Perhaps one of the most unpleasant diseases of the oral cavity is herpetic stomatitis. In adulthood, this disease can be very painful and quite difficult to treat. In order to understand how to get rid of it, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the causes and methods of treating this disease. And to be sure that you have herpes stomatitis and not another, you need to know its symptoms and undergo the correct diagnosis.
Manifestation of pathology
This pathology has one main cause of formation - the herpes virus. However, there are factors that provoke the development of pathology. These include the following reasons:
- mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane;
- burns or dryness of the oral mucosa;
- poor hygiene;
- periodontal diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- stressful situations;
- poor quality food.
Viral stomatitis can appear against the background of any disease that reduces the human immune system, for example:
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis;
- parasitic infestations.
You can become infected with herpes through shared utensils, contact with a sick person, and in any public place. Children under three years of age, adolescents and young adults are especially susceptible to the disease.
Primary infection is characterized by its own characteristics: an acute form of pathology develops. The disease is accompanied by hyperthermia, the general condition worsens, headache and signs of malaise appear. The patient's appetite decreases, the lymph nodes under the jaw swell, and painful sensations appear in the oral cavity. Multiple blisters form on the entire surface of the mucosa.
If the acute form of the pathology is not cured, the disease will take a recurrent form and will constantly appear. Chronic stomatitis is characterized by periodic relapses that appear against the background of a weakening of the body's defenses. That is, the infection is in a “dormant state” until conditions are favorable.
Note! Herpetic stomatitis can occur due to the use of toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfate.
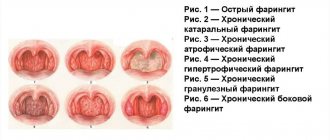
Let us consider the symptoms characteristic of acute and chronic forms of herpetic stomatitis, as well as the features of the manifestation of pathology with varying degrees of damage to mucosal tissues.
Possible complications
It is quite simple to cure a primary infection with herpetic stomatitis if you start using medications at the initial stage of development of the disease.
After 7-10 days, not a trace of the problem will remain. Without drug therapy, the chances of complications increase.
Due to unpleasant sensations and discomfort, the patient refuses to eat and drink, resulting in dehydration. Another equally dangerous complication is herpetic keratoconjunctivitis. The disease affects the eyes and, in its advanced form, leads to blindness.
Acute form - symptoms
Acute herpetic stomatitis is characterized by a latent incubation period of several days. The disease does not manifest itself in any way, then an instant change in the condition of the mucous membrane occurs - swelling, redness, ulceration, hyperthermia. Ulcers can appear not only on the oral mucosa, but also on the surface of the ears, nose and even on the eyelids. A distinctive sign is uncontrolled salivation and a putrid odor. Healing and restoration of the integrity of the mucous membrane occurs in a couple of weeks.
The acute form is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes, which can be noticeable already during the incubation period. Lymphadenitis does not go away immediately after healing from stomatitis, but after a couple of weeks. When the pathology manifests itself, the patient feels severe pain and burning in the areas where the ulcers are located. Ulcers form instead of burst blisters and resemble aphtha in their shape - sometimes herpetic stomatitis is called aphthous.
The disease can occur in various manifestations and forms:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
A mild form of the pathology is characterized by swelling, pain, rashes, and a slight increase in temperature. The average form manifests itself with toxic damage to the body and can occur against the background of a sore throat. In this case, the patient feels severe malaise, a general decrease in body tone, and a severe headache. The temperature can rise to 39. Ulceration affects the entire oral mucosa, eating is difficult or impossible. It is difficult for a person to speak, the movement of the tongue in the mouth causes pain and severe discomfort, salivation cannot be controlled.
The severe form is characterized by hyperthermia, the temperature can reach 40 degrees. The patient's condition is critical.
Treatment of the acute stage
The pathology may manifest itself within three weeks, or may disappear immediately after the start of treatment. This depends on the immune status of the body and the presence/absence of severe diseases of the internal organs. The treatment regimen consists of two stages:
- general therapy;
- local therapy.
For general therapy, the following medications are prescribed:
- Zovirax;
- acyclovir;
- bonafton.
For intramuscular injections, deoxyribonuclease is used. The treatment regimen also includes antihistamines if the patient suffers from allergic reactions. In some cases, herpes can greatly weaken the body, and it responds with allergies to food or drug components.
To strengthen the immune system, multivitamin complexes and immunomodulators are prescribed. If complications occur, metronidazole is prescribed. Patients are also prescribed a diet rich in minerals and vitamins, which promotes speedy healing.
Local therapy
Local therapy includes measures to eliminate visible symptoms of pathology. For example, applications to the tongue using a tampon soaked in leukocyte interferon. Applications are applied up to six times a day.
Medicinal ointments have a good effect:
- helepinova;
- tebrophenic acid;
- Gossypol liniment.
Important! The ointment must be applied not only to the affected surface, but also to adjacent areas of the mucous membrane.
Before eating, local anesthesia must be administered using special aerosols or lidocaine. In this case, the patient will not experience pain while chewing food.
The treatment regimen includes the use of enzymes in the form of solutions: they have antiviral properties and inhibit the activity of herpes. These include lysomidase and deoxyribonuclease. The dose of use will be indicated by the doctor.
To eliminate the virus from the surface of the mucous membrane, use antiseptic rinses with chloramine, furatsilin or hydrogen peroxide. These remedies help to quickly get rid of painful sensations.
For the speedy healing of ulcers and erosions, regenerating oil products are used: sea buckthorn and rosehip oil, fat-soluble vitamins A and E.
Physiotherapeutic procedures must be completed daily until acute herpetic stomatitis in adults is completely healed. They help to quickly eliminate the activity of the virus and eliminate symptoms.
Chronic form - symptoms and therapy
The herpes virus remains in the body fluids forever. Chronic pathology appears as a consequence of untreated stomatitis in the acute phase against the background of a decrease in the protective forces of the immune system. Provoking factors may be:
- colds;
- stress, overwork;
- viral infections and hypothermia;
- diseases of a general somatic nature.
Injury to the mucous membrane, dehydration of the mucous membrane, and increased insolation can also provoke aggression of the virus. Exacerbation of chronic stomatitis is provoked by the patient’s poor nutrition, lifestyle and weakened immune status.
Relapses can occur up to six times a year, sometimes several times a month. Basically, chronic stomatitis is activated in the off-season, but can appear under any favorable conditions. Unlike the primary stage, the chronic form is not characterized by hyperthermia, bleeding from the gums and enlarged lymph nodes. The disease occurs with general malaise.
When the disease manifests itself, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, vesicles appear, which subsequently form erosions with a yellowish coating. If blisters often appear in a certain place, this pathology is called fixed herpetic stomatitis. Healing occurs in 9-10 days, no scars remain at the site of erosion. Chronic herpetic stomatitis must be distinguished from allergic, aphthous and streptococcal.
Causes
Herpes stomatitis (treatment in adults involves a general strengthening of the protective functions of the immune system) can develop only if the oral cavity of a healthy person is infected with viable virions of this virus.
The following causative factors are identified, the influence of which leads to the occurrence of this disease:
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- hematological diseases of the blood and hematopoietic system;
- the presence in the patient’s body of malignant neoplasms, the pathogenic influence of which weakens the protective functions of the immune system;
- infection with accompanying bacterial, viral or fungal microorganisms;
- neglect of the rules of hygienic care for the oral mucosa and gum tissue;
- infection with the herpes simplex virus at the time of kissing a carrier of this microorganism;
- using other people's toothbrushes, which are the source of this disease;
- too poor or unbalanced diet, which leads to weakened immunity;
- infection with the causative agent of herpes stomatitis in medical institutions, when a doctor or junior medical personnel work in violation of sterility rules.
Determining the source of herpetic stomatitis is an important stage in the diagnostic examination of the patient. Establishing the causes that influenced the occurrence of this disease makes it possible to localize the further spread of the viral infection.
Treatment
Therapy methods are aimed at increasing the protective immune forces to overcome the disease. The drug levamisole helps accelerate the onset of remission and eliminates the symptoms of the pathology. If symptoms of herpetic stomatitis appear, you should be examined for the localization of inflammatory processes in the body, since exacerbation occurs as a consequence of a general health disorder.
Note! Self-treatment of the herpes virus is unacceptable.
The treatment plan includes:
- taking ascorbic acid;
- gamma globulin injections;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
At home, the patient should use ointments and applications prescribed by the doctor. After eliminating the symptoms of stomatitis, you can get vaccinated against herpes, which significantly increases the resistance of the immune system against this type of virus.
Diagnostics
A dentist can make an accurate diagnosis of the herpetic form. For this, the clinical manifestations of the disease alone are sufficient. But to identify the virus, it is necessary to carry out laboratory diagnostics and serological studies of scrapings from the affected mucosa.
The most reliable information about the nature of the pathogen is provided by PCR and ELISA methods. For recurrent herpetic stomatitis, it is recommended to evaluate the functioning of the immune system and endocrine glands in order to promptly identify concomitant diseases and prescribe comprehensive treatment.
Herpetic stomatitis in children
Most often, herpetic stomatitis appears in children from six months to three years of age. The culprit of the disease is the herpes virus, transmitted through communication with an infected adult or another child. In children's government institutions, there are outbreaks of a virus epidemic that infects an entire group or several groups of children at once.
The inflammatory process on the mucous membrane is a reaction of the immune system to virus cells that are actively trying to spread on the epithelial surface. The inflammatory process around the “bubbles” prevents further penetration of viral cells into the cells of the human body.
The pathology is characterized by the severity of its course. Babies can develop mild or severe forms of the disease. In mild cases, the child’s temperature may rise slightly (up to 37.5), the mucous membrane swells, and groups of white bubbles appear. Sometimes lymphocytosis may appear. After two days, the symptoms disappear and health is restored.
The average form of the pathology is characterized by intoxication of the body - the child develops weakness, loss of appetite, moodiness and obvious signs of malaise. Although the temperature may be subfebrile (up to 37.5), the child’s health is unsatisfactory. With this form of pathology, there is a noticeable increase in the submandibular lymph nodes. Often these symptoms are accompanied by ARVI and sore throat.
A severe form of the pathology is characterized by the presence of catarrhal inflammation with a high temperature (up to 39). The child's face turns pale, nausea and headache begin, gums bleed and viscous drool flows profusely. The mucous membrane is swollen, with multiple foci of inflammation located on it.
Herpetic rashes in severe form can be localized not only in the oral cavity, but also on the lips, eyelids, nose and even fingers. This pathology can only be treated in a hospital setting, since the virus has spread to the organs of the body.
Treatment of children
The course of therapy is aimed at strengthening the child’s immune forces. Parents should review their baby's diet and include healthy foods in it. Much attention is paid to fresh fruits and vegetables. Vitamins should be in age-specific doses determined by the pediatrician. Before eating, the baby’s mouth should be numbed with anesthetic solutions so that chewing food does not cause pain and tears. Otherwise, the child will refuse to eat.
Also, food should be in puree or liquid form, since solid pieces of food cause pain. During illness, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended - boiled water, freshly squeezed juices, compotes and jelly. Abundant intake of fluid into the body cleanses the blood and lymph of viral toxins. If the child has stopped producing gastric juice, a substitute is given.
In addition to taking medications, the child is given local treatment, which eliminates the visible symptoms of herpetic stomatitis. The use of oxolinic and tebrofen ointments, solutions of neoferon and interferon is indicated. These medications not only treat the affected areas, but also prevent the appearance of new rashes on the mucous membrane. After eliminating the pathological manifestations, antiviral drugs are not used.
To accelerate the regeneration of affected tissues, oil solutions are used - rose hips, sea buckthorn, vitamin A or E, methyluracil. To strengthen local immunity (the mucous membrane itself), the drug imudon is used.
Primary infection
After activation, HSV-1 begins to multiply in the tissues of the oral mucosa. It then penetrates the lymphatic pathways and circulatory system. This is how the infection quickly spreads throughout the body, causing an acute form of herpes stomatitis. It can have three forms of occurrence: mild, moderate and severe.
With a mild course, the symptoms of the disease are subtle. The mucous tissues of the mouth damaged by the virus turn red and slightly swell, and single or grouped transparent blisters appear on them. Gums may bleed. There is no deterioration in health.
Folk remedies
How did our grandmothers treat the disease when modern medicines were not at hand? To eliminate visible symptoms (ulcers), the following methods are used:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- lemon juice;
- soda solution;
- ascorbic acid;
- alcohol.
How to use hydrogen peroxide? To do this, you need to moisten a piece of bandage in the solution, squeeze it out and wrap it around your finger. It should be remembered that peroxide can easily cause burns to the mucous membrane, so do not overdose. You can use peroxide to treat mucous membranes for no more than five days.
Gargling with soda is an old effective method of combating oral problems. You need to rinse frequently - at least five times a day. To do this, dissolve a teaspoon of powder in a cup of non-hot water.
Citric acid destroys the virus. To do this, squeeze a little juice from the fruit and moisten a cotton pad. Apply the disc to the affected areas several times a day.
Lemon juice can be replaced with ascorbic acid. To do this, crush a couple of tablets or dissolve them in a cup of warm water. As with lemon juice, treat the affected surface with a cotton pad soaked in the solution.
Alcohol is used when the virus appears on the outer surface of the lip. You need to cauterize the pimples with a cotton pad soaked in alcohol: it will dry out the virus and prevent it from spreading to neighboring areas of the skin.
Important! Traditional methods help well at the beginning of the spread of infection. If there is no improvement within three days, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
To regenerate mucosal tissue, you can use freshly squeezed cabbage and carrot juices diluted in warm water (1:1). You need to rinse your mouth with juices throughout the day until improvement occurs.
The well-known chamomile, calendula, sage, and oak bark have an antiseptic effect. The infusion is prepared according to the recipe on the packaging box.
Onion peels have a radical cleansing effect. For infusion, you need to brew a handful of washed husks with half a liter of boiling water and leave until the morning. Rinse your mouth with the strained solution. A side effect of this treatment will be stained tooth enamel, but this will soon go away.
Healing applications
To quickly get rid of the symptoms of an unpleasant disease, you need to carry out applications. For this use:
- honey;
- Kalanchoe/aloe juice;
- potato juice.
Important! Before using apitherapy, check the body’s reaction to honey to see if there is an allergy.
Beekeeping products actively fight all types of fungi, viruses and bacteria. Honey and propolis are effective remedies for healing many ailments. Honey has an anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect on epithelial tissue, eliminates itching and burning.
To cure herpetic stomatitis in adults, you need to suck a teaspoon of honey every couple of hours. This is a painful procedure and is therefore not suitable for children. You can also dissolve honey in warm water and rinse your mouth.
Kalanchoe and aloe are centuries-tested healers. You can simply chew the leaves throughout the day, or you can apply the juice to the affected areas. Moisten the gauze and apply to the tongue, gums or other places.
Potato applications are completely painless, so they can be used to treat children. To do this, the fruit is grated and applied to the area where the ulcers accumulate. Instead of raw mass, you can apply thin potato slices for 12-15 minutes.
Relapse Prevention
To prevent the activation of the herpes virus, factors that provoke it are excluded - smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, hypothermia. The best means of preventing the disease include:
- hardening;
- regular physical activity;
- careful oral hygiene;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases;
- taking vitamins, especially in the spring and autumn.
These disease prevention measures can prevent the activation of the herpes virus and reduce the risk of the process becoming chronic.
Herpetic stomatitis can be cured only according to a treatment regimen drawn up by a dentist. Independent attempts to get rid of the disease can cause it to become chronic. The main feature of severe herpetic stomatitis is swelling of the oral mucosa.
Preventive measures
Herpetic stomatitis in a child can be prevented by comprehensively strengthening his immune system, keeping his hands and mouth clean, and limiting contact with strangers. If adults become ill, their dishes should be separated from the common ones and should not be allowed to come into contact with the baby. Regular intake of multivitamin complexes and a nutritious diet will help protect the body from the activity of the virus: a lack of certain microelements provokes the growth of virus cells in the body.
Prevention of herpetic stomatitis in adults is thorough sanitation of the oral cavity and timely treatment of internal diseases. Often the herpes virus is activated during ailments such as gastrointestinal diseases, anemia, nervous disorders and hormonal imbalances. There is no antiviral vaccine for herpes, so health care rests entirely with the individual’s consciousness. Always wash your hands, sanitize your mouth, give up bad habits and cure chronic illnesses - anyone can do this for the benefit of their health.
What to do if a disease appears
If the above symptoms appear, you should urgently consult a dentist or therapist. A qualified specialist can distinguish rashes due to herpes stomatitis from manifestations of herpes, a viral disease. Or enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthema, which we talked about in the article “On the treatment of enteroviral vesicular stomatitis.”
Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthema
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must familiarize himself with the patient’s medical record, assess his general condition, examine the oral cavity, and conduct laboratory tests:
- virological – study of the properties of the virus and its connection with the occurrence of herpes stomatitis;
- immunological – assessment of the state of general immunity;
- serological – study of antibodies and antigens in the blood;
- molecular biological – detection of viral DNA particles in damaged tissues of the oral mucosa;
- cytological - microscopic study of the structure of affected cells.
Only after a full diagnosis will the doctor be able to select the most appropriate therapy for a given clinical case.