme degree of contagiousness, adults rarely get chickenpox. The reason lies in their developed immunity, which appears in case of infection with the disease in childhood.
If this does not happen, then there is no immunity. Accordingly, the person is included in the risk group of potential patients. The emergence of immunity is observed in 95% of the world's population, but there are exceptions.
So, if a carrier of the virus in one of the stages comes into contact with a person who has previously had chickenpox, but is currently experiencing serious health problems, then infection will still occur.
Those at risk for re-infection with chickenpox are:
- People experiencing severe stress and psycho-emotional pressure;
- People suffering from various types of neurotic disorders;
- People who have a basic inability of the body to produce memory cells.
In some cases, re-infection occurs when the body weakens:
- during the activation of peptic ulcer disease;
- for diabetes mellitus;
- for problems with the functioning of the endocrine system:
- for autoimmune diseases, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- for rheumatoid arthritis.
Re-infection is a rare occurrence, but medicine knows cases where a person had chickenpox 3 or even 4 times in his life.
The story of the “victory” over smallpox
Descriptions of cases of smallpox have reached our time from ancient Egyptian wall paintings and Avicenna’s treatises, but the black smallpox epidemic was first documented in China (IV century AD), then in Korea (VI century). Subsequently, with trade caravans and conquests (such as those of Alexander the Great and Arab conquerors), smallpox spread throughout Europe, and by the 15th century the entire territory of European states from Spain to India was a reservoir of smallpox infection.
In the world
It is believed that every year smallpox epidemics claimed the lives of more than one and a half million European citizens, and the number of those whom the smallpox epidemic left disfigured (especially women who suffered from pockmarks on their faces after the disease) cannot even be roughly calculated. With the introduction into practice of the variolation procedure (rubbing the infected contents of rash elements into the skin from a sick person to a healthy person), the number of deaths annually decreased, but only slightly, since this procedure often resulted in a new outbreak of smallpox. A more progressive step was vaccination against smallpox, first used in the middle of the 18th century in England by Jestley, and in Germany by Plett.
Vaccination meant the deliberate infection of a healthy person with the cowpox virus, as a result of which the person who recovered from this disease, which was not dangerous to humans, received immunity to smallpox. Edward Jenner discovered this phenomenon at the same time as other scientists, but was able to defend his arguments in favor of vaccination before the English government, and from 1800 the vaccination procedure became mandatory for military personnel, and later for ordinary residents.
Smallpox in Russia
In Russia, smallpox was also known and until the 18th century it was an absolutely fatal disease; under Empress Catherine II, widespread use of variolation began, and somewhat later - vaccination against smallpox. Vaccination was not mandatory before the revolution, and therefore outbreaks of smallpox were recorded annually.
After the 1917 revolution, compulsory vaccination of the entire population was introduced, and by 1936 smallpox was eradicated from the USSR. The last outbreak in our country occurred in the late 50s, and in the world - in 1977, and since that time smallpox has been recognized as eliminated. On Earth, the smallpox virus remained only in research laboratories in Russia and the USA.
Classification of chickenpox in adults
Chickenpox is classified according to:
- The severity of the current;
- A type of illness.
If a disease is considered by whether the body tolerates it hard or easily, then the following are distinguished:
- Mild form - recorded in approximately 7-11% of cases. The temperature is low and almost never exceeds 38 degrees. Patients have no complaints of severe pain and fatigue, the number of rashes is minimal;
- The moderate form is typical for 80% of patients. The temperature rises to 39 degrees and does not drop below 38 for a long time. Signs of intoxication such as nausea, vomiting, weakness, and headache are observed. Joints and muscles ache, a rash covers most of the body, the skin itches;
- Severe form - diagnosed in only 10% of patients. At the same time, the temperature rises above 39 and 40 degrees. The patient complains of weakness, severe headache, nausea and vomiting do not stop. The rash covers all free areas of the skin, complications may develop.
Mild form Moderate form Severe form
Severe form of the disease is divided into:
- Hemorrhagic - affects patients with an insufficiently strong immune system, who have previously encountered hemorrhagic diseases, problems with blood vessels, diathesis, vasculitis, thrombocytopathy and bleeding disorders. A hemorrhagic rash, hematomas and bruises appear on the skin. The gums and intestines may begin to bleed;
- Bullous - the skin is covered with large flabby blisters - bullae. Each bubble is filled with cloudy liquid and covered with folds. At the site of the burst bubble, long-lasting wounds remain;
- Gangrenous - develops in patients with extreme exhaustion. The reason is lack of personal hygiene and poor care. The papules become infected and are joined by a secondary pathogenic microorganism. This leads to the formation of a black border of dead tissue cells around the papules. The patient has a high fever, the body signals about poisoning.
The typical form of the disease is characterized by similar symptoms:
The atypical form can also develop in different variations:
- Rudimentary;
- Gangrenous;
- Bullous;
- Hemorrhagic.
In the rudimentary form, the temperature rises no higher than 37.5 degrees, there is practically no rash, and acne has the form of spots or nodules. For those who are not aware of the symptoms of the disease in adults, chickenpox in its rudimentary form can go completely unnoticed.
How long does chickenpox last?
Typically, chickenpox in adults lasts no more than 2 weeks. Approximately 10-11 days after the first pimples appear, they wrinkle and shrink.
The liquid gradually leaves them, a crust appears, which soon begins to crumble. Pink circles remain at the site of acne, which negatively respond to exposure to high and low temperatures.
If a complication occurs, the duration of the disease doubles or even triples. Treatment may take from 1.5 to 2 months.
Diagnosis of chickenpox in an adult
Diagnosing chickenpox is not difficult. A good therapist is quite capable of making the correct diagnosis. To do this, it is enough for him to visually examine the patient and question him about the deterioration of his health.
During the preliminary examination, the following are examined and listened to:
- Bronchi;
- Lungs;
- Stomach;
- Liver.
If any doubts arise about the nature of the disease and the factors provoking it, the patient is referred for additional examination and laboratory tests.
Adults suspected of having chickenpox should obtain test results:
- blood (general);
- urine (general);
- contents of blisters, ulcers, crusts, mucus from the oral cavity.
It is not difficult to detect chickenpox, even if its symptoms are masked by signs of other diseases. The disease is detected even by simply examining the rash at close range.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of smallpox involves taking into account the clinical manifestations characteristic of the disease (in particular, we are talking about a rash), which are used for subsequent clinical studies. Thus, diagnosing the disease is based on analyzing the contents of the formed skin elements in one or another stage (vesicle, pustule, vesicle, crust), blood and a smear of mucus taken from the oral cavity are also examined. The presence of smallpox virus in the samples taken is determined by microprecipitation, PCR, and electron microscopy. A preliminary result is obtained within 24 hours; through further, more thorough research of the samples, the virus is already isolated and identified.
Features of treatment and indications for hospitalization
Chickenpox is treated on an outpatient basis, in other words, at home. In this case, the doctor is obliged to carry out explanatory work with the patient about how to behave during illness.
For example, if a patient does not comply with bed rest and personal hygiene, he can aggravate his situation and provoke the development of complications.
Hospitalization for chickenpox is carried out if the following indications are present:
- The appearance of complications;
- The disease is severe;
- The patient does not have the opportunity to isolate himself from healthy people.
In the latter case, the treatment methods used in the hospital are no different from those that the doctor recommends to use at home.
In most cases, a disease such as chicken pox is treated with minimal use of medications, but sometimes synthetic drugs cannot be avoided.
Antiviral drugs
Antiviral agents have a negative effect on the DNA of the virus and slow down the spread of the disease. Prescribed individually, the chosen dose of the drug depends on the form of the disease and the ability of the immune system to protect.
The most effective are:
- Acyclovir - taken orally four times a day in an amount of 800 mg for a week or intravenously at 10 mg per kg of body weight for every 8 hours. The course of treatment is up to 10 days. The cost ranges from 130 to 160 rubles ;
- Famciclovir - take 500 mg three times a day for 7-10 days. The cost of the drug is from 1100 rubles ;
- Valaciclovir - taken 1 mg three times a day for 10 days, average cost 380 rubles .
Acyclovir Famciclovir Valaciclovir
Antihistamines
Aimed at reducing allergic rashes and vascular permeability. After taking them, the nervous system calms down, sleep improves, and itching practically disappears.
The following drugs affect the body in the manner described above:
- Tavegil - tablets are taken twice a day for normal itching and four times for severe itching. Average price 190 rubles ;
- Suprastin - take up to 4 tablets per day, and treatment continues until crusts appear. Average price 130 rubles ;
- Cetrin - you should take one 10 mg tablet per day, either at one time or dividing the dose into two doses, with a glass of clean water. Average price 180 rubles .
Tavegil Suprastin Cetrin
Medications to reduce high fever
Use only when the temperature rises to 38.5 degrees or higher. Aimed at normalizing temperature and slowing down inflammation.
Most often, patients are prescribed:
- Panadol - to reduce the temperature, it is enough to take 1 tablet three times a day, preferably after eating. Average price 60 rubles ;
- Ibuprofen - to achieve a therapeutic effect, take 2 tablets 3-4 times a day. Average price 50 rubles .
Panadol Ibuprofen
Antibiotics
They are used in exceptional cases, mainly when the patient has purulent formations and pustules. Antibiotics can stop the development of infection and acne.
The greatest effect is achieved by:
- Oxacillin - administered intravenously, 1 g four times a day for 7 days. The average price for one bottle is 10 rubles ;
- Cefazolin is an antibiotic intended for intramuscular administration, used three times a day for a week. The average price for one bottle is 25 rubles ;
- Augmentin - taken orally in the amount of 2 tablets per day, with a course of treatment of up to 5 days. Average price 340 rubles ;
- Amoxiclav - taken orally before or after meals; to increase the effectiveness of treatment, you must take 2 tablets per day for 1 week. Average price 210 rubles .
Oxacillin Cefazolin Augmentin Amoxiclav
Drugs to remove harmful toxins from the body
Most often these are solutions intended for intravenous administration into the body. They are able to reduce the amount of harmful toxins, speed up their elimination, and have a beneficial effect on blood circulation. Prescribed to patients with severe forms of chickenpox.
A quick therapeutic effect can be achieved with the help of:
- Glucose 5% - the solution is administered by drip into a vein in the amount of 1000-1500 ml per day. The average price per bottle is 30 rubles ;
- Reopolyglucin - 1000 ml of the substance is injected into a vein every day until the end of treatment. The average price is from 60 rubles per bottle.
Glucose 5% Reopoliglucin
Specific immunoglobulin
Designed to fight the virus in question.
It is isolated from blood with antibodies already present in it.
When it enters the blood of a sick person, immunoglobulin binds the pathogen, which promotes a speedy recovery.
Zostevir enjoys the greatest confidence among specialists.
It is administered intramuscularly once a day in an amount of 1.5-3 ml, depending on the severity of the disease.
Average cost from 500 rubles .
Products for treating rashes
Pimples that appear on the body begin to itch. Under no circumstances should you scratch them; scars may remain.
To get rid of itching, you can use one of the following medications:
- Calamine - contains zinc oxide. Sold in lotion form, it is used to relieve itching, protect the body from bacteria and relieve swelling. Average price 680 rubles ;
- Acyclovir ointment is used to treat all types of herpes. Prescribed in the presence of complications, the treatment of which requires the use of antiviral drugs, topical application. Average price 25 rubles ;
- Rivanol, Fukortsin are analogues of brilliant green and have an antimicrobial effect. The preparations do not dry out the skin, do not stain clothes, and are washed off with water. Applying them to pimples avoids the risk of developing purulent inflammation. The average price of Rivanol solution is 140 rubles , Fukortsin - 60 rubles ;
- Solcoseryl - protects tissue damaged around pimples from pathogenic microbes entering them. The average cost is 310 rubles .
It is not recommended to treat pimples with brilliant green; the solution dries out the skin and causes scars to form at the site of the rash, which is not very pleasant, especially when it comes to visible areas of the skin.
In most cases, drug treatment comes down to taking antipyretics and broad-spectrum antibiotics.
The use of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs can have unpleasant consequences for the body. To avoid them, you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations without trying to treat the disease yourself.
Treatment of chickenpox
Hospitalization of a patient with an uncomplicated infection is not required. It is important to direct efforts to prevent the development of severe consequences of the disease. It is necessary to follow the rules for caring for skin rashes, which are aimed at preventing bacterial flora from entering open defects.
If the disease is accompanied by high body temperature, a person suffers from severe headaches, or has breathing problems, then it is necessary to call an ambulance and go to a hospital for treatment.
Treatment of chickenpox comes down to the following measures:
- Maintain bed rest for a week.
- Dieting. The emphasis should be on dairy products, plant foods, and fortified dishes. It is necessary to remove spicy, salty, and pickled foods from the menu; it is recommended to give up citrus fruits. The fact is that rashes can appear not only on the skin, but also in the mouth, and eating foods containing acids can cause irritation of the mucous membranes.
- It is necessary to drink enough water.
- Bed linen needs to be changed more often than usual. The same applies to underwear. It is recommended to iron the laundry after washing.
- After eating you need to rinse your mouth.
The crusts that cover the elements of the rash are prohibited from being peeled off. This makes the wound more likely to get infected. In addition, a noticeable scar remains at the site of damage. To avoid accidentally tearing off the crust, you need to trim your nails short and wash your hands often. Young children should wear cotton gloves. This will reduce the likelihood of damage to the elements of the rash during sleep.
Chickenpox is not a reason to keep your child bedridden. However, you need to make sure that he does not engage in active and outdoor games. When the body temperature has stabilized and all elements of the rash have crusted over, you can go outside. The decision on the possibility of visiting educational institutions is made by the doctor.
Rash care
If the crust has been torn off and an infection has entered the wound, then an ointment with an antibacterial effect must be applied to the affected area.
External agents with analgesic components are applied to the itchy elements of the rash, which are located in the area of the external genitalia.
The skin will not itch too much if you wipe it with boiled water and vinegar and then sprinkle it with talcum powder.
To make the blistering rash dry out faster, it is recommended to lubricate it with potassium permanganate at a concentration of 10%, or brilliant green. You can also use the drug Delaxin.
If the body temperature rises above 38 °C, then it should be reduced by taking Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
It is allowed to take a bath with potassium permanganate crystals dissolved in it. When the elements of the rash have dried, you can take a bath with plain water, but you should not make it too hot.
Medicines
Drugs that can be used to treat chickenpox:
- Interferon.
- Acyclovir Hexal.
- Viru-merz Serol.
- Hyporamine.
- Psilo-balm.
- Epigen intimate.
- Delaxin.
If the skin is very itchy, you can take Suprastin.
For chickenpox and any other diseases accompanied by high body temperature, children should not be given Aspirin. This drug can cause a dangerous complication called Reye's syndrome. It poses a threat to the child's life.
Acyclovir should not be used to treat pregnant women, as it has mutagenic properties.
If bacterial complications develop against the background of chickenpox, the patient will need to take antibiotics. Their selection should be done by a doctor.
Although medicine has made significant strides in recent years, it is difficult to control the herpes virus that causes chickenpox by any means. Once it penetrates the cells of the human body, it is problematic to influence it, so there are not many drugs to treat this disease. Almost all of them come down to relieving the symptoms of the disease.
If your body temperature with chickenpox does not decrease 4 days after the first rash appears, you should consult a doctor.
Recommendations for treatment
For a speedy recovery you need:
- Maintain bed rest for at least the first 5-6 days after the disease is detected (preferably for the entire 2 weeks while the disease lasts);
- Do not overheat, sweat will only increase the itching and increase the risk of pustules forming;
- Change underwear and bedding every day;
- Drink more water up to 2.5 liters per day;
- Wash your hands with soap;
- Cut your nails short to avoid the risk of scratching a pimple while you sleep;
- Apply a cold compress of baking soda and water to the affected areas, 1 tsp. per glass;
- Add soda to bathing water;
- Observe the temperature of the water;
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with soda, furatsilin solution or decoctions of chamomile, calendula and sage.
If the rash appears in the genital area, then you need to wash yourself daily with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. This will help dry out the pimples and provide the necessary disinfection.
It is not recommended to treat pimples on the mucous membranes, since the skin in these places is very delicate, it can be easily damaged and thereby aggravate the situation.
Where can chickenpox rash appear?
First on the torso and limbs, but not on the palms and feet, and then on the face and head. It also happens in the mouth, causing pain when chewing and salivation; the blisters easily open, forming erosions that heal in 3 days. Blisters also appear on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Papules also grow in the eye and are tolerated quite easily; the vesicle quickly opens, forming an ulcer that goes away without a trace in a couple of days.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic conducts examinations using high-precision equipment, which allows you to quickly make a correct diagnosis and begin treatment without delay.
Diet for chickenpox
Chickenpox in adults does not occur without high fever and intoxication. Being in a weakened state, a person may not feel hungry, but he still needs to eat.
Experts recommend following a special diet during illness that allows you to get maximum nutrients with a minimum number of meals.
Useful for chickenpox:
- Meat or fish broth (not fatty);
- Cutlets or meatballs (steamed);
- Pureed soups;
- Vegetable purees;
- Dairy products;
- Cottage cheese and sour cream;
- Eggs (omelet);
- Juices, fruits and berries;
- Tea with lemon;
- Rosehip decoctions.
They return to regular foods only after complete restoration of the oral mucosa and normalization of temperature.
When following a diet, special attention is paid to the drinking regime. As mentioned above, you need to drink a lot of water, both in its pure form and in the form of decoction, juice, compote.
Traditional methods of treating chickenpox
It is not possible to get rid of the chickenpox virus using folk remedies alone. Baths and decoctions of medicinal herbs are intended only to increase the resistance of the immune system and partially get rid of itching.
To strengthen the immune system, they practice the use of various decoctions and preparations, such as:
- A collection of raspberry, anise, willow bark and linden blossom fruits . The components of the collection are mixed together in equal proportions. To prepare the medicine, 2 tablespoons of the mixture and 0.5 liters of hot water are enough. The collection is filled with water and left for half an hour. Use instead of tea for several days;
- Collecting their chamomile, string and calendula flowers . A mixture of herbs (6 tablespoons) is poured with water, allowed to boil, left for 30 minutes and taken 1 glass 3-4 times a day.
To reduce itching, the following folk remedies are used:
- A decoction of chamomile, peony, string and sage. From decoctions you can make lotions and compresses for damaged skin tissue;
- Tincture of oak bark. Treating pimples with tincture helps speed up their drying and crust formation.
To speed up skin regeneration and consolidate the antibacterial effects of other drugs, use a mummy solution. To prepare it, 10 g of the substance are dissolved in a glass of warm water and taken in the morning before eating, preferably on an empty stomach.
To quickly heal rashes and relieve itching, you need to take baths from:
- oats - you need 1 kg of oats and 5 liters of water. Boil the oats in water for 30 minutes, then strain and add to regular bath water. Oats help reduce itching and soothe the body. It is advisable to take a bath at night. If the itching is severe, you can bathe every 4 hours. At the same time, the oats are boiled anew each time;
- chamomile - for a bath you will need 100 g of flowers and 3 liters of water. Makeshift tea is boiled and added to the water prepared for bathing. It would also be a good idea to add a few drops of tea tree oil. After the bath the patient will feel much better. The itching will disappear for a while, the nervous system will calm down, and the risk of pustules will disappear. This bath can be taken daily.
Traditional treatment methods are designed to relieve symptoms, but not eliminate their source, so you cannot rely solely on such methods.
Possible complications
About 30% of adults with chickenpox develop the following complications:
- Bacterial superinfection of the skin - occurs due to the negative effects of streptococci and staphylococci, manifests itself in the form of boils, phlegmons and abscesses, and is removed surgically;
- Pneumonia - develops when the lungs are infected by a virus and bacterial infiltrates appear;
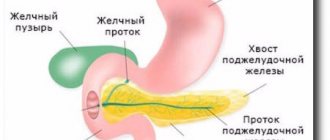
- Internal organs are affected - the liver, spleen, and pancreas are most often affected;
- The central nervous system is depressed - encephalitis may develop, sometimes balance is disturbed;
- Hepatitis - extremely rarely occurs specifically with chickenpox; it is usually recorded in patients with HIV.
Possible complications may appear immediately, or temporarily disguise themselves as an ongoing illness. Thus, the patient can learn about damage to the central nervous system no earlier than 3 weeks after infection with chickenpox, when the symptoms associated with this infection begin.
Pathological histology and anatomy
Histological changes in the skin during smallpox are as follows. The cells of the Malpighian layer appear swollen, clouded, lose their nucleus, merge into clumpy masses and, finally, undergo coagulative necrosis. This process is accompanied by sweating between the cells of the Malpighian layer, as well as hyperemia and serous saturation of the papillary layer. Further accumulation of fluid between degenerated epithelial cells leads to the formation of vesicles, initially multi-chamber, which, due to purulent melting of the septa, turn into single-chamber cavities. Simultaneously with the process of degeneration in the central part of the smallpox, a vigorous proliferation of epithelium occurs on the periphery, surrounding the central necrotic focus in the form of a shaft and leading to the formation of a depression, the so-called smallpox navel. The latter later disappears due to the increasing accumulation of pus in the pustule. If only the epidermis is captured by the suppurative process, healing occurs without scar formation, the epidermis is compensated by the growth of the epithelium from the sides and below; when suppuration penetrates into the dermis, the destroyed areas are replaced by connective tissue. During the healing stage, the contents of the pustule dry out and it turns into a crust. In the hemorrhagic form, pockmarks differ only in that blood is mixed into their contents. Hemorrhages in the skin occur due to diapedesis of red blood cells through the vascular walls.
As for pathoanatomical changes in the respiratory tract, they are present here over a considerable period. Specific rashes are noticeable not only on the nasal mucosa, larynx and trachea, but also in the large and medium bronchi. Only small bronchi are free from rash. In the lungs, foci of bronchopneumonia and often purulent pleurisy can be detected. In the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, pustules are found on the soft and hard palate, on the tonsils, in the upper esophagus and in the lower rectum. Pustules often turn into erosions, and when pockmarks merge, into extensive superficial ulcerations, often occupying the entire area of the hard and soft palate.
In the heart, liver and kidneys, parenchymal, less often fatty degeneration is determined; These changes partly depend on the action of a pyogenic infection.
In smallpox purpurea, parenchymal degeneration may be absent due to the early onset of death.
In the early stages of smallpox, small focal necrosis is sometimes found in the liver, spleen, kidneys, as well as in the bone marrow and testicles.
Consequences
The most dangerous consequences of chickenpox include:
- Weakening of the immune system and, as a consequence, loss of its ability to resist more serious viruses;
- Loss of ability to work due to problems with internal organs;
- Lethal outcome is possible if the patient develops chickenpox pneumonia, encephalitis, high fever and hepatitis.
The described consequences can be avoided if you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his recommendations.
It is not recommended to treat chickenpox on your own, as has already been mentioned several times above. Under unfavorable circumstances, chickenpox may become only the first milestone in a series of health problems.
Latest epidemics
The incidence of chickenpox is widespread in all countries of the world. In Russia, there is an annual increase in the number of diseases of this infection. From 1998 to 2007, the incidence of chickenpox increased 1.8 times annually; 500–700 thousand cases of chickenpox are registered every year.
An interesting fact: the chickenpox vaccine became available in the Russian Federation in 2009. From the end of 2013 to 2015 there was a break in the supply of vaccines to our country. According to Rospotrebnadzor, in 2015 there was an increase in the incidence of chickenpox by 16% compared to 2014.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
A pregnant woman and her unborn child face many dangers, and one of them is chickenpox.
If a woman does not know whether she has had chickenpox, then when planning a pregnancy it is better to get tested for antibodies to this virus. In most cases, they are still found.
If chickenpox does develop, then the degree of its danger depends on the period at which the pregnant woman is:
- In the first 1-10 weeks, chickenpox may cause miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. This is the most dangerous time;
- From 14 to 20 weeks, neither the woman nor the fetus is in danger. Protection is provided by both the immune system and immunoglobulins prescribed by a doctor;
- The danger to the baby reappears 1-2 days before birth and persists for the next 5 days. At this time, the baby’s contact with the virus-infected mother is limited. If this is not possible, then the child receives special treatment starting from the first day of life.
The degree of danger depends on the health of the mother:
- The risk of developing serious complications and deformities in the fetus due to chickenpox is approximately 1%;
- Compared to other diseases, this figure is insignificant , but if infection occurs a few days before birth, the child may receive a congenital disease or die;
- The risk of developing congenital chickenpox is 10-20% ; approximately the same number of babies die due to various pathologies formed under the influence of the virus.
Children with a congenital form of the disease suffer:
- From bronchopneumonia;
- Their internal organs fail.
To avoid complications arising from infection with the virus immediately before childbirth, an artificial delay of 5-7 days is practiced.
Artificially delaying childbirth does not threaten the pregnant woman in any way and allows you to protect the child from the possible development of various kinds of dangerous abnormalities.
Types of chickenpox
Chickenpox can be mild, moderate or severe. All of these forms are typical for chickenpox. If a person has a mild form of infection, then his body temperature does not rise above 38 °C, and there are few rashes on the skin. The rash is represented by single elements. It is stored no longer than 4 days.
If the patient has a moderate form of the disease, then the symptoms of intoxication increase, the body temperature rises to 38.5 ° C, there are many elements of the rash, they all itch very much. The acute period lasts for 4-5 days. After the rash stops appearing, body temperature returns to normal.
If the patient has a severe form of chickenpox, then the rashes are profuse, they appear not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. The body temperature reaches feverish values, the patient feels sick and vomits, he refuses to eat, and sleeps poorly. The rash is very itchy. The acute stage of the disease lasts about 7-9 days.
Sometimes chickenpox can have an atypical course. This infection is rare; most often it is diagnosed in children with a weakened immune system, for example, after leukemia, during treatment with steroids and cytostatics.
Chickenpox with aggravated symptoms can be of the following types:
- Generalized form (visceral or disseminated). A person's body temperature rises. She is reaching feverish levels. The intoxication of the body is severe; there are many blisters on the body. They even appear on the mucous membranes and genitals.
- Hemorrhagic form of the disease. The rashes are accompanied by subcutaneous hemorrhages, they are noticeable in the area of the mucous membranes. The patient complains of frequent nosebleeds and develops vomiting of blood. Hemorrhages into internal organs may occur.
- Gangrenous form of the disease. In addition to the rash, areas of necrosis or gangrene appear on the human skin. They are covered with a hard scab; when the crust falls off, ulcerative defects will be visible inside.
Prevention
It is very difficult to prevent the occurrence of chickenpox and this is due, first of all, to the high degree of contagiousness of the disease.
Preventive measures to combat it in adults should include:
- Vaccination - the vaccine is not administered to everyone, but only to certain groups of people whose bodies are most at risk of infection;
- Isolation of patients - those infected with the virus must remain in isolation for 2-3 weeks;
- Emergency prevention - anti-chickenpox immunoglobulin or a live vaccine is injected into the body.
The latter method of preventing infection is effective only if the live vaccine was used no later than 96 hours after contact with the patient. Ideally, use time is 48-72 hours.
If the vaccine is taken after the specified period, no positive effect can be expected. Emergency preventive measures are used most often in relation to pregnant women who have exposed themselves to the risk of infection. In this case, only immunoglobulin is introduced into the body.
Characteristics of the pathogen
The variola virus is a relatively large microorganism whose particles can be seen under a light microscope. This is exactly how it was discovered many years ago.
There are two types of virus – Variola major and Variola minor. The mortality rate from them during the years of activity varied and ranged from 20-40% and 1-3%, respectively.
Features of the microbe:
The virus has a complex structure. Its virion has an ovoid or round shape. The core, compressed on both sides by lateral bodies, contains genetic material - two strands of DNA and many protein inclusions. On the outside, the virus has a membrane with grooves. Its extracellular particles are also covered with a lipid membrane.- Due to its special structure, large size and the presence of various enzymes, the virus independently builds RNA. Small microorganisms with a normal structure do not have this ability. Having penetrated the cell, the blackpox virus immediately begins to synthesize protein compounds and multiply in the cytoplasm with the formation of inclusions.
- The virus is highly resistant to environmental conditions. It does not lose its pathogenicity during hypothermia and drying out, and easily tolerates freezing. When boiling, the microbe dies only after ten minutes, under the influence of ultraviolet rays - after six hours, in alcohol, hydrochloric acid and acetone - after half an hour. It is resistant to antibiotics and is inactivated by chloramine within an hour. At room temperature, the virus lives for about two years, and in a lyophilized state it remains viable for much longer.
Should adults get the chickenpox vaccine?
Not all children get chickenpox.
Therefore, many parents, aware of the high degree of danger of this disease in adulthood, specifically encourage their healthy children to come into contact with those who are already sick.
If this method was not used, then already in adulthood the question arises about the need to be vaccinated against the virus, its safety and effectiveness.
Whether to get vaccinated or not is everyone’s business, but experts strongly recommend that people undergo this procedure:
- Those planning an organ transplant in the next six months or a year;
- Those with a tendency to a severe course of the disease - problems with the immune system, old age;
- For those suffering from cancer;
- Those with severe chronic diseases - asthma, autoimmune disease, collagenosis, chronic liver failure;
- Those in constant contact with patients include nurses, doctors, school and kindergarten workers.
Vaccination will not interfere with the relatives of a sick child, as well as military personnel.
It is not installed in the following cases:
- During pregnancy;
- When a malignant tumor appears;
- For immunodeficiency and AIDS;
- When receiving medications that suppress the immune system;
- In case of individual intolerance to the vaccine.
Vaccination cannot give a 100% guarantee, but cases of the disease occurring precisely after vaccination are extremely rare, therefore, out of a sense of self-preservation, adults who have not had chickenpox should still, at least partially, protect themselves.