When the reproductive function of the female body begins to fade, a radical hormonal change occurs, which gradually causes the cessation of menstruation. This period is characterized by the appearance of atypical menstrual bleeding and general malaise. How are periods different during menopause? What can be considered the norm, and what should be a reason to contact a gynecologist?
What is menopause
Menopause is an intense hormonal change in the body, during which the supply of female germ cells runs out and the production of the hormone estrogen, which is responsible for reproductive function and the ability to conceive, must cease. Menopause can last from two to fifteen years, during which the menstrual cycle increases, and then menstruation stops completely, which is typical for the complete decline of a woman’s reproductive ability.
There are several stages of menopause, because menstruation does not end immediately during menopause:
- Premenopause should normally begin upon reaching 45 years of age, but cases of earlier or later onset cannot be ruled out. It consists of a decrease in estrogen production when the ovaries and pituitary gland stop producing it. The period can last from 2 to 10 years.
- Menopause is the last critical days after which the female body’s fertility finally ends.
- Postmenopause is the time following the last menstruation. Early menopause can last 5–8 years.
Gynecologists distinguish early menopause, which occurs in women under the age of 40, and late menopause, the manifestations of which occur at 60 years of age and later.
Features of artificial menopause
Artificial menopause is a sudden suspension of ovarian function for a certain period of time. For this purpose, the patient takes medications under the supervision of a doctor that cause the cessation of the synthesis of female sex hormones. This therapy is used in the treatment of various tumors. Indeed, during menstruation, exacerbations of such pathologies intensify.
The peculiarity of the treatment is that the drugs reduce the level of hormones and thereby deprive the neoplasm cells of “feeding”.
Expert opinion
Roman Andreevich
Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-obstetrician, 14 years of work experience.
To get a consultation
An artificial menopause can be caused by a number of drugs: Buserelin, Diferelin, Triptorelin, Goserelin, Zoladex. They must be prescribed by a doctor. The main thing is that the therapy ends on time - you should not take the drugs for longer than 6 months.
A woman in a state of artificial menopause experiences signs of menopause and the main one is the cessation of menstruation. How quickly do menstruation recover after artificial menopause? After you stop taking the drug, menstrual function will recover on its own within 1-4 months.
In some cases, recovery occurs within a year. For some women, menstrual bleeding may begin with spotting. Gradually the cycle will return to normal and there will be no smearing. Pregnancy can occur immediately after the ovaries begin to function.
Causes of early and late menopause
The reasons for early (before 40 years) onset of menopause include:
- hormonal disorders - manifested by pathologies such as diabetes, obesity, thyroid diseases (hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism);
- a large number of abortions performed;
- regular exposure to gynecological pathologies and their long-term treatment;
- self-prescription of oral contraceptives and their incorrect use;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- frequent stress, physical and psycho-emotional overload;
- poor environmental conditions in the place of long-term residence;
- hereditary predisposition, if cases of early menopause were regularly recorded in the female line.
Doctors believe that a later onset of menopause is more favorable for the female body. There are cases of delayed menopause in women who consume seafood for a long time, monitor their health and do not have bad habits.
Pathologically late decline of reproductive function is observed in patients with health problems:
- serious gynecological pathologies;
- the presence of tumors that provoke the release of estrogen;
- oncology subjected to chemotherapy and radiotherapy;
- uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs.
Since uterine bleeding should not normally be observed after the last menstruation and disappears, premenopause and menstruation are closely related, only this period is characterized by the onset of menstrual periods.
If spotting appears 1.5-2 years after the onset of menopause, this indicates excessive growth of the endometrial layer of the uterus, which is characteristic of serious pathologies of the reproductive sphere, which requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
Why do menstruation occur after menopause?
The presence of spotting is considered normal during the premenopausal stage. However, the appearance of menstruation after menopause may indicate pathological processes.
Important! After menopause, periods should stop completely.
Bleeding during postmenopause can occur in the following cases:
- For hormonal imbalance. Endometrial shedding is stimulated by progesterone. The presence of this hormone when estrogen levels decrease can cause bleeding.
- In the presence of diseases of internal organs - the thyroid gland, liver, kidneys, as well as female genital organs.
If a postmenopausal woman begins bleeding, she should immediately consult a doctor for examination and diagnosis.
How to determine that menopause is about to begin
You can determine that menopause is approaching by the characteristics of menstruation that appear before menopause - these are changes in the frequency of their arrival and characteristic symptoms:
- gradual lengthening of the interval between the onset of menstrual bleeding;
- reduction in the duration of menstruation itself;
- change in the amount of menstrual flow - it becomes scanty or, conversely, abundant, intense and spotting bleeding may alternate;
- the appearance of weak bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
Premenopause, during which the active production of estrogen gradually decreases, can last two years or ten years, it depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
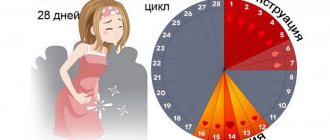
A woman’s normal monthly cycle lasts from 21 to 35 days, on average 28 days, and includes three phases:
- Follicular, during which follicles form in the appendages. One of them becomes dominant over time and displaces the others - the egg that is preparing to become fertilized matures in it.
- Ovulatory, during which the mature gamete leaves the ruptured follicle and moves into the cavity of the fallopian tube, where it prepares to merge with the sperm.
- Luteal, in which, in the absence of pregnancy, the egg, which has not merged with the sperm, dies after two days and comes out along with menstrual bleeding containing the remnants of the rejected mucous layer of the uterus.
During the premenopausal period, cycles without ovulation are increasingly occurring due to a lack of hormones necessary for the maturation of the oocyte, but menstruation occurs as usual. Against the background of changes in the amount of estrogen and progesterone produced by the body, the egg grows slowly. It enters the uterine cavity late, and there is a violation of the standard duration of cyclic phases - this is the reason for regular delays in menstruation during the onset of menopause.
Normal duration
Most women have a cycle length of 21 to 36 days. The ideal duration is 28 days. The blood loss itself lasts from 3 to 7 days, and the exemplary indicator is 4 days. But during the premenopausal period in women, these indicators can vary significantly.
It is rare that scanty periods come twice in a month, but this may also be a variant of the norm.
Most often, there is a significant increase in the cycle for a period of 8 to 20 days.
Many people forget that a woman’s ability to conceive during premenopause remains intact. Hormonal changes do not predict the onset of the next period or the time of ovulation. Therefore, to avoid unplanned pregnancy, contraception methods cannot be ignored.
Throughout premenopause, you need to continue to keep a menstrual calendar.
Unstable hormonal levels also affect the duration of the bleeding itself.
If previously a woman observed corresponding discharge for 4-5 days, now it can be reduced to 3 days. An increase to 7 days is also common, but there should be a significant reduction in daily blood loss.
Associated symptoms
Signs of approaching menopause may vary for each woman, depending on the individual characteristics of the body, age, heredity and other factors.
It has been established that every third woman feels hot flashes before the complete functioning of the reproductive system - this symptom is the most common. The rest are detailed in the table below.
| Sign | Characteristics and causes |
| Tides | Areas of redness suddenly appear on the woman’s face and body, and the temperature rises. Hot flashes are not associated with the onset of menstruation; an attack can last up to half an hour |
| Brittle bones | Against the background of a sharp decrease in estrogen production, calcium begins to be actively washed out of the bones - the deficiency of the substance cannot be eliminated on its own; during premenopause, it is necessary to take calcium supplements and vitamin complexes. At the age of 45–55 years, injuries associated with fractures become more frequent in women |
| Skin changes | The skin loses its former elasticity and smoothness, wrinkles worsen, folds in the area of the nasolabial triangle become more noticeable |
| Emotional condition | A woman becomes prone to stress and depression, tearfulness and suspiciousness appear. Uncontrollable outbursts of aggression and irritability, and anxiety attacks are possible. More sensitive women develop psychosomatic diseases against the background of emotional instability |
| Chronic fatigue | During the period of approaching menopause, a woman may feel weak and tired even after a long night's rest. |
| Sleep disorders | Sleep is characterized by superficiality and sensitivity, and difficulty falling asleep occurs. Immediately after waking up, a woman feels completely powerless and overwhelmed, especially when getting up early |
| Sweating | Increased sweating is caused by hormonal imbalances. The secretion of fluid becomes stronger during hot flashes, but is observed even with low-intensity exercise and physical activity. |
| Decreased sex drive | Decreased libido is also explained by hormonal changes. The mucous tissue of the vagina no longer produces physiological lubrication in the required quantity, which is why intimate contacts become unpleasant and painful |
The listed symptoms may not appear simultaneously, but alternately, changing each other, often the lady is only bothered by hot flashes and sleep disturbances.
To accurately determine that the signs indicate the onset of perimenopause, you should consult a doctor and conduct a hormonal blood test. Every woman should make routine visits to the doctor upon reaching the age of 45.
Treatment
If menstruation lasts more than 7 days, with a constant increase in pain and multiple blood clots, treatment must be used, often accompanied by hospitalization.
After calling an ambulance, you need to lie down and apply a heating pad with cold water to your stomach, which will help slow down the bleeding. Self-administration of medications is completely prohibited, such as warm heating pads, baths, special formulations and other methods of treatment. This will help increase body heat and increase blood flow in the body, only making the condition worse.
Bleeding during menopause is an immediate reason to consult a doctor and use uterine curettage to take material for histology.
The following methods are currently used for therapy:
- Therapeutic gymnastics based on haiha yoga and bodyflex , which helps prevent prolapse of the uterus;
- Taking medications containing estrogen - Cliogest, Premarin, Ovestin, antiestrogens;
- Taking vitamin complexes to help improve the condition of the body. Maltofer will replenish the lack of iron lost along with the blood during menstruation. Vitamins B1 and B6 are prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections;
- Additional treatment in a complex composition in the form of antidepressants and nootropics , normalizing mood swings characteristic of menopause and stimulating brain function.
Cliogest
Maltofer
Ovestin
Premarin
Can I take herbs?
Traditional methods of treatment can help improve well-being during menopause during menstruation, as well as reduce the intensity of discharge.
Recipes:
- Nettle infusion helps reduce the rate of uterine contraction and constrict blood vessels, activating blood clotting. It is an excellent way to get rid of heavy blood loss. Prepared by brewing a spoonful of nettle with 200 ml of boiling water. You need to keep it on the fire for about ten minutes, then cool and strain. Take a spoonful of decoction every 3 hours;
- Tea or infusion of viburnum fruits reduces the tone of the uterus, relieving severe pain and strengthening the vascular walls. This greatly reduces the intensity of menstruation. Brew at the rate of 1 spoon per glass of boiling water;
- Decoction of citrus peel. It is prepared from the peels of 6 selected citrus fruits placed in one and a half liters of water. The mixture is boiled until only a third of the water remains - 500 ml. The broth is cooled and drunk one and a half spoons in three doses;
- A decoction of clove leaves eliminates excessive bleeding and strengthens the elasticity of the walls of the uterus, which greatly lose it during menopause. To create a decoction, 200 g of leaves are poured into 260 ml of boiling water, and then infused for half an hour. The infusion is drunk a spoonful every 4 hours.
In addition to these decoctions, you can apply a number of other herbal medicine procedures:
- infusions of barberry, motherwort and valerian will help avoid stressful conditions in the body and improve the level of health, simultaneously calming nervous conditions that are standard for menopause;
- Chinese lemongrass and ginseng help to improve the tone of the body and uterus;
- To reduce heavy bleeding, not only nettle, but also shepherd’s purse can have a great effect.
Traditional medicine recipes help get rid of heavy menstruation and increase the tone of the uterus, but it is impossible to cure possible pathology. Herbs should be used after a doctor’s prescription and a thorough examination.
Changes in the monthly cycle
To understand how menstruation behaves before the onset of menopause, you need to regularly record the dates of the next menstruation and monitor the duration of the cycle.
If in patients of reproductive age the standard cyclic duration is 28–30 days, then in premenopausal women it changes:
- Bleeding becomes spontaneous - periods come at different intervals, sometimes returning twice a month.
- Often, instead of critical days, only hot flashes come, and bleeding itself is not observed.
- The duration of the cycle changes dramatically - sometimes it reaches 5 months or six months; when going to the doctor, the patient complains that menstruation has not happened for a long time and suddenly it began suddenly.
- Signs of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) intensify - the woman feels severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, nausea with the urge to vomit, and headaches.
- The duration of the bleeding changes - they can be observed for 7-9 days, or sparingly smeared throughout the month.
Since the menstrual cycle becomes irregular during menopause, it is not always possible to determine the nature of bleeding on your own. If there has been no menstruation for a long time, and then a woman suddenly begins bleeding with clots of an unusual scarlet color, this may become a symptom of uterine bleeding. The causes that cause it are uterine fibroids and endometriosis.
The nature of menstruation in premenopause
As we found out above, the premenopausal period involves a gradual decline in fertility. This means that menstruation continues to occur. However, the vast majority of women note a significant difference between menstruation before and with the onset of menopause.
The symptoms of menopause at the very beginning of perimenopause are quite vague. With age, many women experience premenstrual syndrome and its constant companions more clearly:
- headache;
- mood swings;
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- nausea and dizziness;
- anxiety and depression.
Typical menopausal symptoms are also gradually added:
- emotional lability;
- dryness and discomfort in the genital area;
- swelling of the lower and upper extremities and face appears;
- presence of hot flashes and sweating;
- painful menstruation and severe discomfort during it;
- surges in blood pressure.
Often, hormonal changes in the sexual sphere are accompanied by an imbalance of thyroid hormones, joint pain, and metabolic disorders.
Every woman feels the approach of menopause differently. Some people have more severe symptoms, others less. Symptoms can also be aggravated by long-term gynecological and chronic diseases.
In order not to lose sight of truly alarming symptoms, you need to understand how menstruation behaves before menopause, and what kind of spotting cannot be called normal.
Blood before the onset of menopause may appear for natural reasons:
- During menstruation. Menstruation can last up to 7-10 days, and can also be shorter - from 2 to 4 days.
- During ovulation. If a thin blood capillary is damaged during a follicle rupture. Normally there should be little blood, the smear ends after 1-2 days.
- Due to the onset of pregnancy. Since the fertile functions of the ovaries are still working, in premenopause there is a possibility of becoming pregnant. Blood appears when the embryo attaches to the uterus if the endometrial layer is injured. This is a natural phenomenon, but you need to make sure that conception has occurred by visiting a gynecologist.
- Blood after sexual intercourse. Due to a lack of estrogen and progesterone, the cervical canal produces less natural lubrication, which can make sexual intercourse more painful. Dryness of the vaginal mucosa leads to slight injury during sex, so after intercourse a woman may experience bleeding. Normally, such blood is released no longer than a day. Bleeding should not be profuse, but rather scanty and spotty.
The above appearances of blood during premenopause are considered relative normal. However, they all require a medical certificate.
The danger is that before estrogen completely decreases, the woman’s body is in a state of severe hormonal imbalance. This situation is fraught with the development of gynecological and hormonal pathologies that pose a serious threat to women’s health.
Pathological signs of menstruation before menopause
Usually, menstruation at the onset of menopause in women after 45 years of age is practically no different from the usual - they have the same consistency and duration. Only the duration of the cycle undergoes pronounced changes. Against the background of unstable ovulation, the sudden onset of menstruation indicates that the egg has matured this month.
You should not hope that it is no longer possible to get pregnant during premenopause. Since critical days do not occur regularly, but still occur, it is worthwhile, together with your doctor, to select a suitable method of contraception and use it until the onset of menopause.
It is important to remember that the reasons for the absence of menstruation, in addition to pregnancy and menopause, can be chronic pelvic diseases, growing tumors, uterine polyps and other pathologies. That is why, in the absence of menstruation for a long time, if a woman knows that there is no pregnancy, but menopause has not yet occurred, she urgently needs to visit a specialist.
Every woman who notices symptoms of perimenopause should monitor her menstruation in order to detect the existing disease in time. Possible reasons for changes in bleeding patterns are shown in the table.
| Features of menstruation | Causes |
| The presence of a large number of clots | Serious thyroid disease, uterine bleeding |
| Dark brown color of discharge | Uterine fibroids, growing polyps, sexually transmitted infections |
| Light bleeding between periods | Irrational use of hormone-based products, inflammatory process of the vaginal mucosa |
| Long-term, more than 7 days, the volume is insignificant | High blood pressure, blood clotting problems |
| Scanty discharge with bloody streaks | Injuries to the vaginal mucosa as a result of rough sexual intercourse and due to lack of natural lubrication, erosion of the cervix |
| Repeated bleeding after the end of the critical days | Onset of ectopic conception, anovulatory cycle preceding the current one |
How to save the cycle?
Today, early menopause has become diagnosed more often. It can even occur before the age of 40. Some women who want to have more children are not willing to lose their fertility so quickly. In practice, you can restore the cycle if you start preventive measures before menopause. But when it resumes, ovulation and the possibility of pregnancy do not always return. A common cause of premature menopause is genetic predisposition. Other reasons include:
- thyroid diseases;
- nicotine and alcohol addiction;
- eliminating fats from the diet;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- untreated diseases of the genitourinary system.
Women who have repeatedly gone through childbirth have a larger supply of eggs and, accordingly, are less likely to experience menopause prematurely. If signs of early menopause do appear, you may need to take hormonal medications. After preliminary tests, a suitable remedy is selected. A diet rich in phytoestrogens will help you avoid resorting to drug therapy:
- flax seeds;
- soy products;
- parsley;
- lentils.
This “treatment” does not always give the desired effect, but it is safe and has almost no contraindications.
Painful periods
If menstruation at the onset of menopause in women over 50 years of age is characterized by severe pain, common causes of the syndrome are:
- wasting of the appendages;
- death of the endometrial uterine layer;
- trauma to the vaginal mucosa due to sudden hormonal disruption.
The reason may be hidden not in menstruation itself, but in the presence of concomitant diseases - adhesions in the pelvis, inflammation of the urethra or bladder walls (cystitis). When the intensity of pain is much higher than usual, accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, fainting and nausea, you should seek first aid yourself or call an ambulance.
Symptoms of menstruation during menopause
At the first stage of menopause - during premenopause - bleeding becomes scarce. Women may experience other symptoms of the onset of menopause during regular periods:
- Tides. Characterized by intense fever, redness of the skin of the face, neck and hands. Accompanied by profuse sweating.
- Problems with the genitourinary system. These include dry mucous membranes, inflammation of the vagina and bladder, decreased libido, and pain during sexual intercourse.
- Deterioration of hair, teeth, nails, bones, dry skin. The manifestations are caused by a lack of calcium, provoked by a decrease in estrogen levels.
- Emotional instability. Expressed by mood swings, deterioration in concentration, sleep disturbances, irritability, and memory loss.
All these manifestations, along with the cessation of menstruation during menopause, indicate the approach of menopause.
Excessive blood loss and prolonged periods
Bursts of estrogen release provoke long and heavy periods in premenopause - in order to slow down the decline of reproductive function, the body tries to launch all available methods of stimulation. For this reason, the volume of hormones in the blood increases briefly but sharply, and the endometrium grows.
As more cycles occur without ovulation, a noticeable lack of progesterone occurs, causing not only changes in the amount of endometrium shed, but also structural changes. In women aged 40–47 years, the risk of developing the following diseases increases:
- uterine fibroids;
- polyp growth;
- changes in the endometrium of a pre-tumor nature;
- hormonally dependent neoplasms in the chest and cervix.
How to stop heavy periods when menopause has begun - many women are prescribed hemostatic drugs to eliminate blood loss that does not stop, and if their use has no effect, the uterus is removed.
In addition to the hormonal changes normal for premenopause, an increase in the volume of blood released leads to:
- obesity;
- improper functioning of the thyroid gland;
- intrauterine device;
- tuberculosis;
- serious liver and kidney diseases;
- a sharp decrease in the body's immune defense;
- gynecological pathologies - glandular endometrial hyperplasia, polycystic disease, fibroids, vaginitis, malignant tumor in the uterus or cervix.
Patients who have previously suffered numerous abortions, chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvis, and surgeries on the uterus and ovaries are prone to such developments.
Female hormones and menopause
The normal menstrual cycle is regulated by the work of the ovaries, which, in turn, are influenced by a complex hormonal system. The follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones of the anterior pituitary gland are responsible for the production of the main female hormones, estrogen and progesterone. Thanks to these hormones, at the first stage of the menstrual cycle, the dominant follicle and egg mature and ovulation occurs. At the second stage, after the egg leaves the ovary, when conception can occur, the corpus luteum matures and progesterone begins to be produced, which, in the case of fertilization, will support the vital activity of the embryo at first. If this does not happen, the egg reaches the uterus empty, progesterone levels drop and menstruation begins.
As menopause approaches, this perfectly adjusted system undergoes dysfunctional changes. The amount of estrogen changes, which affects the maturation of eggs and the onset of ovulation. Since unusual hormone production affects the maturation of the egg, the menstrual cycle will be unstable when menopause begins.
The lower estrogen levels drop, the less often ovulation occurs. Accordingly, this affects the 2nd stage of the menstrual cycle - the production of progesterone and the onset of menstruation.
Too frequent menstruation
During premenopause, another type of disorder occurs - too frequent menstruation. It develops due to hormonal imbalance and the occurrence of increasingly frequent anovulatory cycles.
In rare cases, repeated bleeding occurs after conception has occurred, when it was in this cycle that the egg matured in the ovary and was fertilized by sperm during unprotected intercourse.
The appearance of scanty but frequent bleeding may indicate the development of endometriosis.
Termination of reproductive function in stage 4
During the period of age-related changes, the ovaries produce fewer hormones, and over time they completely stop working. This explains why menstruation gradually decreases in a large percentage of women during menopause. When the endometrium completely stops functioning and stimulating estrogen production, menstruation ends forever. The adjustment usually takes about 24 months, and since during this period delays in natural bleeding are considered normal, women who are sexually active often miss pregnancy.
From the smooth completion of the reproductive period to complete and natural infertility, women go through 4 stages:
- premenopause - begins with the beginning of the decline of the ovaries and lasts until the discharge completely stops;
- menopause - begins after 12 months from the date of the last monthly bleeding;
- early postmenopause - occurs 24 months from the date of the last regulation;
- Late postmenopause – lasts until the last days of life.
During premenopause, thousands of women's periods initially proceed according to the usual schedule, but the type and volume of blood released changes. The cycle is steadily increasing, the delay ranges from 8 to 45 days.
Discharge of dark blood
The bloody contents acquire a brown tint when the genitals exit, mixing with vaginal discharge, so it does not always indicate pathology. It is necessary to consult a doctor without delay if brown blood leaks against the background of accompanying signs:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen;
- the presence of watery or yellowish inclusions in the discharge;
- frequent urination;
- itching;
- discomfort during intimate contacts;
- burning on the surface of the vaginal mucosa;
- the appearance of ulcers and erosions in the mouth;
- lack of appetite.
Brown menstrual discharge in combination with the listed symptoms can occur with sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia) and growing uterine polyps.
How to help yourself with uterine bleeding?
At the first suspicion of uterine bleeding, you must call an ambulance and follow the steps of the proposed algorithm:
- The woman should lie down, raise her legs and place them on a pillow. In this position, the outflow of blood will increase.
- Cold compresses should be applied to the lower abdomen. This is done correctly this way: put a few ice cubes in a fabric bag or wrap it in a towel and apply it to your stomach for 10-15 minutes. After this, take a 5-minute break and repeat the procedure. You should know what to do if you don't have ice on hand. You can use something very cold from the freezer. To improve blood clotting, the compress should be applied for 1-2 hours.
- Prevent dehydration of the body. To do this, you should often drink several sips of clean water.
- In folk medicine, honey and lemon stop uterine bleeding. Therefore, you can eat honey in large quantities when you are not allergic to it. It is important not to overdo it with lemon, so as not to harm the digestive system.
If the bleeding has not stopped, then you should take hemostatic drugs, but it is advisable to first consult a doctor by phone.
Diagnostics
Before deciding how to stop heavy periods, if they last a long time during menopause, you need to visit a gynecologist and undergo an examination, including:
- examination in a gynecological chair;
- performing ultrasound;
- blood test - how much hormones hCG, FSH, LH, estradiol, thyroid hormones, progesterone are contained;
- smear for degree of purity;
- clotting test;
- biochemical study with liver tests.
To exclude a tumor process, diagnostic curettage is performed (during which polyps and excess endometrium can be removed), and the resulting material is sent for histological examination.
11 best folk remedies for heavy periods
Traditional recipes are often more powerful than pills and medications, so you need to be extremely careful with them. It is ideal to consult a doctor before treatment.
- This popular remedy expresses the positive process of stopping blood, removing discomfort and eliminating inflammation of internal organs. You need to take one rain mushroom, boil it in water, add salt and eat on an empty stomach.
- To get rid of heavy and long menstruation - menorrhagia, traditional doctors recommend this method of making a decoction. It is necessary to mix 20 grams of crushed oak bark, yarrow leaves and cinquefoil, raspberries and strawberries. Add a glass of cool boiled water to 1 tablespoon of the mixed consistency. Let the mixture brew for about 5 hours, then boil the broth and cook over medium heat for 6 minutes. After filtering, the drink is consumed several times a day. The full course is 7 days. The decoction, in addition, can help with inflammation of the stomach.
- Elixir from oak acorns. One teaspoon of crushed material is poured into a glass of hot water and left to cool. It is recommended to drink this drink half a glass 3 times a day.
- An infusion of water pepper has proven to work well for hemorrhage. To make it, add 15 grams of pepper with a small amount of drinking water and bring the drink to a boil. Then the broth must be diluted with a glass of clean water and left for at least 25 minutes. After this period ends, the medicinal decoction is used in a small amount before meals. It is recommended to use an infusion of water pepper, especially during menstruation. Therapy for massive bleeding is carried out for 3 months. What results can be expected from this treatment method? Water pepper relieves PMS, restores normal blood flow, and increases hemoglobin. In addition, the broth has analgesic properties.
- Mix 100 grams of shepherd's purse and nettle, crushed burnet roots. Add 3 tablespoons of the mixture to the pan, pour in 2-3 cups of boiled water, cook the mixture over medium heat for 30 minutes, covering with a lid. Filter the drink and divide 4 times. When consuming, you are allowed to add a spoonful of honey if the suspension seems too bitter.
- You need to take 100 grams of viburnum tree peel and add a glass of water, but before that you need to grind it in a coffee grinder or using a mortar. Cook the broth in a shallow bowl for about 30 minutes over medium heat. Take 3 tablespoons of the prepared mixture every 4 hours. Boiling viburnum peel effectively relieves discomfort and helps relieve indigestion.
- Horsetail will help restore the normal menstrual cycle and reduce discomfort during menstruation. You need to take one tablespoon and pour it with two glasses of boiled water. The consistency should settle, after which it must be filtered. Use one tablespoon of tincture every 2 hours until the excessive blood flow decreases. When normalizing, you should take the medicine a tablespoon 2-3 times every day.
- Red brush is one of the most commonly used plants in the treatment of diseases of the female part. It has various positive effects on the human body. For voluminous menstrual flow, the plant is especially effective if the main factors of this disorder are considered to be hormonal pathologies or a tumor of the uterus. You need to take 2 tablespoons of brush root, crush it and pour two glasses of boiled water. Then boil the drink and leave to cool for 30-40 minutes. Use the broth 20 minutes before meals, 150 ml 3 times a day.
- Prepare a plantain drink. You need to take 15 grams of dried plant and pour a glass of boiled clean water. It is recommended to use the prepared extract 2 tablespoons every 3 hours throughout the day. In addition, plantain nectar, which must be taken in a spoonful before meals, produces excellent results.
- For heavy menstrual flow, you need to mix the following herbs in equal proportions (1 tablespoon each): valerian root, shepherd's purse, mistletoe and knotweed. Then fill them with two glasses of boiled clean water. The solution must be left to stand for 15-20 minutes, then add another liter of drinking water to it and boil again. Diligently filter the medicinal infusion using gauze and cool to normal temperature. Consume half a glass of herbal infusion twice a day. This medicinal tincture helps relieve PMS symptoms and has a beneficial effect on the activity of the uterus.
- Prepare a drink from five chicken or quail eggs and citric acid (half a teaspoon). Use the mixture during menstruation without boiling or other preparation.
If you are going through menopause and something is bothering you, don’t worry, go see a good doctor! Get a monthly journal and track your cycle - all the symptoms, duration, quality of discharge, and so on. It will help you a lot in your treatment. The website matkahelp.ru wishes that your health never lets you down!
Prevention of bleeding
, the unforeseen nature of hormonal cataclysms cannot be discounted . Predisposition to them is also influenced by health status, lifestyle and social status.
General preventive measures to prevent pathological bleeding are timely treatment of chronic diseases and a healthy lifestyle.
Specific methods to reduce their risk include:
- safe (protected) intimate relationships without extremes, using a lubricant with neutral acidity;
- complex vitamin therapy;
- general strengthening physical exercises;
- healthy eating.
Postmenopause
Postmenopause can be called a stage that completely excludes the possibility of childbearing due to a persistent decrease in the level of sex hormones. It lasts until the end of a woman's life. A year after the last period, the ovaries completely cease to perform menstrual function, which means that the egg no longer matures. But at this time, women's health also requires close attention, since organs that have ceased to fulfill their natural duties become very vulnerable. As soon as unusual symptoms occur during the postmenopausal period, you should immediately consult a doctor and also regularly undergo gynecological examinations.
A postmenopausal woman should be alert to any vaginal discharge in the form of blood, mucus or pus; pain in the lower abdomen is also an abnormal sign. They may indicate the presence of a disease or infection that quickly affects the body without hormonal protection and with a weakened immune system.
If after the onset of menopause, after two to three years, frequent periods resume again and they are heavy, this may be a clear symptom of the presence of a malignant tumor. Quite often, women over 60 years of age are diagnosed with cancer of the uterus, appendages, ovaries and other oncological tumors based on such signs.
What kind of discharge may be
Discharge from a woman’s vagina at any period of life can tell a specialist a lot about the state of his patient’s health. Both daily discharge and menstrual discharge have their own specific color, smell and consistency. Knowing what this or that nature of menstruation means during menopause, you can promptly determine the presence of gynecological problems:
- if the amount of discharge is very large and bleeding occurs frequently, this may indicate the presence of malignant and benign neoplasms;
- if the discharge is dark, bloody, and spotting, then we can assume the presence of fibroids, a benign neoplasm, which most often becomes a consequence of disorders in the endocrine system;
- if the discharge is clotted, this indicates problems with the endocrine system (diseases of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or adrenal glands);
- bleeding in the postmenopausal period indicates rupture of the uterine vessels; to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo additional examination;
- if ichor is released, this is a clear sign of the presence of an inflammatory process in the genitals;
- purulent discharge, yellowish in color with a pungent odor, indicates the presence of infection, especially if the woman’s body temperature rises.
When white mucous discharge comes out of the vagina before menopause, this is the norm, thus the body is cleansed of dead epithelial cells. If there is profuse leucorrhoea during postmenopause, then this may be a sign of thrush. When the cycle has become irregular and the doctor has diagnosed the onset of menopause, you should pay attention to the nature of the discharge of each subsequent menstruation in order to identify possible pathology in time.
How to stop heavy periods
Any treatment must be carried out under the strict supervision of a physician. Due to inadequate self-medication, the risks of developing gynecological diseases increase significantly. What should you do if your periods are long and abundant, but you can’t get a consultation with a gynecologist?
- Oral contraceptives. They have the ability to bleed for a long time. After finishing one blister, you should not take a break, but should immediately start taking tablets from the next package.
- Hemostatic drugs. Medications that affect blood clotting or the amount of the hormone progesterone help stop the discharge. These include: Duphaston, Vikasol, Tranexam and other similar medications.
- Ethnoscience. During premenopause, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcoholic beverages, replace sugar with honey, and introduce herbal teas into the diet. Linden, sage and chamomile are great for brewing. It is advisable to always add lemon to drinks. Another effective remedy is parsley infusion. To prepare it, you need to finely chop a bunch of greens, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. Drink in 3 doses.
Don't refuse the examination!
Can menstruation resume after a year during menopause?
Such violations are often noted if the process follows a pathological scenario. This symptom should alert a woman and become a good reason to visit a gynecologist.
To determine the correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a number of studies:
- a general blood test to assess coagulation parameters, determine the presence of infections or an inflammatory process;
- cervical smear for cytology;
- visual examination on a gynecological chair;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- blood test for hormones.
With the onset of menopause, menstruation ends. If you get your period a year later during menopause, then you shouldn’t postpone a visit to the gynecologist. Timely identification of the cause of bleeding will allow you to quickly select effective treatment. Usually it consists of selecting the right hormonal drugs and sedatives.