Hypoglycemia is a one-time or regular decrease in blood sugar to 3.9 mmol/liter or less, as a result of pathologies of the endocrine, cardiovascular or other systems.
Occurs relatively often. Moreover, the process is essentially opposed to diabetes, which is not entirely correct.
In one patient, conditions can change quite quickly, depending on which mechanism in the body prevails here and now. A lot of insulin comes in - sugar drops. Little - it increases. In particular, this may be the result of illiterate treatment of diabetes.
Hypoglycemia is very dangerous because it carries the risk of loss of consciousness, hypoglycemic coma and death from multiple organ failure. When all systems suddenly stop working.
Treatment is necessary. The essence of therapy is to normalize blood sugar levels and eliminate the primary cause of the disorder. The correction is carried out by endocrinologists.
All the necessary information about the disease
A person’s condition directly depends on the level of glucose in the blood. If the values drop to 1.9-2.2 mmol/l in women and to 2.5-2.8 mmol/l in men, a hypoglycemic state occurs. In people with diabetes, such jumps in indicators are not uncommon. This poses a particular danger to the brain. He is the most sensitive in this aspect. Glucose levels are regulated in the body by a number of metabolic processes. In a healthy person, hypoglycemia does not occur because the liver contains a sufficient amount of glycogen.
Mechanism of blood glucose formation
After eating carbohydrate foods, the body receives glucose, which is carried by the blood to all cells. As soon as glucose begins to enter the blood (absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract), the pancreas begins to secrete the hormone insulin, which helps cells use the incoming sugar as an energy source. In healthy people, the amount of glucose supplied and the insulin response are always equal to each other.
In patients with insulin-dependent diabetes, the pancreas is not able to produce the required amount of insulin, and they must inject it externally, and in the correct dose.
What are the varieties?
It is worth noting that hypoglycemia itself is not a disease in the classical sense. This is a condition that occurs due to certain factors and accompanies different types of diseases. Most often we are talking about diabetes mellitus. In medical practice, there are several stages of this condition:
- easy (a person can help himself independently);
- medium (requires help from other people);
- severe (the most severe stage, when a person falls into a hypoglycemic coma).
Consequences
Complications of hypoglycemia are dangerous and often irreversible. Among them:
- Brain disorders. Damage due to hypoxia. Dementia, memory, thinking, concentration disorders.
- Neurological deficit. General and focal.
- Injuries due to fainting.
- Coma, stupor. It is almost impossible to bring patients out of these conditions.
- Death or severe disability.
Hypoglycemia is a dangerous pathological process; it is secondary to the underlying disease. It makes sense to get tested and as quickly as possible. Health and life are at stake.
Possible complications
Signs of hypoglycemia should not be ignored. The deterioration of the condition develops quickly. The worst complication is coma, when a person does not receive timely help and the blood sugar level drops below minimum values. Among the complications, it is necessary to highlight the negative impact on small peripheral vessels that are subject to destruction. The legs and eyes are at risk. The legs and eyes are the first to be affected. Over time, blindness and angiopathy (pathology of the retinal vessels of the eye) may develop. If the sugar level drops below 2 mmol/l, the brain is at risk.
Signs of hypoglycemia by frequency of occurrence:
- Sudden general weakness;
- Feeling hungry;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Sweating;
- Hand trembling;
- Unmotivated aggression and nervousness;
- Dizziness;
- Double vision, colored circles;
- Drowsiness;
- Confusion of speech and understanding of what is happening;
- Fainting;
- Coma;
- Death.
No matter how scary it sounds, this is exactly the scenario that unfolds if help is not provided in time!
Hypoglycemia during sleep
A drop in blood sugar can also happen during sleep. The main symptoms are a sudden awakening from nightmares, sweating, down to a wet sheet. If a person does not wake up in the middle of the night, then the morning symptoms of the condition are fatigue and weakness.
Hypoglycemia in children
The causes of this condition in children are:
- diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems, incl. diabetes;
- unbalanced diet;
- stress;
- physical overload.
In addition to the above, there are 2 fundamental reasons for the development of childhood hypoglycemia:
- Increased levels of ketone bodies in the blood. Such children experience a peculiar acetone odor from the mouth, constant dizziness, vomiting, and fainting caused by the toxic effect of acetone.
- Congenital intolerance to leucine, an amino acid that is part of protein, requiring a special diet. Main symptoms: lethargy, sweating, pale skin, drowsiness.
Frequent hypoglycemic attacks negatively affect the intellectual and physical development of children. Relief of hypoglycemia in children is carried out in the same way as in adults. If you are intolerant to leucine, avoid foods such as eggs, fish, nuts, milk and others containing leucine.
Information about diagnosis and treatment
It is quite simple to notice and determine a change in condition, which is due to characteristic symptoms. For this reason, diagnosis of hypoglycemia is based primarily on an initial analysis of the patient’s condition. After the examination, a number of tests and studies are prescribed to clarify the etiology and diagnosis:
- blood and urine tests;
- study of blood glucose concentration;
- biochemical blood test with determination of albumin and protein;
- urine glucose test;
- insulin level studies;
- assessment of the function of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland and pituitary-adrenal system;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
How to prevent hypoglycemia in type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- Know by heart how to treat this condition and its signs.
- Know your insulin dose and do not exceed it.
- Follow the diet and injection schedule.
- Measure fasting blood sugar in the morning, before every meal and before bed.
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Always carry with you special glucose tablets or any product with simple carbohydrates (sweet caramel, chocolate, dried apricots).
- If you need to take any medications, carefully read how they affect the level of insulin and blood sugar (aspirin, allopurinol, warfarin, probenecid and other drugs enhance the effect of insulin).
Author:
Sabuk Tatyana Leonidovna hygienist, epidemiologist
Self-monitoring of general condition
Hypoglycemia is a condition that can be self-controlled when it is mild. Thus, people with type 1 diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels without the help of doctors and make the necessary adjustments. The diet for hypoglycemia consists of consuming foods with a low hypoglycemic index. It is recommended to avoid those foods that can cause a sharp jump in blood glucose levels. This list includes candies, cookies, cakes and other sweets with fast carbohydrates. They can be used in small quantities if the condition worsens.
Help for hypoglycemia – pre-hospital and in-patient care
To quickly help the body, tablets containing d-glucose (dextrose) or glucagon are produced. All diabetics and people living with them must know the instructions for these medications. Patients prone to hypoglycemia should always carry such medications with them!
In a state of sugar deficiency, both a lack of compensation and an excess of glucose are dangerous. An overdose of glucose inevitably leads to subsequent hyperglycemia, which is no less dangerous for a diabetic.
Providing assistance should begin with measuring blood sugar with a household meter in order to confirm the lack of blood glucose. Blood sugar should also be measured as care is provided. If this is not possible, you should immediately begin to relieve the condition.
Mild degree
You can relieve your condition on your own by taking 12-15 grams of simple, easily digestible carbohydrate orally from the list below:
- d-glucose (tablets). The most preferable method with a predictable scenario for the turn of events, i.e. a gradual increase in blood glucose. 1 gram of glucose increases blood sugar by 0.22 mmol/l. Knowing the initial blood sugar numbers, it is easy to calculate the required dose of tablets;
- 150 g of sweet fruit juice or sweet drink;
- warm tea with 2 teaspoons of sugar;
- 1 banana;
- 5-6 cloves of dried apricots;
- a couple of milk chocolate slices or 1 candy;
- 2 teaspoons honey or sugar (dissolve);
- 2 pieces of refined sugar.
Attention!!! Eat or drink one of the suggested options! The specified quantity must not be exceeded.
If after 15-20 minutes the blood sugar has not increased, and the condition remains unsatisfactory, you should again take 15-20 grams of simple carbohydrate. A person’s condition improves within an hour after taking light carbohydrates, i.e. Don't expect instant relief after taking a glucose tablet.
Severe degree
- Quickly give a person 12-15-20 grams of easily digestible carbohydrate. After 20 minutes, a person should eat another 15-20 grams of complex carbohydrates (bread, crackers, crispbread, porridge).
- If a person is very disinhibited, can swallow, but is no longer able to chew, glucose should be given in the form of a solution, dissolving the required number of tablets in a small amount of water. Or just offer sweet water.
- Glucose is sold abroad in a gel-like state, which can be used to lubricate the oral cavity, where sugar quickly begins to be absorbed into the blood.
Hypoglycemic coma
If a person is unconscious or his consciousness is confused, oral intake of liquids and other products is excluded! You should call an ambulance.
First aid consists of an intramuscular injection of 1 ml of glucagon - express kits with 1 syringe and the drug are sold in pharmacies. In a hospital setting, treatment of hypoglycemia is carried out with intravenous administration of glucose 40%. If the condition does not resolve, they resort to subcutaneous injection of adrenaline and other resuscitation measures.
Why does it occur
The causes of the disease can be very different, however, most often it is a question of the fact that the human body simply produces too much insulin. However, the causes of hypoglycemia may be other. The result of this is a phenomenon in which the normal process of converting carbohydrates into glucose is disrupted, which leads to the formation of a hypoglycemic state.
However, if we study the causes of hypoglycemia, then the most widespread cause is diabetes mellitus. However, medical practice also records other causes of hypoglycemia. And we should consider in more detail those conditions in which a person may be subject to such a pathology:
- the gastrointestinal tract is subject to the development of certain neoplasms;
- a person takes a large number of certain medications (here may be sulfur preparations, quinine, various drugs for getting rid of diabetes);
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, and this form of the disease is one of the most dangerous, here a person can fall into a state of stupor or his mind may become seriously clouded;
- the body is exposed to excessive physical activity;
- a person does not eat properly; his diet is dominated by foods that contain large amounts of carbohydrates;
- the body is affected by various types of severe infectious diseases;
- the presence of renal or heart failure;
- the body is subjected to prolonged fasting;
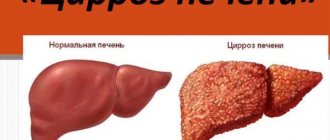
- the liver begins to function with certain disturbances, cirrhosis may occur, enzymes are not produced properly;
- metabolism is impaired;
- the adrenal glands are susceptible to pathological processes;
- the body does not receive the required amount of water, that is, dehydration occurs;
- may be due to a birth defect;
- thyroid function is reduced;
- blood circulation is accompanied by a severe form of insufficiency;
- Alanine synthesis is insufficient.
It should be noted that no matter what the cause of hypoglycemia, you must always closely monitor your health in order to identify any violations in time.
Hypoglycemic coma
At the last stage of hypoglycemic syndrome, coma occurs (loss of consciousness, impaired respiratory function and heartbeat). The reason for this is severe glucose deficiency in the nerve cells of the brain, which leads to their swelling and damage to the cell membranes.
Distinctive signs of this condition are:
- acute onset;
- profuse sweating on the skin;
- absence of acetone odor from the mouth;
- motor activity, convulsions.
Hypoglycemic coma can lead to irreversible pathological changes in the central nervous system and cerebral edema. If glucose deficiency persists for a long time, death occurs. Frequent episodes of severe hypoglycemia later manifest themselves in the form of personality changes, memory loss, psychosis, and mental retardation.
Thermoregulation disorders
The shortage of “universal fuel” has a bad effect on the condition of all organs and systems of the human body. During an attack of hypoglycemia, the patient may experience chills and complain of coldness in the fingers and toes. Cold sweat may occur (the back of the neck and the entire scalp sweat). If an attack of hypoglycemia occurs at night, the whole body sweats profusely: the person wakes up in completely wet underwear.
Source: depositphotos.com