Causes
Syphilis is caused by a bacterium called Treponema pallidum.
Treponema pallidum
Infection most often occurs through sexual contact, somewhat less often - through blood transfusion or during gestation, when the bacterium falls from mother to child.
Bacteria can enter the body through small cuts or abrasions on the skin or mucous membranes. Syphilis is contagious during its primary and secondary stages, and sometimes during the early latent period.
Syphilis is not spread by sharing toilets, bathtubs, clothing or utensils, through door handles and swimming pools.
After treatment, syphilis itself does not recur, but you can become infected again by coming close to an infected person.
Risk factors
You are at increased risk of contracting syphilis if you:
- participated in unprotected sex;
- participated in sex with multiple partners;
- a man who has sex with men;
- infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Symptoms, course of the disease in women
Syphilis develops gradually, and its symptoms change. Therefore, the course of the disease is divided into several stages.
Primary syphilis
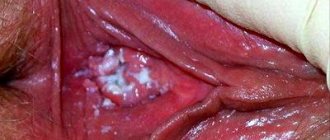
The first manifestation of the disease is chancre. This is an ulcer with clear edges and a dense base, which, due to its painlessness, can go unnoticed. In women, chancroid most often occurs in the perineum and labia, on the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix, and rectum. The mucous membranes of the mouth and lips, as well as many other areas, may also be affected.
On average, after 3-8 weeks, the primary chancre heals, and the woman looks absolutely healthy. However, at this time, treponema pallidum actively multiplies and spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream.
Secondary syphilis
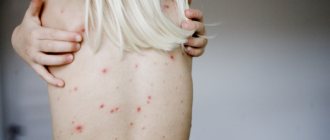
6-8 weeks after the appearance of hard chancre (in 75% of those infected by this time it has already disappeared), active damage to the skin, mucous membranes and other organs and systems begins. A woman may notice rashes on the palms, soles, mucous membranes, and skin that are completely different in appearance (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Rash on the palms of secondary syphilis. Photo: CDC/Susan Lindsley Figure 2. Skin manifestations of secondary syphilis. Photo: CDC Public Health Image Library
Since during this period the pathogen spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream, there are also damage to organs and systems that are invisible to the eye. Those infected may notice weakness and dizziness, nausea, lack of appetite, decreased hearing, vision and other alarming signs of the disease.
Important! The secondary period of syphilis with rashes on the skin and mucous membranes is the most contagious, since in each element of the rash there is an accumulation of treponemes that can infect a healthy person.
Latent period
After a period of secondary syphilis, an asymptomatic, latent period occurs. At this time, the body begins to actively produce protective antibodies to the infectious agent, the reproduction of the bacterium slows down, and all visible manifestations of syphilis disappear.
However, treponemes continue to live in the body, and, depending on the severity and strength of the immune response, they can either not manifest themselves for years or decades, or cause relapses of the disease.
Tertiary syphilis
Today, severe tertiary form of syphilis is rare. This is a late stage of the disease that only develops if left untreated.
Tertiary syphilis develops in a third of infected people who have not undergone treatment.
Clinical manifestations of tertiary syphilis are caused by a weakened immune response and syphilitic damage to various organs and systems: neurosyphilis, syphilis of the aorta, heart valves, syphilis of the bones, etc.
Features of the course of syphilis in women
Does chancroid always occur?
No, if you are infected with syphilis through blood (through blood transfusion, using a needle from an infected person) or transplacentally, hard chancre will not form. In this case, the secondary period of the disease will immediately become visible.
The nature of discharge during infection
Syphilis does not cause specific discharge from the genital tract. This is a disease that can equally affect all organs and systems and is not localized in the genital tract - treponema pallidum penetrates directly into the blood and lymph flow of a person, causing systemic lesions.
Are there any changes in the menstrual cycle?
Menstrual irregularities are not typical for syphilis. However, the menstrual cycle may change in the later stages of the disease due to syphilitic damage to the reproductive system and organs involved in the regulation of the sexual cycle.
Primary signs of the disease
Before you begin treatment for syphilis, it is worth knowing how syphilis manifests itself. So the most important sign of syphilis in a patient manifests itself in the form of a hard, dense chancre and a significant increase in the size of the lymph nodes.
Chankra – Photo of the initial stage
Chancre is an ulcerative neoplasm or a focus of erosion, regular rounded in shape, with clear edges, filled with liquid and most often occurs at the site of contact with the carrier of the disease.
Syphilis also manifests itself with the following additional signs:
- insomnia and increased body temperature in the patient;
- attacks of headache, aches in joints and bones;
- swelling of the genitals and the appearance of such a symptom as a syphilitic rash.
Routes of infection. How long does it take for the disease to make itself known?
Infection with syphilis begins from the moment the pathogen, Treponema pallidum, enters the body. The ideal environment for its habitat is lymph nodes, and in later stages - blood.
Routes of infection by the pathogen:
- The main route of infection is through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person. The causative agent of the disease has the ability to remain active and multiply in all body fluids and especially in male sperm and vaginal discharge in women. Infection is possible not only with traditional sex, but also with anal and oral sex, and the type of sexual contact does not affect the risk of infection; in all cases it is the same. Sometimes, anal contact can be many times more dangerous, since the infection affects through damaged mucous membranes and skin, and the likelihood of cracks in the rectum is much higher than in the vagina. This confirms the statistics that among men with non-traditional sexual orientation the disease is much more common.
- Infection through household contact is much less common due to the fact that the bacterium does not exist in the open air for long. But this route of infection occurs among partners, one of whom does not suspect that the other has the disease and does not take precautions. Infection can occur through kissing or through the use of shared household appliances (dishes, personal hygiene products). Household syphilis can be avoided by observing basic hygiene standards.
- Infection through blood occurs during transfusion from a sick donor and when using the same syringe. The risk group for such infection are drug addicts, as well as homosexuals for sexual infection.
- Occupational infection with syphilis occurs in people in the medical profession. In this case, everyone who comes into contact with fluid secretions from the patient’s body and has microcracks and injuries on the skin (dentists in contact with saliva, surgeons in contact with the patient’s blood, midwives in contact with the secretions of a woman in labor) are exposed to infection.
- Infection of the fetus from the mother , through the placenta during pregnancy. This type of syphilis in medicine is called congenital.
- Infection of a child during labor as it passes through the birth canal.
- Infection of a child during breastfeeding through mother's milk.
95% of all syphilis infections occur through unprotected sex.
Important. Unprotected sex with an infected partner leads to infection in 45% of cases.
Video in this article:
Incubation of the disease
The period of manifestation of the disease and the first signs of syphilis in women can appear from a week to more than three months, but the average period is from 15 to 40 days. In other cases, there are factors that slow down or accelerate the onset of symptoms.
The long incubation period is influenced by:
- old age of the infected person;
- hyperthermic reaction with concomitant diseases;
- therapy of other diseases using antibacterial agents that slow the spread of infection.
A reduction in the incubation period occurs when:
- weakened immunity of the infected person;
- when a large amount of the pathogen enters the body at one time.
Important. The microbe that causes syphilis retains its activity and the ability to multiply for up to 48 hours in a humid environment with a temperature of about 37°C. For example, wet bed sheets at room temperature.
Incubation period and its symptoms
Symptoms of syphilis during its incubation, latent period do not manifest themselves as such - in this case, the disease is diagnosed not by its external manifestations, but based on the results of tests carried out using the PCR technique. The duration of the incubation period is 2-4 weeks, after which the disease passes to the stage of primary syphilis.
Primary stage of syphilis and its symptoms
Every person should know how the disease manifests itself - the sooner it is diagnosed, the sooner treatment for syphilis is started, the better the chances of a successful recovery.
First of all, treponema, after entering the body, affects nearby lymph nodes, beginning to actively develop and multiply in them.
The first symptoms of syphilis will manifest themselves in the formation of a chancre at the site of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms - a hard, regular oval shape, which will open as the disease progresses, forming an ulcer.
Most often, chancre does not cause concern, is not painful and is mostly localized in the area:
- genitals;
- groin area;
- less often on the thighs and abdomen;
- near the anus;
- mucous tonsils;
- vagina.
After a certain period of time, the patient is diagnosed with enlarged lymph nodes located near the chancre - most often they are localized in the groin area. A person can independently identify this symptom in himself - in this case, a nodular-shaped compaction that is hard to the touch is palpated.
In certain cases, due to problems with the outflow of lymph, the patient is diagnosed with swelling of the genitals, tonsils and larynx - it all depends on the location of the source of infection, the place of introduction of pathogenic microflora.
Primary syphilis as a stage of the disease lasts about 2-3 months - if treatment is not started in a timely manner, then the negative symptoms simply disappear. This does not indicate a complete recovery of the patient, but rather signals the transition of the disease to a new, next level of progression in its manifestation.
Briefly about the main thing
Syphilis is not just a dangerous, but in a sense an insidious infection. It’s insidious because its first stage is easy to miss, and the secondary stage is more pronounced and more difficult to treat. The following photos are intended to show all possible manifestations of infection in the second stage and, possibly, prevent big problems.
Neonatal or congenital syphilis
Neonatal syphilis in pregnancy results in fetal death in 40% of infected pregnant women (stillbirth or death soon after birth), so all pregnant women should be tested for syphilis at their first prenatal visit.
Diagnosis is usually repeated in the third trimester of pregnancy. If infected children are born and survive, they are at risk of serious problems, including developmental delays. Fortunately, syphilis during pregnancy is treatable.
Vesicular syphilide
Vesicular syphilide occurs in severe syphilis. The main places of localization of syphilides are the skin of the extremities and torso. On the surface of the formed plaque, which is red in color, many grouped small vesicles (bubbles) with transparent contents appear. The vesicles quickly burst. In their place, small erosions appear, and when they dry, crusts form on the surface of the rash. When cured, a pigment spot with many small scars remains at the site of the lesion.
The rashes are resistant to therapy. With subsequent relapses they appear again. Vesicular syphilide should be distinguished from toxicerma, simple and acute herpes.
Manifestations of the disease in both sexes
In men, syphilis most often affects the penis and scrotum - it is on the external genitalia that the disease primarily manifests itself in the form of negative symptoms.
In women , the disease most often affects the labia minora, vagina and mucous membranes. If sexual partners practice oral or anal sex, infection and subsequent damage to the circumference of the anus, oral cavity, mucous membrane of the throat and skin in the chest and neck area occurs.
The course of the disease is long-term, if it is not treated in a timely manner, it is characterized by a wave-like manifestation of negative symptoms, a change in both the active form of the pathology and the latent course.
Basic terminology
Tripper, Lewis or syphilis are all names for the same disease, caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. This microorganism does not care whose body it infects. At the same time, syphilis occurs more often in women than in children and men. The following photos will help you understand all the main features of this insidious and extremely dangerous disease.
How is syphilis diagnosed?
In the process of diagnosing such a serious disease, you should not diagnose yourself, even if its characteristic symptoms and signs are clearly expressed. The thing is that rash, thickening and enlargement of lymph nodes can also manifest themselves in other diseases as a characteristic sign. It is for this reason that doctors diagnose the disease itself by visually examining the patient, identifying characteristic symptoms on the body, and by conducting laboratory tests.
In the process of a comprehensive diagnosis of the disease, the patient undergoes:
- Examination by a dermatologist and venereologist. It is these specialists who examine the patient, his genitals and lymph nodes, skin, collect anamnesis and refer him for laboratory tests.
- Detection of treponema in internal contents, gum fluid and chancre using PCR, direct reaction to immunofluorescence and dark-field microscopy.
In addition, doctors conduct various tests:
- non-treponemal - in this case, the presence of antibodies against the virus, as well as tissue phospholipids that are destroyed by it, are detected in the blood in the laboratory. This is the Wasserman reaction, VDRL and others.
- treponemal, when the presence or absence of antibodies to such a pathogen as treponema pallidum is diagnosed in the blood. These are RIF, RPGA, ELISA, immunoblotting level research.
In addition, doctors also prescribe instrumental examination methods to search for gummas - this is research using ultrasound, MRI, CT and x-rays.
Third stage of the disease
Nowadays, stage three syphilis is not often encountered. This is very good news not only for doctors, but also for the patients themselves. Due to the fact that the infection is diagnosed in time, doctors prescribe the optimal treatment, which allows stopping the disease in the initial stages. If the disease is not treated, it may not make itself felt for the first couple of years, slowly affecting the body from the inside.
In no more than five years, syphilis will slowly but surely enter its third stage. During this period, internal organs and the endocrine system are seriously damaged. The disease greatly affects the senses. Even at this stage, the patients' bodies are covered with small tubercles called syphilides. When they are opened, pus is released. Sometimes syphilides appear only on the body, but with advanced disease they can form on internal organs, which in turn is fatal.
Cartilage and other soft tissues will undergo severe deformation. They can degenerate into tumors, which are called gummas.
Syphilis is not only a serious, but also a very dangerous disease. The danger lies in the fact that for many years it may not manifest itself, proceeding exclusively in a latent form. Sometimes external signs appear only at the third stage. To protect yourself from troubles and identify the infection at the earliest stages, you need to undergo a routine examination with a doctor.
Modern treatment of syphilis
Modern treatment with effective drugs allows us to talk about timely cure of the patient, but only if the disease has not progressed to the last stage of its course, when many organs, bones and joints are destroyed and damaged, which cannot be restored.
Treatment of pathology should be carried out exclusively by a qualified venereologist in a medical hospital, based on the results of an examination, a survey of the patient and the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
So treating syphilis at home, using your own and folk methods and recipes, is unacceptable. It is worth remembering that this disease is not just an acute respiratory viral infection, which can be cured with hot tea with raspberries - it is a very serious infectious period that destroys the body from the inside. At the first suspicion or symptoms of the disease, immediately consult a doctor, undergo an examination and a prescribed course of treatment.
The course of therapy takes a lot of time - the recovery process itself is long and the main thing here is to have a lot of patience.
As medical statistics and the practice of doctors show, advanced cases can be treated for more than one year. You can talk about recovery only after laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis - healthy, but do not stop it after all the pimples and ulcers and hardening of the lymph nodes have disappeared from the body.
The main thing that the patient himself should remember while undergoing treatment is to completely exclude any sex during this time.
Even if the partner’s results showed a negative result for the presence of a pathogen in the body, he is still recommended to undergo a course of preventive treatment. The course of treatment for syphilis itself includes several directions - this will be discussed further.
Course of antibiotic treatment
Each patient, man and woman, is prescribed antibiotics during the course of treatment - the causative agent of this infectious disease is sensitive to them. So the drug itself, the duration of its use and dosage are prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis, taking into account all the tests and results of the patient’s examination.
The disease is sensitive to the following groups of drugs:
- drugs containing penicillin;
- macrolides and the antibiotic Ceftriaxone .
Thus, antibiotics containing penicillin act very effectively during treatment, having a detrimental effect on the causative agent of the pathology. When diagnosing primary syphilis, they provide excellent treatment dynamics.
Today, dermatovenereologists do not practice the method of the first loading dose of penicillin administration; the method of intramuscular administration of the drug at intervals of every 3 hours is more effective, which ensures its constant concentration in the body.
Penicillin (a product made from certain types of mold)
Thus, drugs containing penicillin are excellent in combating the early stages of neurosyphilis, but so far the nervous system has not undergone irreversible changes in its functioning, and also given the congenital nature of syphilis damage to the body.
Diagnostics
Since syphilis can be easily cured in the early stages of the disease, at the first suspicious symptoms you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you suspect the presence of symptoms of syphilis, you should not immediately make a frightening diagnosis and panic. You need to see a doctor. At the first stage of diagnosis, a general practitioner or therapist (you can make an appointment with a doctor at your place of residence or at any consultative and diagnostic center) will conduct an initial examination and, if necessary, give a referral to see a specialist.
Further examination is carried out by a dermatologist or venereologist at a consultation center or dermatovenerological dispensary, and prescribes tests and treatment.
What tests should I take?
There are two groups of methods for diagnosing syphilis - specific (treponemal) and nonspecific (non-treponemal) methods.
Blood tests
In the patient’s blood, doctors can detect antibodies that are produced in response to the entry of an infectious agent, Treponema pallidum, into the body.
Non-treponemal tests
Nontreponema tests are based on detecting antibodies that the patient's body produces in response to lipids contained in the membrane of Treponema pallidum (and not to Treponema pallidum itself). These antibodies can appear in the blood 1-2 weeks after a chancre has formed on the skin, that is, on average 4-5 weeks after the bacteria enters the human body.
These tests are screening tests. This is an express diagnosis that does not require much time or money. At the same time, it is important to understand that a positive test only indicates that the person has encountered the pathogen previously, but does not answer the question of whether there is an infection in the body at the moment.
Nontreponemal tests often give false negative results. They are not highly sensitive at some stages of the disease. False-positive reactions may also occur, so these methods require confirmation through additional studies.
Treponemal tests
The technique in this case is similar to the previous one. Treponema tests are based on the detection in the patient’s blood of antibodies produced by the body to the treponema itself. They require more time and expense, but such tests are more accurate in the early stages of the disease. When detecting later forms, sensitivity decreases. Treponemal tests include various serological tests, such as the Wassermann test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Wasserman reaction
This is a standard serological reaction that is still used today. Treponemal antigen is added to the blood sample, which reacts with antibodies in the blood if they are present.
The reaction is insensitive at the very beginning of the disease (becomes positive only after 6-8 weeks), as well as in the tertiary stage. Easy to perform, but often gives a false positive result.
Linked immunosorbent assay
It is most often used in diagnosing the disease, as it is the most sensitive of the treponemal tests. The purpose of the analysis is to determine the total amount of antitreponemal antibodies. A solid carrier is used on which syphilis antigens are collected and to which a sample of the patient’s blood is added. As with other treponemal tests, false-positive results are possible.
Smear or scraping
A smear is taken from a woman’s urethra or cervical canal, and a scraping is taken from the rashes that appear with syphilis, regardless of the location of the rash element. This can be the skin, and the mucous membrane of the oral cavity or rectum. The purpose of a scraping or smear is to determine the presence of treponemes. This is possible either by the microscopic method (even a living treponema can be seen through a microscope) or by the PCR method.
PCR is a modern diagnostic method that allows you to detect pathogen DNA even if its content in the material is small. The method is not cheap, but it has very high sensitivity and a low probability of obtaining an unreliable result.
What to do if you find out about the disease?
- Do not panic. Modern medicine has learned to cope with both syphilis itself and its consequences. If treatment is started in a timely manner, syphilis is completely curable (which is why it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist and conduct periodic examinations).
- Stop being sexually active and tell your partner about your diagnosis. Consult your doctor - he will help you determine the estimated duration of the disease depending on the test results.
Follow-up
After you are treated for syphilis, your doctor will ask you to:
- periodically take blood tests to ensure that the body responds positively to the usual dosage of penicillin;
- avoid sexual contact until treatment is completed and blood tests show that the infection has been completely cured;
- inform your partners about the disease so that they also undergo diagnosis and, if necessary, treatment;
- be tested for HIV infection.
Neurosyphilis. Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of tertiary syphilis are manifested by the following diagnoses:
- Asymptomatic neurosyphilis occurs 1-1.5 years after infection. There are no external signs yet, but tests show inflammation and infection of the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Gummy neurosyphilis is a lump (gumma) lying deep under the skin. Causes an increase in blood pressure in the patient.
- Syphyletic meningitis is the occurrence of serious disorders of memory, general and emotional state, thinking and memory.
- Meningovascular neurosyphilis. In other words – chronic meningitis. Symptoms: destruction of brain vessels occurs. There are seizures and even strokes.
- Tabes dorsalis. Destruction of spinal cord fibers. Symptoms of the disease: loss of orientation in space in the patient.
- Paralysis that progresses. A sign of this diagnosis is the complete loss of a person’s personality.
- Loss of vision. With optic nerve atrophy, one eye is first affected, then the infection spreads to the second. Such changes are irreversible.
- Late visceral syphilis is the syphiletic destruction of tissues of internal organs. Most often it affects the heart and liver. Other organs – rarely. Serious complications arise. The patient becomes ill even with little physical activity.
- Late syphilis on bones and joints. Gummas appear on the bones.
Complications associated with syphilis
Pregnant mothers and newborns
Mothers infected with syphilis are at risk of miscarriage and premature birth. There is also a risk that a mother with syphilis will pass the disease to her fetus. This type of disease is known as congenital syphilis (discussed above).
Congenital syphilis can be life-threatening. Babies born with congenital syphilis may also have the following conditions:
- external deformity;
- developmental delays;
- seizures;
- rashes;
- fever;
- inflammation of the liver or spleen;
- anemia;
- jaundice;
- infectious diseases.
If a child has congenital syphilis and it is not detected, the child may develop late stage syphilis. This can lead to problems with:
- skeleton;
- teeth;
- eyes;
- ears;
- brain.
Neurological problems
Syphilis can cause a number of problems with your nervous system, including:
- stroke;
- meningitis;
- hearing loss;
- loss of pain and temperature sensations;
- sexual dysfunction in men (impotence);
- urinary incontinence in women and men;
- sudden, lightning pain.
Cardiovascular problems
These can include an aneurysm and inflammation of the aorta—your body's main artery—and other blood vessels. Syphilis can also damage the heart valves.
HIV infection
People with syphilis are much more likely to become infected with HIV. Ulcers on the patient’s body facilitate the penetration of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) into the body.
It is also important to note that people with HIV may experience different symptoms of syphilis.
Symptoms of primary syphilis. initial stage
The disease begins with the appearance of chancre (the first sign), as was written earlier. Patients with syphilis do not feel any discomfort.
After a while, the chancre rots. It takes on a scarlet or very bluish color.
During the first week from its appearance, the lymphatic system and blood vessels in the area of the chancre are affected (regional scleradenitis). They form noticeable swelling and swelling.
If the chancre is in the mouth, then its inflammation makes it difficult to eat, breathe, and even communicate. Scleradenitis in the genital tract complicates movement and bowel movements.
Primary rashes
Prevention of syphilis
To date, doctors and scientists have not yet invented special vaccines that are effective in preventing syphilis.
If the patient has previously had this sexually transmitted infection, he can become infected and get it again. As a result, only preventive measures will help avoid infection and thereby prevent damage to the internal organs and systems of the body.
First of all, it is worth excluding promiscuous sexual relations with an untested partner, especially without a condom. If you have had such sex, immediately treat your genitals with an antiseptic and visit a doctor for a preventive examination and examination.
Having syphilis once does not mean that a person is protected from it. Once it is cured, you can change it again.
It is enough to understand that not every person knows that he is currently a carrier of the infection and, if the patient has a regular sex life, doctors recommend regular examinations by highly specialized doctors, tests for STDs, thereby identifying the disease in its early stages currents.
Domestic infection
In addition to a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease (syphilis on the genitals), in the modern world you can also find a household version of the disease. Sometimes it can form in the mouth. You can become infected with household syphilis through household items used by an infected person. This includes any utensils used by the infected person, lipstick, can of soda, etc.
During the incubation period, a person does not yet know that he has become infected, but already at this moment he is dangerous to those close to him. Relatives, close friends, and also a partner can easily become infected with household syphilis without even knowing it.
Medicines
Photo: diagnosislab.com
The following representatives of the penicillin antibiotics can be used to treat syphilis: bicillin-1, bicillin-3, bicillin-5, sodium salt of penicillin, potassium salt of penicillin, novocaine salt of penicillin.
Antibacterial agents of the penicillin series have a bactericidal effect, which is associated with their ability to disrupt the synthesis of the cell wall of microorganisms. Penicillins are well distributed throughout the body, quickly reaching therapeutic concentrations in almost all tissues and body fluids. There are low concentrations of penicillins in the cerebrospinal fluid, the internal environment of the eye and the secretion of the prostate gland. Representatives of this group of antibacterial agents have low toxicity, but the following side effects may occur when taking them: nausea, vomiting, flatulence, stool upset, headache, dizziness. Before prescribing the drug, the presence of allergies to drugs is clarified, since there is a concept of cross-allergy between all penicillin antibiotics, as well as partially cephalosporins and carbapenems.
Folk remedies
Photo: aktei.ru
Of course, there are no folk remedies that can cure a person of syphilis. However, there are preventive measures that, if followed, will significantly reduce the risk of contracting syphilis. These include:
- presence of a permanent sexual partner who has a health certificate;
- exclusion of casual sexual relations;
- use of barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse. However, it is worth noting that the presence of skin defects that are not covered by a condom does not protect against the possibility of transmitting syphilis;
- Regular screening for syphilis.
If you have had sexual or close household contact with a person with syphilis, you should immediately contact a medical facility. The appropriate specialist will prescribe a range of laboratory tests, based on the results of which, if necessary, prescribe treatment. In addition, it is important to remember that when diagnosing syphilis, you should never have sexual contact with other people in order to prevent them from becoming infected.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.