Each person reacts individually to the development of the hepatitis C virus and to the treatment prescribed by the attending physician.
In some patients, the symptoms are pronounced, while the other half accidentally find out that they are a carrier of this virus. We will look at what the obvious external signs of hepatitis C look like in this article, because with such a serious illness, not only the color of the skin changes, but also the condition of the liver, the color of the whites of the eyes and the general appearance of the patient.
What kind of disease is this?
HCV is a viral disease characterized by inflammatory processes in the liver and general malaise. The hepatitis C virus belongs to the flavavirus family. The highest concentration of hepatovirus is found in the blood of an infected person. Small amounts are found in the saliva, semen, vaginal secretions and mucus of an infected person.
Thus, viral hepatitis C is transmitted through blood. The disease is characterized by a chronic course. It is for this reason that HCV is called the “gentle killer.” Chronic hepatitis C occurs without any obvious symptoms. The patient may feel completely healthy, and discover the disease at a late stage or during routine diagnostics.
Approximately 15% of the total number of cases develop an acute form of HCV. The following symptoms are typical for this condition:
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Jaundice discoloration of the skin and eyeballs
- General malaise reminiscent of influenza
- Darkening of urine to the color of dark beer and discoloration of stool
- Sleep disorders (insomnia, drowsiness)
- Loss of coordination and lethargy
- Depressive disorders.
Despite the apparent severity of the acute phase, it is during this period that the body actively fights the hepatovirus.
Signs of acute hepatitis
It is considered a severe form of the disease, and accordingly passes with vivid symptoms, developing rapidly, combined with general malaise, pronounced signs of fever, destroying the liver.
The main features of this form:
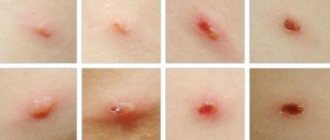
- The jaundiced color of the skin and the white membrane of the eyeball is characteristic (there are cases without jaundice), and this symptom (including the jaundice of the upper palate) also occurs in a mild form;
- change in the color of urine (very dark) and feces (white-clay color due to impaired synthesis of bile acids);
- Itching of the skin is noted, red dots and symptoms of a neurotic state also appear.
An increase in size of the liver, as well as the spleen, can be detected by palpating with your fingers.
When was HCV discovered?
In the 70s of the last century, the causative agents of hepatitis A and B were identified. In the process of laboratory research, scientists discovered that there are also several strains that are not related to those presented above. They received a common working name - non-A, non-B hepatitis, or NANBH (“neither A nor B hepatitis”).
Later, in 1989, a decisive step was taken in isolating the pathogenic agent of HCV. In the blood samples studied, RNA of the pathogen, characteristic of the flavavirus family, was detected. This pathogen was named the hepatitis C virus.
Prevention of infection
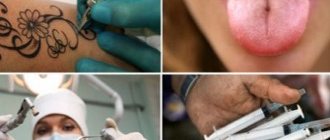
The main route of transmission of hepatitis C is parenteral. For prevention purposes, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of contact with someone else's blood. For injections, use disposable syringes.
Require the use of disposable instruments when visiting dental offices and tattoo parlors. Practice protected sex. Do not use other people's razors or toothbrushes. Be tested annually for markers of hepatitis.
Hepatitis C is a dangerous disease. The virus has the ability to mutate, which makes treatment difficult. Modern drugs can stop the multiplication of virions and completely cure the patient. It is necessary to undergo an examination, determine the genotype, and select the appropriate drug. Following the doctor's recommendations and following dietary measures is the path to successful healing.
How was the disease treated before?
The first treatment regimen used in the treatment of viral hepatitis C is Interferon-alpha + Ribavirin. These drugs do not directly affect the virus, but can provide stable remission due to drug enhancement of the natural protection of hepatocytes. Interferon is used in the form of injections, Ribavirin is used in tablet form.
This treatment regimen has many disadvantages:
- Severe side effects. Interferon is poorly accepted by the human body. During therapy, the patient may lose significant weight and hair.
- Duration of therapy. Medicines are used for 6-12 months. This can negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys and endocrine system.
- Negative effect on the biochemical composition of the patient’s blood. The level of lymphocytes and platelets increases significantly, which can lead to pernicious anemia. For this reason, patients have to undergo regular blood tests and urgently interrupt therapy if an alarming trend is detected.
- Low efficiency. The disease can be stopped in 70 cases; it is practically impossible to completely cure hepatitis with the help of Ribavirin and Interferon.
Currently, the interferon method of HCV therapy is used in budgetary medical institutions and is gradually becoming obsolete.
Medical examination
In medical institutions, analysis for hepatitis is carried out using various methods:
Biopsy - based on laboratory testing and a medical examination by a therapist or gastroenterologist.
In laboratory conditions, biochemical tests are carried out, the amount of bilirubin is checked, the presence of prothrombin, the level of coagulation, and others are also determined.
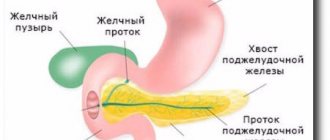
The condition of the liver tissues (their sound permeability) is determined by the results of an ultrasound examination, the size of the spleen, and sometimes the pudendal vein.
The state of the liver blood flow, the pathways of bile excretion are examined, and palpation is performed.
What is the current percentage of infected people?
Currently, according to the history of hepatitis C, 8 genotypes of the causative agent of the disease are known. The first 6 of them are the most common. In this case, the percentage of infection:
- 1, 2 and 3 gen higher on the European continent, in particular in the territory of the former USSR
- Genotype 4 is highest in the USA and North Africa
- 5 gen is increasingly increasing in Asian countries
- Genotype 6 is high in Southern African countries
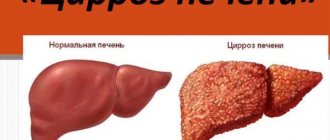
Currently, about 150 million people suffer from chronic hepatitis C. All these patients are at risk of developing cirrhosis and liver fibrosis.
Statistics in this regard are not reassuring. Annually:
- More than 350 thousand infected people die from complications associated with viral liver damage.
- More than 3-4 million people become infected through contact with infected blood.
Currently, in Russia the number of patients with HCV is about 11 million people. Unfortunately, this figure is growing steadily. At the same time, the flavavirus mutates intensively. According to research, over the next 10 years the number of infected people may increase sharply.
Manifestations of chronic hepatitis
Symptoms of this form include several signs of the disease:
- asthenovegetative (in which a person quickly gets tired, feeling constant weakness, while sleep is upset, overcome by headaches, characteristic mental mobility);
- dyspeptic (characterized by nausea, often vomiting, with decreased appetite, weak stools and gases, alternating with constipation, when belching there is an unpleasant smell of bitterness and a taste in the mouth);
- pain syndrome (pain is felt in the hypochondrium on the right, a violation of the diet or physical activity causes pain to intensify);
- low-grade fever (a slight increase in body temperature may persist for several weeks);
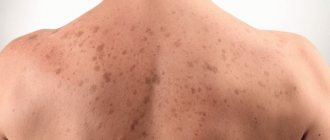
- redness of the skin of the palms persists for a long period, the shoulders, neck and face are covered with reddish spots in the form of stars;
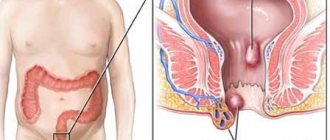
- hemorrhagic (the appearance of bruises or bruises on the body, nosebleeds, hemorrhoidal or uterine);
- jaundice (body skin or mucous surface becomes yellowish);
- a noticeable increase in the size of the liver, and the spleen may also increase.
Development of new drugs against HCV
In 2011, the American corporation Gilead began intensive development of innovative direct antiviral drugs (DAAs). In 2013, Sofosbuvir, a nucleotide analogue that is a direct inhibitor of flavavirus NS5B polymerase, was released.
The medicine was subjected to a number of laboratory and clinical studies, the results of which showed that Sofosbuvir is equally effective both with and without Ribavirin. The development of a nucleotide inhibitor made it possible to abandon dangerous injections of Interferon-alpha.
Sofosbuvir is not used in monotherapy. In combination with it, NS5A inhibitors, developed somewhat later, are used:
- Ledipasvir is used to treat genotypes 1, 4, 5 and 6. Developed by Gilead Sciences.
- Daclatasvir - used in the treatment of genotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4. Developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb.
- Velpatasvir is effective in treating any genetic type of HCV. Developed by Gilead Sciences.
Currently, the USA and India are engaged in the production of original DAAs.
Medicines from the USA
American Sofosbuvir (400 mg in 1 tablet) entered the world market under the trade name Sovaldi in 2014. A little later, the following drugs were released:
- Daclinza - 60 mg Daclatasvir per tablet;
- Epclusa - 100 mg Velpatasvir, 400 mg Sofosbuvir;
- Harvoni - 90 mg Ledipasvir, 400 mg Sofosbuvir.
The latest DAAs were of the highest quality and effectiveness. At least 97% of the total number of patients recovered after taking these medications. The course of their administration is relatively short - 12-24 weeks. The drugs do not affect the biochemical composition of the blood and do not cause severe side effects.
But American-made drugs have a significant drawback. Because corporations have to cover development costs, the cost of drugs is extremely high. For one package of Sovaldi, for example, you will have to pay at least 126,000 rubles.
Indian medicines
The extremely high cost of DAAs from America has caused a storm of criticism. After all, the majority of infected people live in poor countries. These people cannot afford such expensive medicines.
The situation was saved by the provision of an international license to Indian pharmaceutical giants for the production of drugs to combat chronic hepatitis C. The license allows the production of DAAs according to the original recipe, and since India only pays for the annual renewal of the agreement, the medicines it produces are 20 times cheaper than American ones.
In total, 11 pharmaceutical giants received a licensing agreement, including Zydus Heptiza, Natco Pharma, MyLan and Hetero. Below is a list of the main products of these concerns:
| Analogue from the USA | Zydus | Natco | Aprazer | Hetero | Mylan |
| Sovaldi / Sovaldi | Sovihep | Hepcinat | Sofokast | Sofovir | MyHep |
| Epclusa / Epclusa | SoviHep V | Velpanat | Velakast | Velasof | MyHep All |
| Daclinza / Daklinza | Dacihep | DaclaHep | Dacikast | Natdac | MyDacla |
| Harvoni / Harvoni | LadyHep | Hepcinat LP | Ledikadt | LediFos | MyHep LVIR |
The international agreement allows Indian manufacturers to distribute their products outside their country. However, by agreement, wholesale quantities of drugs can be sent only to 105 third world countries, the list of which is indicated in the license. Russia is not included in this list, however, drugs can be legally ordered through the official representative office of Zydus Heptiza with direct delivery from India.
Indian drugs for HCV are a new word in the history of hepatitis C. Thanks to the license obtained by Indian manufacturers, even low-income patients have a chance for a quick recovery.
Diet
The basis of any therapy is diet. For hepatitis, table 5 is prescribed. Features of the use of products are as follows:
- Reduced fat content.
- The temperature of the food should not be cold.
- Products are prepared by boiling, stewing, and baking.
- Salt content is limited.
- Diet: six times a day, every three hours.
- Portions are prepared in small sizes.
- Fluid consumption is one and a half liters.
The following are prohibited:
- Fried, spicy, smoked, salted, pickled, fatty.
- Alcohol.
- Carbonated drinks with dyes.
- Coffee, cocoa, juices.
- Delicious baked goods.
- Vegetables and fruits that have not undergone heat treatment.
- Fatty types of meat, poultry, fish.
- Spices, seasonings, sauces.
- Chocolate, seeds, fatty desserts.
- Sausages, sausages.
- Fatty dairy products.
Allowed to use:
- Porridge.
- Vegetarian soups.
- Kissels, fruit drinks, compotes.
- Fermented milk products.
- Lean meat, fish.
- Rusks, rye bread.
- Marmalade, soufflé.
Where can you get infected?
Due to the specific nature of virus transmission, there are a number of establishments with an increased risk of infection.
- Cheap and mid-price catering establishments - blood is less likely to be saliva; infection through microcracks or wounds in conflict situations.
- Public toilets, showers - particles of blood, saliva, sweat from the wearer - microcracks, damaged nasopharyngeal mucosa, recipient's eye mucosa.
- Hairdressers, dental offices.
- Cosmetology salons.
- Production workshops – use of sharp objects.
- Medical institutions where preventive measures for the virus are neglected.
Risk group
The main risk group is laboratory assistants at medical institutions. Infection of drug users is not so widespread. There is a risk of infection when engaging in activities involving the use of cutting objects.
Alcoholism is not a risk factor for infection. Alcohol contributes to the rapid development of the disease and the rapid occurrence of cirrhosis.