Scabies is an infectious skin disease (pruritic dermatosis) caused by itch.
Similar mites also parasitize animals, but only this species can reproduce in human skin. Scabies is characterized by extremely high contagiousness (infectiousness) and is widespread everywhere. Children, especially younger ones, become infected more often.
Scabies (see photo) is a strictly anthroponotic disease, that is, humans are the only carrier and host of this mite in nature. The transmission mechanism of scabies is contact and contact-household. Infection can occur through touching, shaking hands, or using contaminated objects and clothing. In this article we will talk about scabies, symptoms and treatment, types of this skin disease.
Classification
Depending on the course of the disease, there are several types of scabies:
Typical scabies;
- This is the most common form of the disease and occurs with pathognomic (unambiguous) signs of scabies.
Scabies without passages;
- A characteristic feature of this form of the disease is the absence of the main symptom – scabies. Instead, there are vesicles about 2-3mm in circumference. This type of disease occurs in those people who had contact with the patient, but the infection occurred not with adult ticks, but with their larvae.
Scabies of “clean people”;
- this form of the disease is typical for people who have the habit of washing frequently, or there is a need for frequent washing due to the nature of their work. This type of scabies occurs in the same way as the typical form, but the symptoms are less pronounced due to the mechanical removal of most of the mites.
Norwegian scabies;
- the most severe and highly contagious form of the disease. Up to a million adult mites parasitize the patient’s skin, whereas with ordinary scabies their number does not exceed 15-20 individuals. Its appearance resembles psoriasis-like dermatitis, skin hyperkeratosis is pronounced (proliferation of the upper layer of the epidermis), and there is no itching. It is often diagnosed in people with weakened body defenses (HIV-infected, tuberculosis patients), as well as in people with mental illnesses and drug addicts.
Nodular scabies;
- is characterized by the formation of bluish or brown hardenings on the skin, which reach 2-20 mm in diameter and persist for several weeks even after treatment. There are no mites in the nodules.
Pseudosarcoptosis (pseudoscabies);
- This form of the disease is characteristic of persons whose infection occurred not from humans, but from animals. The main symptom is severe itching and the absence of scabies. This form heals itself after the person has stopped contact with the infected animal.
Complicated scabies;
- This is a form of typical scabies, which has not been treated, and is characterized by the addition of a secondary infection.
Diagnostics
In a clinic setting, to differentiate scabies from psoriasis, dermatitis, etc., studies are carried out using:
- Carrying out express analysis by exposing the skin to 40% lactic acid.
- Examination of skin scraping with a possible scabies tunnel under a microscope.
- Detection of eggs and mites on a section of the epidermis using an alkaline solution.
It is difficult to recognize scabies on your own, but it is possible. To check the typical form, the following test is suitable: if you lubricate the skin with iodine along the path of the rash, the presence of darker scabies becomes noticeable.
Features of the life cycle of the scabies mite
The clinical manifestations of the disease are determined by the manifestation of the life cycle of scabies mites, so it is worth dwelling on it in detail.
An adult female scabies mite is about 1/3 mm in size. Their photo is shown on the right. Males are approximately 1.5 times smaller and the manifestations of the disease have no significance in the clinical picture.
Like all insects, scabies mites go through larval and adult stages in their development. After fertilization, the female penetrates into the superficial part of the skin (epidermis). Feeding on the epidermis, it moves, making passages in it, where, in addition to the products of its vital activity, it leaves eggs. In one intraepidermal passage, 3-4 fertilized eggs can be detected at different stages of development. Females make holes above the laying site to facilitate the release of the offspring to the surface of the skin. On the skin, the larvae, spreading around, penetrate into the hair follicles (hair roots), under the keratinizing scales of the skin, into various elements of the rash (especially vesicles). There they undergo transformation, bypassing intermediate stages, immediately into adult, sexually mature ticks. Mating occurs on human skin, after which the females penetrate the epidermis, and the males are cleaned off by combing, separated with microscales of the skin and die. The average lifespan of a female is 6-8 weeks, during which she lays about 60 eggs. It is estimated that the potential production of adult ticks from one female in three months can be up to 150 million individuals.
Once removed from the skin, scabies mites can remain viable in the environment at room temperature for about a week. Under less favorable conditions, females live for about three days, and larvae for about two.
A healthy person is infected through close contact with a sick person or indirectly through his things (combs, washcloths, towels, etc.).
Incubation period
Scabies, the first symptoms of which will be described in detail below, does not always immediately give obvious signs of infection. In different cases, the incubation period will last from several hours to several days (weeks), as it is determined by the age of the individual that came into contact with the skin.
If tick larvae come into contact with the skin, the incubation period will be 12-14 days. The larva penetrates the hair follicle and remains there until it matures. After this, the tick crawls out and bites into the skin, making tunnels in it.
When infected by an adult specimen, the incubation period lasts several hours. Ticks immediately penetrate the upper layers of the skin, beginning to gnaw passages and multiply, which provokes itching.
How can you get infected?
Scabies almost always occurs through prolonged direct skin-to-skin contact. The predominant route of transmission is sexual. Children often become infected when they sleep in the same bed with sick parents. In crowded groups, other direct skin-to-skin contacts are also realized (contact sports, children fussing, frequent and strong handshakes, etc.). Although a number of manuals continue to reproduce outdated information about the transmission of scabies through household items (household items, bedding, etc.), experts agree that this route of infection is extremely unlikely. The exception is cases of Norwegian scabies, when up to several million mites live on the patient’s body (in typical cases this is 10-20 mites).
The key experiment, which proved that direct contact with the patient’s skin plays a dominant role in the transmission of scabies, was performed in 1940 in Great Britain under the leadership of Mellanby. Of 272 attempts to infect volunteers by placing them in a bed from which patients with severe scabies had just risen, only 4 attempts led to illness.
Such features of the transmission of parasitosis are explained by the following data on its biology:
- the scabies mite is inactive during the day; females come to the surface only in the late evening and at night;
- The tick needs about 30 minutes to penetrate the host’s skin;
- in the external environment the tick dies quickly (at 21°C and humidity 40-80% the parasite dies in 24-36 hours), the warmer and drier the faster; The tick loses activity even earlier.
Currently, more and more manuals and medical reviews include scabies along with phthiriasis in the list of sexually transmitted diseases, although for the transmission of these parasitoses it is not so much coitus itself that is important, but rather prolonged contact between bodies in bed.
How to understand that scabies is going away
Treatment with modern drugs eliminates scabies in a maximum of 3 days. The symptoms that accompany it (itching, rashes) can bother you for quite a long time. This is due to the fact that there are still dead individuals and their waste products in the skin. The side effects of the disease disappear completely within 3 weeks.
If, after a month, the itching and rash do not disappear, then it is necessary to undergo a re-examination.
Scabies is an extremely contagious disease from which no one is immune. The most important preventative measure is health literacy. At the first symptoms of infection, it is necessary to contact a specialist (dermatologist and infectious disease specialist). It is important to remember that timely treatment is a guarantee against complications.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Symptoms of scabies in humans
The very first symptoms of scabies in humans:
- A rash in adults and children, localized in different areas and worsening at night. This is due to the fact that it is during the night hours that females are active in terms of their life activities.
- Formation of noticeable scabies-like passages.
- Polymorphism is characterized by the formation of papules and vesicles, which are covered with a hemorrhagic crust.
- Favorite sites of infection are the abdomen, folds between the fingers, lateral areas, thighs and gluteal muscles, in women - on the chest, in men - in the groin. The rash on the hands becomes especially noticeable.
- When the disease occurs, red spots form on the body, always itching, they are “covered”, “surrounded” by lines that have an unattractive gray tone.
From the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of scabies, less than a day can pass, sometimes a week or more. The incubation period of the disease may vary. It is determined by the time of year and the number of parasites that get on the skin.
- The main symptom of the initial stage is itching. Its intensity is increasing. This symptom becomes especially strong in the evening and at night. This can be explained by an increase in pathogen activity towards the end of the day.
- Presence of scabies. Scabies are slightly raised straight or curved white, gray lines on the skin, less than one centimeter long. At the blind end of the passage, a vesicle is visualized, in which the female mite is located. Often, burrows appear in those areas of the skin where the stratum corneum is thickest.
- The waste products of the scabies mite cause an allergic reaction, manifested by skin rashes (papules, vesicles). Due to itching, a person scratches the elements of the rash, in place of which erosions and then bloody crusts appear. Dotted bloody crusts in the elbow area are called Gorchakov's symptom.
Typical sites of scabies rash:
- almost everyone has interdigital spaces and lateral surfaces of the fingers,
- in 50% - the area of the wrist joints,
- 50% of men have genitals,
- 25% have feet,
- 20% - torso,
- in 17% - arms and legs (excluding hands and feet),
- 10% of women have mammary glands.
And also: flexion folds of the forearms and shoulders, buttocks, hips and popliteal cavities.
A typical scabies rash consists of small red nodules that over time turn into small blisters that will soon burst, leaving behind a bloody or purulent crust.
Clinical manifestations and symptoms
To avoid accidental contact infection, it is necessary to know the signs of different types of scabies.
Typical form: what it looks like
What visual signs can be used to identify:
- On the surface of the skin there are barely visible grayish-white, slightly tortuous short strips of internal tunnels gnawed by mites.
- Elements of a rash (red blisters), usually in pairs, appear along them.
- Pimples and blisters are localized on the interdigital spaces, wrists, intimate areas, abdomen, under the breasts (in women, children), and armpits.
- Papules and blisters itch constantly, and the intensity of the itching increases at night.
After scratching the vesicles, crusts form on them, under which not only mites live, but also numerous pathogenic bacteria are concentrated.
Clean
Appears in people who carefully monitor body hygiene: frequently wash their hands, take baths and showers daily.
Due to the fact that there is a constant mechanical removal of mites from the skin with water and soap, the signs of scabies are usually erased:
- The vesicles of the rash are located rarely and are hardly noticeable, or instead there are only red spots.
- There may not be any convolutions from the moves, but if there are, they are isolated.
- There are few short spots and scratches from scratching.
- Localization - in the navel area, between the fingers, on the chest.
- Itching during the day is mild, but worsens at night.
It is scabies incognito that poses a danger. Untimely or incorrect treatment (due to the difficulty of identification) leads to the development of severe forms of parasitic disease: nodular and Norwegian scabies. As the number of mites constantly increases, the body’s allergic reaction also intensifies. It also increases the likelihood of infection of epithelial wounds with purulent bacteria.
Nodular: signs
On the surface of the skin are formed:
- The nodular rash is small with gray exudate, becoming covered with dense dark scabs after scratching.
- Red-bluish large papules and spots, blisters, on top of which passages of itching are visually noticeable.
- All tumors itch terribly at night.
If patients ignore normal treatment, they risk scabious purulent pyoderma.
Cortical
The danger of Norwegian scabies (crusted) is the increase in general intoxication of the body due to the vital activity of an incredibly large number of itches.
Signs:
- Numerous elements of the rash merge together.
- Their surface is a dense, dry brown shell or a purulent continuous mess.
- Inside this mass of growth on the skin, there is a multi-row (deeper into the epidermis) layering of scabies containing itch eggs.
- A person's lymph nodes become enlarged.
- Itching may be minor (due to a decrease in the sensitivity of neuroreceptors due to their extensive damage).
- The number of mites sometimes reaches more than 150 mites per 1 cm of skin.
Fortunately, this form develops very rarely in modern society, since doctors today have many methods for detecting scabies.
Scabies of clean people
This is an erased form of the disease that occurs in people who have normal immunoreactivity, as a result of which there is no allergic reaction to the presence of mites.
Increased attention to personal hygiene, when people take a shower several times a day and change their underwear and bed linen, also contribute to the erasure of clinical manifestations of scabies. It is characterized by single rashes on the chest and around the navel, which practically do not macerate and do not cause discomfort, only itching is noted at night.
Hemorrhagic crusts may appear.
Treatment of the initial stage of scabies at home at the first symptoms
At the first symptoms of scabies, essential oils of green tea, lavender, cinnamon and tea tree can provide effective treatment at home. You can use them as a bath supplement, or mix a few drops of oil with honey and apply to the affected areas of the epidermis.
By mixing celandine leaves and petroleum jelly in a ratio of 1:4, you can get an excellent remedy for fighting scabies mites. This mixture eliminates itching and relieves inflammation.
A popular method of getting rid of ticks is to use vegetable oil in which tomatoes were fried. To prepare the required mixture you will need ½ liter of oil and 1 kg of red ripe tomatoes. Fry the diced tomatoes in a hot frying pan for 20-25 minutes, then remove from the oil. After cooling, the oil mixture must be filtered through gauze and applied several times a day to the affected areas of the skin.
Since ancient times, parasitic lesions have been treated with ordinary tar. For this method of treatment, it is enough to apply the product to the affected areas for 2-3 hours, and then wash off with warm water and soap.
Another time-tested and effective method of treating the disease is an ointment based on lard, laundry soap, tar and sulfur. To do this, mix the ingredients in a ratio of 1:1:0.5:1 and apply to the affected areas of the skin for a week.
Norwegian scabies
Named this way because it was first described in Norway in patients with leprosy (leprosy) in the mid-19th century.
This is the most contagious and malignant form of scabies. Occurs in individuals who have persistent background suppression of the immune system for various reasons. For example, after undergoing chemotherapy for cancer, during hormonal therapy for some severe diseases with corticosteroids. Patients with Down syndrome and HIV-infected people are at risk of developing a severe form. Skin sensitivity disorders observed with paralysis of various etiologies, some other diseases, and congenital features of keratinization of the skin can also contribute to the transition of the classical form of scabies to the Norwegian one.
Characteristic features:
- A variety of rash elements that are confluent in nature, from spots to blisters, the presence of ulcerated cracks in the skin.
- The appearance of crusts of various shades of yellow and brown. Increasing in thickness and merging, they can form a kind of “shell” over parts of the body.
- In the crusts, when studied, a huge number of mites are revealed at different stages of their life cycle. Sometimes their number reaches 200 per cm².
- The parasite can also be detected on the nail plates, which, under the influence of fungal flora, thicken and become loose, convenient for the tick to inhabit and the development of its offspring.
- Joining the described picture with extensive pustular skin lesions, furunculosis, due to the addition of a secondary infection.
- There is a prolonged rise in temperature.
Nodular scabies
The nodular form of scabies develops as a result of the body’s most pronounced reaction to the waste products of the parasite. In response to the formation of toxic substances, the immune system responds with allergic manifestations: the appearance of a red rash in the form of nodules and intense itching.
- The nodules are located directly above the scabies passages and, when scratched, become covered with rough, dry crusts.
- Round nodules reach a diameter of 20 mm, they are few in number and are located in the groin area, on the inner thighs, in the armpits, on the buttocks or on the chest.
Complications
Due to severe scratching, bacterial infection of the primary elements sometimes occurs, after which pyoderma appears.
In some rare cases, this condition leads to post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis or rheumatic heart disease. With pyoderma, boils, ecthyma and abscesses often occur, which are accompanied by lymphadenitis and lymphangitis.
Also, patients with scabies may develop allergic dermatitis or microbial eczema. Approximately half of patients with scabies are diagnosed with complications in the form of pyoderma and dermatitis. In addition, in more rare cases, other complications may occur: pyogenic pneumonia, panaritium, erysipelas, septicemia, regional lymphadenitis, internal abscesses.
Some patients develop nodular scabies, the signs of which are the appearance of bluish-purple or brownish round lumps of the skin. Such formations may not disappear for several weeks even in the absence of parasites. In addition, the manifestation of atypical forms of scabies is possible - Norwegian scabies, pseudosarcoptosis, scabies of “clean people”.
First signs
The first sign that will unmistakably indicate a scabies infection is itching, which gets worse at night. Red spots and rashes appear on the body. In addition, scabies canals are clearly visible on the skin, about 1 cm long. They look like a small white stripe.
Location in an adult:
- palms;
- elbow bends;
- stomach;
- feet;
- buttocks;
- armpits.
Children experience this disease more severely, as it spreads throughout the body, even covering the scalp.
How to treat scabies?
There is a whole range of fast-acting drugs, medicines, and various ointments that help in the fight against scabies. The medicine eliminates the problem on the skin and the symptoms of the disease. Doctors have developed regimens that are important to use for certain forms of severity and stages of disease development.
Scabies at an early stage with a small number of foci of the disease includes treatment to prevent re-infection. Scabies in adults with a large number of lesions is treated with drugs that are carefully rubbed into the skin in the infected areas. The exception is the area of the face, neck, and scalp.
Treatment of scabies in humans is most effective when the mite is active - in the evening and at night. To relieve immunoallergic symptoms, antihistamines, antipruritics and corticosteroids are prescribed.
How to cure scabies on the face without leaving scars
Typically, in adults, ticks do not live on the face and do not dig burrows, since the structure of the skin is quite dense. In exceptional cases (with complications of scabies), the following remedies will help.
List of effective drugs
Fast acaricidal preparations that prevent the formation of deep and long tick burrows under the skin:
- Spregal (aerosol).
- Lindane (lotion).
- Crotamion (lotion).
- Malathion (lotion).
The use of these products instantly destroys adult itches and prevents their penetration into the thickness of the epidermis. Prevents acne infection by pathogenic microbes.
Best anti-scarring cream
In order for the ruts in the mite tunnels to smooth out more quickly, after treating scabies, you need to lubricate your facial skin with one of the medicinal gels (creams):
- Contractubex.
- D-Panthenol.
- Liniment Aloe.
- Vulnuzan.
All of them have excellent regenerative and dermatoprotective properties. Accelerate epithelization of the skin, nourish and smooth it.
Medicines and preparations for the treatment of scabies in 1 day
The goal of treating any form of scabies at home is to completely destroy the mite and its larvae. Therefore, medications should loosen the stratum corneum of the skin, penetrating deep into the scabies tracts.
Currently, for the quick treatment of scabies, the following drugs, ointments and aerosols are used, which can get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of scabies in 1 day:
- Benzyl benzoate (ointment 20-30 rubles, emulsion 100 rubles) is contraindicated in children under 3 years of age, during pregnancy and lactation. Before applying the ointment, it is necessary to bathe the patient. The ointment is applied to the entire body except the head and face at night, rubbed in with hands, and hands are not washed until the morning. Only on the 4th day the treatment is repeated and on the 5th day the bed and underwear are changed.
- Lindan. Available in the form of ointment, cream, lotion. This drug is applied to dry skin for 6-24 hours and then washed off. Apply once or twice.
- Crotamiton. Used to treat pregnant women and newborns. The course of treatment is 5 days.
- Esdepalletrin (A-Par aerosol 600 rubles, Spregal aerosol 800-900 rubles). A synthetic drug, available in the form of an aerosol, is used once and is considered very convenient and low-toxic. Contraindicated for bronchial asthma and breastfeeding.
- Permethrin (Medifox bottle, gel 100-140 rubles, Nyx cream 320-400 rubles, head lice remedy Hygia 180 rubles) is rubbed into the skin of the entire body and washed off after 8-14 hours. Apply once.
- Ivermectin. Used once orally. Contraindicated for women during pregnancy and children under 5 years of age.
Principles of treatment of scabies in humans
Also during treatment you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- All patients from the same epidemic. lesions must be treated simultaneously.
- Rub the preparation with bare hands, because the hands are most often affected by scabies.
- Trim your nails: there may be tick eggs under them due to scratching.
- Remember about disinfection of linen and clothes: the tick is reliably killed by boiling for 5-10 minutes in a solution of soda or washing powder, you can also iron the clothes with a hot iron, but for the laziest there is a very simple way: the linen is removed and packed in a plastic bag for 5 days or hung outdoors. After 5 days, the clothes are considered disinfected, because hungry ticks do not survive for that long. Please note that you need to treat all fabrics that come into contact with the body - clothing and bedding. If you don't want to remove your bedding, give your sheets, pillowcases, and duvet covers a good run with a hot iron. If disinfection is carried out poorly, the remaining mites can infect you again.
- Treatment of complicated scabies is best done with benzyl benzoate ointment
or
Spregal
. - Norwegian scabies is treated in a hospital.
Sulfur ointment (33%) can be used to treat scabies in patients over 12 years of age. It is used to treat the body at night for 5-7 days. For children 2-7 years old, use 10-15% sulfur ointment twice with an interval of three to four days.
Antinistamines should definitely be used to treat scabies, including Claritin, Cetrin, Zodak, Zyrtec, Erius, etc., 2nd and 3rd generation drugs have a longer effect and have a slight sedative effect.
The Demyanovich method is also based on the acaricidal effect of sulfur. It consists of sequentially applying a 60% sodium hyposulfite solution and a 6% hydrochloric acid solution (for children, the concentrations are reduced to 40% and 4%, respectively). Between using the first and second solutions, take a break of 10 minutes. After the procedure, all clothes are changed. You can shower only on the fourth day after treatment.
The effect of the therapy is largely determined not by the drug itself, but by the correctness of its use, therefore, when treating scabies, it is important to follow several rules:
- Taking a shower, a complete change of bed linen and clothes are carried out before and after the course of treatment;
- Skin treatment should be carried out in the evening before bedtime;
- It is necessary to treat not only the affected areas, but also the entire surface of the body;
- It is necessary to regularly sanitize personal clothing and premises;
- Antiparasitic ointments should not be used for longer than directed by the doctor (even if the skin itching continues), since the drugs can cause an overdose. If itching continues after treatment, you should continue taking antihistamines.
Odorless zinc ointment for scabies and other effective remedies
Odorless zinc ointment, used for scabies, is a less effective remedy, but it copes well with the consequences of the disease. Most often, this medicine is used in combination with other drugs.
The best remedy for scabies, which quickly and effectively relieves itching in the first hour of application, is Krotamiton. It is available in the form of a lotion, which allows the drug to be quickly absorbed into the skin. Not recommended for use by children under 12 years of age. Before application, shake the product thoroughly and use 2 times a day.
To treat scabies at the initial stage, use Wilkinson's ointment, the composition of which is based on sulfur. It is enough to use 3-4 days to completely eliminate the infection. It is not recommended to apply to the skin of the face and head, or to treat children. It has a sharp tar smell and a persistent color that remains on clothes.
Permethrin ointment for scabies is suitable for people without allergies and hypersensitive skin. The drug has a strong and rather persistent odor, so it is applied only in a ventilated area with gloves and not on all areas of the skin. Not suitable for use on the face and neck. Can be used to disinfect infected clothing. Not recommended for use in children under 5 years of age.
An effective proven remedy for scabies is Vishnevsky ointment. Although it has a specific tar smell, it perfectly fights scabies pests, relieves itching and heals wounds.
Folk recipes
Remember that before using any folk recipes, you should consult with specialists who will tell you about the nuances of certain remedies and the possible consequences of their use. We list the most effective recipes:
- mix 1 tbsp. spoon of turpentine with 2 tbsp. spoons of butter. The resulting mixture is applied to the skin before bedtime;
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of celandine is mixed with 4 tbsp. spoons of Vaseline. The product is intended for external use. The whole body is treated, not just the affected areas;
- Birch tar is applied in an even layer to itchy areas, washed off after 3-4 hours with warm water.
Prevention
Prevention of scabies is quite simple. Upon completion of treatment:
- Thoroughly wipe all surfaces that an infected person may have touched;
- throw away old bedding and underwear;
- take a course of vitamins to restore the body's defenses.
Help prevent infection:
- washing hands thoroughly after visiting public places;
- maintaining household hygiene;
- a reasonable approach to choosing a sexual partner.
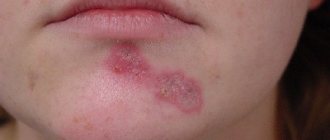
Scabies is a contagious skin disease, so if you experience an itchy rash, as shown in the photo, be sure to consult a dermatologist.
Causes of the disease
The causative agent of scabies is called the scabies mite. The female is predominantly active: her size is larger than that of the male (can reach 0.4 mm), and she lays her eggs in passages made between the granular and stratum corneum of the epidermis. Afterwards, larvae emerge from them, quickly mature and also begin to be active. There is a certain set of factors that stimulate infection and development of the disease:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules - unscrupulous people are affected by scabies mites with greater frequency and transmit pathogenic microorganisms with greater activity.
- Staying in a crowded group - large crowding (especially in the cold season) increases the chances of long-term contact between a tick carrier and a healthy person. If you are constantly among people (boarding schools, military units, dormitories, orphanages), the risk of a scabies epidemic increases even more.
- A decrease in the immune response to the pathogen - due to the genetic characteristics of the body, taking medications, and the presence of HIV infection. If the immune system is weakened, tick reproduction occurs uncontrollably, but is often asymptomatic. Such a person is a carrier, unaware of his own danger to others.
- Nervous stress and stressful situations are secondary factors that provoke a decrease in the body’s defenses.
Disinfection of housing and household items
The scabies mite lives outside of human skin for a very short time - about 5 days. In dry and hot conditions (at a temperature of 60 degrees) it dies within an hour, and at temperatures below 0 or boiling - almost immediately. Disinfection methods for scabies are based on this feature:
- underwear and bed linen, towels are boiled in a 1-2% soda solution for 5-10 minutes from the moment of boiling;
- clothes that cannot be boiled should be ironed with a steamer on both sides;
- outer clothing, as well as pillows, mattresses, blankets are placed in the open air for 5 days. In winter, one day is enough for this purpose.
Currently, the drug “A-PAR”, produced in the form of an aerosol, is used to disinfect the premises and personal belongings of the patient. It is used to process things that cannot be boiled or ironed: mattresses, pillows, blankets, outerwear, etc. In addition, the aerosol can be used to treat the room - walls, floors, door handles, furniture. Bedding should be sprayed twice.
The product does not leave stains, so there is no need to wash items after treatment, but they can be used after 2-3 hours.
Hygiene during treatment
The main conditions for the successful destruction of itches:
- Nails should be cut short.
- Linens should be washed at the highest possible water temperatures.
- It is better to throw away socks and tights worn during illness.
- Anything that cannot be washed is treated with steam from an iron, acaricidal sprays (which were applied to the skin), or Sanox or A-PAR products.
- The same preparations are used to clean household items and furniture, as well as floors, from ticks.
All children and adult families are treated at the same time.
Forecast
In the case of preserved immune status, the disease does not pose an immediate threat to life. Timely adequate treatment allows you to completely eliminate the symptoms and consequences of the disease. Working capacity is completely restored.
In rare cases, observed mainly in poorer countries, complicated scabies can lead to post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis and possibly rheumatic heart disease.
In children, scabies can be complicated by severe pyoderma and sepsis, even leading to the death of the patient. The prognosis for Norwegian scabies is questionable, treatment is ineffective, and there are frequent cases of death resulting from intoxication of the patient or damage to cardiac activity.
Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis): symptoms, treatment, photo Demodicosis in humans: photos, symptoms and treatment Tick-borne encephalitis Enterobiasis Tularemia in humans Psoriasis