If this ratio is observed, the woman does not experience any problems with intimate health. But when the balance of microflora is disturbed, so-called vaginal dysbiosis or dysbiosis develops.
Lactobacilli produce a number of antimicrobial substances that effectively eliminate pathogens that enter the genitals from the environment. They also suppress the growth of opportunistic fungi and bacteria, preventing the development of diseases such as gardnerellosis, ureaplasmosis, vaginal candidiasis and others.
Normal microflora is supported by the immune system: it does not attack lactobacilli and promotes their restoration in case of minor disturbances. Also, the state of vaginal microbiocenosis is influenced by a woman’s hormonal background: during the monthly cycle, the quantitative ratio of microorganisms can change. But there should not be strong deviations: a sharp drop in the number of lactobacilli provokes a rapid growth of opportunistic microflora, the balance is upset, and the woman faces the first manifestations of vaginal dysbiosis.
What it is
This disease has other names, for example, vaginal dysbiosis or bacterial vaginosis. Some people call it gardnerellosis or vaginal candidiasis, which is completely wrong, because these symptoms are only one type of vaginal dysbiosis and need to be treated differently. What kind of illness is this?
The genital organs of each woman have a special bacterial environment. Most of them consist of beneficial lactobacilli, most of which enter the body and bifidobacteria. But the source of the problem is the remaining 1% of microflora. These are the so-called key cells of the vagina. These include, but are not limited to, Candida fungi.
When disturbances occur in the internal environment of the female genital organs, bacteria in this category begin to behave somewhat aggressively, and their number increases. At first, the body copes with this problem, but if the immune forces become insufficient, we can say that vaginal dysbiosis has developed. The microflora balance is disturbed, and if it is not restored to normal, this can lead to serious consequences.
Reasons for development
The exact causes of bacterial vaginosis are difficult to identify because there are so many factors that can trigger this disorder. However, this does not have much impact on the treatment of this disease. If the internal mechanism of vaginosis is clear, what external pathogens can cause it?
Vaginal dysbiosis can occur for the following reasons:
- stress;
- irregular sex life;
- frequent change of partners;
- Sex without using contraception;
- Sexually transmitted infections;
- Failure to adhere to best personal hygiene practices;
- Do not use tampons or pads during menstruation;
- Infections of the pelvic organs;
- Pregnancy;
- immunological abnormalities;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- sudden changes in climatic conditions;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- Hypothermia;
- entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the vagina;
- hormonal changes;
- imbalance of the microflora of the body as a whole.
The development of the disease can be triggered by one of these factors, as well as several at once. If an infectious disease occurs first, every effort should be made to eliminate it.
What is the danger of this disease?
Vaginal dysbiosis itself does not pose a particular danger to a woman’s health. It occurs in almost every second woman, but much depends on the patient’s further actions. If the symptoms indicate a serious disorder, you experience discomfort and abdominal pain, it means that the disease is progressing and has probably already developed into a new form.
Dysbacteriosis of the genital organs can provoke the development of other diseases, such as:
- adnexitis - inflammation of the appendix;
- Endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa;
- Cervicitis - inflammation of the cervix;
- vaginitis - inflammation of the vaginal walls;
- colitis;
- Cystitis;
- urethritis, etc.
In the presence of such complications, the stomach of a sick person may experience pain during sexual intercourse, urination, and fever. The discharge becomes purulent, and the unpleasant odor only intensifies.
They will be much more difficult to treat, and some may even lead to infertility. This is why it is so important not to delay visiting a doctor if such a problem arises.
Pathogenesis
With vaginal dysbiosis, there is a sharp qualitative and quantitative change in the microflora, which is characterized by a decrease in the number of lactobacilli that provide a protective function.
Normally, the vaginal microflora includes different types of microorganisms - gram-positive and gram-negative, aerobic, facultative anaerobic and obligate anaerobic. In the normal state of microflora, it consists of about a hundred species of different bacteria. The predominant species are lactobacilli. If a woman is healthy, then lactobacilli make up 95-98% of all vaginal microflora. Another typical representative of the normal vaginal microflora is bifidobacteria . Like lactobacilli, they produce substances that maintain a stable vaginal microbiocenosis.
If vaginal dysbiosis develops, lactobacilli are replaced by other microorganisms. In particular, anaerobic bacteria multiply. If anaerobic dysbiosis develops, this leads to an increase in the concentration of amines and a change in the vaginal environment to an alkaline one. Reproducing microorganisms release amines and organic acids that destroy epithelial cells and have a cytotoxic effect. As a result, conditions are created in which pathogenic microorganisms actively grow and develop.
Symptoms
Vaginal dysbiosis is dangerous not so much by its nature as by delaying the development of the disease at an early stage. Many women simply do not notice the alarming symptoms, and when they become quite pronounced, the disease has already managed to take hold and is much more difficult to overcome.
The following symptoms are typical for vaginal dysbiosis:
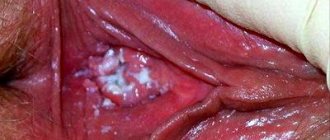
- cloudy landing and genitals white or yellowish;
- Itching;
- unpleasant odor;
- Smoking;
- pain during intercourse;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- vaginal dryness;
- urinary tract insufficiency;
- Heat.
At first, a woman may not notice any changes. Over time, the discharge becomes larger, and the color and smell differ from normal. If you do not follow hygiene standards, you will very quickly feel severe itching and burning. Usually it is at this moment that a woman realizes that something needs to be done. If you ignore it, then with bacterial vaginosis, the pathogenic microflora continues to develop and leads to more serious symptoms, up to the development of purulent inflammation.
Often, bacterial errors manage to enter the chronic stage. In this case, symptoms develop during an exacerbation, and during the period of remission the disease does not manifest itself in any way.
Immediately after noticing such symptoms, you should contact a gynecologist to clarify the situation and, if necessary, begin treatment. The sooner you do this, the lower the risk of complications.
Complications and consequences
A common complication of vaginal dysbiosis is the involvement of other organs in the process. Thus, patients are often diagnosed with cystitis, adnexitis, and vaginitis. When the infection spreads to the cervix, cervicitis develops. It is especially dangerous if the body of the uterus is involved in the pathological process during pregnancy. This can lead to infection of the fetus, premature birth, and miscarriage. During childbirth, the baby can become infected with dangerous bacterial diseases.
Diagnostics
Immediate treatment is half the battle. First you need to clarify the diagnosis. Naturally, the main specialist in this case is a gynecologist. For many doctors, it is enough to hear the patient’s complaints about the unpleasant symptoms that have appeared in order to determine what the problem is. In any case, however, further research is necessary to ensure the correctness of their decision and determine the direction of treatment.
If vaginal dysbiosis is suspected, a smear is always taken to analyze the microenvironment. If the slightest deviations are detected, the type of vaginosis is determined. In this case, thrush can be detected if the number of Candida fungi exceeds the norm.
Also, in some cases, it is necessary to conduct a bacterial analysis of vaginal discharge. If a sexually transmitted infection is suspected, additional diagnostics are carried out, for example, PCR.
Vaginal suppositories for restoration, normalization and improvement of vaginal microflora
Vaginal suppositories are small, oblong-shaped preparations that look like a ball, oval, cylinder or cone, with a diameter of about 1-1.5 cm and weighing from 1.5 to 6 g. They are inserted intravaginally (into the vagina) - with or without an applicator him. Vegetable and animal fats, glycerin or gelatin are used as the basis for the manufacture of vaginal suppositories. Under the influence of body temperature, suppositories lose their solid form, due to which the active substance is able to act on the vaginal mucosa.
To restore the vaginal microflora, suppositories are used based on active ingredients such as lactobacilli acidophilus, bifidobacterium bifidum, ascorbic acid, lactic acid, etc.
Treatment
If the diagnosis confirms the suspicion of vaginal dysbiosis, a course of treatment should be established. Traditional methods primarily involve medication. In this case, treatment consists of three directions.
- Suppression of the active life of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Colonization of the vagina with healthy bacteria.
- Activation and balancing of the body's immune forces.
In order to eliminate the problem at the local level, special vaginal suppositories and ointments are used. Spraying with a weak solution of boric and lactic acid has also proven to be an effective way to combat heavy secretions and microbes. As a last resort, strong systemic antibiotics are used.
In addition, vaginal dysbiosis involves taking medications aimed at restoring beneficial microflora. For this purpose, local biological products are prescribed.
The third stage of treatment is strengthening the immune system. To do this, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes, immunostimulants, and dietary supplements. In addition, you should pay attention to hormonal compensation.
Bacterial vaginosis can also be treated with different physical therapy approaches. The specific course of treatment and prescription of drugs is the task of the participating gynecologist. Don't make these decisions on your own!
ethnoscience
If vaginal dysbiosis is just beginning to develop, the woman’s body tries to cope with it on its own. In this case, drug treatment is not required. You can help your immune system fight disease. For this, various traditional medicine methods are used. How to treat vaginal dysbiosis with non-traditional means?
For this purpose, various decoctions and ointments are usually used. The basis of therapy is a local antiseptic. To wash away pathogenic bacteria, spray with the following decoctions:
- bird cherry fruits;
- Chamomile;
- grosbeak flowers;
- Oak bark, etc.;
- You can also use a weak solution of manganese.
A bath with alkaline ingredients such as iodine and baking soda is also helpful. A good solution would also be a bath with propolis, oak bark and flower honey. For local effects on the vaginal environment, tampons soaked in olive oil, flaxseed or sea buckthorn oil, aloe juice, and propolis are used.
The best proven immunostimulating agent for dysbacteriosis. To do this, you first need to adjust your diet. Including more vitamins in the daily menu: fruits, vegetables, compotes and snacks. In winter, it is useful to eat dried fruits, as they contain a sea of useful microelements.
Be sure to include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet.
Treatment with folk remedies is a good help for the traditional course. It can also be used as a basic therapy, but it is better to be under the supervision of a gynecologist so as not to miss the moment when more aggressive measures are required.
Dysbacteriosis during pregnancy
Vaginal dysbiosis often develops in pregnant women. This is mainly due to changes in the hormonal levels of pregnant women. This disease is manifested by cloudy, sticky discharge with an unpleasant odor, accompanied by itching and redness of the vaginal mucosa.
The danger is that the rapid proliferation of microbes causes an inflammatory process that can directly affect the fetus. This is associated with the transmission of inflammation to the child, impaired fetal development, birth defects, and even frozen pregnancy and miscarriage.
It is worth remembering that the method of treating dysbiosis in pregnant women varies. Most of the drugs used in ordinary cases have a strong specific action. It is not recommended to use any antibiotics during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Therefore, therapy is aimed at local elimination of symptoms using milder methods.
For this purpose, sanitization of the vagina, traditional methods of cleaning the environment from pathogens, and local antibacterial suppositories are carried out. The introduction of an active course is possible only after stopping breastfeeding.
To prevent vaginal dysbiosis from turning your life into suffering, do not let it progress. To do this, you need to regularly visit the gynecologist, without waiting for the first signs of the disease, and apply preventive measures. If the problem cannot be avoided, follow the recommended course of treatment for a speedy recovery.
Causes of vaginal dysbiosis
The vaginal microflora is sensitive to both external and internal influences, and dysbiosis can be caused by many reasons.
Internal reasons include:
- changes in hormonal levels caused by pregnancy, approaching menopause, taking oral contraceptives, gynecological treatment and other factors;
- endocrine disorders due to chronic diseases, such as diabetes;
- a course of antibiotic treatment without subsequent use of probiotics;
- uncontrolled use of medications;
- previous injuries or surgeries;
- gynecological diseases;
- congenital anomalies of the genitourinary system;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- general hypothermia of the body;
- avitaminosis.
Among the external factors that provoke vaginal dysbiosis, gynecologists identify:
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules during menstruation;
- strong physical and intellectual stress;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- unfavorable environmental conditions (poor urban environment, work in production);
- unbalanced diet: excessive consumption of fatty, smoked, salty foods, flour products;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- change of climate zone.
Girls who often change sexual partners are at risk. But the absence of sexual activity does not protect against dysbiosis: it can develop under the influence of other factors.
Prevention
To avoid suffering from treatment, which can become a regular necessity for chronic bacterial vaginosis, it is important to monitor your health. To prevent dysbacteriosis, it is necessary to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- The rules of intimate hygiene should be observed;
- Change tampons and pads regularly;
- Wear underwear made from natural, breathable materials;
- Use condoms;
- Eat a healthy diet;
- Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics.
It is also necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist during treatment at intervals of 2-3 months throughout the year. This will allow you to evaluate the final result and prevent recurrence of the disease.
Diet
Diet for thrush
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a month
- Terms: 3 months or more
- Cost of products: 1400 - 1500 rubles per week
Nutrition should be balanced. But at the same time, the amount of fatty foods should be kept to a minimum. It is also better to exclude canned food, smoked meats, pickles, alcohol and coffee from the diet.
Useful foods for dysbiosis are: any fermented milk food, fresh vegetables, sauerkraut, herbs, fruits, whole grain porridge.
How to treat?
Treatment of bacterial dysbiosis includes following a special diet with a complete avoidance of foods containing chemical additives, as well as sugar, seasonings, smoked and pickled foods. It is also recommended to avoid coffee and carbonated drinks until the acute process is stopped.
Particular attention should be paid to intimate hygiene. Bed linen and underwear should be made of natural cotton or linen fabrics
Underwear should be changed every day after hygienic washing. Bedding should be changed every 3-4 days. If the fabric from which duvet covers and pillowcases are made allows it (for example, bleached calico with a density of 140 g/m), it is better to wash bed linen at high temperatures - from 90° to 100°.
Treatment regimen for vaginal dysbiosis
You can wash yourself during the treatment period with decoctions of medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and bactericidal properties. These are calendula, sage, St. John's wort, chamomile. In case of severe inflammation of the skin of the genital organs, you can prepare a decoction of oak bark - this is a powerful antibacterial agent that is not inferior in effectiveness to some medications. To prepare the decoction, pour 2 tablespoons of bark into 500 ml of boiling water and simmer over low heat for 15 minutes.
Drug treatment
To eliminate the symptoms of bacterial dysbiosis and destroy pathogenic flora, doctors can prescribe medications containing beneficial microorganisms or local antibiotics (depending on the indications). Most often, for women who are sexually active, doctors prescribe medications in the form of vaginal suppositories, for example:
- "Acilact";
- "Terzhinan";
- "Pimafucin";
- "Bifidumbacterin";
- "Ginolact";
- "Flagyl".
Prevention of vaginal microflora disorders
Vaginal suppositories should be used 1-2 times a day for 5-10 days (exact information is contained in the instructions for the specific drug). Before inserting a suppository or vaginal tablet, you must wash and dry the skin of the perineum. After this, you need to lie on your back and bend your knees. Using your finger (or a special applicator, if included), insert the suppository to the maximum depth. After administration, the suppository will begin to melt, so you need to turn over on your stomach and lie there for 15-20 minutes to prevent the medicine from leaking out.
Video:
In case of a complicated course of the pathology, a woman may be prescribed systemic drugs in the form of capsules and tablets for internal use. The most commonly used drugs in combination therapy are:
- "Trichopolus";
- "Metronidazole";
- "Metrogil";
- "Flagyl";
- "Clindamycin";
- "Dalacin."
How to quickly determine vaginal acidity
Additionally, you can take orally medications containing bifidobacteria, probiotics, prebiotics and lactic bacteria: “Normobakt”, “Bifidumbacterin”, “Yogulakt”, “Linex”, “Bifiform”.
Vaginal dysbiosis cannot be called a dangerous disease. Nevertheless, this pathology is extremely unpleasant. Painful symptoms and discomfort disrupt the quality of a woman’s daily and intimate life. Violation of the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic microorganisms increases the risk of developing infectious diseases of the vulva, vagina, bladder, appendages, uterus
For this reason, it is important to seek medical help in the early stages of pathology.
Women at risk are recommended to pay special attention to hygiene and nutrition and undergo annual drug prevention of bacterial dysbiosis, selected by a local gynecologist
Necessary tests
Since pathologies are often asymptomatic, many women find out about their presence only during an examination by a gynecologist. If the doctor suspects that something is wrong with women’s health, then he takes the appropriate tests.
Most often, a urogenital smear is done to determine the state of the microflora.
Laboratory tests will help determine the presence of certain diseases, inflammatory processes, and the cause of dysbiosis.
Before taking the test, you must follow the following recommendations:
- the day before the tests, refrain from sexual intercourse;
- within 3 days, stop using tampons, suppositories and other means that can worsen hygiene;
- stop taking antibacterial agents for several days.
You can find out the results in 2-3 days. According to the test results, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment, which must be started immediately.