A concussion can be caused by an unfortunate fall or blow. With such an injury, the work of the reticular activating system, which is responsible for consciousness, information processing, sleep and awakening, is disrupted.
A person may not immediately realize that a concussion has occurred - symptoms may take several days or even weeks to appear, so it is imperative to provide first aid and consult a doctor to exclude brain contusion, hemorrhage and swelling, which are more dangerous consequences of a head injury.
Description
As a result of contact of the brain substance with the cranial bones, the following usually happens:
- changes in a number of chemical or physical characteristics of neurons, due to which the spatial organization of protein molecules may change;
- The substance of the brain of the head as a whole is susceptible to pathological influence;
- temporary separation of signal transmission and relationships between synapses (a synapse means the place of contact of two neurons or a neuron and an effector cell receiving a signal) of cellular neurons and parts of the brain. This contributes to the appearance of functional defects.
Degrees of concussion
Depending on how serious the patient’s condition is and what clinical signs are observed, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- Mild concussion. Consciousness is not impaired. The victim may experience dizziness, disorientation, nausea, and headache during the first twenty minutes after injury. Symptoms of a mild concussion go away quickly. Then general health returns to normal. The temperature may rise briefly (up to 38 degrees).
- Moderate degree of concussion. There is no loss of consciousness, but pathological signs such as nausea, headache, disorientation, and dizziness are present. They all last longer than twenty minutes. Also, with a moderate concussion, amnesia (short-term memory loss) may occur. It is predominantly retrograde in nature with the loss of several minutes of memories immediately before the injury.
- A severe concussion is very dangerous. Loss of consciousness necessarily occurs for a short period of time, usually from several minutes to several hours. In this case, the patient does not remember what happened to him - retrograde amnesia occurs. For one to two weeks after a grade 3 concussion, a person is bothered by pathological symptoms: nausea, disorientation, headache, sleep and appetite defects, dizziness, fatigue.
Relevance of the problem
In the structure of brain injuries, concussion accounts for about 70–80%. Its social and medical significance is due to several reasons:
- A wide variety of types of injuries - domestic, industrial, transport, children's, sports, etc.
- The difficulty of diagnosis in the absence of loss of consciousness or due to the presence of alcohol intoxication accompanying the concussion (in 30% of cases), osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, hypertension, chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency, especially in the elderly, and other diseases. Moreover, in such cases, underestimation of symptoms or, conversely, overdiagnosis occurs in 50%. The difficulty of diagnosis is often also due to the lack of specificity, insufficient and unpredictable dynamics of symptoms.
- Insufficient qualifications of non-specialized medical personnel.
- The immediate and especially long-term consequences of a concussion, called post-concussion (after a concussion) syndrome.
According to WHO data, about 20–30% of people who have suffered a concussion suffer from unmotivated irritability, fatigue, causeless headaches and dizziness, vascular disorders, and short-term episodes of disorientation. Sometimes the aggravation of these processes leads to cognitive problems, that is, mental disturbances in the perception and processing of information coming from outside.
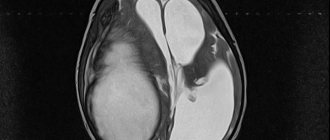
Similar brain dysfunctions have been found in people suffering from schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, autism and some other mental disorders. When testing using MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), in most cases, structural changes were found in the parts of the brain responsible for processing and remembering information. The reasons that caused such changes in the mental activity of the brain in some people who suffered a skull injury, and their absence in others, have not been established.
These facts confirm the importance of the need for treatment not only in severe cases, but even in the treatment of mild concussions.
Signs and symptoms
A concussion is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Consciousness is depressed immediately after contact with a traumatic force. And this is not necessarily a loss of consciousness, it may be stupor (stunning), a kind of incomplete consciousness. The defect of consciousness is short-term, lasting from several seconds to several minutes. This period most often reaches five minutes. If the victim is alone at this time, he will not even be able to say that he lost consciousness, since he simply does not remember it.
- Amnesia (memory defect) for events that preceded the concussion, the concussion itself and a short time period after it. However, memory is restored quickly.
- Single vomiting after injury. Vomiting is of cerebral origin, it most often does not recur and is used as a clinical way to distinguish a concussion from a mild bruise.
- Slower or faster heart rate and higher blood pressure for a period after injury. These changes usually go away on their own and do not require drug treatment.
- Immediately after the concussion, breathing quickens. It normalizes earlier than the indicators of the heart and blood vessels, so this sign may go unnoticed.
- Body temperature does not change (the absence of changes is also a differential diagnostic criterion for head contusion).
- A specific “vasomotor game”. This is a condition in which the paleness of the facial skin changes to redness. It occurs due to a violation of the tone of the nervous autonomic system.
When consciousness is fully restored, the following signs appear:
- headache (can be felt both at the site of injury and in the head as a whole, has a different character);
- noise in ears;
- sweating (wet feet and palms all the time);
- dizziness;
- flushing of the face, accompanied by a feeling of heat;
- general malaise and weakness;
- sleep disorders;
- decreased concentration, accelerated physical and mental fatigue;
- staggering while walking;
- High sensitivity to bright light and loud sounds.
Neurological disorders, especially with severe concussion, are as follows:
- pain when moving the eyeballs to the sides, inability to move the eyes to the extreme position;
- in the first hours after injury, a slight narrowing or dilatation of the pupils may be detected, while their reaction to light is normal;
- slight asymmetry of skin and tendon reflexes; they differ when evoked on the right and left. Moreover, this sign is quite labile, for example, during the initial examination, the left knee reflex is somewhat more lively than the right; upon repeated examination, literally a few hours later, both knee reflexes are identical, but a difference in the Achilles reflexes appears;
- horizontal small nystagmus (shaking involuntary movements) in the most extreme positions of abduction of the eyeballs;
- unsteadiness of the patient in the Romberg position (straight arms extended forward to a horizontal level, legs together, eyes closed);
- There may be a slight tension in the muscles of the back of the head, which goes away within three days.
A significant diagnostic criterion for mild concussion is that the symptoms are reversible (except for subjective ones). All neurological signs disappear within a week. Asthenic complaints of dizziness, poor memory, headache, weakness, and fatigue are not included in this count, as they may persist for some time.
It should also be noted that a concussion of the head is never accompanied by fractures of the cranial bones, even if it is a small crack. If there is a bone fracture, the diagnosis in any case is at least a mild degree of brain contusion.
How is the severity of damage to health determined from a concussion?
Diagnosis of pathology
This diagnosis is almost entirely clinical, since the main criteria for diagnosis are clinical signs. It is quite difficult to recognize the disease in cases where there are no witnesses to what happened, since most complaints in this condition are subjective in nature, and the patient himself does not always remember the change in consciousness. In this case, external head injuries come to the rescue.
The degree of concussion in adults is determined based on the history of the time of loss of consciousness and injury, patient complaints, results of a neurological examination and instrumental examinations. In the immediate period after the injury, in the neurological status, unstable and slight asymmetry of reflexes, small-scale nystagmus are observed, in young victims - Marinescu-Radovic syndrome (muscular homolateral contraction of the chin against the background of irritation of the eminence of the thumb), sometimes mildly manifested meningeal (meningeal) symptoms. Since more serious brain disorders can be hidden under a concussion, great importance is given to monitoring a person over time. With a correctly established diagnosis, deviations identified during examination by a neurologist disappear 3-7 days after the incident.
Diagnosis in children and the elderly
Particular attention should be paid to diagnosing concussion in infants and young children, since it often passes without disturbances of consciousness:
- the skin turns pale at the time of injury (primarily the face), the heartbeat quickens, followed by drowsiness and lethargy;
- Infants experience vomiting and regurgitation during feeding, sleep disturbance and anxiety are noted; all manifestations disappear after 2-3 days;
- In preschool children, a concussion most often resolves without loss of consciousness, and the condition generally improves within 2-3 days.
In elderly patients, primary loss of consciousness during a concussion is much less common compared to middle-aged and young people. At the same time, pronounced disorientation in time and space quite often occurs. Headaches are often pulsating in nature and localized in the occipital region. Such disturbances occur from three to seven days and are very intense in patients who suffer from hypertension. In this case, patients need to pay special attention during the examination.
In case of a concussion, additional diagnostic methods are carried out for differential diagnosis to confirm the functionality of changes in the brain of the head. With any more severe traumatic brain injury, structural abnormalities are found in the brain, but this does not happen with a concussion.
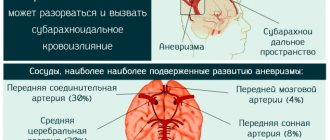
For example, if a patient has tension in the muscles of the back of the head, which is a symptom of irritation of the meninges, it becomes necessary to confirm the absence of subarachnoid hemorrhage. For this purpose, a spinal puncture is performed. In case of a concussion, the results of the analysis of the obtained cerebrospinal fluid do not differ from normal values, which makes it possible to exclude such a diagnosis as subarachnoid hemorrhage (if it exists, a blood impurity is found in the cerebrospinal fluid).
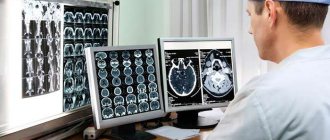
Computed tomography, as the main research method for traumatic brain injuries, also for concussions, does not detect pathological changes, thereby confirming the correctness of the diagnosis. By analogy, neither echoencephalography nor MRI detect abnormalities if a person has a concussion.
The next retrospective confirmation of the correct diagnosis is the disappearance of neurological symptoms within a week after the injury to the victim. With a mild concussion, they go away almost immediately.
What it is?
Concussion is damage to the bones of the skull or soft tissues, such as brain tissue, blood vessels, nerves, and meninges. An accident can happen to a person in which he can hit his head on a hard surface, this is precisely what entails such a thing as a concussion. In this case, some disturbances in brain function occur that do not lead to irreversible consequences.
As already mentioned, a concussion can be caused by a fall, a blow to the head or neck, or a sudden slowdown in head movement in the following situations:
- at home;
- in production;
- in a children's group;
- when practicing in sports sections;
- in case of traffic accidents;
- in domestic conflicts with assault;
- in military conflicts;
- with barotrauma;
- for injuries with rotation (turning) of the head.
As a result of a head injury, the brain changes its location for a short time and returns to it almost immediately. In this case, the mechanism of inertia and the peculiarities of fixation of brain structures in the cranium come into force - not keeping up with the sudden movement, some of the nerve processes can stretch and lose connection with other cells.
The pressure in different parts of the skull changes, and the blood supply, and therefore the nutrition of nerve cells, may be temporarily disrupted. An important fact about concussion is that all changes are reversible. There are no ruptures, hemorrhages, or swelling.
First aid to the victim
If the victim is unconscious, you should immediately call an ambulance. An unconscious patient should be placed on the right side on a hard surface with elbows and legs bent. Throw your head up, turn it towards the ground - this position allows you to ensure excellent airflow through the respiratory tract, prevents aspiration, that is, the entry of foreign substances into the respiratory tract when inhaling, liquid during vomiting.
If a person is bleeding from a head wound, a bandage must be applied to stop it. If the victim has regained consciousness or has not fainted at all, he needs to be laid horizontally, his head raised, his consciousness monitored all the time and not allowed to sleep.
Not everyone knows what the severity of a concussion is. It is important to remember that all patients with a head injury, regardless of their health and severity, must be taken to a trauma center. The traumatologist will decide whether they can be monitored on an outpatient basis by a neurologist, or whether hospitalization in the neurological department is required for the purpose of monitoring and diagnosing the condition.
It should also be noted that if the victim loses consciousness and is unable to independently determine the degree of severity, it is recommended not to touch it at all, not to try to turn it again or turn it over. If there are factors that threaten human life, for example, bulk substances, liquids, small objects that can get into the respiratory tract, they need to be eliminated.
Caring for a Patient with a Mild Concussion
After an injury, the victim can walk on the first day; he does not have to constantly lie down. First, you should insure the person, especially if his movements are unstable. If the victim remains at home, he needs to be woken up 2-3 times during the night.
During the day, you need to constantly talk with the person, monitor the adequacy of his answers to any questions. At home, there are no restrictions on the patient’s diet. The only exception is alcohol consumption. If you have pain, you can use any over-the-counter analgesics.
Drug therapy
In case of 1st and 2nd degree concussion, drug treatment should be careful. It is mainly necessary to prescribe symptomatic medications to the patient:
- painkillers to eliminate headaches (combined drugs such as Solpadeine, Pentalgina, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- drugs to relieve dizziness (Platifillin with Papaverine, Vestibo, Betaserc);
- sedatives (to calm the nervous system), their range is quite wide, depending on the individual need in each case: from plant extracts to tranquilizers;
- for insomnia - sleeping pills;
- general health-improving drugs (antioxidants, vitamins, tonics).
Metabolic maintenance of the brain is carried out through neuroprotectors. These include a large group of medications. For example, it could be “Nootropil” (“Piracetam”), “Pantogam”, “Encephabol”, “Glycine”, “Picamilon”, “Actovegin”, etc.
On average, the patient will have to spend about a week in a hospital setting, and then he will be discharged and treated on an outpatient basis. In addition to symptomatic medications, at this time medications are prescribed that improve blood supply to the brain (Nicergoline, Trental, Cavinton, etc.).
Some patients will need a month of drug treatment for complete recovery, others – three months. But in any case, if all the points listed above are observed, recovery occurs.
Within a year after a concussion occurs, you need to be periodically examined by a neurologist, who will conduct follow-up monitoring of the patient.
Is outpatient treatment possible for varying degrees of concussion severity?
What medications should I take?
Treatment of a mild concussion is impossible without medications.
The prescription course includes many medications:
Phenazepam, Elenium and other sedative drugs. They normalize the activity of the nervous system.
Analgesics - Pentalgin, Analgin and others. Medicines for pain relief.
Vasotropic and cerebrotropic medications aimed at restoring the brain.
Multivitamins to prevent the effects of a concussion.
Cavinton. The medicine restores and normalizes the activity of blood vessels.
There are contraindications, consultation with a specialist is necessary!
Ambulatory treatment
Despite the fact that a concussion is classified as a mild traumatic brain injury, it requires mandatory treatment in an inpatient setting. This is due to the unpredictability of the post-traumatic period, since there are situations when a patient, against the background of symptoms of a concussion, experiences a subarachnoid hemorrhage or an intracranial hematoma (of course, this happens rarely, but it is possible). When a patient is undergoing outpatient treatment, he may not notice the first signs of a deterioration in his condition, which is fraught with risk not only for health, but also for life. While in hospital, he will be provided with qualified assistance from doctors throughout the entire period of treatment.
Biomechanical processes of traumatic brain injury
Mechanical effect
A concussion can occur either through a direct impact on the skull or as a result of an axial load on it through the spinal column, for example, when falling on the buttocks or unsuccessfully jumping on the feet.
To understand the causes of the consequences and even minor symptoms of a concussion in adults and children, it is necessary to have a general understanding of the processes occurring at the time of injury.
In the skull, in a confined space, the brain “floats” in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). At the moment of sudden physical impact on it, the inertial movement of the brain continues in the opposite direction to the impact. As a result, there is a sharp increase in the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid between the brain and the inner wall of the skull. A hydraulic or even mechanical shock to the brain occurs, depending on the force of the impact.
At the opposite pole, negative pressure is created, which causes even greater damage to tissue structures (hydraulic “counter-shock”). Because the brain “floats”, it undergoes oscillatory movements, accompanied by repeated damage. In addition, with a strong impact, rotational displacements around the axis occur with additional damage to the internal protruding areas of the skull bones. Thus, the area and depth of tissue injury are directly proportional to the strength and suddenness of the mechanical impact.
Biological changes
Despite the fact that direct damage to the blood vessels does not occur, a cascade chain of sequential reactions of brain vessels, nerve pathways and their connections (synapses), as well as the nerve cells themselves, occurs. After an experimental concussion on animals with subsequent electron microscopy, damage to nerve cells was discovered in the form of displacement of their nuclei, damage to membranes, mitochondria and other structures, swelling of nerve processes, and an increase in the spaces between cells.
All these processes are united by one name - traumatic brain disease. It is expressed:
- in the initial spasm (constriction) of blood vessels, followed by their expansion and disruption of cerebral blood flow; with mild injury, it recovers quickly, but in different ways in different parts of the brain. In more severe cases, there is congestion of blood vessels, slowing of blood flow and, possibly, intracellular edema;
- in changes in the physicochemical properties of brain matter, metabolic disorders, changes in colloidal (protein) balance due to a short-term change in pressure inside the skull at the time of injury; in experiments on rodents, a violation of ionic intracellular and extracellular metabolic processes, the vulnerability of nerve cells, and a discrepancy between their energy needs and energy delivery by the blood were also established;
- in the short-term loss of relationships between individual nerve cells and brain centers while maintaining the physical integrity of their structure;
- in the separation of a functional nature between the hemispheres of the brain and the trunk, in which the main vital centers are located (cardiovascular, respiratory, temperature); during rotational displacements, rupture of the nerve processes connecting the hemispheres with a more fixed trunk is also possible.
A correct understanding of the general mechanism of injury allows you to understand the symptoms and what to do in case of a concussion.
Actions after a concussion: treatment at home
The most important thing in treating a concussion is to adhere to bed rest, prevent mental and physical stress, especially in the first days, and get proper rest and sleep. If the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations and begins treatment on time, a concussion almost always ends in absolute recovery and his ability to work is restored.
Some victims may still have residual effects of their injury over time. These include decreased concentration, high fatigue, irritability, depressive disorders, headaches, memory impairment, sleep disorders, and migraines. As a rule, all these symptoms soften after a year, but it happens that they bother the victim all his life.
For a month after receiving a concussion, it is undesirable to do difficult physical work; you need to limit sports activities. Violation of bed rest is strictly prohibited; it is best to avoid being at the computer, watching TV and reading books for a long time. It is recommended to listen to calm music; you should not use headphones.
The prognosis depends on the severity of damage to health due to a concussion.
Rehabilitation
Regardless of the degree of brain damage, specialized rehabilitation is indicated for the victim.
It begins in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor. The duration of the recovery period is determined by a neurologist and can range from six months to several years. The first weeks of this period are considered critical, so compliance with the rules is especially important. Goals and methods of rehabilitation:
- restoration of lost brain functions - achieved through regimen, diet, drug therapy or taking traditional medicine;
- prevention of relapse - getting a concussion is often associated with violation of safety regulations, neurological disorders, and alcohol consumption. It is useful to carry out information work with the victim and treat existing disorders;
- prevention of complications - an important point is the prevention of stress, work to restore the patient’s normal psycho-emotional background.
By paying sufficient attention to the rehabilitation process, it is possible to speed up the patient’s recovery and prevent a decrease in his quality of life. Every controversial point is agreed upon with the doctor. Any negative changes in the victim’s condition should also be reported to a specialist.
The clinical picture of a concussion is obvious in most cases. If you associate the onset of symptoms with a recent trauma the patient has suffered, you can quickly suspect the diagnosis. If symptoms characteristic of TBI occur, you should immediately seek medical help. This will reduce the possible likelihood of adverse consequences.
Forecast
In 97% of all concussion situations, the person recovers completely, without any consequences. The remaining three percent of cases are characterized by the development of postconcussion syndrome, which consists of various asthenic manifestations (impaired concentration, memory, increased anxiety and irritability, poor tolerance of various stresses, dizziness, recurrent headaches, appetite and sleep disturbances, etc.).
Statistically, there used to be a much higher percentage of negative consequences from concussions. This is most likely due to the fact that CT scans did not exist; some mild head contusions were classified as concussions. A bruise always damages brain tissue, so it has consequences more often than functional changes.
We looked at the severity of harm caused by a concussion.
Pressure and shaking
A concussion is a skull injury of varying severity, which is characterized by disruption of the central nervous system (CNS). With mild damage, pressure fluctuations are not observed provided there are no underlying diseases. In case of severe injury, both an increase and a decrease in the tonometer readings are possible. Treatment requires drug intervention.