SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate surgeon Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers Residents m district For pensioners Promotions at the clinic
What is the reason for the absence of menstruation, although all the expected dates for the arrival of the “red days of the calendar” are long gone and the pharmacy pregnancy test is negative? Delays of menstruation in girls by 1, 2, 3 and 5 days or more are quite common. What to do if there are frequent delays and which doctor should you go to in this case?
To begin with, do not go to extremes: rejoice uncontrollably or fall into despair and panic. There may be many reasons why there are no periods, but usually they come down to two main ones - the onset of pregnancy, or manifestations of a malfunction of the ovaries. The absence of a monthly cycle during menopause is a separate, independent topic that we will consider later.
WHAT IS A NORMAL WOMEN'S CYCLE. The beginning of the cycle is counted from the first day of menstruation. It lasts on average 27-30 days. In gynecology, a cycle of 21-35 days is considered the norm. The important factor in this matter is its regularity, and not its duration. A delay in menstruation is considered to be a period that exceeds five days. Such delays up to twice a year are considered normal. In order to control the onset or delay of monthly bleeding, each woman should keep a special calendar, marking the day the next menstruation begins. In this case, failures in the cycle will be immediately noticeable.
Why does this happen every month?
During the follicular phase of the cycle, a pituitary hormone stimulates the appearance of follicles in the ovaries, creating the main follicle. But it already forms the sex hormone estrogen - it activates the growth of the uterine mucosa. It is also needed so that the egg has the opportunity to fixate on the uterus in the future - each menstruation provides for the onset of pregnancy.
Simultaneously with the growth of the endometrium, a follicle with an egg matures in the ovaries. When its size reaches two centimeters, a rupture occurs and the egg is released - ovulation . This is the most successful period to get pregnant.
The next phase is luteal .
Where the egg is released, the corpus luteum appears, producing progesterone, a hormone that makes the endometrium optimal for the fertilized egg. If fertilization does not take place, the brain receives a signal that it is no longer necessary to produce progesterone. Thus, detachment of the uterine mucosa begins.
After this, the last phase begins - menstruation .
Blood flowing from the vessels that formed during the entire cycle is added to the menstrual flow.
What should a normal (regular) menstrual cycle be like?
The female reproductive system works like a clock and every month goes through a certain sequence of stages, which are actively influenced by female sex hormones. These cyclical changes are called the menstrual cycle. It begins on the first day of menstruation in the form of bloody discharge from the uterus, the duration of which varies from 3 to 8 days. Normally, its duration is from 26 to 36 days.
A delay in the onset of menstruation by 5–7 days is not a deviation if it does not occur regularly.
Each menstrual cycle goes through four stages: egg maturation, ovulation, descent of the mature egg into the uterus and rejection of the uterine lining with the unfertilized egg in the form of menstrual blood.
Menstruation instability is indicated if the following occurs:
- Critical days begin at different intervals, and it is quite difficult for a woman to predict the start date of her next menstruation.
- My periods are irregular. This means that sometimes they last 3 days, and the next month they last more than 8 days.
- There is a change in the intensity of menstrual flow, which can be either heavy or scanty. Such periods can be considered irregular.
- The absence of menstruation is stated, which is not associated with fertilization.
Painful critical days
Among women, pain during menstruation is a fairly common complaint. In medicine, such unpleasant manifestations are called algodismenorrhea. Its main symptoms are cramping or aching pain in the lower abdomen, which can sometimes radiate to the lower back, and is also accompanied by poor health.
Types of algodismenorrhea:
- primary;
- secondary.
Primary appears in young girls during the establishment of the menstrual cycle. Usually during this period the level of sex hormones changes, causing pain during menstruation. After a year and a half, primary algodismenorrhea disappears.
Secondary occurs in older women, caused by other factors:
- change in the location of internal organs;
- diseases of the pelvic organs, uterus and appendages;
- stress, poor sleep patterns and unbalanced diet;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- individual pain threshold;
- injuries after childbirth.
What other pain occurs during menstruation?
The nature:
- Compensated. All obvious manifestations of the process do not change over a long period of time.
- Decompensated. The severity of symptoms increases every year, accompanied by dizziness and loss of consciousness.
By intensity:
- Easy. It can be alleviated with antispasmodics or analgesics - no-spa, nurofen, ibuprofen.
- Moderate. Although taking analgesics minimizes pain, it lasts longer. You may also experience headache, dizziness, or bowel dysfunction.
- Heavy. Conventional analgesics help little with it. There is a sharp pain in the lower abdomen, vegetative syndromes, nausea, diarrhea, headache, and impaired activity.
Tolerate or not?
It all depends on the intensity of the pain. The course of menstruation changes periodically depending on seasonal climate changes, lifestyle, etc. Mild discomfort in the lower abdomen, weakness, drowsiness and sensitivity are considered normal for a woman during her menstrual period. However, if the discomfort is severe, bloating, migraine, chills, fever or even loss of consciousness appears, you should consult a doctor.
Main causes of hypomenorrhea
The most serious and common pathological cause of the development of hypomenorrhea in women of reproductive age is dysfunction of the ovaries and pituitary gland, which are regulators of menstrual function. For example, pituitary insufficiency, Sheehan syndrome, can lead to a complete absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) or other menstrual dysfunction.
Ovarian dysfunction
Various inflammatory processes, hormonal imbalances, and external factors can lead to ovarian dysfunction:
Various inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs
These are inflammations of the uterine appendages - adneskitis (salpingoophoritis), inflammation of the ovaries - oophoritis, caused by various pathogens, STIs. They can occur from severe hypothermia, frequent improper douching (douching is harmful or beneficial), and other infectious diseases that lead to the transfer of the pathogen through the bloodstream from other organs to the female genital organs.
- Psychological fatigue, nervous strain, irrational rest and work schedule, physical and psychological fatigue.
- Mini-abortion, medical abortion, spontaneous miscarriage, especially during the first pregnancy, when sudden hormonal changes occur - all this provokes the development of stable ovarian dysfunction.
- Underdevelopment of the genital organs, abnormal development of the uterus and uterine appendages.
- External factors such as taking certain medications, radiation damage, climate change, excessive exposure to sunlight or abuse of solariums.
- Incorrectly selected oral contraceptives or their long-term use contributes to weakening of ovarian function (see the negative consequences of taking oral contraceptives in the article on birth control pills)
- Obesity, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland can cause ovarian dysfunction.
Why don't I get my period?
A common reason for the absence of menstruation is pregnancy, so it is advisable to immediately take a test on the first day of the delay.
However, there are other factors that can influence the onset of menstrual periods:
- stress, depression;
- colds, flu;
- hormonal disbalance;
- obesity or underweight;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- neoplasms in the uterus or ovaries;
- starting to take hormonal contraceptives.
Prevention
Menstrual irregularities, which are manifested by the fact that menstruation does not end, can be quite easily controlled and measures taken throughout life to prevent their occurrence.
To do this, you need to observe a number of basic points:
- A woman should eat well and follow a work-rest schedule.
- Eliminate heavy physical activity and heavy lifting from your life.
- Take a responsible approach to issues of creating offspring. If you do not want to have children in the near future, you need to contact a specialist to select the optimal birth control pills. Do not terminate pregnancy, use protection during sex, and avoid uncontrolled unauthorized use of hormonal medications.
- Do not abuse medications that can affect the circulatory system.
- Regularly visit a gynecologist , and, if necessary, other specialists, monitor the regularity of menstruation and at the first manifestations when they do not end, seek medical help, and do not self-medicate.
How to induce or delay your period
Often “guests from Krasnodar” come precisely during vacations, birthdays, weddings or other important periods of life. Then most girls wonder: how to speed up periods or stop them?
Experienced doctors do not advise making adjustments to the start or end of menstruation, established by nature. Because by changing the cycle at least once, you can treat the consequences for a long time in the future. However, if you are determined to do this, you need to consult with your gynecologist, changing the onset of the “red day on the calendar” solely on his advice.
There are two medical ways to change the onset of menstruation:
- Often the doctor prescribes combined oral contraceptives. They should be used before you plan to delay “day X”.
- Gestagens or progestins. Doctors prescribe these drugs for the treatment of amenorrhea and endometriosis. Application: 5-14 days before the start of menstruation and until the last day. They will come after three days of completing the course.
Treatment
Drugs
Choosing medications in the event that your period does not end is quite dangerous and at the same time responsible.
That is why only a qualified specialist can solve the problem, who will first determine the problem of menstruation, and only based on the results of laboratory and instrumental research methods will choose treatment tactics.
First of all, drug therapy should be aimed at eliminating the main cause of menstruation irregularities:
- This may be taking medications to treat the thyroid gland or other body hormones.
- In the case of endometriosis of the uterine body, gestagens or oral contraceptives with a gestagenic effect have a good effect.
- For fibroids, the effect of drug therapy is not high, so drugs can only to a small extent relieve a woman from the fact that her period does not end. These may be drugs to stop menstruation such as Tranexamic acid or Etamsylate.
- In a stressful situation, you can include sedatives, mainly plant-based, in your diet. It could be motherwort, valerian, etc.
- With polyps, menstruation is difficult to eliminate with medications.
Folk remedies
There are quite a lot of folk remedies if menstruation does not end.
More often these are herbal preparations, the mechanism of action of which is aimed at affecting the circulatory system:
- Among the effective and most popular remedies is nettle. This plant, due to the vitamin K it contains, has a powerful hemostatic effect. Nettle is taken orally as a decoction during menstruation. As a result, volume and duration are rapidly reduced. But such a plant has a number of contraindications and precautions in taking it. During menstruation, nettle should be consumed for no more than 7 days, otherwise hypercoagulation or thrombosis may occur, leading to a threat to life.
- Horsetail decoction helps solve the problem when menstruation does not end. Sometimes horsetail is prepared in the form of a tincture. The duration of the course of therapy is on average one month, sometimes the period can be extended.
- To a small extent copes with the problem of menstruation, which does not end with a decoction of chamomile or mint.
- Viburnum is used less , although its hemostatic effect is clearly visible.
How to induce menstruation at home
You will find a lot of advice for yourself on the Internet, but remember that the same remedy can have different effects on each person. And it’s not a fact that the drug that helped your friend will be a good option for you.
What can help you get your period earlier?
- A strong decoction of parsley or chamomile. You need to drink it twice a day for a week.
- A large dose of vitamin C. This can be in the form of pharmaceutical products, and in the form of ordinary citrus fruits, especially lemons. There is no need to worry about an overdose, because the vitamin does not accumulate in the body; it is excreted in the urine.
- Hot bath. Taking it will improve blood circulation, including in the pelvis, thereby increasing the risk of uterine contractions and there will be a chance of a quick onset of menstrual periods. It also helps to relax and remove stress, which sometimes causes delayed menstruation.
- Warm compress. It can be applied to the lower abdomen. It acts like the same warm bath.
What to do in case of prolonged bleeding?
If it is currently not possible to visit a specialist, but menstruation does not stop, you can use methods of stopping menstruation, such as a one-time dose of hemostatic agents, Tranexamic acid or Etamsylate.
You should definitely know that no hormonal medications should be used during menstruation that does not end. You should contact a medical facility as soon as possible.
Etamzilat
Tranexam
Heavy periods
Critical days, like any other process in the functioning of the human body, may have deviations from the norm. Therefore, problems with the menstrual cycle are common. Painful, scanty or, conversely, abundant, occurred in approximately 30% of beautiful ladies.
Heavy menstruation (menorrhagia, hypermenorrhea ) is a disorder that is manifested by an excessive amount of liquid discharge from the vagina.
In ordinary life, a woman at any age loses up to 250 ml of blood (one glass) or 40-60 ml per day (two to four tablespoons) during menstruation. And for the entire reproductive period - 90 liters. A healthy body tolerates such a loss easily. If only because menstrual fluid consists of more than just blood. It also includes a mucous substance secreted by the glands of the cervix, vaginal secretions (lubricant) and endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus). And the rich and intense color of the discharge is not explained by the presence of a large volume of blood in the liquid, but by the fact that it contains a special set of enzymes. So normal periods by themselves cannot cause anemia (even in its mild form).
However, if there are deviations from the norm - heavy or scanty periods, then this may be an indicator of the presence of some disease, which will subsequently lead to another problem. For example, due to intense doses there is a risk of developing anemia with a significant decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
Why do you have heavy periods?
Usually the reasons for heavy periods are quite serious. Too long (8 or more days), as well as excessive (400 ml of blood) flow of menstrual fluid is an indicator of not just regular renewal of the uterine cavity, but rather uterine bleeding. In often advanced cases, it requires a rapid hemostatic procedure or even a blood transfusion to increase hemoglobin levels.
Due to the fast pace of life, girls often experience heavy bleeding on their legs, forgetting that during this hemoglobin will drop, the body weakens due to weight loss and the risk of accidental fainting subsequently increases.
Causes of hypermenorrhea
The most common causes of excessive hemorrhage are the presence of serious gynecological diseases, namely:
- endometriosis;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- fibroids or uterine leiomyoma (benign tumor of the uterus)
- polyposis of the cervix and/or uterine cavity.
The presence of blood clots in the discharge, and especially pieces of flesh that look like raw chicken liver, allows preliminary detection of fibroids. In this case, you need to contact a gynecologist as soon as possible for further examination. Taking a sample of the isolated tissue for histological examination will help exclude the possibility of cancer.
There are also other reasons for heavy periods:
- hereditary predisposition to menorrhagia;
- changes in hormonal levels (adolescence, beginning of intimate life, use of hormonal drugs and contraceptives);
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- poor blood clotting (lack of vitamin K, hemophilia, thrombocytopenia);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- diseases of the liver, cardiovascular system, kidneys, thyroid gland;
- stress, physical strain.
Heavy and prolonged periods: treatment
There are two types of treatment for hypermenorrhea: conservative (medication) and radical (surgical). It all depends on the severity and nature of the disease.
With conservative therapy during heavy menstruation, the specialist prescribes a set of procedures:
- the use of anti-inflammatory drugs (to normalize the duration and volume of bleeding);
- hemostatic therapy (in case of severe uterine bleeding);
- the use of iron supplements (for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, which arose as a result of menorrhagia);
- an individual course of oral contraceptives containing hormones (to reduce the proliferation of endometrial tissue and reduce the volume of discharge);
- normalization of work and rest regimes, proper nutrition, increasing general immunity.
A balanced diet really helps to achieve the desired goal - to reduce severe hemorrhage. During a special diet, alcoholic beverages, pickles and spicy foods are strictly excluded from the diet: pickled cucumbers or tomatoes, soy sauce, ginger, pepper, and so on. Of course, all these products are quite useful for the body, however, with menorrhagia they can contribute to increased bleeding.
Radical hysterectomy is resorted to when the disease is in an advanced state and is quite severe - the risk of malignant degeneration of the fibroma is very high or the transition to a tumor has already occurred. In this case, the doctor and patient come to the decision to remove the uterus along with the appendages. The operation itself is carried out according to vital indications. This means that its implementation is necessary to preserve the health and save the girl’s life.
What are the dangers of prolonged menstruation?
Long periods can be associated not only with discomfort, but also with a threat to the life and health of a woman.
To do this, you should know that menstruation can cause problems with well-being, manifested in weakness, dizziness, sudden loss of strength, etc., but blood loss leads to severe anemia and the possible development of a blood clotting disorder.
Do I need to see a doctor?
At the first signs that your periods are irregular in rhythm (they can end and start again after a week) or do not end, you should seek help from a specialist.
You should not self-medicate or select diagnostic methods first. This is due to the fact that they do not always give the desired result and lead to aggravation of the pathological process.
That is why a woman initially needs to see a gynecologist. If a concomitant pathology is identified, the help of related specialists will be required.
When does your period start after childbirth?
It all depends on the type of feeding the baby: natural or artificial. In a woman who has just given birth, milk is produced by the pituitary hormone prolactin. The level of estrogen does not increase, so menstruation during breastfeeding occurs two months after the birth of the child, especially when feeding him by the hour. But for some young mothers, critical days do not begin for a year or, conversely, resume a month and a half after giving birth. On average, the onset of menstruation varies from three months to six months.
Methods for correct cycle calculation
Many people say that they count their periods based on the number of days they menstruate. This is wrong. For correct calculation you need a pencil with a calendar. If the cycle is just beginning, you need to monitor for six months what days it appears on and directly mark them on your calendar.
An example of how to count a cycle in a table:
How to calculate your menstrual cycle correctly? You need to count the days from the day blood appears until the day the next one appears - this will be 1 cycle. If clots and brown discharge appear, this should also be taken into account. It is the first day of menstruation that is the day from which you can count. For example, if the cycle is 25 days, the last menstruation was on January 25, then the next one will appear on February 18 or 19. But, as a rule, it is impossible to predict the attack exactly in time. This occurs in only 45% of women. Therefore, always leave two or three days in reserve. Various deviations, illnesses, unsteady cycles and many other factors postpone the start date of women's days. For this reason, undergo a medical examination every six months.
To calculate your cycle, you can use an electronic menstrual calendar, which can be downloaded from the Internet for free and installed on your computer. In it you can mark not only the days of the onset of menstruation, but also put notes on different days of the cycle, from which you can see the general picture of your condition at different times.
Menstruation during pregnancy
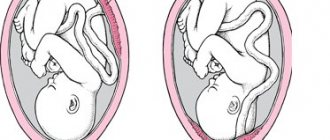
Sometimes girls wonder: can you be pregnant and have your period at the same time? Of course, during this period, some expectant mothers experience red discharge, which is mistaken for their period. However, this is not them.
There should not be full periods during pregnancy. The endometrium, a layer of cells lining the inside of the uterus, is released along with blood during menstruation, and during pregnancy helps the placenta develop while remaining in the body. Therefore, during this period, the monthly renewal of the endometrium stops.
Unfortunately, sometimes spotting occurs during an important period for a woman. Their appearance may indicate that some kind of malfunction has occurred in her body or there is a pathological condition. For example:
- hormonal imbalance;
- risk of miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Alas, many expectant mothers are not worried about the appearance of this symptom, thinking that menstruation during pregnancy is possible. They don't make an appointment with a gynecologist until the situation gets worse. But it is a timely visit to a doctor that can save not only the unborn baby, but also the life of the mother.
What to do if you don't have your period?
A delay in menstruation, not exceeding 5-7 days and occurring in rare cases, is not regarded by modern gynecology as a pathology. The female cycle is a subtle mechanism, dependent on the influence of many external and internal factors.
☛ What is the correct thing to do in a situation when the time seems to have come, but your period is late? First, you need to understand what it is: a delay or a pregnancy? The question of why the failure occurred can only be answered by an experienced gynecologist based on examination, tests and a full examination. If no fertilized egg is detected in the uterus, then the direction of further examination and treatment depends entirely on the cause that caused the cycle disruption. These questions are within the competence of a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
If this is a pregnancy and it is desired, you register, are seen by an obstetrician-gynecologist, give birth safely and receive a long-awaited addition to your family.
If, for some reason, pregnancy is not currently part of your plans, the development of further events follows a completely different scenario (see How to terminate an early pregnancy - medical abortion).
How to save the cycle?
Today, early menopause has become diagnosed more often. It can even occur before the age of 40. Some women who want to have more children are not willing to lose their fertility so quickly. In practice, you can restore the cycle if you start preventive measures before menopause. But when it resumes, ovulation and the possibility of pregnancy do not always return. A common cause of premature menopause is genetic predisposition. Other reasons include:
- thyroid diseases;
- nicotine and alcohol addiction;
Women who have repeatedly gone through childbirth have a larger supply of eggs and, accordingly, are less likely to experience menopause prematurely. If signs of early menopause do appear, you may need to take hormonal medications. After preliminary tests, a suitable remedy is selected. A diet rich in phytoestrogens will help you avoid resorting to drug therapy:
- flax seeds;
- soy products;
- parsley;
- lentils.
This “treatment” does not always give the desired effect, but it is safe and has almost no contraindications.
Age-related skin changes: urgently go to a gynecologist - endocrinologist
A comment
It would seem that the signs are quite obvious, but most women cannot say for sure whether they are associated with the approach of menopause or whether it is just a coincidence. In the end, all symptoms of menopause are atypical. People suffer from insomnia for a variety of reasons; bad mood is also characteristic not only of women during menopause, and fatigue in the modern rhythm of life is a completely natural thing. To track the onset of menopause and take timely measures, any woman over 40 years old should regularly, approximately once every six months, visit an endocrinologist. Today, there are specific tests for follicle-stimulating hormone levels—they are often called “menopause tests.” These tests are very accurate and can definitely tell whether menopause has begun or not. You can even buy such a test strip at a pharmacy, but its accuracy in comparison with laboratory research methods is not as high.
Symptoms that require attention
Menstruation during menopause in women is unstable and can be either weakly intense or heavy. Despite the fact that many symptoms are a variation of the individual norm, some of them may indicate pathology. You should not ignore situations with the following changes:
- menstruation occurs two or more times a month several times in a row;
- the color of the discharge has changed;
- bleeding occurs very intensely, there are clots;
- menstruation does not end for more than a week;
Each of the symptoms separately does not always mean the presence of disease. But often other characteristic manifestations are added to them:
- pain when urinating;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- dryness and vaginal itching;
- weakness and apathy.
When such a clinical picture appears, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs is usually performed, a smear is taken for flora and cytology, and blood tests are prescribed.
Reasons for deviations
It is important to notice deviations in the course of menstruation in time to prevent the development of the disease. To do this, you need to understand the possible causes of certain spotting during premenopause.
If the discharge continues for a long time, this can be the onset of anemia. It affects the skin, performance and impairs the oxygen supply to the body. In this case, additional treatment will be necessary.
Heavy bleeding
Periods that do not end for more than a week, come at unusual times, and are also heavy in nature may be common in premenopause. The culprit of this phenomenon is low progesterone. Also, a woman may experience physical or psychological fatigue, which leads to changes in the menstrual cycle.
Uterine devices often cause severe bleeding.
You should be wary if menstruation begins for the second time in one month, and you have to change sanitary pads more often than usual. The reason for this is not in physiology, but in a serious pathology - uterine bleeding. He is called:
The number of women with uterine bleeding during premenopause reaches 50%. Among patients who sought medical help during menopause, 70% suffer from this pathology. Its characteristic signs are pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, bloating and fever. Cases of painless bleeding are also common.
Pain during menstruation
Discomfort during menstruation is considered a normal manifestation of menopause. Many cells experience a decrease in the main female hormones, reacting painfully to this. Lumbar pain and lower abdominal pain are common. Causes of discomfort during menstruation:
- ovarian depletion;
- death of the endometrium;
- vaginal injury caused by hormonal changes.
Often the reason lies not in the menstruation itself, but in accompanying pathological processes. For example, in cystitis, urethritis, adhesions. Other reasons may be psychosomatics and some gynecological diseases. Menstrual discharge with painful sensations differs in their manifestation:
- Menometrorrhagia and metrorrhagia. Characterized by prolonged uterine discharge after a delay, as well as in the middle of the cycle. The duration of bleeding varies each month.
If no other pathologies are detected, the end of such pain should be expected only with the completion of the restructuring of the body. Or you can try to stop it with painkillers.
Why does the cycle change?
The average age of onset of menopause in women is about 46 years. Early menopause is considered to be 40 years of age, and late menopause - up to 56 years of age. But changes may begin to occur 1-2 years before. Many women report increased irritability, fatigue and changes in the nature of menstruation. Such manifestations are considered normal and do not require treatment.
Gynecologists note the increasing frequency of early menopause.
Menstruation is an indicator of a woman's fertility. Its decrease with age is associated with depletion of egg reserves.
Until the complete loss of the ability to fertilize, each cycle the uterus goes through the following stages of hormonal changes:
- Start of cycle and low estrogen.
- Increased levels of progesterone and estrogen, growth of the endometrium. Preparations for conception are underway.
- The rise of luteinizing hormone during ovulation, the formation of the corpus luteum.
- A drop in hormones involved in menstruation. Endometrial shedding begins.
As menopause approaches, the level of luteinizing hormone increases. At the same time, the ovaries decrease in size, estrogen and progesterone are produced less and less. It is with their deficiencies that the usual changes in the body before menopause are associated.