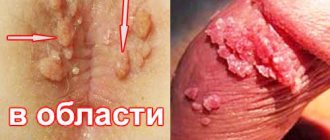
Perianal condylomas are growths on the skin in the form of papillae, which are located in the anal folds and around the anus. They can be single or form large foci. Despite their apparent harmlessness, these tumors pose a danger to human health. Their appearance is caused by the activity of the human papillomavirus, and under certain conditions, condylomas can cause squamous cell carcinoma.
Of the 100,000 residents of St. Petersburg, 165 people are infected with HPV subtypes that provoke the formation of perianal condylomas.
What are condylomas?
Condylomas are genital warts, which are one of the manifestations of infection of women with papillomavirus. There are many strains of this DNA virus, so it is so important to conduct a thorough examination and identify the one that caused candilomatosis. Otherwise, treatment may be ineffective.
Important! According to statistics, on average, up to 30% of women are carriers of the virus and never develop condylomas. But in general, 90% of people have papillomavirus without showing any signs of it. Moreover, different strains of HPV can be present in one body at the same time.
Progress of the disease
After introduction into a woman’s body, the human papillomavirus goes through the following stages:
- Incubation. The carrier does not show any concern at this time, and there are no signs of illness. It is important to remember that the ability to become infected at this stage is no less than with visible signs. This stage varies significantly in duration among different people and ranges from several days to several years. The duration of incubation is primarily determined by the state of health and general immune status.
- The onset of manifestations occurs when the presence of human papillomavirus in the body increases or the protective reactions weaken.
- Active stage with rapid manifestation of symptoms.
After active growth of condylomas occurs, the disease develops in one of the possible directions:
- Complete cure with final regression of growths. This picture is observed in 16-17% of cases and almost always after pregnancy.
- Slow course of the disease with the cessation of the increase in lesions and the absence of their growth. At this stage, the disease is in a “frozen” state.
- Rapid progress of condylomas with a sharp increase in size and merging of nearby groups. This scenario requires urgent surgical intervention.
- Degeneration of benign formations into malignant ones. A similar picture is observed in approximately 5% of cases in the absence of treatment for 5 years from the onset of growths.
Causes of condylomatosis
Condylomas on the labia
The main cause of condylomatosis in women is sexual contact of any form (oral, anal, vaginal) without contraception. There is an opinion that HPV is transmitted through household means - through personal hygiene items, underwear, but this has not been scientifically proven.
Condylomatosis in women can actively manifest itself against the background of factors provoking the activity of the virus.
These include:
- Damage to the mucous membranes and skin of the genital organs;
- Stress and constant nervous tension;
- Fatigue, lack of sleep, excessive exercise, poor diet or inappropriate diets;
- Decreased immunity - seasonal, during pregnancy and the postpartum period, with hormonal disorders in the body;
- Overheating or freezing of the body;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Uncontrolled use of pharmaceuticals that can cause microflora disturbances.
Routes of entry into the body and risk factors
To activate in a cell, a viral agent must enter the body in one of the possible ways:
- Sexual contacts. This route of infection serves as the route of transmission of the disease in the vast majority of cases. The pathogen penetrates epithelial tissue during oral, anal or vaginal sex. Contrary to popular belief, a condom does not guarantee complete protection against transmission of the disease, since the virus can also spread from surrounding skin. In addition, infection can occur during kissing.
- Contact and household path . Since the pathogen is present in all physiological fluids of the body, a woman can get the disease through contact with personal belongings of the patient: cutlery, linen, wet bathrobes or towels. The presence of the pathogen in saliva, urine, blood and semen makes infection possible in a public toilet, swimming pool, sauna, and transport. This route of infection is not widespread, since the virus lives in the external environment for a short time.
- Infection of a child from the mother . The pathogen enters at the last stage of labor when the fetus moves through the birth canal. Infection from a sick mother does not always occur, since the baby’s blood contains maternal antigens that have entered his bloodstream. But with a significant weakening of the immune system or extensive injuries to the skin, such a possibility exists.
- Self-infection . It is possible to transfer the pathogen to other parts of the body by hand. Most often, this picture is observed when shaving intimate areas or during hair removal.
Infection occurs much more often than clinical manifestations appear, since the virus is present in almost half of women. The majority have carriage, which is determined only by clinical tests, but does not cause symptoms.
Due to increased sexual activity, a sharp increase in cases of human papillomavirus infection occurs between the ages of 17 and 28.
Factors that contribute to pathogen transmission:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- promiscuity and lack of barrier contraception;
- sexual contact with people who have previously had human papillomavirus or other STDs;
- injuries to the mucous epithelium and skin;
- vaginal dysbiosis;
- endometriosis;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- pregnancy is a period of special stress on the immune system;
- obesity;
- lack of B vitamins and folic acid;
- chemotherapy;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland and insulin metabolism in the body.
The risk of infection is contributed by poor personal hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in which sexual contacts take place.
Infection does not always occur after contact with the pathogen. If a woman’s immunity is high, the virus can be dissolved by phagocyte cells of the body. And even after the introduction of a pathogenic agent, the disease may not begin if the immune system restrains its development. Viral suppression sometimes continues for life.
After entering the body, the virus migrates through the bloodstream and enters cells, where it displaces the host’s DNA and integrates its genetic strand. The new gene program ensures continuous cell division, which causes the growth of condyloma.
How dangerous are condylomas if left untreated?
Women do not experience pronounced painful sensations in the presence of small or single genital warts. But this does not mean at all that such formations are not dangerous and should not be removed.
Here are just a few risks associated with the lack of proper treatment for genital warts in women:
Vaginal infection
- Transformation of warts into malignant tumors;
- Development of cervical cancer;
- Development of other infectious diseases against the background of suppressed immunity;
- Complication of childbirth due to loosening of vaginal tissue and damage to a large area of the mucous membrane and skin of not only the external but also the internal genital organs due to the abundant blood supply to genital warts;
- Infection of a newborn with condylomatosis, which can appear not only on the genitals, but also on the eyelids and in the mouth.
Important! During pregnancy, women are usually not prescribed antiviral and immunostimulating drugs aimed at combating HPV, as this can provoke rejection of the fetus by the body - miscarriages, premature birth. Treatment of condylomatosis is often carried out locally, under the supervision of a doctor.
Related article:
How to choose an effective remedy for papillomas? Treatment with pharmaceutical drugs and folk remedies
Video about complications
Prognosis and complications
The prognosis for the course of condylomatosis, if a woman consults a doctor in time, is quite favorable. Sometimes it is possible for condylomas to disappear on their own, but this happens extremely rarely, and you should not hope for such an outcome. Thanks to a modern approach to treatment, which includes the use of medications and hardware methods for removing tumors, you can get rid of condylomas forever in just a few months.
If you do not consult a doctor and let the disease take its course, then dangerous complications may arise, such as:
- malignant tumor;
- bleeding (in case of condyloma injury);
- intestinal obstruction;
- disturbances in the process of chewing, swallowing, breathing;
- urinary retention;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- decreased libido due to discomfort during sexual intercourse.
All these complications can develop over years or in just a few weeks. In each individual case, the growth and progression of condylomas can occur at different rates (this depends on the amount of virus, the degree of decreased immunity, the presence of concomitant diseases, the woman’s age, the individual characteristics of the body and many other factors). However, doctors claim that the main cause of complications is self-medication and untimely access to a medical facility. Therefore, it is so important to consult a gynecologist as soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear. This will help cure condylomatosis faster and avoid complications. You can learn about condylomas in men in this article.
What types of condylomas are there? What is the difference?
There are 2 main types of genital warts in women:
- Pointed. They most often form on the genital mucosa - the tissues of the labia minora and majora, on the clitoris, near the urethra and anus. They can also be found in the vagina, groin area, thighs and buttocks, and rectum. They are papillary growths on a thin stalk. When the virus actively multiplies, the formations are multiple, eventually merging and becoming ridge-like.
Genital warts in the vagina - Flat or wide condylomas. This is a more complex type in which tissue damage occurs inside the vagina. The danger of this type is that it is impossible to notice them without special tools, and this causes a delay in the start of treatment for papillomavirus in a woman.
Flat condylomas on the labia
Also, genital condylomatosis can be in different forms:
- Latent: the virus is present in the body, but does not manifest itself in any way;
- Clinical: genital warts are formed;
- Subclinical: flat and inconspicuous plaques are observed.
How to distinguish papilloma from condyloma
Knowing the difference between papilloma and condyloma is necessary to determine further actions. While some can remain on the body throughout life and cause only cosmetic discomfort, others carry the risk of malignant degeneration.
| Index | Papilloma | Condyloma |
| Structure | Homogeneous | Heterogeneous, small, papillary |
| Form | Round or oval, located on a soft stem | Arbitrary, located in clusters, in the form of ridges. Characterized by a narrowing from the stem to the end |
| Size | Up to 10 mm. As a result of traumatic exposure, it may increase by 2-15 mm. | Also capable of growing |
| Color | Weak or intense pigmentation | Virtually no different in color from surrounding tissues |
| Localization | Preferably on the skin | On the mucous membranes, mainly of the urogenital area; on skin folds subject to friction from clothing |
| Peculiarities | Causes aesthetic discomfort. Rarely inflamed, usually only due to injury | It often becomes inflamed and infected. Possible ulceration of the body of the growth, pain |
| Main route of infection | Contact and household | Sexual |
| Exciter type | Typically 2, 7 and 28 strains | 6, 11, 16, 18, 39, 54, 56, 73 strains |
| Risk of malignancy | No | Yes |
Symptoms of the initial stage of genital condylomatosis
Classic symptoms of condylomatosis include the following:
Vaginal discharge during condylomatosis
- Formation of small protruding or flat formations on the skin;
- Itching, burning sensation;
- Feeling of constant humidity at the site of condylomas;
- The appearance of a foul odor;
- Bloody discharge is possible if the condylomas have been mechanically damaged.
Important! If, after the appearance of a condyloma, insufficient blood flows to this area of the skin, it may dry out and fall off without any outside intervention. But most often, literally a few hours are enough for the formation to grow to a size of 6 mm or more.
Symptoms
The incubation period of the disease depends on the state of the immune system and can last from 3-6 months. up to several years.
The first signs develop rapidly and appear:
- slight redness;
- mildly noticeable itching;
- unexpressed burning sensation.
These symptoms subside after the appearance of a vesicular tuberosity at the site of pathogen reproduction. Genital warts in women, photos of which will help determine their size, can be up to 1-5 mm in diameter and located singly. Such growths are almost not felt. There may be discomfort during sexual activity. As the size increases, the symptoms become more pronounced.
The clinical picture includes:
- pronounced redness of the affected area;
- burning sensation;
- feeling of itching;
- if touched, it will be painful.
An unpleasant odor comes from the location of the warts. There may be phenomena of bleeding and the occurrence of secondary infection. Condylomas, reaching a diameter of 8-10 mm or more, limit the entrance to the anus, vagina, urethra or partially enter the cavity of these organs, causing burning, discomfort and pain during urination and defecation.
When warts are localized in the oral cavity, swallowing problems and foreign body sensation may occur.
Diagnosis of genital warts
The primary diagnosis of activation of the HPV virus in the form of condylomas is a visual examination of condylomas. Also, in order to obtain a complete picture of the extent of damage to the mucous membranes and skin, an examination of the vagina, cervix, and vulva is carried out.
Next, the patient is prescribed tests according to the following scheme:
- Cytological analysis - this method makes it possible to identify changes in cell structure.
- Cytological
PCR analysis is a smear from the vagina and uterine walls. - Colposcopy - allows you to identify malignant tumors, their nature, as well as the main source of infection.
- Blood test for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, HPV to determine the strain.
- Biopsy - for this analysis, a piece of damaged tissue is taken to exclude or confirm the oncological nature of the origin of condylomas.
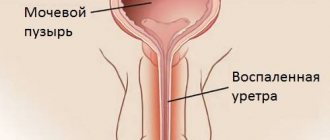
- Endoscopy is prescribed if the presence of condylomas in the rectum and anus is detected or suspected.
- Urocystoscopy - the procedure is performed if condylomas form near the urethra.
- Digene-test - prescribed to determine the concentration of the virus.
Video about PCR analysis in women
When should you see a doctor?
The penetration of the papilloma virus into the human body may not manifest itself clinically for a long time, but its activation and the formation of condylomas in advanced cases can lead to cancerous tumors. It is very important to immediately consult a doctor if you notice symptoms of this disease. In addition, you should contact a gynecologist if a woman has had unprotected sexual contact with an infected partner who has penile condylomas.
A modern visit to a specialist will help prevent the development of complications and the formation of condylomas on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Treatment of condyloma virus in women
Today, several methods of treating condylomas in women are practiced:
- Mechanical.
- Therapeutic.
- Antiviral.
Mechanical methods of treating condylomas
- Thermocoagulation. Warts are cauterized by exposure to high temperatures. Since this is a painful procedure, it is performed under local anesthesia. The disadvantage of this technique for treating condylomatosis is that nearby tissues are captured, in place of which a scar then forms. Wound healing after the condyloma scab falls off can occur from 7 days to 2 months.
- Cryodestruction. In this case, genital or flat condylomas are burned out with liquid nitrogen. The method is old, but still one of the most effective, although sometimes the procedure requires several stages.
- Chemodestruction. Nitrogen is also used here as the main active ingredient, only in the form of an acid.
- Laser therapy. The impact of a directed laser beam allows you to destroy the tissue of condylomas with minimal damage to adjacent tissues.
- Radio wave method. The principle is the same as in other methods, only in this case, highly targeted high-frequency radio waves are used to treat genital warts. The high price of the procedure is fully justified by the fact that the skin at the site of the condyloma remains undamaged, healing occurs in a maximum of 24 hours and there are no scars.
Chemodestruction of condylomas
Important! There is no universal way to get rid of the HPV virus and its manifestations in the form of genital and genital warts once and for all. Therefore, it is not uncommon for growths to appear again on the same or adjacent area of skin after some time. But the duration of the delay depends on the general condition of the body.
Treatment of genital condylomatosis with pharmaceutical drugs
If genital warts are small, local non-invasive treatment is possible.
The patient is prescribed:
- Condilin solution Solutions
- usually they have a fairly aggressive chemical composition, so the treatment of condylomas is carried out by a gynecologist in her office, and not by the patient herself at home; - Ointments - have an anti-inflammatory effect, help dry out the tissues of condylomas and disrupt their nutrition;
- Vaginal suppositories - give a local effect on genital genital warts;
- Rectal suppositories have a broader therapeutic effect, so they can be used when genital warts are detected in the vagina, near the anus, and near the urethra.
The following drugs have shown the greatest effectiveness in the treatment of condylomatosis:
- Betadine suppositories
Vaginal suppositories “Betadine”; - Rectal suppositories “Viferon”, “Panavir”;
- Ointments - salicylic, oxolinic, as well as Panavir and Viferon;
- “Condilin” is a solution based on the plant extract of podophyllin, the course of treatment for condylomatosis is carried out cyclically, not suitable for pregnant women;
- “Solcoderm” is an aggressive drug based on acetic, lactic, nitric and oxalic acid, so treating genital warts with this product is painful, and the skin may become scarred after disappearance;
- Trichloroacetic acid - the solution is applied once, after which it is neutralized with soda, the skin is dried with powder, the procedure is repeated after a week if necessary.
Solcoderm ointment - “Imiquimod” is an expensive, toxic, but effective drug for genital warts that is exclusively for external use, but has many side effects - redness, burning, itching, swelling, skin erosion;
- “Condyline Nycomed”, “Podophyllotoxin” are very toxic drugs for condylomas, the application of which is unacceptable more than once every 12 hours, and on large areas of the skin.
Antiviral complex therapy
It is advisable to carry out comprehensive treatment of genital warts in women, and not just remove the growths themselves.
To do this, the doctor prescribes special drugs that have an inhibitory effect on the HPV virus. The following performed best during complex therapy:
- Panavir
"Groprinosin" - taken 2 times a day for 2-4 weeks; - "Panavir" - prescribed in the form of vaginal and rectal suppositories, as well as a solution for injection;
- “Immunal” is a herbal preparation for viruses, including condyloma, in tablets or in the form of a syrup based on echinacea extract, not suitable for pregnant women;
- “Polyoxidonium” is an immunostimulating and detoxifying tablet preparation based on azoximer bromide;
- "Reaferon" - powder for preparing an antiviral and immunostimulating solution;
- "Epigen Intim" is a spray that increases local tissue immunity when used 4 times a day for 2 weeks.
Reaferon
Removal methods
Removal of condylomas is carried out in various ways. These are considered the most effective procedures. Let's look at them in table form
| Name | How it manifests itself | How long does it last and is there any pain? |
| Cryodestruction | Characterized by the effect on the growth of nitrogenous contents. Using a special tool allows you to freeze condyloma. After some time it disappears on its own. In most cases, warts disappear forever. | The method is absolutely painless. Complete healing of the treated area occurs on days 14-20. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. |
| Laser coagulation | Suitable for pregnant women. It is characterized by the use of a strong stream of light, which increases the temperature in the tissues. In this case, healthy tissues are not affected. Using this method, you can remove condylomas that have formed in the vagina, on the cervix, in the opening of the urethra, in the inside of the anus. After treatment, the condyloma evaporates. A crust remains in its place, which falls off very quickly. | The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. During the manipulation, pain is felt, so before performing it, the doctor will treat the desired area with an anesthetic. |
| Electrocoagulation | The essence of the method is cauterization of the growth with low-frequency electric current. The process uses a special device - an electric knife, which passes the current. | The procedure is quite painful, and therefore the doctor uses an anesthetic. After electrocoagulation, there is a high probability of scarring and cicatricial formation. The procedure is carried out once (10-15 minutes). The manipulation does not require any preliminary preparation. |
| Radio wave method | The essence of the method is to influence the growth of high-frequency radio waves. For this purpose, a special device called “Surgitron” is used. Resists the spread of cancer cells (not during the active period). Does not leave scars or scars. The exception is the removal of large areas of damage. | Manipulations, according to reviews, are absolutely safe and painless. Lasts about 15 minutes. |
| Removal with a surgical scalpel | Today it is rarely used. It consists of excision of the affected area with a scalpel and subsequent application of surgical sutures. | The wound takes a long time to heal. At the same time, there is a high probability of scarring and cicatricial formation. The manipulation lasts up to 1 hour. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. |
| Chemical cauterization | It is carried out only in a hospital setting. To eliminate warts, aggressive chemicals are used - Imiquimod, Podophyllinotoxin, Collomac, Fluorouracil. Before the procedure, the skin is treated with a protective cream. | The products are applied exclusively to the surface of the wart. |
After removal of genital warts on the genitals, women will experience a slight burning sensation, tingling, and discomfort during bowel movements and urination.
Attention! It is not allowed to pick off the scabs remaining after removing the wart. For some time it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse and visiting public places - baths, saunas, swimming pools. After removing condylomas, it is recommended to treat the wound with antiseptic drugs.
Condylomas during pregnancy - remove or leave?
There are different medical points of view regarding whether it is worth treating condylomas during pregnancy:
- Those who believe that this should be done operate on the basis that in the presence of such growths on the mucous membranes of the birth canal, infection of the fetus during delivery is possible.
- Those who argue that it is better to leave everything as it is also have their own reasonable justifications: after childbirth, hormonal levels will stabilize, immunity will increase, and all condylomas will go away on their own.
The conclusion about whether it is worth treating condylomas during pregnancy can be made as follows:
- If this is a single condyloma in a woman, it does not bother her much, and does not increase in size, then it is better not to take any measures until the end of pregnancy;
- If the virus behaves actively and affects large areas of the skin and mucous membranes, it is imperative to remove condylomas, only using suitable methods.
When to remove genital warts in pregnant women?
For the treatment of condylomas in pregnant women, there are favorable and unfavorable periods that must be taken into account when prescribing therapy, taking into account the possible risk to the fetus:
- It is not recommended to treat and remove condylomas in the first half of pregnancy;
- The favorable time for all procedures is the period from 28 weeks, but only under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Video about removal of condylomas in pregnant women and children
Technologies for the treatment of condylomatosis
Condylomas during pregnancy can be removed in the following ways:
Electrocoagulation
- Electrocoagulation;
- Surgical cutting;
- Acidic solutions.
Drugs containing interferon may also be prescribed.
Important! Methods such as cryodestruction, laser therapy, and cytostatic drugs are strictly not suitable.
be careful
The presence of papillomas, warts, condylomas, moles and spines on the body is the first sign of malignant melanoma!
We hasten to warn you that most medications “treat” warts, papillomas, moles, etc. - this is a complete deception of marketers who make hundreds of percentage points on drugs whose effectiveness is zero. They do not cure the disease, but only mask the symptoms.
The pharmacy mafia makes huge money by deceiving sick people.
But what to do? How to treat if there is deception everywhere? Doctor of Medical Sciences Anatoly Makhson conducted his own investigation and found a way out of this situation. In this article, the Doctor also told how to 100% protect yourself from melanoma, for only 149 rubles! Read the article in the official source via the link.
Condylomas in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's body undergoes great changes. The most serious of them are hormonal imbalance and weakening of the immune system. It is these factors that provoke the development of HPV.
Condylomas do not have any effect on the fetus in the womb. However, when they appear, it is necessary to regularly visit the doctor, since the child may become infected during childbirth. The specialist will monitor their condition and the health of the woman herself.
Folk remedies for the treatment of condylomas
Papillomas have been affecting the human body for many centuries, so many practical means have been identified that will help get rid of growths on the skin.
Here's what you can use to treat genital warts at home:
Kalanchoe leaves porridge
- Sour juices - pineapple, apple;
- Juice of grapevine, garlic, duckweed;
- Alcohol tincture of celandine;
- Egg white;
- Castor oil;
- Kalanchoe leaf paste;
- Onion, soaked for an hour in vinegar - left on the condyloma overnight.
Important! It is unacceptable to use any folk remedies to treat genital warts in women. Otherwise, there is a high probability of burns to the mucous membranes.
How to cure
To date, there is not a single proven treatment for HPV in the world.
The tactics for combating papillomas and condylomas are as follows:
- removal of formation;
- antiviral therapy – to suppress the activity of the virus;
- immunomodulatory therapy – to improve the functioning of the immune system.
To get rid of the growth, various methods are used:
- laser removal;
- cryodestruction;
- radio wave exposure;
- electrocoagulation;
- chemical removal;
- traditional surgery.
The choice of method is made by the doctor depending on the type of formation, its location, size, etc.
Prevention of genital condylomatosis
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from the HPV virus, but you can reduce the risk of genital warts if:
- Do not have promiscuous sex without condoms;
- Pays attention to your health - eat right, establish a proper work and rest schedule, regularly take measures to strengthen your immune system;
- Observe the rules of personal, and especially intimate hygiene.
Infection with the condyloma virus is not a death sentence! Many people live for years and are able to control HPV activity through a healthy lifestyle. You should also strive for this if the first symptoms of condylomatosis appear and you have successfully overcome them!
Preventing HPV infection
Condylomas must be prevented by preventive measures:
- use of contraceptives during sexual relations;
- increasing immunity;
- proper balanced nutrition;
- taking vitamins;
- compliance with hygiene standards;
- fight against bad habits;
- increasing stress resistance.
Regular visits to the doctor are a good preventative measure. The use of antiviral ointments, as well as vaccination against HPV, is prevention that will make people’s lives full.
How to get rid of genital warts in pregnant women?
Therapy during pregnancy is carried out using gentle methods that do not affect the development of the fetus. Various procedures are not carried out when carrying a child, since pregnancy is a contraindication for all instrumental methods of influence.
It is allowed to use topical preparations that contain various acids. Interferon-based drugs, immunostimulating and immunomodulating agents can be used with great caution.
Taking vitamin complexes, as well as traditional medicine methods, is not prohibited. The condition of a pregnant woman should be monitored daily by the attending physician to avoid the development of factors that negatively affect the unborn child.