Timely detection of pathology of the heart (the central circulatory organ) and blood vessels is important and one of the most popular procedures in Russian medicine.
Almost every person has encountered pain, heaviness, a burning sensation in the chest or chest area in their life. And if these symptoms recur systematically, there is a desire, and sometimes even a need, to consult a doctor.
At an appointment with a therapist or cardiologist, the patient, after an oral interview, should receive a referral for an electrocardiogram, which will provide graphical information about the work of the central circulatory organ.
Nerve impulses that coordinate the work of the heart muscle are captured and read by the device in the form of electronic signals, then reflected in the form of teeth of different sizes on a paper tape. The therapist will help you understand what the cardiogram shows.
After analyzing the results of the study, he will draw conclusions either about the presence of any abnormalities in the functioning of the heart, or he will reassure the patient, saying that he has normal test results, everything is fine with his heart and there is no reason to worry.
If the doctor finds a deviation from the norm on the cardiogram, then additional diagnostics are carried out. In this case, an ECHO CS - an echocardiogram of the heart - is required.
This type of diagnosis has several other names (echo ecg, cardiac echography, echocardiogram, echocardioscopy), but the essence of the study is always the same.
Trying to understand cardiac ultrasound on your own and interpreting the results and making a diagnosis is not recommended.
The essence of the technique and what it shows
As already mentioned, cardiac ECHO is a modification of standard ultrasound of internal organs. However, unlike other methods that are similar in meaning, the cardiography apparatus can operate in several modes.
For example, duplex scanning is available to a diagnostician. Doppler ultrasound is used, among other things, to examine the speed of blood flow. Its quality. This is important when diagnosing, for example, ischemic disease, assessing the condition of an organ after a heart attack.
Like other ultrasounds, echocardiography is completely safe.
What does ECHO show as part of a routine examination:
- Mass, the amount of muscle tissue in the area of the left ventricle of the heart. As a rule, it changes with a prolonged increase in pressure. Untreated hypertension is especially dangerous.
- An echogram of the heart will show the intensity of blood movement through the pulmonary artery. This vessel is one of the largest. Any violation is fraught with immediate complications. Up to and including death. Especially the increase in local pressure.
- Stroke volume. The amount of blood that the heart throws into the aorta and “drives” in a large circle. Many defects change these indicators, so deviations are quite informative.
- Condition of the left atrium.
- Wall thickness.
- Echocardiography of the heart shows even the slightest changes in cardiac structures: the position of the myocardium, heart valves (tricuspid, mitral, etc.) at the moment of contraction and return to a calm state. This indicator is defined as end systolic and diastolic volumes.
- General position of the heart. Its dimensions, anatomical location. Including regarding other organs of the chest.
The technique shows the morphological features of cardiac structures.
How does an ECG differ from an EchoCG?
Patients often wonder what is the difference between an electrocardiogram and an echocardiogram? Both methods help diagnose cardiovascular pathologies, but are carried out according to different principles.
An ECG is a method during which special sensors are attached to a person’s chest to record the electrical impulses of the heart. The sensors convert the signals into a complex curve, from which the specialist evaluates the main indicators of the functioning of the organ.
EchoCG differs in that the examination uses high-frequency ultrasound waves, which penetrate into the tissues of the organ and are reflected by it. This makes it possible to see the picture on the monitor in real time. An electrocardiogram provides information about the electrical conductivity of the heart, calculates the heart rhythm and its electrical axis.
An echocardiogram determines the direction and speed of blood flow, helps to see the condition of the arteries and valves, the thickness of the myocardium and the size of the ventricles.
Important! ECG and EchoCG are widely applicable diagnostic techniques that are often used in combination with each other.
What diseases can be detected
Based on the results of echocardiography, specialists make several diagnoses.
Arterial hypertension
This process can be identified indirectly. We are talking about a stable and regular increase in pressure in the vascular bed. If we talk about a full diagnosis, the condition should be called hypertension.
The long course of the pathological process leads to organic changes in the heart - the left ventricle is transformed. The muscle layer at the level of this chamber becomes thicker.
Read more about left ventricular hypertrophy in this article.
This is a kind of compensatory mechanism. This way, the cardiac structures can pump blood with greater force. The intensity of each blow increases. This is not normal, but an understandable phenomenon.
The longer the pathology exists, the worse the situation becomes. Possible cardiomegaly. Excessive growth of a muscular organ. Then they will not be able to perform their functions.
Heart defects
Both congenital and acquired. Mainly those that affect the valves - aortic, mitral, tricuspid, less often the septum between the chambers.
Such conditions are extremely dangerous. Because without treatment early on they lead to generalized dysfunction and circulatory disorders. And this is a direct path to death from heart failure or heart attack. Therefore, immediately after detection, the issue of treatment is decided.
Some congenital anomalies are classified as defects very conditionally. For example, an open oval window. In this case, they usually do nothing. They simply observe the patient from time to time, every year.
Thromboembolism
Dangerous disorder. Its essence is the blockage of large vessels with blood clots. A cardiac echo is a method that allows you to see blood clots in the pulmonary artery and coronary vessels. Thanks to this, you can receive treatment in a timely manner. The patient will remain alive.
Read more about the types of thromboembolism here; blockage of the pulmonary artery, possible risks and treatment methods are described here.
IHD in the form of angina pectoris
Classic situation: disturbance of trophism (nutrition) of the heart and its tissues. Accompanied by severe chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea and other symptoms. It's not a heart attack yet, but it's not that far off. One step left.
Unstable angina is especially dangerous. It proceeds unpredictably, so no one can say in advance how the process will end during the next attack.
An echocardiogram gives a picture in which areas of dystrophy are clearly visible, and areas where blood flow is impaired will be detected by echocardiography with Doppler analysis.
Symptoms of an angina attack and methods for correcting the condition are described in this article.
Actually a heart attack
Emergency condition. When it happens to a patient, there is little time for diagnosis. Usually the fact is stated after the initial treatment measures.
The chances of recovery depend on how quickly therapy is started. Through ECHO Kg, a focus of necrosis (death of cardiac structures) is noticeable. The smaller it is, the easier the treatment will be.
Heart sclerosis
Consequence of heart attack, inflammatory processes in cardiac structures. This is a condition in which certain areas of the myocardium become scarred.
Connective tissue of this kind is unable to contract or stretch. Therefore, part of the organ falls out of work.
The condition is dangerous because it provokes further worsening of dystrophy and problems with the nutrition of the heart. Lifelong treatment is required. Echocardiography shows both the focus of cardisclerosis itself and the degree of impairment.
Tumors
Neoplastic processes in a muscle organ, oddly enough, are quite rare. However, they pose a huge danger.
There are two reasons:
- The first is that even benign formations (for example, myxoma), having reached a size of more than 1 cm, compress and squeeze the heart. Hence the violation of the shape of the organ, dysfunction, and insufficient nutrition.
- Secondly, if the tumor is malignant, it grows through the muscle tissue. Which means it destroys them. Compression is also present, the harm is double.
Treatment is urgent, surgical.
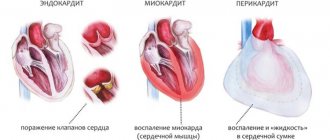
Pericarditis
Inflammatory process. Provocateur - pyogenic flora and other agents. As a rule, streptococci or staphylococci are to blame. Rarely seen.
A special case is the accumulation of fluid in the pericardium - hydropericardium. If the pericardial sac fills with effusion and blood, local pressure increases. As soon as the indicator becomes equal to that inside the chambers of the muscular organ, cardiac arrest occurs. Therefore, the condition is classified as urgent.
Myocarditis
Inflammatory disease of the heart itself. Accompanied by severe pain. When scanning, foci of changes are noticeable. If not treated in time, consequences will occur like a heart attack. Perhaps even harder.
Cardiomyopathy
A typical pathological process for those who engage in intense physical labor. For example, for athletes. Alcoholics and heavy smokers are at increased risk.
The essence of the process is a change in the myocardium: the muscle layer grows, becomes excessively large, or stretches.
This is not normal and requires therapy. As a rule, medicinal. Plus lifestyle corrections.
Read more about the types of cardimopathy and treatment methods in this article.
Rhythm disturbance
Various. From atrial fibrillation to paroxysmal tachycardia. Echocardiography alone is unlikely to help here. To identify functional disorders, an ECG will also be required.
Changes in the anatomical position of the heart
For example, mirror (dextrocardia). It can be a defect or a natural and completely normal phenomenon.
Approximately such diagnoses can be made or confirmed based on the results of echography. In addition, other examinations are also needed. ECG, stress tests, bicycle ergometry, monitoring, etc.
Indications and contraindications
Since the technique is universal, there are quite a lot of reasons for ECHO CG.
- Chest pain of unknown origin. The patient is not always right in assessing his well-being. Discomfort occurs with stomach diseases, intercostal neuralgia and other conditions. The pain is successfully masked. But it is necessary to check the position of the muscle organ.
Read about how to understand that it is the heart that hurts and distinguish heart pain from others.
- Systematic increase in blood pressure. Hypertension does not happen out of the blue. Secondary forms are caused by kidney disease and hormonal dysfunction. And the primary ones develop in pathologies of cardiac structures. Therefore, you need to check the culprit using an ultrasound technique.
- Heart rhythm disturbances. Using the ultrasound method, organic changes can be detected. Doctors do not always receive information. Therefore, echocardiography is supplemented with an ECG, often also with 24-hour Holter monitoring. When an automatic device reads blood pressure and contraction frequency of a muscle organ throughout the day.
- Visible symptoms of possible heart disease. For example, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. Paleness of fingers, etc. Including shortness of breath. That is, those manifestations that usually indicate pathologies of a muscular organ. In this case, the technique is used as a preventive measure.
- Suspicion of a tumor. Indirectly, the same symptoms as above indicate a neoplastic process. Shortness of breath, weakness, blue discoloration of the area around the mouth, pallor, rhythm disturbances. Ultrasound gives a rough idea of neoplasia. The exact same result can be obtained through MRI.
- Exercise intolerance. Decreased tolerance. Accompanies angina pectoris and ischemic disease. An ultrasound is mandatory.
- Treatment being carried out. In this case, echocardiography is used to identify possible complications and side effects of therapy. Also as part of a preventive examination.
- Already established cardiological diagnoses. To identify deterioration (to study the dynamics of the disorder).
- Evaluation of treatment effectiveness. Including surgical.
Why is echocardiography performed?
EchoCG is used to identify changes in the structure of cardiac muscle tissue, dystrophic processes, malformations and diseases of this organ.
A similar study is carried out on pregnant women if there is a suspicion of pathology of fetal development, signs of developmental delay, the presence of epilepsy, diabetes mellitus, or endocrine disorders in the woman.
Indications for echocardiography may include symptoms of heart defects, suspected myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm, inflammatory diseases, neoplasms of any etiology.
The study should be carried out if there are varicose veins and thrombophlebitis to exclude the danger of thromboembolism.
An ultrasound of the heart must be performed if the following symptoms are observed:
- chest pain;
- weakness during physical activity and regardless of it;
- cardiopalmus:
- interruptions in heart rhythm;
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- complications after influenza, ARVI, sore throat, rheumatism;
- arterial hypertension.
The examination can be done at the direction of a cardiologist or at your own request. There are no contraindications to its implementation . There is no special preparation for a cardiac ultrasound; it is enough to calm down and try to maintain a balanced state.
During the study, the specialist
- the state of the myocardium in the phase of systole and diastole (contraction and relaxation);
- the size of the heart chambers, their structure and wall thickness;
- the condition of the pericardium and the presence of exudate in the cardiac sac;
- functioning and structure of arterial and venous valves;
- the presence of blood clots, neoplasms;
- the presence of consequences of infectious diseases, inflammation, heart murmurs.
The results are most often processed using a computer program.
More details about this research methodology are described in this video:
Who is the study contraindicated for?
Contraindications are minimal, but they still exist.
- Lung diseases. Because patients with respiratory failure find it difficult to lie still for 10-20 minutes.
- Deformation of the sternum. For example, a hump. In this case, there will be problems with visualizing heart tissue.
- Inflammatory processes of the skin of the breast.
- Mental disorders. Excluding adequacy. For example, exacerbation of schizophrenia.
Contraindications are not absolute. Doctors are considering options to perform the procedure.
Types of Echo CG and their differences
There are several types of cardiac ultrasound. Basically, methods are divided according to the method of access to the muscle organ.
- Classic or transthoracic form, through the anterior wall of the sternum. This is the most common option. Gold standard for primary diagnosis. The ultrasound sensor is placed on the chest, after which the doctor changes its position. To visualize tissues in different projections and from several angles.
- The second option is an ECHO study with contrast enhancement. In essence, it’s the same transthoracic ultrasound. But this time special substances are injected intravenously. They accumulate in blood vessels, tissues and enhance the reflection of ultrasonic waves. Makes the picture clearer. In general, the method differs little from the previous one. From a technical point of view, everything is the same. But with contrast you can get much more information.
- Finally, transesophageal echocardiography. Invasive research. Due to its high complexity, it is performed only in a hospital setting. Moreover, problems and unforeseen disorders are possible afterwards. It is considered a particularly accurate method compared to others. The technique is used if previous modifications have not produced results.
Another way of classification is by the nature of the study.
- ECHO at rest. Occurs especially often. This is a typical cardiography.
- Assessment of cardiac condition after exercise. Appointed in controversial situations.
Basic information
Examination of the heart using ultrasound is a labor-intensive process and requires great professionalism from a medical specialist. EchoCG can be understood if you understand the main components of the study - modes.
B-mode
This study consists of assessing the structures of the heart in two dimensions. In this mode, the dimensions of the chambers in the 4-chamber position, the condition of the valves, the thickness and condition of the heart walls, and their contractility are assessed. Diagnostics should be carried out polypositionally to exclude the influence of artifacts.
M-mode
This method is based on assessing the linear parameters of the heart chambers, walls and their movement, as well as the state of the valves using a graphical image. This mode is of secondary importance, since in the assessment of these dimensions a large error is possible if the measurement rules are not followed, and in the assessment of the valve apparatus, all detected signs are indicative in nature and require a more detailed assessment in other modes.
Dopplerography
This mode is represented by a combination of individual high-tech techniques.
The essence of pulsed wave Doppler is to graphically display the flow in a specified volume. A limitation of the use of this method is the inability to use it on high-speed flows. In the latter case, it is optimal to use continuous wave Doppler. It allows you to record flows at speeds of more than 2.5 m/s.
Color Doppler shows blood flow and its direction in color mode (blue indicates flow from the sensor, and red indicates flow towards the sensor). This method allows you to evaluate the direction of blood flow, the presence of pathological flows and shunts.
Indications for such an examination are shortness of breath, poor physical tolerance. stress, dizziness, fainting, identification of noises and rhythm disturbances, changes in ECG graphs
Tissue color Doppler, by painting the walls of the chambers in blue and red colors when moving (similar to color Doppler), allows you to identify areas with impaired contractile function.
There are a number of other varieties of the method (tissue nonlinear, tissue pulsed wave Doppler, vector high-speed image), but they are of an auxiliary nature and their use is very limited by the complexity and higher cost of devices of the required class.
The result of the examination is a form in which all the data obtained during the procedure are entered. After analyzing the information received, the sonologist prescribes the necessary treatment and makes a conclusion about the patient’s health.
Preparation
No special events needed. Conventionally, we can name the following requirements:
- The day before the test you should not smoke. Otherwise, the vessels will narrow and the doctor will detect false changes. In the coronary and pulmonary arteries.
- The same goes for alcohol. You should give up alcohol a few days in advance. To make the results more accurate.
- On the day of the procedure, you should not engage in intense physical activity. You need to follow a gentle regime. Peace is desirable.
- You must arrive at the appointed time. It is recommended to take a towel or disposable napkins with you. To remove excess gel after echocardiography.
Otherwise, no preparation is needed. You can do everyday, familiar things.
Progress of the study
The patient goes to the office of a functional diagnostics specialist. Next, the procedure is carried out according to the usual scenario for many, like a regular ultrasound.
- You need to lie down on the couch.
- The doctor will lubricate the chest with a special gel. It conducts ultrasonic waves better, so the picture will be more accurate.
- The specialist places a sensor and begins to study the anatomical area.
- During the procedure, the doctor changes the position of the scanner and examines the organ from different angles. Works in several modes. Do not be afraid of the strange sounds that the device makes. This is fine.
- During the scan, the specialist may ask you to hold your breath. Roll over on your side. The patient's job is to follow the doctor's instructions. After the procedure is completed, you can go home.
Other modifications differ. If a contrast study is prescribed, a standard ultrasound is first performed, then contrast is administered and the procedure is repeated. Everything takes about 10-20 minutes. Plus or minus. Transesophageal ultrasound of the heart requires more time.
The echocardiogram is given to the patient after another 10-20 minutes. Because a specialist must give an opinion. Sometimes a person receives only a diagnostic protocol, without the doctor’s explanation.
Examination methods
Echocardiography is a complex research method that includes M-mode, B-mode, and Doppler.
One of the new directions in cardiac ultrasound is the use of three-dimensional and four-dimensional echography.
B-mode is an access in which the intensity of the received signals corresponds to the brightness of the points on the screen of the echocardiograph. M-mode is a time distribution of the M-mode. A graphic image of the movement of heart structures that are intersected by one ultrasound beam is recorded on the screen
These techniques are auxiliary and should be carried out in conjunction with the B-mode. However, their undoubted advantage is obtaining a three-dimensional image of the heart with the ability to assess hemodynamics.
In addition to standard ultrasound examination of the heart, there are additional, less commonly used methods: transesophageal cardiography, intravascular and intracardiac examination, stress echocardiography, and research using contrast agents.
This procedure must be performed in patients with ischemia and signs of heart failure, as well as in cases of complaints of pain in the area of the heart and chest.
Decoding the results
The interpretation is carried out by the treating specialist. Cardiologist. Understanding what's what on your own is extremely difficult. Special medical knowledge is required. To an inexperienced person, the conclusion and protocol will seem like Chinese writing.
Attention:
The results need to be deciphered in a system and not individually. Cardiography alone is not enough to draw far-reaching conclusions. Although there are exceptions.
Normal indicators for an adult are presented in the tables:
Left ventricle and atrium
| Index | Men | Women |
| Myocardial mass | 85-220 g | 65-160 g |
| Volume at rest | 165-195 ml | 60-135 ml |
| Size during diastole | 35-55 mm | |
| Size during systole | 25-35 mm | |
| Left atrium size | 25-35 mm | |
| Ejection fraction | 55-70% | |
| Shortening fraction | 25-40% | |
| Rear wall thickness at rest | 8-11 mm | |
| Interventricular septal thickness at rest | 8-10 mm | |
Right ventricle and atrium
| Index | Meaning |
| Relaxed size | 75-110 mm |
| Pancreas wall thickness | 2-5 mm |
| Right atrium size | 25-45 mm |
| Right ventricle size | 20-30 mm |
| Thickness of the interventricular septum at systole | 10-15 mm |
| Thickness of the interventricular septum at diastole | 6-11 mm |
Blood flow speed
| Name | Index |
| Transmitral | 0.5 – 1.5 ms |
| Transtricuspid | 0.3 – 0.7 ms |
| Transpulmonary | 0.6 – 0.9 ms |
| Transaortic | 1 – 1.7 ms |
Other
| Index | Meaning |
| Normal fluid level in the pericardium | 10-30 ml |
| Aortic root diameter | 20-35 mm |
| Amplitude of opening of the aortic valve leaflets | 15-25 mm |
Pros and cons of the diagnostic technique
There are many advantages of the study:
- Simplicity. An ECHO device is available in almost any district clinic. Even in the regions, not to mention the capital and large cities.
- Safety. The technique does not create harmful radiation exposure. The study can be carried out as often as the clinical case requires.
- High scanning speed. Everything takes about 10-20 minutes. Plus or minus.
- Information content. Despite the accessibility and simplicity of the technique, it is effective enough to detect most diseases.
- Non-invasive and painless. Not counting the transesophageal method. It is still classified as invasive. But, nevertheless, well tolerated. And the procedure is rarely required.
- Minimum contraindications. They are rather formal.
- Variability. Several scanning modes. For example, echocardiography with Doppler analysis is a way to study not only the heart itself, but also the vessels of the local circulatory network.
There is only one minus - ECHO CG does not provide accurate information in many cases. It is necessary to appoint auxiliary measures. Can this be called a negative trait? Hardly. Because the method copes with its tasks one hundred percent.
ECHO of the heart shows the condition of the myocardium, the entire organ and the local circulatory network. The initial parts of the aorta, pulmonary artery. This is a universal, safe and effective diagnostic technique.
Use among pregnant women
During pregnancy, women are susceptible to many diseases. Due to changes occurring in the body, the load on the heart also increases.
Echocardiography is often performed on pregnant women
Indications for echocardiography:
- diabetes;
- hereditary predisposition to heart disease;
- if the patient fell ill with rubella while carrying a baby, or a high concentration of bodies for this disease was detected in the plasma;
- if in the first trimester the woman took any strong medications;
- in the presence of miscarriages in the medical history.
Ultrasounds are often performed on an unborn baby in the womb. The procedure is performed to detect heart defects in the fetus at an early stage and is performed at 18–22 weeks.