Hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of cerebral vessels and hemorrhage in brain tissue. Depending on the localization and extent of the process, the prognosis of the disease is determined. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs less frequently than ischemic stroke, but the prognosis of the disease is more unfavorable.
The Yusupov Hospital treats patients with strokes and provides emergency care with the patient being transported to the intensive care unit. In the hospital, the patient will be examined using innovative equipment and will receive effective treatment using minimally invasive neurosurgery methods, the latest developments in the field of stroke treatment, and modern medications. The hospital provides comfortable rooms, dietary meals, and doctors create an individual treatment and rehabilitation program.
Some numbers and facts:
- Only 15% of all strokes are hemorrhagic.
- However, this condition is responsible for 40% of all deaths from cerebrovascular accidents.
- The main causes: hemorrhages in the brain as a result of increased blood pressure, weakness of the walls of blood vessels, decreased blood clotting, rupture of aneurysms (pathologically dilated sections of arteries with a thinned wall).
- Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke occurs as a result of one of two types of hemorrhages (depending on location): intracerebral or subarachnoid.
Right side
If the right side is affected, the most dangerous consequence is damage to the brain stem, in which a person's chances of survival are close to zero. This department is responsible for the functioning of the heart and respiratory system.
Diagnosing a hemorrhagic stroke on the right is quite difficult, since the centers of orientation in space and sensitivity are located in this part. This lesion is determined by speech impairment in right-handed people (in left-handed people the speech center is located in the left hemisphere). In addition, there is a clear relationship: if the functionality of the right half of the brain is impaired, the left side suffers and vice versa.
Possible consequences of hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke more often than ischemic stroke leads to the death of patients. If a person survives, there is a high probability that in the future he will continue to have complications that will make him disabled:
- Paralysis. Different muscle groups may be involved, depending on in which vessel the disaster occurred and how many nerve cells died. Often half of the body is completely paralyzed, and the patient remains bedridden.
- Impaired function of the muscles of the mouth and throat. The pronunciation of words is impaired, speech becomes slurred (dysarthria). There is discomfort and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
- Loss of sensitivity, pain. Certain parts of the body stop feeling touch, injections, high and low temperatures. At the same time, pain and various unpleasant sensations (numbness, “crawling”, etc.) may bother you.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence. Brain hemorrhage can cause loss of bladder and rectal control.
- Impairments in the cognitive sphere. A condition known as vascular dementia may develop. Problems arise with memory, thinking, and other cognitive functions.
- Problems in the psycho-emotional sphere. A sick person may become depressed, withdrawn, moody, irritable, and impulsive.
In some patients, it is possible to restore impaired functions at least partially, while others remain deeply disabled. It's individual. In order to achieve the best correction, you need to go to a medical center to see a doctor as soon as possible and begin rehabilitation treatment. Usually different specialists work with such patients: neurologists, speech therapists, psychologists, physical therapy doctors.
Recovery
Rehabilitation of patients after an attack of hemorrhagic stroke includes a whole range of measures.
The person is again taught to walk, perform activities to ensure everyday independence, and perform voluntary movements. Physical therapy is required. Initially, it is carried out from a lying position, sitting, and includes eye movements, blinking, and bending of fingers.
As recovery progresses, the set of exercises expands.
Massage is prescribed up to two times a year, general, acupressure, and acupuncture are prescribed. They make applications from ozokerite, paraffin, and electrophoresis. It is recommended to carry out exercise therapy, often using special simulators.
For reference. Recovery after a hemorrhagic stroke includes treatment with a psychiatrist for psycho-emotional disorders and depression. Classes are aimed at returning reading, thinking, and counting skills. The goal of speech therapy procedures is to eliminate speech disorders.
When the length changes or the movement of a limb in a joint decreases, the use of special orthopedic shoes is prescribed. The use of preventive measures is indicated.
During the rehabilitation period, medications are prescribed. They are aimed at restoring neural connections (Somazin), lowering blood pressure (Nifedipine), and reducing depressive symptoms. Sedatives are used.
Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke
The best thing you can do if you are near a person who has had a hemorrhagic stroke is to immediately call an ambulance. The minutes count down literally. A person’s life may depend on how quickly treatment is started.
Until the doctors arrive, someone should always be with the patient to monitor his condition.
Goals of emergency therapy: stop bleeding, eliminate compression of the brain. The doctor may prescribe:
- drugs that reduce general blood and intracranial pressure;
- drugs that eliminate vasospasm;
- anticonvulsants.
If the patient has previously taken medications that reduce blood clotting, the doctor will prescribe medications and blood transfusions to reverse their effects.
After bleeding from the affected vessels has stopped, further maintenance therapy is carried out. If the bleeding is large, surgery may be required, during which the doctor removes blood clots and relieves compression on the brain.
If a hemorrhagic stroke is caused by an aneurysm or an arteriovenous malformation (an abnormality in the blood vessels that causes the walls to become thin), surgery may be performed to correct these conditions.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a dangerous condition. However, in many patients it could be prevented. Visit a neurologist, learn about your risks and get recommendations for prevention. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone
With a hemorrhagic stroke of the brain, two groups of symptoms arise that are associated with corresponding disorders:
- Neurological disorders associated with the death of nerve cells in various areas of the brain.
- General symptoms associated with increased intracranial pressure.
Medical care in hospital
All patients receive intensive therapeutic care at an early stage in a neuro intensive care hospital. Initial treatment measures are aimed at:
- normalization of microcirculation, hemorheological disorders;
- relief of cerebral edema, treatment of obstructive hydrocephalus;
- correction of blood pressure, body temperature;
- functional regulation of the cardiovascular system;
- maintaining water and electrolyte balance;
- prevention of possible seizures;
- prevention of extracranial consequences of inflammatory and trophic nature (pneumonia, embolism, pulmonary edema, pyelonephritis, cachexia, DIC syndrome, endocarditis, bedsores, muscle atrophy, etc.);
- providing respiratory support (if the patient needs it);
- elimination of intracranial hypertension in HI with dislocation.
Neurological disorders
Hemorrhage in the brain can lead to the death of nerve cells responsible for various functions. Accordingly, neurological disorders can also be varied:
- Muscle weakness (paresis) and complete loss of movement (paralysis). Disorders can affect half the body or individual muscle groups: legs, arms, face. Paralysis develops, which neurologists call spastic. At first, the tone of the affected muscles decreases, and reflexes disappear. Then the spinal cord partially takes over the functions of the brain. On the contrary, muscle tone increases, and uncharacteristic reflexes appear.
- Decreased or complete loss of sensitivity. The affected parts of the body do not feel touch, vibration, cold or heat.
- Impaired coordination of movements, sense of balance.
- Speech disorders. It becomes slurred, and it is difficult for the patient to repeat phrases spoken by others. He has difficulty understanding what is said to him and cannot read what is written.
- Visual impairment. Double vision and narrowing of the field of vision may occur.
- Memory and thinking disorders.
These symptoms can be expressed to varying degrees, depending on which nerve centers have been damaged and how severely. The chances of recovery vary among patients. Early initiation of treatment and rehabilitation of stroke in a neurological center is of great importance.
Left-hand side
If the left side is affected, the consequences are characterized by disruption of the right side of the body. The patient experiences complete or partial paralysis, and not only the leg and arm are affected, but also half of the tongue and larynx. Such patients develop gait disturbances and a characteristic posture of the right hand (folded in a boat).
The victim experiences deterioration in memory and speech, and the ability to clearly express thoughts is impaired. Damage to the left hemisphere of the brain is characterized by problems with recognizing time sequences; it cannot decompose complex elements into components. Impairments in written and oral speech appear.
The first signs of a hemorrhagic stroke: when should you call a doctor?
Stroke disorders do not always manifest themselves clearly. Sometimes they are quite difficult to recognize. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of a stroke, it is always better to play it safe and call an ambulance. The earlier treatment is started, the better the prognosis.
To identify additional symptoms yourself, you can perform some simple tests. Ask the patient to smile (the mouth on the affected side will remain lowered), show his tongue (when protruding, it will noticeably deviate to the side), raise his hands (the hand on the affected side will not rise as high or will not rise at all), repeat some phrase (this will cause difficulties).
If you notice any suspicious manifestations, call a doctor immediately.
In our clinic, you can visit a neurologist and undergo an examination, learn about your risks of stroke, and receive recommendations for prevention. Make an appointment with a doctor by phone: +7 (495) 230-00-01
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
What are the main causes of hemorrhagic stroke? What factors increase the risk of this condition? How do intracerebral hemorrhages differ from subarachnoid hemorrhages?
With a hemorrhagic stroke, an area of hemorrhage occurs in the brain, which causes swelling, compression of the brain, and increased intracranial pressure. As a result, brain tissue is damaged and nerve cells die.
Is it possible to prevent hemorrhage?
Although hemorrhagic strokes occur less frequently, their risk factors can also be calculated and reduced:
- Learn to monitor your blood pressure daily, record your readings, and take medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid fatty, fried foods, simple carbohydrates, and excess sugars. Eat more vegetables, fruits, nuts, fish.
- Take essential omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E. use the amino acid glycine for severe emotional stress.
- Pay attention to physical activity: walk 30-40 minutes daily, dance, ride a bike. However, if you have high blood pressure, which increases in response to intense physical activity, avoid lifting weights and jumping.
- Quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption. Introduce new healthy habits: meditation, diaphragmatic breathing.
Be sure to consult a doctor to monitor blood counts, blood pressure, and the condition of internal organs.
The main reasons that can lead to hemorrhagic stroke:
- Increased pressure in cerebral vessels.
- Thinning of the vascular walls.
- Blood clotting disorders, taking medications that reduce it.
- Aneurysms are dilated areas of cerebral arteries with a thinned wall. They break more easily.
- Arteriovenous malformations are “incorrect” communications between arteries and veins when they connect without passing through the capillaries.
Hemorrhages can occur in different parts of the brain, depending on this they can be intracerebral or subarachnoid.
How do intracerebral hemorrhages differ from subarachnoid hemorrhages?
The causes of hemorrhagic stroke of the brain can lead to two types of hemorrhages, depending on their location:
Intracerebral. Most common. As a rule, such hemorrhages occur as a result of arterial hypertension and age-related changes in the walls of blood vessels. Arteriovenous malformation may also be the cause. This vascular anomaly is congenital; at present, it is not completely known why it appears.
With intracerebral hemorrhages, blood accumulates in the brain tissue, compressing it. As a result, the death of nerve cells occurs.
Subarachnoid. The human brain is surrounded by three meninges: soft (adjacent directly to the brain), arachnoid (located between the soft and hard), and hard (outermost, adjacent to the bones of the skull). Under the arachnoid membrane is the subarachnoid, or subarachnoid, space. Blood flows into it during subarachnoid hemorrhages.
The main causes of this type of hemorrhagic stroke: aneurysms, impaired blood clotting, and head injuries.
Whatever the cause of a hemorrhagic stroke, treatment should be started immediately. Having noticed the first signs, you need to immediately call an ambulance.
Classification
The variety of features and manifestations of the lesion allows us to create a multifactorial classification:
- According to the location of the hemorrhage. The leakage that occurs in the ventricles is called ventricular, and in the space between the membranes is called subarachnoid. Several areas indicate a combined appearance. In more than 80% of cases, the lesion occurs in the hemispheres. From the point of view of localization, left-sided and right-sided hemorrhage are also distinguished.
- According to the location of hematomas. Lateral indicates damage to the basal ganglia, medial to the thalamus, lobar to one of the lobes. With multiple hematomas they speak of a mixed type.
- By origin. A hypertensive crisis leads to a primary lesion, congenital and acquired vascular anomalies lead to a secondary one.
- According to the affected area. With an extensive hemorrhagic stroke, several areas are detected at once. The development of edema progresses very quickly. Microstrokes are characterized by a small size of the pathological focus and fairly mild symptoms. Ignoring the signs and recommended treatment, however, leads to a repeat attack of hemorrhagic stroke.
What tests help detect the cause of a hemorrhagic stroke?
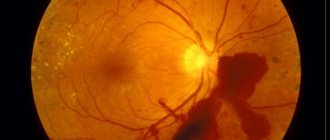
It is important for a doctor to quickly understand the causes of the patient’s condition, because treatment and prognosis depend on this. This helps with examining the patient, conducting laboratory tests and instrumental studies using modern equipment. Computed tomography is especially important - it helps to quickly detect the source of hemorrhage in the brain.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a serious condition, and its severe consequences are often very difficult to deal with. Therefore, timely prevention is important, before a catastrophe occurs in the blood vessels of the brain. People in high-risk groups should visit their doctor regularly and get tested. Start taking care of your health right now, book a consultation with our neurologist by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
If there is a suspicion that a person has had a hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to establish the correct diagnosis and begin treatment as quickly as possible. The sooner the doctor takes the necessary measures, the sooner it will be possible to stop the bleeding, save more nerve cells, and therefore increase the chances that the patient will survive, and reduce the risk of severe complications.
The cause of the stroke may be indicated to the doctor by some characteristic signs during an examination or questioning of the patient’s relatives. The doctor can also judge the severity and location of the disaster in the brain.
For a more accurate diagnosis, special instrumental studies and laboratory tests are required. In addition, similar symptoms may occur with some other diseases.
Epileptic seizure
In some cases, the disease is preceded by an epileptic seizure, which is characterized by suddenness and spontaneity. The man screams, falls to the floor, throws his head back and convulses, wheezing. Foam may come from the mouth, sometimes even with blood (the presence of blood is explained by the fact that the patient may bite his tongue during a fall or convulsions). During convulsions, the patient’s gaze is directed towards the hemorrhage, on the same side the pupil is more dilated, sometimes there is strabismus, the eyeballs seem to float, the gaze “wanders”. On the side of the face opposite to the hemorrhage, a “sail” symptom is observed, when the corner of the mouth is relaxed and slightly lowered than the other, and the cheek does not hold air when exhaling. The upper eyelid is also drooping.
Instrumental diagnostic methods:
- CT scan. Helps to detect the area of hemorrhage and other pathological formations in the cranial cavity. For a more accurate diagnosis, the study can be carried out with the introduction of contrast into the vessels of the brain.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Helps to identify the site of hemorrhage and distinguish ischemic stroke from hemorrhagic. It can also be performed with contrast enhancement.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels. A radiopaque contrast agent is injected into the brain vessels, after which X-rays are taken. The study allows you to detect sites of hemorrhage, aneurysm and other pathologies.
Don't self-diagnose. Don’t expect that any problems that arise will “go away on their own.” Call a doctor immediately or go to the neurological center yourself. It's important to act quickly.
Differential diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke
Diff. Diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke is carried out with the following diseases:
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Hemorrhage into a brain tumor.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Uremia is poisoning of the body with toxic metabolic products that are retained in the blood due to severe impairment of the kidneys.
- Coma caused by a sharp increase or decrease in blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes.
- Epileptic attack.
Sometimes the symptoms are so similar that even an experienced neurologist during an examination cannot immediately establish the correct diagnosis. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods help to understand.
Only in a hospital setting can a comprehensive examination be carried out, the cause of the disease be reliably determined and the correct measures taken. If you are near a person who is experiencing signs of a stroke, your main task is to immediately call an ambulance. At our neurology clinic, you can make an appointment with a specialist by calling.
The material was prepared by Ekaterina Anatolyevna Tafintseva, a general practitioner and head of the hospital at the Medicine 24/7 clinic.
Conclusion
To eliminate or at least reduce the consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke, competent and long-term rehabilitation is necessary. The victim will need special drug therapy, physical therapy, a change in diet, giving up bad habits, and of course a great desire to recover.
The help of relatives is important. Only with comprehensive and thorough treatment can one avoid severe consequences and the development of repeated hemorrhages, and also prolong the life of a stroke survivor to the maximum.