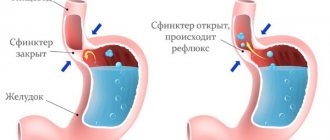
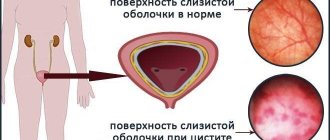
A healthy person does not experience discomfort when urinating. But for some people this process is accompanied by severe pain and burning.
There are two types of urination disorders diagnosed by these symptoms:
- Urethritis, in which pain during urination is caused by infectious agents (bacteria or microscopic fungi);
- Dysuria, in which the same symptoms are caused by compression or blockage of the urethra by a hematoma, tumor or stone.
They affect both men and women at different ages.
- Sexually transmitted sexually transmitted diseases
- Pain when urinating in children
- Treatment in women
- Herbal preparations
Why does it burn in the bladder in men and women?
Problems in the functioning of most organs of the hip part of the body cause pain and a feeling of heat in the lower abdomen. Most of these diseases are more common among the fair sex, since the genitourinary system in women and men is very different. The most common disease of the fairer sex that causes burning is cystitis. Other provocateurs of the sensation of painful heat include:
- Pathological processes in the bladder and urethra, the result of which are pathogenic bacteria.
- Inflammatory processes in the kidneys caused by infection. Often, pyelonephritis occurs as a result of advanced cystitis and urethritis.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Allergic reaction.
- Traumatization of the urinary system. Occurs due to medical examination, surgery, salts or kidney stones.
- Neurogenic bladder syndrome causes urinary disorders.
- The occurrence of tumors and polyps.
Urethritis is more common in men. Like women, men suffer from cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urolithiasis, but the more typical diseases for them are urethritis and prostatitis. Most ailments that cause a burning sensation in the lower abdomen are sexually transmitted. Benign and malignant foreign bodies in the urinary system can also cause pain and fever in the bladder. Other reasons include allergies, poor diet and gastrointestinal problems.
The first symptom of cystitis
This disease causes a burning sensation in the bladder area in a third of women. It occurs due to the entry of pathogenic organisms into the unpaired hollow organ of the excretory system and the destruction of its walls. In a healthy body, the infection is not able to develop into a full-fledged disease. In case of hypothermia, poor hygiene, stress, diseases of the endocrine system, or surgery, immune resistance decreases and bacteria multiply, inflaming the bladder.
Burning sensation with urethritis
This disease affects women and men equally, but due to the peculiarity of the urinary canal, the stronger sex more often notices the symptoms of the disease, and their course is acute. This disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the urethra and can be infectious or non-infectious. When the disease has become chronic, even if the burning and pain are minor, and there is no discharge when urinating, it needs to be treated. Pathogenic microflora tend to grow during periods of weakening of the body.
Cause: pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis can be caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This disease occurs due to pathological processes in the kidneys and their parts. Exacerbations of pyelonephritis are accompanied by the spread of infection to other organs. If the disease is not treated, the tissues die, lose their functionality and the kidney stops working. The causative agents of the disease are:
- E. coli;
- Proteus;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- staphylococci;
- enterococci.
For prostatitis in men
A burning sensation in the urinary canal in men is most often caused by this disease. The prostate gland becomes inflamed in half of men over 50 years of age. The main symptom of prostatitis is trouble urinating. Symptoms in the form of pain and pain in the bladder gradually progress. Sexual dysfunction occurs, accompanied by problems with erection and pain during sexual intercourse. This disease is provoked by infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Kidney stone disease
Urolithiasis can develop due to a sedentary lifestyle. This disease is manifested by the formation of stones in the kidneys, ureter or bladder. Salt stones appear due to problems with metabolism. In addition to genetic predisposition, low fluid intake and a sedentary lifestyle, the following provocateurs of urolithiasis are identified:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- poor metabolism;
- pathological processes in the pelvic organs;
- kidney injuries and abnormalities.
Other diseases
Other diseases that often cause burning in the urinary area include neurological disorders. They are a consequence of the low supply of organs and tissues with nerve cells. Women often suffer from pain in the lower abdomen not only due to the urinary, but also the genital organs. Minor disturbances in the anatomical structure or functional state of the vagina lead to burning during urination.
Who to contact if there is a problem
The appearance of discharge from the urethra in men, accompanied by redness of its opening and burning, is not common, but it is not so rare.
A big mistake a man makes when such symptoms appear is to ask his friends what they did in this case.
Having received an answer to a pressing question, the man begins to take pills and use ointments.
In some cases, the problem disappears, but only for a certain time. When symptoms reappear with greater intensity, a person may recognize a chronic form of the disease.
When self-medicating, only the symptoms of the disease are eliminated at a certain stage; the cause that caused the appearance of unpleasant symptoms must be treated.
Basics of diagnosis and treatment
An accurate diagnosis always requires further examination. Bladder burning is no exception. In order to clarify the cause of the pathology, the doctor may prescribe laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Urine tests: general, Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky tests, bacteriological culture.
- Blood tests: general, biochemical, sampling for markers of tumor processes is possible.
- Ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system and abdominal cavity.
- Smear for specific diseases (latent infections).
- Examination of the bladder mucosa through optics (cystoscopy).
If there is a suspicion of pathological changes in nearby organs, extensive further examination may be required.
Treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist
Treatment is carried out by a doctor in accordance with the identified pathological process. The general principles of therapy consist of:
- antibacterial drugs, decoctions of uroantiseptics (infectious and inflammatory causes);
- correction of glycemic levels (for diabetes);
- alpha-blockers (prostate hyperplasia);
- surgical treatment in case of tumor process.
Any discomfort, burning or pain in the genitourinary tract requires medical consultation. All diseases with such symptoms can be stabilized and cured if therapy is carried out in full and on time.
Diagnostics
Severe burning in the urethra is a reason to contact a urologist if the day before the man did not undergo a smear test for sexually transmitted infections and did not undergo surgical treatment through transurethral access. A smear from the urethra is taken using a bristly probe, after which discomfort continues for several days.
The basic analysis is a smear from the urethra, which is examined by three methods:
- Microscopic analysis.
- Diagnostics of biomaterial by PCR method.
- Culture for nonspecific infections.
If no pathogens are identified, then tests are prescribed to identify pathologies of the bladder and prostate. This could be an ultrasound, MRI, x-ray, urinalysis. To check the condition of the mucous lining of the urethra, urethroscopy is prescribed. A burning sensation in the urethra can provoke herpes, so it is advisable to get tested for IgG and IgM.
Doctors know how to help
Timely diagnosis is the key to successful treatment
To identify a number of infections, the doctor prescribes a smear test. To find out the reasons causing a burning sensation in the lower abdomen, the doctor prescribes urine and blood tests. To detect infections such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, gardnerella, etc., the doctor makes a smear. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs and the space located below the diaphragm and entirely filled with abdominal organs is performed. The inner lining of the bladder is examined using an endoscope. If problems with nerve cells are detected, additional examinations and consultation with a neurologist are necessary.
The most effective treatment
Measures to combat symptoms can only temporarily eliminate the signs of the disease, but not cure it, so you should not self-medicate. It is important to determine what ailment is causing the burning sensation. Depending on this, medications and preventive measures will be prescribed. For common diseases such as cystitis and urethritis, there are many herbal and synthetic drugs that will help get rid of the disease. If the cause of the burning sensation is urolithiasis, then the deposits are examined and, depending on their nature, the type of treatment is prescribed.
For diseases of a neurological nature, “Sedavit” or “Fitosed” are used. To the listed drugs add diuretics or decoctions of rose hips, knotweed, parsley, nettle, and juniper.
Treatment
Treatment methods are chosen depending on test results. If an infection is suspected, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. The causative agent is often a nonspecific infection, which is detected during bacterial culture, and this analysis can take more than a week. If the prescribed antibiotic does not relieve the symptoms, then after obtaining the culture result, the drugs are selected taking into account the sensitivity of the identified pathogen to them.
Medicinal and minimally invasive surgical techniques are used to remove stones from the kidneys and bladder.
Pudendal neuropathy is treated with muscle relaxants, vitamins, physical therapy, and anticonvulsants.
In some cases, idiopathic (according to test results) burning sensation, which torments for months, can be eliminated by taking a uroantiseptic called Furagin (a tablet three times a day for a week) plus Lomexin cream 2 times a day for 10 days.
Furagin is an antibacterial drug used for acute and chronic urinary tract infections: pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis. Price in pharmacies from 136 rubles.
How to relieve pain
The burning sensation when urinating can be dulled with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Ketorol. These products are more effective in the form of suppositories (the active substances will enter the pelvic bloodstream faster).
If it is not possible to see a doctor, and the pain is very severe, then you can buy Fitolysin paste at the pharmacy. This is a herbal medicine that effectively relieves inflammation in the genitourinary organs. As a last resort, you can purchase Monural. This is a fairly strong antibiotic, active against a wide range of nonspecific infections that cause burning in the urethra. It can help with infection with E. coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus. The drug is powerless against fungus. Flucostat and Fluconazole may help. As a last resort, douching with a weak soda solution.
Phytolysin is a combined herbal preparation that has a diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic effect. Price in pharmacies from 398 rubles.
If there is no pharmacy nearby, then you can use available antiseptics: Miramistin, chlorhexidine, a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Among the folk remedies, you can try douching the urethra with a decoction of chamomile, sage, diluted aloe juice, and strong green tea. To do this, you can use a syringe without a needle.
The above methods, except for painkillers, are used only in extreme cases before taking tests. If you have a burning sensation in the urethra, you should immediately go to a urologist or a private laboratory. After independent manipulations, the test results will be blurry.
Diet
A diet will help prevent increased burning during treatment. Basic principles:
- Avoid alcohol, strong tea, coffee, spicy foods;
- Minimum marinade, smoked meats, pickles;
- More water, compotes, fruit drinks, herbal teas.
Alcohol itself can provoke a burning sensation, since its consumption reduces immunity and activates hidden infections.
Preventive actions
Only with their help can final recovery be achieved. Experts advise not to overcool your feet and not sit on cool surfaces. It is necessary to carefully follow hygiene rules and use protective equipment when planning an intimate relationship with a new sexual partner. This is guaranteed to protect you from sexually transmitted diseases.
It is very important, if you feel a slight urge to secrete biological fluid, immediately visit the toilet. The constant presence of urine in large quantities in the bladder has a negative effect on the organs of the ureteric system.
It is best if the underwear is made of natural material, preferably cotton. During the winter period, you need to wear warm clothes that do not hinder your movements.
Another important recommendation is to avoid getting excess salt into your body. And this can be achieved by creating the right diet.
A burning sensation in the bladder is a sensitive, extremely unpleasant problem that every person can face. The vast majority are infectious in nature. Women, due to the anatomical features of the urinary tract (short, wide urethra), face the problem more often than men.
Constant discomfort in the lower abdomen and burning affect the normal routine of life and bring many unpleasant moments.
What diseases have such a symptom and how to cope with them is the main topic of the article.
Sexual infections
Diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact provoke inflammation not only of the external and internal genital organs, but also of the urethra. Sexually transmitted problems are characterized by burning and redness in the vagina and perineum. Provided that the localization of the disease has spread to the urethra, pain is noted when urinating.
Chlamydia
The cause of the disease is considered to be chlamydia; these microorganisms are not viruses or bacteria.
The course of the disease almost always occurs without pronounced symptoms or with minor manifestations. Characteristic signs are pain in the lower abdomen, a slight increase in overall body temperature, discharge with pus and mucus, and a burning sensation when urinating.
Gonorrhea
The insidiousness of the disease is that it can negatively affect other systems and organs. Symptoms are pronounced and can be noted at the first manifestation. Patients experience unpleasant discharge on their underwear, discomfort in the genital area, and pain when urinating and defecating.
Trichomoniasis
The primary manifestation of the disease is vaginal discharge with a strong odor.
Further, you can note the manifestation of redness on the genitals, itching and burning.
Signs may vary depending on the location of the infection.
If the vagina is affected, there may be no pain when urinating.
Ureaplasmosis
Inflammation in this disease occurs due to ureaplasma bacteria. It is noted that during labor it is possible for a child to become infected from his mother.
Often there are no symptoms of the disease; if certain factors are absent, such as pregnancy or problems with the immune system, then ureaplasmosis manifests itself as follows:
- pain when going to the toilet;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- pulling sensations in the lower abdomen;
- discharge from the vaginal cavity is colorless and odorless.
Provided that the localization of the inflammatory process becomes larger, the discharge acquires a yellowish tint and a pronounced odor.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Ultrasound diagnostics
The specialist conducts an examination during which he examines the condition of the abdominal cavity. Additionally, tests and ultrasound are prescribed. In the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys or bladder, large numbers of leukocytes will be detected in the urine.
An ultrasound will show whether there are visible changes in the kidneys. If these types of studies do not bring results, the doctor will prescribe a cytological examination. This type of analysis reveals the presence of tumors and polyps in the patient's body.
Establishing diagnosis
For diagnostic purposes, at the first stage of the medical examination, the doctor asks the patient in detail about all the circumstances associated with the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Conducts an external inspection.
The next stage involves laboratory testing:
- smears taken from the external mucous membranes of the genitals and near the urinary opening to determine the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- blood for the presence in it of an increased amount of uric acid and creatinine (which indicates failures in the filtration of urine by the kidneys), high cholesterol levels (which indicates depressed renal functionality and disruptions in lipid metabolism), excessive concentrations of fibrinogen and changes in ESR - rate, with in which red blood cells settle (which signals the presence of inflammation);
- urine to determine its consistency (low density is a sign of renal failure), the number of red blood cells in it (if there are more than normal, then this is an indicator of the presence of stones or sand in the organs of the urinary system), leukocytes (an increased content of which indicates inflammatory processes), the presence of protein and mineral salts (which means dysfunction of the kidney membranes), as well as bacteria and mucus (markers of infection).
In addition, the patient is sent for an ultrasound (examination of the pelvic area using ultrasound). Only after receiving objective data will the doctor be able to determine a specific diagnosis and draw up a therapeutic plan.
How to treat?
Before starting treatment, an accurate diagnosis should be established.
You should immediately contact a urologist and undergo examination as soon as the first unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the bladder appear.
Treatment methods depend on the original cause of the pain. There are 3 main methods of treatment : medication, physiotherapy and surgery, which are often used in combination:
- Cystitis and urethritis - treatment is carried out with antibacterial drugs to eliminate the infection (Furagin, Furadonin, Cefuroxime, Norbactin).
To reduce the level of pain, antispasmodics (Drotaverine, Baralgin and No-Shpa) will help; they relieve spasms that cause pain.
Additionally, warm baths and large amounts of fluid are used to rinse the bladder and urethra. To facilitate the process of urination, the patient may be temporarily given a special catheter.
- Prostatitis - antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs (Levomycetin, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline).
- Urolithiasis - a special diet is prescribed to dissolve the stones. If the stones reach large sizes, surgery will be required.
- Bladder injury - only surgical intervention by a surgeon will help.
- calamus;
- fennel;
- Melissa;
- St. John's wort;
- thyme;
- dill;
- chamomile;
- eucalyptus leaves;
- wild rosemary;
- oregano;
- bearberry;
- nettle.
If you have any pathology of the bladder, you need to follow a drinking regime and adhere to proper nutrition.
The patient is contraindicated from spicy, salty or spicy foods, which irritate the bladder and urethra. You should also not consume canned food, marinades and alcohol. It is useful to drink various mineral waters, compotes, natural juices and fruit drinks.
For diseases of the bladder and genitourinary system, herbs that have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect . Infusions and decoctions are prepared from them, which will help alleviate the condition. These include:
They are best used as adjunctive therapy to standard drug treatment.
Treatment and prevention of cystitis with folk remedies - read our article.
Pain when urinating in women: treatment
Pain when urinating in women, causes
What to do if a woman experiences pain in the lower abdomen or vagina when urinating, has incontinence and an unpleasant smell of urine, a specialist must decide. Which doctor should I contact in such cases? This should be a urologist. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will need to collect anamnesis, conduct a visual examination, and analyze data obtained from laboratory tests (usually a general and biochemical urine test, urine culture, and a general blood test). Additional examinations may also be required - ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, cystoscopy.
Treatment depends on the diagnosis. If the disease was caused by the growth of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora, antibiotics are an effective remedy.
To relieve attacks of pain, analgesics and antispasmodics are used. When treating pain with frequent urge to urinate, it is important to follow a diet and adhere to the correct drinking regimen. It is believed that drinking enough fluid helps flush out pathogenic microflora from the bladder and reduce inflammation.
To eliminate the discomfort that occurs during painful urination, you can use the intimate restorative gel “Gynocomfort”. The product contains tea tree oil, chamomile extract, bisabolol, lactic acid and panthenol. These ingredients have a regenerating, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect, due to which the burning and itching go away much faster. The positive effect of using this product was proven in clinical studies conducted at the Department of Dermatovenerology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlov under the leadership of Ignatovsky A.V. and Sokolovsky E.V.
Restoring gel "Ginocomfort" has all the necessary documentation and certificates of conformity.
Non-infectious causes
A burning sensation in the urinary tract can be caused not only by infections. Often this feeling occurs with the development of such diseases:
Stones in the kidneys
- Oncological diseases.
- Formation of sand and kidney stones.
- Renal colic caused by heavy physical exertion.
If an oncological tumor develops, a growth forms in the bladder, which does not allow urine to flow out normally. To restore function, surgical removal of the tumor is required. As for kidney stones and sand, most cases also require surgery to remove foreign bodies from the kidneys. In the presence of renal colic, patients are recommended to undergo special therapy using painkillers. It is also necessary to minimize physical activity and adjust the diet.
Diagnosis of urinary disorders
Typically, after visiting a specialist, the patient is prescribed the following examinations and tests:
- General blood analysis;
- Cytoscopy;
- Culture of a smear of the contents of the cervical canal;
- General urine analysis;
- Bacteriological examination of urine;
- Urinalysis using the Nechiporenko method;
- Uroflowmetry (determining the rate of urine excretion);
- Ultrasound of all organs located in the pelvic area:
- Analysis for all STIs (sexually transmitted infections) using ELISA and PCR methods;
- If necessary, study the lumbar and sacrum using MRI.
After a thorough examination, the specialist prescribes treatment. Typically, treatment consists of taking appropriate antibiotics, selected taking into account the specifics of the pathogen. In addition, immunotherapy will be prescribed to restore and activate the body's protective functions. If necessary, local treatment will be carried out - the introduction of medications directly into the affected organ.
If the cause of discomfort during urination is not of an infectious nature, then treatment depends on identifying the cause of the discomfort. Surgery is possible if there are injuries, tumors, or large kidney stones.
In addition to treatment, the patient will be recommended a lifestyle that promotes a speedy recovery. This includes drinking plenty of fluids to increase the volume of urine, complete or partial refusal of hot and spicy foods, fast food, alcohol, avoiding severe cooling and overheating (for example, in a bathhouse). Sexual abstinence will also be recommended until recovery.
Why does it hurt?
The most common causes of pain are diseases such as:
- prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate gland;
- urethritis – inflammatory processes of an infectious nature in the urethra (urethra);
- cystitis - inflammation of the bladder;
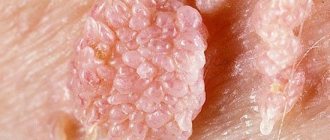
- papillomas - benign formations in the urethra that prevent the normal outflow of urine;
- urolithiasis - the formation of stones in the urinary system with subsequent blockage of the ureters.
In other cases, the reason may be:
- injuries;
- tumors;
- inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis);
- bladder rupture;
- venereal diseases;
- suffered hypothermia;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- stagnation of urine.
At the initial stage, you should find the cause of the problem, and only then begin treatment.
Prostatitis - a source of burning in the urethra
Inflammation of the prostate is of an infectious nature and occurs without the participation of infectious agents.
Agents for the occurrence and development of the disease are microscopic fungi, bacteria, protozoa, and viruses. More often than others, chlamydia, trichomonas and gonococci provoke inflammation of the prostate.
The disease makes itself felt by spreading pain from the prostate to the perineum and areas of the pelvic girdle.
To treat prostatitis, the cause and type of disease are diagnosed. If prostatitis is infectious, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Non-infectious prostatitis requires further examination and the development of an individual algorithm for eliminating the disease.
Treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system
After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medication. The patient can also pay attention to traditional methods of combating the disease. It is very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene. It is necessary to wash regularly using water at room temperature or chamomile decoction. The doctor may prescribe painkillers: “Spazmalgon” or “No-shpu”. The exact dosage and method of application are indicated by a specialist. If the examination reveals pathogenic microelements, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Together with antibiotics, it is recommended to take medications that contain beneficial bacteria for the proper functioning of the intestines.
Preventive actions
For a complete recovery, it is important to follow preventive measures. It is recommended to avoid hypothermia of the lower extremities and not sit on cold surfaces. Do not neglect personal hygiene and contraception if your sexual partner is unstable. This will help protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases. It is important to go to the toilet at the first urge to urinate. The constant accumulation of urine negatively affects the health of the genitourinary system and the entire human body. Underwear should be chosen from natural fabrics, preferably cotton. In winter, clothes should be warm and not restrict movement.
Treatment of burning sensation in the urethra
Medications should be prescribed if:
- burning in the urethra lasts more than two days;
- painful sensations, itching and atypical discharge appear;
- the number of urges to urinate increases;
- back pain added;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- The temperature rose and a headache appeared.
Specialists who will help make the correct diagnosis:
- gynecologist;
- dermatovenerologist;
- venereologist.
General treatment for burning in the urethra is focused on restoring the vaginal microflora. It is also necessary to restore the layers of the urethra and increase the immunity of the body as a whole.
Medication
In case of acute inflammation, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken.
When a diagnosis of urethritis is made, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics.
Most Popular:
- Amoxiclav.
- Ciprofloxacin.
- Norfloxacin.
- Pefloxacin.
Amoxiclav
Ciprofloxacin
Norfloxacin
Pefloxacin
These drugs are used to prevent inflammation in the genitourinary system. Vaginal suppositories and antibacterial tampons are also used.
Procedures aimed at warming areas of the body are prescribed - mud and paraffin applications. This procedure will give a slight irritating effect, increasing blood flow in the urethra and optimizing metabolism.
In addition, they undergo immunotherapy, which helps restore the body's active resistance to disease.
Consumption of alcohol, hot and spicy foods is prohibited.
Mycoplasmosis
Antibiotics are also the basis of therapy for mycoplasmosis:
- Azithromycin.
- Vilprafen.
- Tetracycline.
- Erythromycin.
- Klacid.
- Macropen.
Azithromycin Vilprafen Tetracycline
Erythromycin
Klacid
Macropen
The doctor individually chooses the method of administering the drug - tablets, injections or ointments.
During pregnancy, antibiotics are not prescribed if the harm from them exceeds the potential harm from mycoplasmosis.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics:
- Ofloxacin;
- Cefixime;
- Ciprofloxacin.
Ofloxacin Ciprofloxacin
Cefixime
After completing the course of antibiotics, patients are prescribed physical therapy:
- inductothermy;
- laser therapy;
- UHF and electropheresis;
- Darsonval and ultrasound therapy.
After completion of all procedures, the patient undergoes a control examination. The results make it possible to confirm final recovery.
A diet with plenty of dairy products and plant-based products is recommended.
Candidiasis
You can get rid of candidiasis with antifungal medications:
- polyenes – Levorin, Nystatin, Amphotericin B, Pimafucin;
- imidazoles – Nizoral, Clotrimazole;
- trinazoles – Orungal, Fluconazole.
Medicines come in different forms: suppositories, injections and tablets.
Candles have proven their effect well:
- Clotrimazole;
- Miconazole;
- Natamycin.
Clotrimazole
Miconazole
Pimafucin (natamycin)
A regimen for the treatment of trichomoniasis can only be prescribed by a doctor. Moreover, both partners must undergo treatment for 7-14 days.
The most effective ones are:
- Metronidazole (droppers, tablets, injections or gel);
- Tinidazole and Nitazole;
- Klion-D.
During pregnancy, the disease poses a danger to the woman herself, and not to the fetus.
Folk remedies
Herbal medicines can be used as auxiliary agents.
Medicinal plants and decoctions from them are used for douching, medicinal baths and vaginal tampons:
- Trichomoniasis is treated with a decoction of 1 tablespoon of oak bark , a tablespoon of chamomile flowers, 3 tablespoons of nettle leaf, and 5 large spoons of knotweed herb. Mix the composition and pour two tablespoons of the mixture into a liter of boiling water. Leave in a dark place, strain.
- When treating female urethritis, the inclusion of parsley, celery, and beets in the diet has a positive effect.
- To get rid of the burning sensation, it is recommended to make a decoction of 2 large spoons of linden blossom. Pour 400 ml of hot water over them and set on low heat. Cook for 10 minutes, then strain and cool. Take a glass in the morning and at night.
- Treatment of cystitis is usually carried out in courses of 2 months. There should be a break of 7-14 days between courses. Bearberry decoctions and kidney teas are successfully used. Along with this, medicinal mixtures are used, consisting of chamomile, St. John's wort, plantain, horsetail and calamus. If herbal medicine is combined with warming procedures and diet, the result will be in 2 weeks.
When to see a doctor
A person should seek medical help if a burning sensation when urinating lasts longer than a few days, or if there is:
- blood in urine
- fever
- lower back pain
These may be signs of serious illnesses such as a kidney infection.
Older adults, children, and pregnant women should see a doctor if they have symptoms of a UTI.
A UTI can affect any part of the urinary tract, which includes:
- ureters
- bladder
- urethra
- kidneys
Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men because the female urethra is shorter. A short urethra makes it easier for bacteria to access the bladder, ureters or kidneys. Research shows that about 40-60% of women have UTIs. The urethra is also closer to the anus, which contains bacteria that cause UTIs.
Pain when urinating in women, video
Gynecologist of the highest category Irina Vladimirovna Garyaeva about the causes of pain when urinating.
Source - KVD - dermatovenerological dispensary Sources:
- DIAGNOSTIC AND TREATMENT ASPECTS OF URINARY DISORDERS IN WOMEN. Danilov V.B., Volnykh I.Yu., Bakhareva O.M. // Pacific Medical Journal. – 2003. –№2. – P.20-25.
- URINARY DISORDERS IN WOMEN OF DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS. Danilov V.V., Volnykh I.Yu., Bakhareva O.M., Mukhotina A.G. // Pacific Medical Journal. – 2003. – No. 1. – P.76-77.
- Detrusor overactivity and urge urinary incontinence. Al Shukri S. Kh., Kuzmin I. V. // St. Petersburg. — 2001.
- Urology and nephrology. Trapeznikova M.F., Bazaev V.V., Golubev G.V. and others // 1996. – No. 2. – P. 2-4.
- Neurogenic bladder dysfunctions. Ed. M.D. Javad-Zadeh and V.M. Derzhavina. // M.: Medicine. — 1989.
- https://www.dissercat.com/content/imperativnye-narusheniya-mocheispuskaniya-u-zhenshchin-diagnostika-medikamentoznoe-lechenie
- https://www.webmd.com/women/dysuria-causes-symptoms#1
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323105.php
- https://www.healthline.com/health/urination-painful
- https://www.globalhealingcenter.com/natural-health/frequent-urination-in-women/
Symptoms
A burning sensation in the bladder area is not the only complaint; each nosology (disease) is characterized by a combination of symptoms, on the basis of which the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes diagnostic procedures to confirm it. In the first place in etiology are infectious processes, a little more about each of them below.
Urethritis
Inflammatory changes in the urinary canal are accompanied by pain and a burning sensation during urination. Hyperemia around the urethra and changes in urine clarity may occur.
Cystitis
Inflammation of the mucous (inner) lining of the bladder in both sexes is clinically manifested by dysuric disorders: discomfort and burning in the lower abdomen, painful and frequent urination. Increased pain with a full bladder. Temperature changes are not typical. Urine is cloudy.
Prostatitis and prostatic hyperplasia
The anatomical location of the prostate around the urethral canal is the reason for changes in the function of urine excretion in any pathology of the organ. Main complaints:
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- a constant feeling of heaviness, discomfort, and sometimes pain in the perineum;
- increased frequency of urination at night;
- change in urine stream (volume, strength);
- inability to pass urine (at large stages of adenoma) - acute retention - requires urgent assistance from medical personnel.
Prevention
The easiest way to prevent a disease is to avoid suffering from its symptoms later. There are several measures to improve the functioning of the genitourinary system.
What to do to prevent painful urination:
- A sufficient amount of fluid must enter the human body every day. According to doctors, approximately 8 glasses of clean water is considered the norm.
- As soon as you feel the urge to go to the toilet, you need to immediately empty your bladder. After going to the toilet, it is advised to immediately perform hygiene of the external genitalia. If possible, wash with warm water.
- Underwear should be made of natural fabric; synthetics do not allow the skin to breathe. In principle, artificial fabrics and excessively tight underwear have a detrimental effect on women's health.
- After sexual intercourse is over, it is worth visiting the toilet and performing intimate hygiene.
- If therapeutic therapy does not give the desired result, then it is better not to take a bath, but to carry out water procedures using a shower.
- After washing, the genitals must be wiped or dried. For this purpose, use cotton towels or soft paper napkins.
- Flushing the ureter has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the ureter. Unsweetened teas, warm compote and still water are good for this purpose.
- Sometimes the process of emptying the bladder is too slow and painful, so it is worth helping the body. You can perform the process while in a bathtub with water.
Pain when urinating cannot be tolerated; when the first signs appear, you should visit a specialized doctor. Otherwise, there is a risk of developing a serious pathology in a chronic form.
Causes
In half of the cases, burning sensation when urinating in women is caused by inflammatory processes in the urogenital system. Less commonly, the symptom is caused by changes in the structure of the mucous epithelium of the genital tract, the release of sand due to urolithiasis. Conditions accompanied by a burning sensation when urinating can be identified fairly quickly - it is carried out by a doctor.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra occurs with diabetes mellitus, as well as due to a number of reasons:
- Rubbing the urethra with excessively tight underwear
- Scratching the genitals and damaging their mucous membranes
- Failure to observe personal hygiene, including after sexual intercourse, visiting the toilet, during menstruation
- Allergies to the latex from which condoms are made, or to contraceptives used externally
Urethritis also occurs due to hypothermia, alcohol intake, treatment with potent drugs, and abuse of pads during menstruation. The main symptoms of the disease are a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, discomfort in the suprapubic region, and an increased urge to urinate.
Choose a specialist, read reviews and make an appointment with a urologist online
Bacterial cystitis
Inflammation of the bladder, occurring in acute and chronic phases. When the disease takes a protracted form, its clinical manifestations become less pronounced. In acute cystitis, a woman is bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, discomfort during urination, increased urge, and a slight increase in body temperature. In the chronic form of the pathology, the listed symptoms manifest themselves to a lesser extent, but the inflammatory process still progresses.
The main reason for the development of bacterial cystitis is the penetration of a pathogenic microorganism into the bladder cavity, which is facilitated by:
- Hypothermia
- Sexual intercourse with a partner who does not observe good personal hygiene
- Entry of an infectious pathogen into the bladder from other inflammatory foci present in the body
- Severe food or drug poisoning
If inflammation of the bladder is not completely eliminated, but only healed, the disease will subsequently worsen at the slightest hypothermia.
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of the renal pelvis, which develops as a result of exposure to low temperature and stagnation of urine. An additional reason is the entry of an infectious pathogen from nearby pathological foci. In its acute form, the disease manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. When the patient does not receive the necessary treatment, the pathology takes a chronic course. In this case, the manifestations of the disease become less pronounced.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis:
- Increase in body temperature to high numbers
- Girdle pain in the lumbar back
- General restlessness
- Dyspeptic disorders
- Weakness, lack of appetite
- Increased urge to urinate
Pyelonephritis is treated in a hospital setting, since the patient should remain in bed. Simultaneously with the main treatment, a woman needs to adhere to diet therapy. A dietary feature is to avoid eating salty, sour and spicy foods. The listed type of nutrition causes irritation of the kidneys, which contributes to the expansion of the spectrum of inflammation. The patient is advised to limit water intake and stop drinking coffee.
Sometimes pyelonephritis occurs simultaneously with cystitis or contributes to the development of bladder inflammation. This is explained by the anatomical features of the organs of the urogenital tract. The kidneys are connected to the bladder by ureters - thin canals. Along them, inflammation passes from one part of the urogenital system to another.
Vaginal candidiasis
The second definition of the disease is “thrush”. The pathology is caused by fungi of the genus Candida. A woman can become infected with them during diagnostic or therapeutic manipulation of the organs of the urogenital system. Other reasons for the development of vaginal candidiasis are diabetes mellitus, intimate intimacy with a partner who does not follow the rules of personal hygiene; long-term use of antibiotics. Fungal infection of the vagina occurs due to intestinal dysbiosis, which is associated with a violation of its natural microflora.
Clinical manifestations of the disease:
- The appearance of copious amounts of curdled secretion from the vagina
- Swelling, redness of the vulva (determined during external examination on the gynecological chair)
- Severe discomfort when urinating
- Intense itching in the genital tract
- The appearance of an unpleasant fishy odor from urine, sometimes a change in its shade to a lighter color
- Decreased libido caused by pain
If vaginal candidiasis is caused by intestinal dysbiosis, an indispensable condition for removing the disease is the restoration of microflora in the digestive tract.
Genital herpes
Infectious and inflammatory lesions of the genital mucosa. The main route of transmission is sexual. Manifestations of the pathology are pain when urinating, decreased libido, swelling of the genital mucosa. As the herpes virus progresses in the blood, the patient develops rashes on the genitals.
Inflammatory elements are in the form of blisters, they are grouped and painful. Treatment consists of the use of antiviral drugs, while the woman’s sexual partner undergoes therapy. While undergoing therapy, you should not engage in intimate intimacy. Genital herpes burdens the process of bearing a child and causes complications in the development of the fetus.
Atrophic vaginitis
Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, which occurs due to endocrine diseases, stress, hormonal imbalance, and increased blood sugar. Due to pathological changes, the vaginal tissue becomes thinner, which negatively affects the general condition of the organ and the woman’s well-being.
Symptoms of atrophic vaginitis:
- Feeling of increased dryness in the vagina
- The appearance of small cracks and erosions on the mucous membrane of the genitals
- Cutting, burning when urinating
- Severe discomfort during intimacy
If the disease is caused by a deficiency of hormones, the patient is administered synthetic analogues of these biologically active substances. Replacement therapy helps restore their balance and has a beneficial effect on the condition of vaginal tissue.
Gonorrhea
One of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. The main route of infection is sexual. Clinical manifestations of gonorrhea:
- Discharge of a drop of pus after each urination
- Increase in body temperature to low numbers
- Severe and regular vaginal itching
- Intense pain when urinating
- Cystitis
- Abundant purulent and mucous secretion from the vagina, having a pungent putrefactive odor
When examined in a gynecological chair, the doctor reveals swelling of the vaginal walls, the presence of discharge, and redness of the mucous membrane of the genital tract. During therapy you should not have intimacy. At the same time as the patient, her sexual partner should undergo treatment.
Trichomoniasis
Sexually transmitted disease. The main reason for the development is the entry of a pathogenic pathogen into the urogenital tract during intimacy. Clinical manifestations of the disease: burning sensation when urinating, menstrual irregularities, light-colored foamy vaginal secretion. Additional signs are vaginal itching, discomfort during sexual intercourse, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, weakened libido.
Ureaplasmosis
A sexually transmitted infection, the main route of transmission is sexual. Manifestations of the disease are purulent vaginal discharge, bursting pain during intimacy, decreased libido, and menstrual irregularities. Additional symptoms are slight itching in the genital canal, the appearance of a putrid or fishy odor from the urine. Ureaplasmosis is the leading cause of cystitis. Therefore, with frequent exacerbation of inflammation of the bladder, a woman should donate blood to exclude the presence of ureaplasma in it.
Menopause, menopause
With age-related changes in the body, hormonal imbalance may develop. It negatively affects the condition of the mucous membranes of the reproductive system. Burning sensation when urinating is one of the many signs of menopause. Menopause is accompanied by increased sweating, dizziness, a feeling of a rush of heat to the face, and increased blood pressure.
Taking medications
Potent medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants), if the dosage is exceeded, can cause discomfort inside the urethra. Burning sensation when urinating is caused by irritation of the vulnerable mucous membrane of the urogenital tract. Additionally, there is a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen, a sensation of hot air in the genital canal.
Movement of sand or stones in the ureter
With urolithiasis, stones are formed - stone-like deposits. Regardless of their exact location - inside the kidneys, bladder or ureter - they can change their position and begin to move outward. Then the woman experiences a whole range of symptoms:
- Pain in the lumbar back extending to the lower abdomen.
- Increase in body temperature to insignificant limits.
- A general restless state, including irritability, short temper, and inability to assume a comfortable body position.
- Severe nausea and repeated vomiting, which does not bring relief.
- The appearance of blood in urine, and it takes on the appropriate shade.
- Increased urge to urinate or complete cessation of urine production - depending on the size of the stone, the amount of sand, and their location. Stones can block the ureters or compress the renal pelvis, making it difficult for urine to flow out, or stimulating increased urine production.
The main reasons for the formation of stones are poor diet, hereditary predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, and systematic stagnation of urine. The removal of sand or stones is provoked by a sudden change in body position, lifting heavy objects, exposure to hot water during bathing or showering.
Why does a burning sensation occur after urination in men?
In men, the length of the urethra is much longer than in women, so bacterial inflammation occurs less frequently in them, and among the main causes, in addition to sexually transmitted infections, the following can be identified:
- The consequences of inflammation of the urethra are urethritis.
- Urolithiasis, when sediments of urine, consisting of insoluble salts, irritate the mucous membrane, passing through the urethra.
- Most often, burning sensation after urination in men occurs in the presence of various diseases of the prostate gland (for example, prostatitis), which provoke a violation of the outflow of urine.
Preventing painful urination
To avoid diseases that can provoke symptoms such as painful urination, you must remember the following rules:
- Maintain body hygiene: take a hot shower with soap at least twice daily, which can get rid of pathogenic bacteria.
- When washing underwear, you should never use strong chemicals with a bleaching effect, as their particles can remain on the fabric pile and cause irritation.
- Hypothermia should not be allowed, especially if there is already a history of kidney and bladder disease. It is necessary to wear warm, waterproof shoes, and avoid prolonged exposure to damp or cold rooms, such as basements. For at least one year after suffering an acute urinary tract infection, it is not recommended to swim in open water, even in very warm weather. It is also very important to pay attention to the purity of the water: if it raises suspicions, you should not swim in it in principle.
- It is very important to empty your bladder when you feel the urge. Long-term patience makes urine more concentrated, which provokes the development of cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urethritis.
- And finally, it is very important to maintain a healthy diet: limit the use of chemical dyes and preservatives. This will keep your immune system healthy so that it can fight and resist any infections that come through.
What will happen if left untreated?
If a woman refuses treatment, pain complications and their consequences begin to appear, which can go into an acute or chronic phase, but in themselves represent a much more serious problem than it was before. The female urethra is physiologically wider and shorter than that of men. Any inflammation or infection quickly spreads to other organs that are located higher: the bladder, ovaries, kidneys and others.
Complications
Since pain during urination appears more often with sexually transmitted infections with impaired microflora, women almost always experience inflammation. Such changes affect the cervix and can develop into erosion.
Complications can be very serious, for example, erosions without treatment turn into cancer, and some viruses are completely oncogenic, including papilloma, and types 16 and 18 increase the risk of cervical cancer. Infectious inflammation leads to adhesions. In addition to direct complications, without treatment, inflammation or viruses spread to other internal organs, causing:
- perihepatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- appendicitis;
- peritonitis.
An urgent visit to a doctor is needed not only for regular pain, but also for fever and non-physiological discharge from the urethra.
Consequences
The most dangerous consequences are associated with the female reproductive system and pregnancy. The described complications lead to:
- infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- unfavorable course of pregnancy with an increased risk of miscarriage, miscarriage or early birth;
- disruption of fetal development due to transmission of infection in utero;
- infection of the child during childbirth and serious pathologies in the future.
Pain and discomfort during the outflow of urine should raise suspicion in patients. If symptoms do not go away within several hours or days, then you should immediately consult a doctor.