Any modern geneticist knows that Wilson-Konovalov disease (hepatolenticular degeneration) is a severe lesion of the central nervous system, as well as internal organs. The second name is hepatocerebral dystrophy (HCD). It can be inherited. The problem is that the body is literally poisoned by excess copper. The main task of treatment is to remove copper. If this is not done, the patient will die.
Konovalov's disease is inherited. If the parents are carriers, there is a 25% chance that the child will get the disease. In this case, the carrier can be absolutely healthy. Scientists have found that to get sick, you need to have two mutant genes. This means that both parents must be carriers. This happens extremely rarely. If a child inherited the mutant gene from only one parent, he will not get sick, but will be a carrier (in this case, heterozygous).
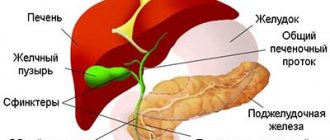
The gene that is responsible for this mutation was discovered only recently. Scientists have studied well how Wilson-Konovalov syndrome develops. The reason lies in the fact that the exchange of copper and the proteins that contain it is disrupted. This results in too much “free” copper. It is deposited in the brain, liver, and cornea of the eyes. Tissue degeneration gradually occurs, the endocrine system and brain suffer, and Fanconi syndrome may develop (the genitourinary system suffers).
To detect the disease, an analysis is performed for copper metabolism disorders. Now it is possible to diagnose the presence of a “broken” gene through a DNA test (they find an autosomal recessive gene).
All lesions are very serious and eventually lead to organ failure. It is extremely important to carry out diagnostic measures at an early stage of the disease, before the organs are poisoned.
Due to the fact that copper collects in the cornea, a so-called Kayser-Fleischer ring is formed. It can be visually recognized by its greenish-brown tint.
About 15% of all liver problems among children are associated with Wilson-Konovalov disease.
A little history
This is a very ancient disease. Scientists have analyzed an image of the famous Egyptian pharaoh Tutankhamun and concluded that he may have had hepatolenticular degeneration.
The name of the disease is associated with the name of Wilson, an English neurologist. Back in 1912, he described in detail the typical dystrophic changes in the brain during the development of cirrhosis. This is how a new disease was described - progressive lenticular degeneration.
This was preceded by a description of pseudosclerosis by K. Westphal and A. Strumpell. Patients with liver problems developed dementia.
This pathology was studied by Academician N.V. Konovalov. One of his monographs on this topic received the Lenin Prize in 1964. Then the pathology was carefully studied at the Institute of Neurology (neurogenetic department). For more than 40 years in a row, scientists have observed families in which this serious illness appeared.
Experience has shown that the main thing is to diagnose the disease at the initial stage of development. It is best if treatment is started before symptoms appear (pre-symptomatic stage). It is important to prevent damage to the brain and major internal organs.
If it turns out that there is a sick child, you need to immediately examine everyone who has been in contact with him. The syndrome appears more often in childhood or adolescence. But sometimes it can make itself felt even in adulthood. The first manifestations after 50 years are extremely rare.
Causes
So far, the main cause of the disease is considered to be a gene mutation . The ATP7B gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 13. It is he who is responsible for encoding P-type ATPase, which in turn transports bile and copper.
To date, about 300 mutations of this type have been described. Most often, the disease develops against the background of a small number of changes that are considered specific to such populations.
Mutations may vary depending on where the patient lives. For example, the Western mutation H1069Q is isolated, which was noted in 35-63% of cases of the disease.
In China, such changes are almost never seen. But the R778L mutation is more commonly diagnosed.
It is difficult to say whether these mutations affect the rate of progression of the pathology. However, there is evidence that with H1069Q, patients begin to suffer from neurological manifestations much later.
The disease belongs to the category of autosomal recessive. This means that patients may only receive a gene with a defect that could cause permanent changes from both parents.
If only one of the parents has it, then the child becomes a carrier of this gene. In this case, he may have mild symptoms, but there will be no noticeable manifestations.
Statistics data
Recently, more cases of the disease have been diagnosed. 0.56% of the world's population are carriers of a pathologically altered gene.
In those regions where marriages between close relatives are practiced, the incidence of the disease is higher. The incidence does not depend on gender. But in children and young people it is diagnosed more often. Symptoms may appear by age 19-20. Symptoms may be completely absent for up to five years.
If the pathology is not treated, the mortality rate is 100%. Such patients rarely live past 30. The cause of mortality is hemorrhagic complications, liver and kidney failure.
Why does our body need copper?
Copper is an important trace element for our body. It consists of many enzymes. Excess copper produces a toxic effect. Damage to cell membranes is observed, nuclear DNA is disrupted, and lysos is destroyed.
Due to a mutation in the gene on chromosome 13 (there are currently about 200 mutations), copper excretion is impaired. It collects first in the liver, and then in other tissues. The kidneys, heart, central nervous system, brain, bones, and joints suffer. Damage to the listed organs is observed. Their functions are gradually impaired.
Pathogenesis of Wilson-Konovalov disease
The main role in pathogenesis is played by the imbalance between the intake and excretion of copper. The excretion of copper through bile is significantly reduced. Because of this, it accumulates in hepatocytes.
The excretion of copper is impaired due to a deficiency or absence in the body of the protein that transports it. It is activated by the disrupted gene. In a healthy body, this protein (P-type ATPase protein) transports copper to the so-called Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes then release it into bile.
The incorporation of toxic copper into ceruloplasmin is also impaired. Its synthesis is carried out by the liver. Because of this, patients with Wilson-Konovalov disease have a critically low level of ceruloplasmin in their plasma. This is also a sign of illness.
Copper accumulates in large quantities in all organs. Since accumulation begins in the liver, all symptoms are initially associated with this organ. The first symptoms appear at 8-12 years of age.
Treatment options
Therapy is focused on reducing the intake of the substance into the patient’s body. To do this, it is recommended to exclude foods that contain copper from your diet. Lamb, pork, squid, shrimp, crab, mushrooms, dried fruits, and chocolate are removed from the menu. You can eat dairy products, fruits, vegetables, chicken, chicken eggs, and baked goods.
To reduce the copper content in the body when it is steadily increasing, medical experts recommend taking anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive medications. The treatment regimen includes choleretic drugs, antioxidants, and preparations with zinc.
The dosage is determined individually for the patient. Usually the smallest one is prescribed and the dynamics of improvements are monitored. Additionally, it is recommended to take vitamin and mineral complexes. Before purchasing these, you need to carefully study the instructions; they should not contain copper.
If drug treatment does not give the desired effect, the patient’s well-being worsens, then the only option is liver transplantation. After surgery, maintenance medications are continued.
Possible complications
It is better to start treatment immediately after identifying the disease, even when there are no obvious symptoms. This will alert the clinic and help slow the progression of the disease.
The most common complication is liver pathology. They are manifested by symptoms:
- Yellowing of the skin.
- Deformation of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities.
- Dilated veins on the anterior abdominal wall.
- Swelling of the legs.
Patients often experience bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Liver failure develops, the symptoms of which include sleep disturbances, behavioral disorders, and in severe cases, hepatic coma is observed.
Complications include neurological disorders. These are muscular dystonia, dysarthria, behavioral disorders, personality disorders, and epileptic seizures. In women, fertility is impaired.
Symptoms
In Wilson-Konovalov disease, symptoms are mainly associated with liver damage (cirrhosis, liver failure), mental disorders, central nervous system, and combined manifestations. Symptoms do not immediately indicate that Wilson's disease has begun. Only after reaching the age of five can the child show its first signs.
Symptoms include jaundice and pain in the right side. Over time, digestive problems occur.
An undeniable symptom of Wilson's disease is a yellow-brown ring located on the cornea (Kayser-Fleischer ring). This is accompanied by dysfunction of the liver, kidneys, neurology, etc.
Forecast and preventive measures
A favorable prognosis is possible only in one case - if the disease is detected at an early age, therapy with highly effective medications is immediately started. It is important to begin a therapeutic course before damage to the central nervous system and liver.
Taking medications improves liver functionality and eliminates negative symptoms from the central nervous system. Already 6 months after the start of therapy, the patient’s well-being significantly improves. More pronounced improvements are visible after 2-3 years.
If treatment is absent, started late, or the effectiveness of therapy is insufficient, then death occurs at 35-40 years of age. As a rule, the cause is liver failure. In case of serious damage to the gland, an organ transplant is required. The sooner it is done, the better the organ will take root. Survival rate among patients 20 years old is 80%.
There are no specific preventive measures, because the disease is associated with human heredity. Those who are at risk are advised to periodically visit a doctor, undergo examinations, exercise, and completely stop drinking alcohol.
Diagnostics
If Wilson Konovalov's disease develops, diagnosis is highly desirable in the early stages. Pathology can be identified using molecular genetic and biochemical examination. Held:
- Physiological research.
- Analyzes. Biochemistry in the blood can detect a decreased level of ceruloplasmin and an increased level of copper in the urine).
- Imaging methods (MRI, CT, ultrasound). They help identify spleno-, hepatomegaly, and degeneration of the basal ganglia (brain).
- Liver biopsy may reveal increased copper levels.
- Genetic testing.
Wilson-Konovalov disease can be suspected based on the following signs:
- had jaundice;
- bleeding from the nose regularly occurs;
- there are a lot of bruises;
- bleeding gums are observed;
- spider veins appear on the chest and back;
- “stripes” appeared in the armpits and on the thighs. They periodically turn from white to reddish-bluish;
- girls experience dysmenorrhea or amenorrhea;
- in young men, nipples become rough (gynecomastia);
- the chin and nose become enlarged, the lips thicken (acromegaly);
- intelligence decreases;
- mood changes frequently;
- it is difficult to learn new material, which is why the child lags behind in school.
Clinical classification
Hepatolenticular degeneration is divided by modern pediatricians into 5 clinical forms in accordance with the predominant damage to a particular organ (brain or liver) and the corresponding clinical signs of the disease. Among them are:
- extrapyramidal-cortical is caused by pronounced changes in brain tissue, manifested by the development of severe paralysis and dementia; duration without necessary treatment no more than 6-8 years;
- the trembling-rigid form is most common, lasts for 5-6 years, clinical signs correspond to the name;
- the trembling form first appears in adolescence, progresses very slowly, the patient’s psyche gradually changes, convulsive seizures are noted;
- rigid-arrhythmohyperkinetic is most relevant for patients of preschool age, manifests itself in a variety of mental and motor dysfunctions, and progresses very quickly;
- The abdominal form is characterized by predominant liver damage.
Clinical manifestations of the above described forms do not differ in children of different ages; the general principles of treatment and diagnosis are similar.
How to treat
The earlier Wilson-Konovalov began, the more severe it will be (assuming no treatment). Now there are effective methods of therapy. Proper treatment of Wilson-Konovalov disease will help alleviate the symptoms as much as possible and even eliminate them completely.
If treatment brings the desired effect, patients are able to take care of themselves, study successfully, work, and start a family. A woman can even carry and give birth under the supervision of a doctor. Such patients need to be monitored regularly.
Even if pregnancy occurs, copper chelators should not be avoided. The doctor should only reduce the dose. If a caesarean section is required, the daily dose of D-penicillamine is reduced to 250 mg.
note
Traditional medicine is powerless in the fight against Wilson's syndrome. If you are offered an “effective” folk remedy, do not believe it! By wasting time on useless self-medication, you can put the patient’s life at risk! This disorder can be successfully treated only with modern medications. It is important that the regimen is selected by an experienced doctor.
A strict diet is needed (table 5a). Its goal is to preserve liver function. You should completely exclude foods that contain a lot of copper (legumes, nuts, coffee, chocolate, etc.).
The main treatment is to regularly take medications that can remove copper. This is, first of all, D-penicillamine. Its domestic analogue is not suitable. It is highly toxic. Since you need to take the drug all your life, side effects appear over time (anemia, dermatitis, etc.). An alternative treatment using zinc salts is now offered. You can also combine drugs.
Such drugs are prescribed according to a special regimen. The dose is gradually increased. Treatment will be lifelong.
Liver transplants have begun to be practiced abroad to combat this pathology. It is used in severe cases of the disease, if conservative methods have failed. After this you will no longer need to take medications.
Hepatoprotective treatment is also extremely important. Its task is to preserve liver function as much as possible. To preserve brain function, observation by a neurologist will be required.
If you choose the right treatment methods, complete recovery (80% of all cases) or noticeable improvement is possible. But such a positive effect is observed only if the disease is detected at a very early stage. At the same time, catastrophic poisoning of organs and tissues with toxic copper has not yet occurred, and painful neurological symptoms have not appeared.
Is prevention possible?
Doctors emphasize that in the case of Wilson's disease, primary prevention is possible. It consists in the fact that tests are carried out at the embryonic stage, when the child is in the womb. The current level of development of genetics makes it possible to detect the disease already during this period.
Secondary prevention is also possible. It consists in the fact that treatment is prescribed even before the first symptoms appear. Such therapy is appropriate if the diagnosis is accurately made. It is also important to check all family members.
The patient needs to be carefully examined and a urine test performed for the presence and level of copper in it. If there are such patients in the family, their children need to be re-examined over a period of 5-10 years (starting from the age of six).
If a patient is diagnosed with this and receives systematic treatment, he should be constantly monitored by a gastroenterologist. He carefully monitors changes in the patient’s condition and the body’s reaction to medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease are carried out by a gastroenterologist, nephrologist and hepatologist. Since pathology is directly related to neurology and genetics, appropriate specialists are also involved in conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient. In addition, they resort to professional consultations with an ophthalmologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, and rheumatologist. Only through the joint efforts of these highly specialized specialists is it possible to make a correct diagnosis and identify the patient for observation in a special medical institution.