Chorea is a pathological disease of the nervous system in which signs of hyperkinesis of different muscle groups develop. Hyperkinesis manifests itself in erratic, chaotic and sweeping movements, similar to normal movements, but the gestures are very pretentious and abrupt.
Most often, choreic hyperkinesis affects children and adolescents and is congenital; in adults, from 30 years of age, the disease is acquired.
Chorea occurs due to disruption of the ganglia of the brain, as well as the cerebellar nuclei - this occurs under the influence of certain factors. Such pathological phenomena disrupt the process of dopamine transmission, which leads to chaotic uncontrolled muscle movements.
Huntington's chorea, what kind of disease is it?
According to its typology, Huntington's chorea is a neurodegenerative disease during which a person experiences elongation of repeats of the gene that is responsible for the huntingtin protein. Until now, scientists have not been able to unambiguously establish the function performed by the protein. However, in medicine there are certain standards that indicate the length of triplets (genes) in a healthy person.
Huntington's chorea, what kind of disease is it from the point of view of complex human genetics? In healthy people, the number of repetitions of the huntingtin protein varies depending on age and other characteristics in the body, ranging from 11 to 34 triplets. When diagnosing Huntington's chorea, the number of repetitions starts at 37 and can reach 100 triplets. This gene defect does not begin to appear from birth, but only after a person reaches the age of 30-40 years.
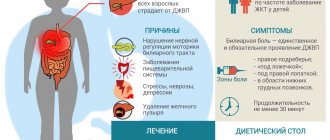
Symptoms
In medicine, there are several symptoms that are characteristic of any type of chorea:
- involuntary movements of the limbs (an important diagnostic symptom);
- head twitching;
- decreased muscle tone;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- grimacing;
- gesticulation is increased;
- if you ask a person to write something, you can notice a change in handwriting;
- memory loss;
- hyperkinesis in this disease disappears during sleep;
- dancing gait;
- temperature increase;
- all the movements that a person tries to control, he performs with great difficulty.
Choreic hyperkinesis
Huntington's chorea disease
Scientists have proven that in more than 90% of patients worldwide, Huntington's chorea is diagnosed at the age of 40-50 years. It is during this period of life that the patient begins to actively manifest all the symptoms and signs of a gene disease that cannot be stopped. Currently, this disease is considered incurable, since it manifests itself against the background of a violation of the genetic structure of the brain. Treatment of chorea is based on the principle of making life easier for the patient and reducing the manifestation of symptoms associated with dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system.
Throughout the world, the disease varies in the length of time a person survives after diagnosis. The average life expectancy of a patient with Huntington's chorea is 15 years. Such a long period is observed only in people receiving constant conservative treatment. Those patients who do not receive proper treatment and are not observed by specialists live no more than 7-9 years.
Folk remedies
Photo: beardoholic.com
Chorea is a serious disease that requires medical attention. Under no circumstances should one assume that folk remedies can save a person from this illness. As was written earlier, sedatives are used in the treatment of chorea. Many of them are based on plant components. Therefore, they can be safely replaced with traditional medicine.
There are many folk recipes that have a sedative effect:
- Infusion of oregano, calendula and tansy. To prepare a soothing mixture, you will need to mix the listed herbs in equal quantities, pour boiling water over it, wrap it up and let it brew for at least half an hour. After preparation, the infusion is used three times a day, 100 ml. For one glass of boiling water you will need 1 tablespoon of the mixture.
- An infusion of lemon balm leaves is also easy to prepare. To do this, you will need 3 tablespoons of crushed lemon balm leaves, which are poured with a glass of boiling water and simmered in a water bath for 10 - 15 minutes. After which the infusion should be cooled and strained. You need to consume 100 ml twice a day.
It’s even easier to make lemon balm tea, which is no less beneficial than the infusion.
Mint is very popular, and many people grow it in their summer cottage. To prevent such a wonderful herb from going to waste, you can brew tea using it. This tea will not only improve your mood and relieve irritability, but also help you fall asleep quickly.
There is another sedative based on honey and beet juice. To prepare it, you need to mix beet juice and honey in half. The resulting mixture should be taken 0.5 cups 3 times a day for 10 days, after which a break is taken.
Herbal baths before bed are also effective. For example, to prepare one of them you will need 1 kg of herbs (wormwood, linden, rosemary). After mixing, the herb is poured with 4 liters of cold water, then boiled over fire for 5 minutes and infused for the next 15 minutes. After preparation, the resulting broth is filtered and poured into a warm bath.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Symptoms of Huntington's chorea
Most often, the onset of symptoms occurs in adults over 30 years of age, but there are always exceptions and the disease may begin to develop earlier. All symptoms appear mild at the very beginning of the disease and begin to progress over time. The main symptoms of Huntington's chorea are as follows:
- It is very difficult to diagnose a specific disease for an ordinary person or a relative of the patient, since during the first 6-12 months chorea may simply resemble a person’s increased fussiness or restlessness.
- After the development of the first symptoms, the intensity of disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system gradually begins to increase.
- Even in a calm state and without physical activity, a person can experience sudden cramps in the upper and lower extremities of the body. One of the symptoms is spasms of the facial muscles, which appear during conversation or look like grimacing. Over time, increased gesticulation begins to appear, becoming out of place. Attention and thinking become scattered, confused and difficult.
- At an advanced stage of the disease, an unsteady gait, reminiscent of a person in a strange dance, is added to the symptoms. This occurs due to impaired coordination of the musculoskeletal system under load.
Causes
Chorea develops against the background of damage to the central nervous system, which in turn can be caused by various diseases, injuries or poisoning. There are also diseases whose main symptoms are choreic. Such diseases include Huntington's chorea and Sydenham's chorea. A common cause of the described syndrome is also a violation of cerebral circulation, mainly as a result of stroke, ischemic and hemorrhagic. Chorea can also accompany other diseases, such as AIDS, antiphospholipid syndrome or toxoplasmosis.
Signs of Huntington's chorea
Unlike the symptoms of the disease, the signs of Huntington's chorea can only be recognized by a professional doctor. In medical practice, to make a diagnosis, it is necessary to identify 3 groups of characteristic signs of nervous and mental disorders in a patient. They are the most common, and begin to appear after a person’s motor reflexes are impaired. Neuropsychiatric signs are conventionally divided into 3 subgroups:
- signs of impaired cognitive function, which most often affect orientation in space and visual touch of objects. Emerging problems prevent the sick person from seeing normally the image or picture happening around him. Every day it becomes more and more difficult to recognize any schematic drawings, elements on a TV screen or letters in a newspaper;
- signs associated with impaired consciousness or impaired intellectual function of the patient. Memory failures appear, but this does not affect the ability to remember information from the past, but the performance of the brain. A person can no longer, as before, be productively engaged in several things. The patient experiences difficulties when planning his time or organizing activities;
- signs manifested in violation of emotional and behavioral functions. The patient may notice sudden outbursts of aggression or irritability that were not caused by anything. Almost half of patients suffer from depression, but they themselves do not realize it.
Diagnosis of Huntington's chorea
If a person complains of the above symptoms, and relatives or friends observe the development of all signs of the disease in the patient, then the diagnosis of Huntington’s chorea first begins with a trip to the doctor and prescribing a genetic test for the patient.
Diagnostics will allow us to identify a pathological gene in a person that led to the development of Huntington's chorea. Only in this case can we talk about confirming this diagnosis. In addition to genetic research, computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the cerebral cortex are used as types of disease diagnosis in medical practice.
A complex genetic study consists of DNA analysis, based on the results of which a doctor can judge whether a person has an abnormal gene. The disease can be inherited, since with a probability of more than 50% repeated genes are passed on to children from one of the affected parents.
Patient assistance
If chorea is confirmed, the doctor prescribes the following treatment:
- medications are prescribed that help absorb copper to a lesser extent, the excess of which is a consequence of genetic predisposition;
- Antibacterial therapy is prescribed for severe Genington's chorea;
- tranquilizers and neuroleptics reduce the manifestation of hyperkinesis, and also reduce emotional and intellectual disorders;
- drugs that normalize blood pressure levels, necessary for impaired blood supply to the brain;
- reducing the dosage or abandoning antiemetic medications prescribed by psychiatrists;
- for inflammatory processes in the brain, hormonal drugs are prescribed;
- in extreme cases, brain surgery is prescribed, after which the patient’s uncontrolled movements decrease.
Also, in addition to medications, vitamin therapy and physical therapy are prescribed as auxiliary methods that will help reduce the symptoms of the disease.
Treatment and rehabilitation is a very difficult process. When therapy is carried out at the initial stage of the disease, there is a chance to stop the progression of the disease.
Treatment of Huntington's chorea
The disease is a genetic disorder of a person, so there is currently no specific treatment for it. All the efforts of doctors can be aimed at maintaining a person’s mental balance, as well as eliminating movement and behavioral disorders. Thanks to special medications, it is possible to minimize problems with a person’s gait or being in society.
To treat and prevent the development of Huntington's chorea, complex treatment is used, but only after a deoxyribonucleic acid test and medical genetic counseling. The mutant gene cannot be treated, and it is important in the initial stages of the disease not to confuse it with schizophrenia, hereditary ataxia or Alzheimer's disease. This is precisely why DNA analysis is performed, since in other mental disorders the number of trinucleotide repeats does not increase.
History of the term
At this stage of development of medicine, three main names are used:
The first term has been known since medieval times and was coined by people far from medicine and the peculiarities of neurology.
Saint Vitus is a historical character known to all Orthodox people who lived during the defeat of the Roman Empire. Saint Vitus was a young righteous man who died as a result of the persecution of Emperor Diocletian against all representatives of the Christian faith. After more than a millennium, the name of this saint began to be associated with “dance”, as a result of which a certain belief even appeared in Germany.
Its essence was that every person who dances next to the statue of St. Vitus on June 15 (his memorial day) will receive a boost of energy for the whole year ahead. This led to the fact that every year there was a queue of many kilometers at each statue of the saint, and most of the dances were quite expressive.
The second term appeared from the lips of professional neurologists, who decided to call uncontrollable movements chorea.
In turn, the third term has been known to people since 1872, when George Genington presented a detailed description of all the features of this disease at the Medical Scientific Society held in Ohio.
Medicine to treat Huntington's chorea
Until now, there is no medicine in the world that could completely cure a person from Huntington’s chorea. But the whole essence of treatment in modern medicine comes down to reducing the symptoms of the disease. Medicine for the treatment of Huntington's chorea, more precisely for the elimination of disorders associated with behavioral and motor functions, can be selected from 3 main pharmacological groups of prescription drugs:
- Phenotosians help block dopamine receptors in the human body. Most drugs from this group, for example, Promethazine or Fluorophenazine, suppress the functioning of human histamine and serotonin receptors.
- The haloperidol group of drugs is aimed at reducing behavioral disorders. The drugs have antipsychotic properties, help block dopamine receptors in the human body and partially restore behavioral functions. However, while taking potent drugs, the patient very often develops side effects such as constant drowsiness, sudden motor movements that are beyond the patient’s self-control, and a decrease in the muscles of the whole body.
- A group of benzodiazepines as part of medications is prescribed to patients to reduce the body’s convulsive reactions. In addition, benzodiazepine-based drugs help the patient sleep better. The effect of such drugs is achieved by inhibiting GABA (aminobutyric acid) receptors, which are stimulated by the nervous system.
Huntington's Chorea Clinic
Treatment of the disease should be carried out only under the guidance and supervision of doctors at a psychiatric clinic. A genetically complex disease can manifest itself differently at any time, so it is important not to miss the moment when symptoms begin to appear. A Huntington's chorea clinic should specialize in neurological disorders in humans.
A slowly progressing disease of the nervous system and cerebral cortex is incurable, but a person with such a diagnosis must be constantly under the supervision of a specialist who can correctly calculate and apply a medication in an emergency. Sick people require careful care, as well as the supervision of doctors such as psychiatrists, neurologists, psychologists, ophthalmologists and orthopedists.
Forms
- hereditary forms. This includes Huntington's chorea. This hereditary disease comes in two types: chronic with late onset and non-progressive with early onset;
- chorea in extrapyramidal diseases. This type often develops with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, hepatocerebral dystrophy;
- secondary forms. They occur when the basal structures of the brain are damaged. The reasons may be different - infection, trauma, etc. Secondary forms include minor chorea. It develops due to streptococcal infection entering the circulatory system. The source can be carious teeth and inflamed tonsils. “Target organs” for infection: joints, heart valves, brain. The disease in most clinical cases affects young children whose bodies are weakened. It is characterized by a relapsing course.
Huntington's chorea
Clinical guidelines for Huntington's chorea
The list of basic recommendations should be compiled individually after examining the sick person by a psychiatrist and neurologist. The main clinical recommendations for Huntington's chorea are highlighted, which must be followed while in the hospital or when the patient is at home. The patient should regularly receive drugs that reduce the activity of dopamines in the cerebral cortex, the dose being increased every 3 days.
Parents, one of whom has been diagnosed with a genetic disease, are not recommended to have children. The probability of inheriting Huntington's chorea exceeds 50%; if pregnancy occurs, a DNA test is required for the unborn child. Statistically, people with Huntington's chorea most often die from pneumonia, cardiac activity, or other congestive processes in the body, so it is important to promptly treat any secondary diseases.
Rheumatic chorea - complications
Associated complications of CC:
- arthritis
- joint pain
- inflammation of the heart valves leading to irreversible damage
- ongoing fever
Symptoms of CC usually last from 3 weeks to 6 months. And although almost everyone recovers, symptoms can persist for up to 2 years.
RH can recur, according to NORD, young women in the first trimester of pregnancy have a higher chance of experiencing symptoms of recurrent rheumatic chorea.