Menstrual irregularities
- a reason to seek advice from a gynecologist. Critical days are the calling card of a woman’s body condition. Any cycle failure is a signal calling you to pay attention to your health. This may be a delay in menstruation in the absence of pregnancy, scanty menstruation or, conversely, too heavy menstruation. If there are such violations of the monthly cycle, it is imperative to be examined, determine their cause and begin treatment. We must always remember that dangerous diseases can be hidden behind menstrual irregularities.
When do girls' first periods begin?
The normal age range of occurrence in a teenager is from 12 to 15 years. Often, the initial discharge appears in a young girl at the same age in which her mother had it.
Deviation in the occurrence of discharge from the specified age interval of 1 year is an acceptable phenomenon in adolescence.
Some studies link the onset of menstruation to reaching a certain weight value = 47 kg. In accordance with this, we can conclude that thin girls get their periods a little later than overweight girls.
If discharge occurs before 9 years of age or does not occur after 16 years of age, you should take this alarming signal, and if it appears, it is recommended to immediately arrange a visit to a medical specialist.
Physiological symptoms
The main signs of the onset of menstruation appear a week before the onset of discharge. Their timely fixation minimizes pain. A girl should listen to her body’s signals. There are more than 200 known signs of PMS. The greatest discomfort is caused by unpleasant physical changes:
- nausea or vomiting;
- headache in the temporal lobe, migraine;
- weight gain;
- heart rhythm disturbances - rapid heartbeat;
- swelling of the limbs;
- ovaries hurt before menstruation;
- chest and lower back pain;
- hypertensive crises;
- chills;
- diarrhea, stool disorder;
- increased body temperature;
- thirst;
- uncontrolled appetite;
- sweating;
- numbness of hands;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- acne;
- increased sensitivity to light and sound;
- Abdominal bloating is often indicated before menstruation.
Physiological symptoms of PMS are provoked by a lack of magnesium or vitamin B6 in the body.
Such signs that come before menstruation should be systematic. Single manifestations may indicate a disruption in the functioning of other body systems.
To accurately determine PMS, you need to keep a special self-observation diary, and also seek advice from a gynecologist.
How does the first period begin?
Discomfortable sensations in the abdominal area will serve as the first signal that premenstrual syndrome is occurring.
Typical symptoms for this:
- sudden changes in mood;
- strong level of irritation and desire to cry;
- fatigue and apathetic mood.
If traces of brown or red color are found on your underwear, this is an indication that the menstrual process has begun. You should not be afraid of the volume of discharge; a large amount of it is normal.
There is no standard here; this happens on an individual basis for everyone. In this case, pain in the lower abdomen may occur. In many ways, this depends on heredity and the way the menstrual process goes through a young girl is similar to how it went through her mother.
Poor blood flow during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is extremely important to continuously monitor the state of the maternal body of the mother and the baby, it is important that they perform all vital functions. One of the most significant studies is the analysis of blood flow in the arteries of the uterus, the woman’s umbilical cord, as well as cerebral vessels and the fetal aorta. The main causes of perinatal morbidity and mortality include disorders of the uteroplacental blood flow of 1A, 1B, second and third degrees.
Blood flow in the placenta
The placenta, in which the fetus is located, supplies the embryo with nutrients, as well as oxygen from the mother’s blood; it also removes waste products from the child’s body. It is this organ that unites two rather complex vascular systems - the female, which connects the vessels of the uterus and placenta, and the fetal, which passes into the umbilical arteries and leads to the child.
The circulatory systems mentioned above are separated by a membrane, which does not allow maternal and child blood to mix. The placenta is a kind of barrier that is resistant to numerous harmful substances, as well as viruses.
Often, for completely different reasons, placental insufficiency may appear, which inevitably affects the performance of transport, metabolic, trophic, endocrine and other vital functions of the placenta. In this condition, the metabolism between the maternal and child organisms deteriorates significantly, which is fraught with various consequences.
What are the causes of impaired placental blood flow?
Poor circulation in the uterine cavity can be caused by pneumonia, increased blood pressure, various intrauterine infections, as well as insufficient oxygen supply to the child’s body (hypoxia).
To diagnose the blood flow system in modern obstetric practice, three-dimensional ultrasound (so-called Doppler ultrasound) is used, with which the vessels are visible in a 3D (three-dimensional) image. With the help of this diagnostic technique, there is a prospect of diagnosing retroplacental bleeding and assessing cardiac malformations by monitoring blood flow. This technique is irreplaceable, since with its help it is possible to examine defects even in the most microscopic vessels that form the microvasculature, to observe the peculiarities of the formation and development of intraplacental hemodynamics, and in addition to control the amount of nutrients, as well as oxygen, that should enter the fetal body . New prospects have opened up for the early detection of obstetric complications, and if treatment or correction is started without wasting time, then circulatory disorders and subsequent pathologies associated with it can be almost completely avoided.
Hemodynamic disorders during pregnancy
Hemodynamic disorders are divided into 3 degrees of severity:
1. 1st degree includes two subtypes:
- disturbance of patello-placental blood flow 1Is the mildest. Fetal-placental blood circulation is preserved with it. Intrauterine infections often lead to this problem;
- in degree 1B, uteroplacental blood flow is preserved, but fetal-placental pathologies appear.
2. Grade 2 is characterized by the presence of disturbances in both blood flow systems, however, these disturbances do not carry any fundamental changes. 3. In grade 3, uterine circulation disturbance causes defects in normal blood circulation at the level of the fetus.
In the case of the first degree of violations, timely detection and adequate treatment can avoid fetal death. In the case of the second degree, perinatal mortality is about 13.3 percent, in the case of the third - 46.7 percent. During Doppler diagnostics, it was revealed that treatment aimed at correcting placental insufficiency in women with third-degree uterine blood flow disorders was ineffective. In this situation, with conservative childbirth, perinatal mortality was 50 percent, then, thanks to a cesarean section, losses can be avoided. 35.5 percent of newborns are admitted to the intensive care unit with grade 1 blood flow disorders, 45.5 percent with grade 2, and 88.2 percent with grade 3.
What does a girl's first period look like?
Brownish or red discharge is the first symptom indicating the onset of the menstrual process.
In this case, the color of the discharge may not be stable and may change, depending on what day of the cycle it is. The color of the discharge can be red, brown or dark brown.
The most initial ones can be different, because not only blood makes up them, but also the layer of the mucous membrane of the uterus (endometrium), as well as vaginal discharge.
The intensity level of the initial menstruation is not too great. But depending on hereditary predisposition, the opposite may also occur.
You should not worry about this, since this is a completely normal phenomenon.
Normal deviation
How to correctly calculate your menstrual cycle? Examples of a possible break between menstruation and the timing of it are now clear. But no organism can work like a clock. Sometimes some processes in it begin a little earlier or later than expected. This is quite normal.
Menstruation comes at the same time interval, but there are exceptions. What deviation from established norms should not cause concern for a woman?
Critical days may come a week earlier or later than expected. This is not considered a reason to panic. But a longer delay or too short a break between menstruation (less than 2 weeks) should alert you.
How long does menstruation last?
The standard value at which you should not worry is 3-7 days.
In the first few days, the strongest discharge is observed; towards the end, it weakens more. On the last day there was almost no discharge.
The duration interval during the first cycle of such days (from the beginning of the first cycle to the transition to the second) is not fixed and each girl has her own.
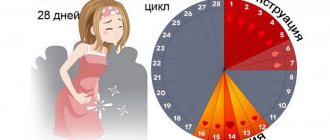
The average duration is 28 days, but fluctuations are allowed from 21 to 35 days.
These values may change if the girl had stressful situations or had to move from one city to another (change in climatic conditions).
Duration standards
How can you understand what kind of cycle a particular woman has? To do this, you need to know the average difference between menstruation under certain circumstances.
It is recommended to focus on the following standards:
- normal cycle - 28-31 days;
- short cycle - less than 21 days;
- long cycle - more than 35 days.
In the case of irregular periods, everything is clear - you can never say exactly how much the difference will be between the critical days. It changes every time.
What to do if your period starts?
Some periods can come completely suddenly and take the girl by surprise. No need to worry. Constant use of panty liners will give you confidence.
In addition, you can take tampons or standard pads with you. This will increase preparedness in case of unexpected discharge and allow you to quickly take the necessary measures for continued comfort.
It's normal to feel nervous, especially during your first period.
But to minimize nerves, you should follow these rules:
- Organize yourself a calendar in which to mark these days.
- Use pads regularly during your period and change them actively.
- If these days don’t come as planned, and you don’t have sanitary pads with you, you can always ask your friends for them. This will help you get out of an awkward situation.
- In order not to miss the start of your period, it is recommended to visit the toilet more often on the corresponding day (every 3-4 hours) in order to use pads if necessary.
- During your first period, you can carry not only pads, but also an extra pair of underwear.
Treatment with medicinal herbs
Restoring the cycle is possible if traditional methods of treating menstruation failure are added to the main methods. It is possible that medicinal plants, if used incorrectly, can cause harm to the body, so before use, you must always consult a doctor and identify the main cause of the disorders.
Medications for heavy menstruation:
- You will need: horsetail (100 g), peppermint (20 g), chamomile (150 g), shepherd's bag (50 g), yarrow (150 g), lungwort (50 g), acorn grass (50 g). The decoction for one dose is prepared as follows: 1 tsp. collection is boiled in 200 ml of water. Drink once a day before bedtime. Course duration – from 3 weeks;
- You will need: shepherd's bag (1 tbsp), yarrow (1 tbsp), oak bark (1 dl). Pour the collection with 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes under the lid. After straining, drink in 2 doses (in the morning and before bed).
Medicinal herbs for painful periods:
- Peppery knotweed. Pour 1 tbsp. crushed plant 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. Take the decoction 3 times a day, 1 tablespoon;
- Chamomile, mint and valerian root (3:3:4). Brew 1 tbsp. collection in 200 ml of boiling water. Take during menstruation several times a day;
- Raspberry leaves. Pour 1.5 tbsp. raw materials 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 15 minutes. Take several doses of infusion a day in small quantities.
Medicinal herbs to stabilize the cycle:
- Cornflower flowers. Pour 1 tbsp. plants 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 60 - 80 minutes. Drink the decoction 3 times a day, 1/3 cup. The course of therapy is at least 3 weeks;
- Parsley seeds. Pour 1 tsp. crushed raw materials 0.5 liters of warm water for 8 hours. Drink the infusion 4 times a day, half a glass without straining;
- Sagebrush. Pour 1 tbsp. herbs 300 ml of boiling water and let it brew in a warm place for 4 - 5 hours, then strain. Drink the infusion 3 – 4 times a day, a quarter glass.
Why do we need periods?
The menstrual process is a period when the uterine epithelium is renewed every month.
During this process, irreversible changes occur in the epithelium, and it is removed from the body, since it can no longer be used. Instead, a new epithelium is formed in the body, which is successfully involved in internal processes.
Functional purpose:
- Degeneration of cells. The menstrual process allows you to renew epithelial cells, which provides an important role for a girl’s reproductive ability.
- Natural protective. The menstrual process involves a separate layer of the uterus, which is responsible for analyzing problems in eggs that are not fertilized and preventing the implantation of these eggs. Such eggs are excreted from the body along with the epithelium every month.
Read also Apoplexy (rupture) of the ovary - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Changing your contraceptive method
The body's reaction to a particular method of contraception may be unpredictable due to the characteristics of the body itself. If, for example, as a result of taking contraceptives, a sharp disturbance in the menstrual cycle is observed, then it is recommended to change the drug to another with a higher dosage or composition. It is necessary for the doctor to assess the situation and adjust the contraception.
If the reason for the failure of menstruation is the intrauterine device, and menstruation does not normalize within the allowable period, then the only solution is to remove the device and choose another method of contraception.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
This process has 2 phases, in the middle of which the ovulation process occurs.
The ovulation process involves the release of eggs suitable for fertilization into the abdominal cavity and travel to the uterus. By the time of puberty, a girl’s body contains up to 400,000 eggs.
The primary ovulation process occurs shortly after puberty, the final ovulation process occurs after menstruation no longer occurs (menopause). During pregnancy, this process does not occur, but it is restored after childbirth has passed and the child is born.
Key phases:
- Follicular. At this stage, follicular development occurs, during which the release of the egg is observed. This stage occurs from the first day of the menstrual cycle and ends when the ovulation process begins. At this stage, estrogens are produced. During the stages, the basal temperature is less than 37 degrees.
- Luteal (corpus luteum phase). The corpus luteum is created in the ovary, in the area from which the egg left. This stage occurs after the ovulation process and lasts until the corpus luteum lives, approximately up to two weeks. The key point at this stage is maintaining a balanced degree of hormonal levels of estrogen and progesterone, which the corpus luteum secretes to prepare the body for a possible pregnancy. During this phase, the basal body temperature can remain at 37 degrees, and then, before the onset of menstruation (menstrual bleeding), drop sharply.
Ovarian cyst
Often, due to impaired maturation of the follicular component and accumulation of fluid in the cavity, a benign formation appears - a cyst.
It can often be diagnosed in fertile women. The cyst may disappear and appear on its own. The disease occurs in 70 percent of women. Ovarian cysts are classified according to the area of occurrence:
- follicular;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- paraovarian.
If the cyst does not go away within 1-2 cycles or does not disappear after childbirth in pregnant women, it must be removed surgically.
The menstrual cycle and its features
The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormonal factors. The regulation process involves hormones of the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, pituitary gland and endocrine glands. It is hormones, acting on the organs of the reproductive system, that cause all the processes that occur during a woman’s menstrual cycle.
According to gynecologists, the normal menstrual cycle ranges from 21 to 35 calendar days. Most often, women note the duration of the monthly cycle from 26 to 30 days. In the absence of serious pathologies of the reproductive system, women's periods are regular and stable. At the same time, a shift in a certain stage by several days is not a pathology and is considered a normal physiological phenomenon.
When considering the stages of the menstrual cycle, it should be mentioned that its beginning is always considered the first day of menstruation. This means that the female cycle is considered “from period to period.” However, when it comes to gynecological stages, experts suggest considering a slightly different classification of stages.
Stage No. 1 – Follicular period of menstruation
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, a woman’s body exhibits a very low concentration of the female hormones estrogen. Such a low level becomes a stimulus for the hypothalamus to produce special releasing hormones, which subsequently act on the pituitary tissue. It is in the pituitary gland that two main hormonal substances are produced that regulate the monthly cycle - follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
These chemicals enter the bloodstream and reach the woman's ovarian tissue. As a result of this interaction, the ovaries begin to produce the same estrogens that are not enough in the body in the first days of the menstrual cycle. A high level of estrogen in the blood is necessary for the process of active growth of follicles (female germ cells) to begin in the ovaries.
Every month, several such cells begin to mature in the female body, among which one dominant follicle stands out. It is the process of maturation and growth of the follicle that formed the basis for naming the first stage of the menstrual cycle, which is called follicular. The duration of the first stage may vary for each woman, but on average, with a 28-day cycle, follicle maturation takes about 14 days. The longer this stage lasts, the longer the woman’s entire menstrual cycle.
Stage No. 2 – Ovulation
As mentioned above, during the first stage the dominant follicle grows actively and rapidly. During this time, its size increases approximately five times, as a result of which the enlarged cell protrudes beyond the ovarian wall, as if protruding from it. The result of such protrusion is the rupture of the follicle membrane and the release of the egg, ready for further fertilization. It is at this stage of the menstrual cycle that the most favorable period for conceiving a child begins. Calculating the date of ovulation is not difficult, especially if a woman has a stable and regular menstrual cycle. The day of ovulation occurs exactly 14 days before the first day of your period.
Stage No. 3 – Corpus luteum phase
After the follicle ruptures, the so-called corpus luteum forms on the wall of the ovary. This formation actively secretes pregnancy hormones - progesterone and estradiol. If during ovulation the fusion of the egg and sperm occurs and conception occurs, the placenta is formed from the corpus luteum. If fertilization does not occur, a small area of scar tissue forms in place of the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum phase lasts for almost 14 days in almost all women.
Stage No. 4 – Zero phase of menstruation or menstruation
If pregnancy does not occur, dystrophic changes occur in the functional (mucosal) layer of the uterus, which causes its rejection. This is called menstruation. During this process, the vessels supplying the uterine endometrium rupture, which is accompanied by bleeding. As a result, during menstrual periods, a woman notes that, along with blood, particles of the rejected mucous layer of the uterus come out of the uterus through the vagina.
Thus, during menstruation, the processes of separation of the uterine endometrium and its subsequent restoration, which begins already on the second day of critical days, occur simultaneously. Over the entire period of the menstrual cycle, the upper mucous layer of the uterus thickens 4-5 times, after which all stages are repeated.
The interval between ovulation and the next periods
The length of the interval between menstruation is in most cases determined by the moment when ovulation occurs. The normal indicator is the release of the egg from the dominant follicle on the 14th day after the start of regulation. If the cycle is 28 days, then 14 days should also pass from ovulation to the next menstruation, but a minimum delay of 1-2 days is allowed.
If it is typical for a woman to have menstruation every 28 days, but for some reason ovulation occurs earlier, for example, on days 11-12, then menstruation will also occur earlier on days 25-26. A similar situation may occur after successful completion of treatment for any pathology. In a similar way, the body shows that it has recovered and is ready to bear offspring. Rest in a hot climate zone or on mineral waters can reduce the duration of the first phase of the cycle. If your period comes a little earlier than usual, there is no need to panic, it is important that the cycle does not become less than 21 days.
The second, luteal phase from ovulation to the arrival of the next regula lasts exactly 14 days, but the first part of the cycle is too susceptible to the influence of various factors, which leads to both slow and rapid maturation of the egg, and this entails a lengthening or shortening of the cycle as a whole . With age, the interval between menstruation increases, and closer to menopause it can reach 40-48 days; this is not a pathology if the figure is approximately the same from month to month.
When should the first menstruation occur?
The first time menstruation occurs at the age of puberty. According to medical statistics, this age range is from 8 to 16 years. Most often, a girl experiences her first menstrual flow between the ages of 11 and 14 years. By this age, the mother or other older relative must prepare the girl for this process, since the lack of a sufficient level of knowledge can lead to psychological trauma for the child. Signs indicating the imminent onset of menstruation are:
- enlargement of the mammary glands;
- active hair growth in the pubic and armpit areas;
- uncharacteristic vaginal discharge.
According to medical research, the age at which mother and daughter have their first menstruation often coincides, so you should prepare for this age milestone in advance.
Types of PMS
For each woman, the precursors of menstruation manifest themselves individually, taking into account genetic predispositions and characteristics of the body. The following types of PMS are distinguished.
Neuropsychic change
Destabilization of the emotional state is expressed by unmotivated aggression, depressed state and excessive resentment. Changes occur in the central nervous system.
The appearance of edema
Edema manifestations are associated with fluid retention in a woman’s body during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. Before menstruation, the legs and face swell, and itching may occur. It is these menstrual symptoms that provoke swelling of the mammary glands.
Neurological or cephalgic disturbances
These changes are characterized by headaches, attacks of nausea or vomiting. I often feel dizzy before my period.
Crisis manifestations
Crisis manifestations intensify in women before menopause. Sympathoadrenal crises often occur, which are accompanied by an abnormal heart rhythm and increased blood pressure.
Mixed manifestations
This is a combination of several types of PMS at the same time. The edematous form is complemented by an unstable emotional state.
Atypical manifestations are rare
In this case, atypical symptoms are combined: suffocation and migraine, allergic reaction and vomiting.
When does menstruation stop?
Non-occurrence of the next menstruation may indicate either the woman’s pregnancy or the onset of menopause. Sometimes the absence of menstruation is a symptom of a serious pathology in the body, and therefore the first thing to do in this situation is to consult a gynecologist. The age of menopause in a healthy woman varies between 45-55 years, but cases of both earlier and later menopause have been recorded. The entire process of menopause usually takes about two years, during which the woman experiences irregular menstruation with an unusual course.
Read also Ovarian cancer - tumor markers, prognosis, surgical treatment
The issue of restoring the menstrual cycle after pregnancy and childbirth deserves special attention. If a woman does not breastfeed, menstruation usually returns within 2-3 months. If a young mother has normal lactation, the period of absence of menstruation may last for the entire period of breastfeeding. The fact is that the specific hormone prolactin is responsible for the production of milk in the mother’s body, which prevents the restoration of the menstrual cycle. However, if a woman returns to her period during breastfeeding, this is not considered something abnormal and pathological.
What is needed for calculations
Would you like to know the first day of your menstrual cycle? How to count the interval between critical days, and also calculate the exact date when they arrive?
You can use special programs and web services for this, or you can give preference to the classic method of calculating menstruation. For him, the girl will have to prepare:
- something to write on (pencil, pen or marker);
- notepad;
- calendar (it’s better to take a pocket calendar).
It would be enough. If you use web services or special “female” programs, none of this is required. All information will have to be entered electronically using a keyboard and mouse.
Menstruation - normal and pathological
So, a normal menstrual cycle lasts from 21 to 35 days. The critical days themselves are observed for 3-6 days, during which a woman loses from 50 to 250 milliliters of blood every day. A healthy representative of the fair sex should not experience severe pain or notice any obvious pathological symptoms. Any violations and deviations from these norms are considered a pathology and require mandatory medical intervention.
Gynecologists identify the following possible pathologies of the menstrual cycle:
Amenorrhea - delayed menstruation
This term means the absence of menstruation for at least three months, without a physiological reason. This means that the absence of menstruation during amenorrhea is not associated with pregnancy, lactation or menopause. Amenorrhea can be a symptom of such dangerous pathologies as resistant ovarian syndrome, cervical atresia, virilizing ovarian tumors, intrauterine synechiae (Asherman's syndrome), etc. Also, the absence of menstruation can become a characteristic sign of serious hormonal disorders in the body, as well as psychogenic disorders. Sometimes amenorrhea occurs in a woman after severe weight loss.
Menorrhagia or hypermenorrhea - heavy periods
Too heavy or prolonged periods, which are accompanied by significant blood loss. This pathological condition is indicated if critical days last more than 7 days or daily blood loss exceeds 200 milliliters. Usually, with menorrhagia, other pathological symptoms are completely absent, but the woman experiences significant discomfort due to such heavy discharge. The causes of excessively heavy periods can be diseases of the female reproductive system such as endometriosis and uterine fibroids. In rare cases, this deviation from the norm is caused by a blood clotting disorder. A similar menstrual dysfunction can also be observed in women who have previously had an intrauterine device installed for contraception.
Dysmenorrhea - pain during menstruation
It is menstruation, which is accompanied by intense pain that interferes with a woman’s normal professional activities and physical activity. The pain is usually localized in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lumbar region. Acute pain may also be accompanied by bloating. According to doctors, more than 50% of all women periodically experience dysmenorrhea. The search for the cause of this condition should lie in the field of research on endometriosis, fibroids, and inflammation of the fallopian tubes.
Irregular menstruation
Some women note that they have an unequal period between the onset of their periods. If irregularities in the menstrual cycle occur at least 3 times a year, doctors talk about the likelihood of pathological processes in the woman’s body. The causes of irregular periods can be gynecological tumors, cysts, endometrial polyps, inflammatory diseases of the myo- and endometrium, uterine fibroids, endometriosis. Often this disorder is a consequence of hormonal imbalance. Physiological causes of irregular periods include the consequences of abortion, curettage and childbirth.
Definition
Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining and its subsequent removal from the body. It is accompanied by heavy bleeding lasting from 3 to 7 days.
From what day do you start counting your menstrual cycle? First you need to understand what period of time we are talking about. Otherwise, you may make a serious mistake.
The menstrual cycle is the period between the two “extreme” periods. With its help, you can determine various processes occurring in the body. For example, to judge the presence of chronic diseases. Menstruation is an important process for every sexually mature girl.
Menstruation often indicates the presence of hormonal imbalances, as well as chronic diseases. Lack of menstruation is a reason to visit a gynecologist and take a pregnancy test.
Bleeding between periods
If a woman experiences any bloody discharge from the genital tract between the 10th and 25th day of the menstrual cycle, they speak of intermenstrual bleeding. In the middle of the cycle, this phenomenon can be caused by the physiological process of ovulation, namely the rupture of the follicle. In this case, the woman notes the appearance of transparent mucous discharge streaked with blood. Also, similar manifestations are observed in some representatives of the fair sex who have started taking hormonal contraceptives or have taken medications for emergency contraception. Pathological causes of bleeding between menstruation include hormonal changes, genital injuries, endometrial polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, cysts and ovarian tumors.
Separately, a complex of symptoms called premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is considered as a deviation from the norm. This condition is observed in many women and is accompanied by pain in the abdomen and mammary glands, headaches, irritability and fatigue, the appearance of acne and uncharacteristic vaginal discharge. All these unpleasant manifestations are usually noted a few days before the onset of menstruation and can persist throughout the entire period. An unambiguous list of causes that provoke PMS has not yet been identified, however, most experts believe that all pathological manifestations before menstruation are associated with hormonal imbalance in the body.
What affects the duration of regulation?
Based on the genetic characteristics of the structure of the genital organs, blood clotting, and hormone secretion, an approximate characteristic of the regula is established, so for women of the same family, the intensity, volume, type and duration of menstruation often coincide.
Age affects the condition of the ovaries, body structure, metabolism, and psycho-emotional health. Due to changes in these criteria, changes in the secretion of substances continue, and the duration of menstruation depends on the work of the hormone-producing glands.
Among the independent factors, the state of women's health is affected by any temperature, climate, or natural changes.
| Factor | Additional pathogen | Consequence |
| CNS dysfunction | Stress, depression, overwork | Excessive secretion of cortisol (stress hormone) |
| Diseases of the female organs | Infections, inflammation, heredity, ovarian dysfunction | Violation of the structure of the mucous membranes of organs, tissue damage (excessive blood loss) |
| Changes in the functioning of the endocrine system | Deviation in the functioning of the endocrine system | Cycle failure |
| Poor nutrition | Overeating, fasting | Hormonal imbalance due to loss of vitamins |
| Ecological situation | Change in climatic conditions | Increase duration for a short time |
The fight against negative factors must begin with lifestyle changes, which play an active role in the formation of a stable cycle.
Proper alternation of work and rest, absence of overexertion, regular maintenance of muscle tone, restrictions on exercise, a nutritious diet and sleep are the first steps towards normalizing regulation.
Pain during menstruation
Reproductive hormones are responsible for the occurrence of menstruation. The menstrual cycle lasts approximately 28 days and during this time hormone surges are observed.
For most women, this condition passes without any special consequences and the only discomfort for them is bleeding, but for some women, periods are accompanied by pain.
The reasons for this may be the following:
- negative prostaglandins, causing spasms of the muscular wall of the uterus and constriction of blood vessels;
- insufficient level of endorphins, enkephalins;
- increased pain sensitivity;
- luteal phase deficiency.
Treatment of pain during menstruation
If the pain is too severe, then you should immediately contact a gynecologist to solve this problem. This will make sure that there are no signs of pathological processes in the body.
In the absence of pathological processes, pain can be reduced as follows:
- Massaging the abdominal area.
- Warmth on the stomach;
- Taking the “embryo” pose.
- Proper nutrition on a light diet.
- Taking painkillers.
What should you not do during your period?
In order to avoid negative consequences, it is recommended to follow standard rules during the discharge period. This will help you keep your well-being positive and not harm your health. There are many “dos” and “don’ts”; below are just the key ones.
During the menstrual cycle it is not recommended:
- Perform active physical activity.
- Relax in a bathtub with hot water.
- Perform sexual intercourse without contraception.
- Perform operations.
- Use contraindicated medications.
- Go to a public pool or open water bodies.
- Consume food or drinks that cause an allergic reaction or are generally contraindicated.
- Hold off on peeling procedures.
- Do not comply with personal hygiene requirements.
Read also Reproductive medicine
Reasons for the “jumping” cycle: menstruation failure is dangerous
An irregular menstrual cycle often indicates that there is a problem in a woman’s body. The main reason for its occurrence is hormonal imbalance, which can be triggered by a number of factors. It is customary to distinguish between physiological, drug and pathological causes of a disrupted cycle.
Physiological causes of menstrual irregularities
Physiological causes are the least dangerous and are easier to eliminate than others. These include:
- stress and nervous tension, lack of sleep, chronic fatigue;
- severe physical overload;
- body weight disorders (obesity and wasting);
- sudden climate change;
- activation or lack of sexual activity;
- strict diets, consumption of alcohol, tobacco, drugs, excessive caffeine consumption;
- postpartum period and lactation period;
- various cleanings, scrapings;
- radiation and poisoning.
All of these factors lead to a state of shock in the body. A stress hormone (adrenaline, prolactin or cortisol) is released. It blocks the ovaries, i.e. interferes with the production of female sex hormones, and thereby disrupts the menstrual cycle.
Violation of body weight can lead not only to cycle failure, but even to its temporary absence. This occurs due to the production of the male hormone androgen in adipose tissue, and the more this tissue, the more hormone is released.
Pathological causes of problems with menstruation: urgently see a gynecologist!
Pathological causes are more dangerous and can lead to serious complications if not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. These include the following main diseases:
- tumor and polypous formations, various “omas” - for example, uterine fibroids, which disrupt the proper functioning of the reproductive system;
- ovarian pathologies (cyst, polycystic disease, dysfunction);
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the genital area;
- endometriosis of the uterus;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- thyroid diseases;
- other diseases of the “non-sexual” area that cause hormonal imbalance (blood diseases, diabetes, etc.);
- hereditary predisposition.
The range of such provoking diseases is wide: from mild colds of the genital organs to oncology. This can also include frozen pregnancy, miscarriage and complications after an abortion. Often the pathology is asymptomatic, the general condition is satisfactory, but the menstrual cycle is irregular. In this case, a special examination will be required to confirm or refute the presence of pathology.
Medicinal causes of menstrual irregularities
Medicinal causes include taking medications. Almost any medicine that enters the body affects all organs and systems, especially the reproductive one. The following drugs can disrupt the cycle:
- Antidepressants – cause a delay in menstruation and reduce the amount of discharge;
- Anticoagulants and blood thinners – increase the intensity of bleeding;
- oral contraceptives - long-term use of hormonal drugs shortens the duration of menstruation and makes them scanty, and the wrong choice can radically change the cycle. Cancellation of oral contraceptives often also leads to disruption of the cycle, but this does not pose a danger to the body. Full recovery in such cases occurs after 2–3 months of the cycle;
- Hemostatic drugs - reduce the amount of discharge;
- Antiulcer drugs – cause a delay in menstruation;
- Intrauterine device - the body perceives its installation as a stressful situation, so even if it is performed correctly, minor cycle disruptions occur.
Incorrect placement of the intrauterine device or illiterate installation often provokes uterine bleeding or serious cycle disorders. Normally, its stabilization should occur within 3–4 cycles.
Hygiene during menstruation
During this period, you should take a bath and shower more often than usual, this will help get rid of many negative consequences. In this case, it is recommended to change pads or tampons at least every four hours.
During this process, the girl sweats more. This is due to increased production of hormones in the body. Therefore, washing the problematic part of the body must be of high quality and complete (both front and back), so that harmful microorganisms are not given the opportunity to reproduce.
It is important to understand that on such days a full bath, swimming pool or sauna is prohibited. This leads to unwanted overheating of the body, which leads to blood flow towards the pelvis and more abundant discharge.
In addition, this allows more microbes to enter the body, to the uterus, since during this period it is the most open. This is facilitated by the non-sterility of the liquid.
What product to use when washing or showering should be determined individually; in many ways, the girl’s skin type plays a big role here.
For example, you should understand that any product has a highly alkaline composition and puts a lot of pressure on the skin, adding new tension to the body and preventing relaxation.
If a girl has dry skin, then the more alkali there is in the product, the more irritation of the skin it will lead to.
In such cases, it is recommended to refuse to use soap and give preference to gel products. Gels will remove all contaminants from intimate areas more gently, without causing the skin a new degree of irritation.
Soap for children is also a good option, especially for those with very sensitive skin. A separate advantage is that it does not contain aromatic additives or harmful elements that can cause irritation or lead to an unpleasant allergic reaction.
How often should you change your underwear?
It is very important to choose the right underwear for yourself. During menstruation, you should give preference to natural fabrics rather than synthetic ones.
In addition, it is worth choosing simple models in which the number of lace and other elements is minimized.
Such preferences will allow the skin to “breathe”, lead to more favorable well-being, and minimize the risks of many complications.
Underwear should be changed at least twice a day. This avoids the formation of harmful microorganisms.
Changing lifestyle and habits
If the disruption of the cycle is associated with a woman’s lifestyle and her bad habits, then to stabilize it you just need to change it: give up excessive consumption of caffeine, get rid of bad habits, do not overload the body physically, get enough sleep, protect yourself from nervous stress, eat right etc.
Following these simple recommendations will have a beneficial effect on restoring the menstrual cycle, only if this is the cause of the failure.
Hygiene products on critical days
Key ways to protect against leaks: sanitary pads and tampons. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. The ideal solution is to use them alternately.
Gaskets
This solution can be used at any age, after the menstrual cycle begins.
The presence of gynecological diseases is also not a contraindication for use.
The pads have a specific shape suitable for underwear. They have several layers for better absorption of secretions.
The bottom layer is always sticky to make it easier to place the product on your underwear and avoid problems with secure fastening.
Certain types of pads have increased reliability due to the side “wings”, which provide additional attachment to the underwear.
The top layer of the gasket can be made of both artificial and natural materials. Artificial materials absorb moisture better, but can cause allergic reactions. Natural materials do not cause allergic reactions, but absorb secretions less well.
The level of moisture absorption is indicated by drops on the pad packaging. The more drops, the higher the level. Pads should be selected accordingly, depending on the intensity of the discharge. The higher the intensity, the more absorbent pads you should choose.
The pads are conveniently divided into types: for daytime and nighttime use. Daytime pads are most often not as dense as nighttime pads and are narrower. Night ones are focused on long-term use, without frequent changing of the pad.
Many pads are scented, but you should be careful when choosing them as they can cause an allergic reaction.
Kotex Libress Always Naturella
Tampons
They are more comfortable and, unlike pads, are invisible even with the thinnest underwear.
In structure, they are a tube with a draw-type thread. Some tampons have an applicator, which makes it easier to place the product in the vaginal area.
Tampons are divided into mini, normal and super according to their type. The “super” type is the most absorbent and is recommended for use if the discharge is heavy.
If they are not abundant, you should use mini or normal tampons.
Tampons should be changed at approximately the same frequency as pads. If this is not done, then the risk of various diseases is quite high. You shouldn’t let it get to this point, otherwise great treatment difficulties will arise in the future.
Bella Tampax Ob Kotex
Diagnosis of bleeding in the middle of the cycle
First of all, to diagnose the causes of intermenstrual bleeding, a gynecological examination is necessary. In addition, you must undergo the following examinations:
- cytological studies of aspirate from the uterine cavity;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- study of the hormonal background of the body;
- thyroid examination;
- hysteroscopy and curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal;
- histological examination of scrapings obtained from the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
Also, if necessary, the gynecologist can prescribe a study of the pituitary gland using magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, computed tomography. Sometimes the brain is also examined using these methods.
The significance of the first day of the cycle
There are days that are significant when planning pregnancy, for conducting diagnostic studies and laboratory tests.
How to determine the first day of your menstrual cycle?
The first day of the cycle is the day when menstrual bleeding begins. It is taken into account when establishing the gestational age and estimated date of birth, when ordering an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs; different concentrations of sex hormones are determined in different phases of MC.
Knowing 1 day of the menstrual cycle will help you calculate the date of the next menstruation using a paper calendar or an electronic women's period calendar on your phone.
Based on knowledge of the day the female cycle begins, we can assume the most favorable period for conception.
Normally, the menstrual cycle lasts 28–32 days. A cycle less than 21 days long is called short, and more than 36 days is called long. A shift in the start date of the MC by up to a week (earlier or later than expected) is a variant of the norm. The absence of menstruation for more than 5 weeks or the start of a new one in less than 2.5 weeks is already a serious reason to seek qualified help.
According to the amount of discharge, menstruation can be heavy or light. The norm is a blood volume from 20 to 120 ml, that is, no more than half a glass.
What are the dangers of heavy menstruation?
Any changes in the nature of menstruation should be alarming. Normal periods for girls last no more than 6–7 days. If their duration and amount of blood increase, this is a dangerous symptom.
Heavy and frequent discharge can cause dizziness. This phenomenon is associated with large blood loss from the body. So, when menstruation lasts more than 7 days, the following risks arise:
- Development of anemia. Together with the blood, the body loses useful microelements that it needs for normal functioning. Since during menstruation there is insufficient amount of potassium and magnesium in the blood, the body weakens.
- Dehydration. During menstrual bleeding, a large amount of fluid is lost. This negatively affects the functioning of the liver, kidneys, heart and other organs. To prevent dehydration, drink plenty of fluids.
- Failure of the hormonal system. Often hormonal changes are provoked by infections that settle on the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
To prevent the development of dangerous gynecological pathology, a woman must monitor her cycle and the nature of her menstrual flow.