Causes of broken toes
A fracture of the bone of the toes, as a rule, is the result of a strong and sharp blow with a heavy or sharp object, stumbling, twisting, or falling. Less commonly, the cause of injury is the foot being driven over by a vehicle or uneven bending of the toes.
You can get injured while walking, running, or playing sports. Injuries in work environments and on the road are common.
The risk of fracture increases if you have:
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system: flat feet, osteoporosis, tuberculosis or bone cancer;
- history of bruises and toe fractures.
Anatomy of the foot
The human foot consists of 26 bones, divided into three sections:
- Phalanges of fingers - 14 bones;
- Tarsus - 7 bones make up the back part, which connects to the tibia;
- Metatarsal bones - 5 bones make up the middle part, forming an elastic arch.
In addition, many people also have two sesamoid bones.
The tarsal section is the cuboid, sphenoid, navicular, as well as the largest bones of the section - the talus and calcaneus.
The heel is the largest bone, located in the back. Takes on the maximum load, regulates balance and external pressure by distributing weight. The bone is anchored by many ligaments, including the Achilles tendon, and includes six articulations.
The highest bone, the talus, connects the foot and lower leg. It has five cartilaginous joints, but no attached muscles. Thanks to this bone, an angle of rotation of almost 90 degrees is formed, which allows a person to raise and lower the foot.
The navicular bone is located parallel to the talus and forms the instep of the foot. It is tightly connected by tendons to the three sphenoid and cuboid bones, resulting in a low-moving joint.
Some people have a couple of extra bones that cause a person a lot of problems throughout life. For example, the accessory navicular bone (1 in 10 people) is often the cause of shoe rubbing due to the arch of the foot being too high. In other cases, the triangular bone in the posterior process of the talus causes discomfort. It is problematic for such people to stand “on their toes” due to the fact that the extra bone puts a lot of pressure on the heel.
The metatarsal section is a combination of five small tubular bones. The first metatarsus is the thickest and strongest, the second is the longest of the five. The entire department is responsible for the full functioning of the fingers and the location of the arch.
The bodies of the bones are pyramid-shaped, and the anterior ends of the heads are rounded. The articular surfaces located on these heads are connected to the lower phalanges of the fingers, and the joints at the base of the bone are connected to the anterior tarsus. The proximal parts of the bones are connected to the elements of the hindfoot.
A common cause of most valgus changes is a malfunction of the first metatarsus. Salt deposits often form on the head of this bone.
The phalanges of the fingers are 14 bones that provide a person with proper walking. The bone of each finger consists of three phalanges, with the exception of the thumb: it has only two tubular bones. All bone elements are connected to the foot by the articular surfaces of the proximal phalanges. On the little fingers, the second and third phalanx are often fused, which does not in any way affect the overall functionality.
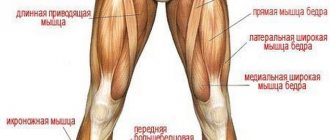
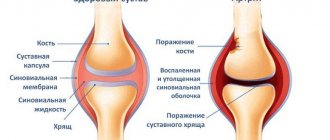
In addition to bones, joints and ligaments, the full structure of the ankle is provided by functioning nerve fibers, blood vessels and muscles.
The muscles of the foot are responsible for the extension of the four small toes, except the big one, and represent the dorsal group. On the sole of the foot there are additionally small muscles that provide full flexion, abduction and adduction of the toes.
Ligamentous apparatus
All joints together provide the necessary mobility of the foot.
- Tarsometatarsal - small joints of a flat, specific shape with limited mobility. They form a solid base of the foot thanks to the many ligaments in the tarsal bone.
- Interphalangeal - secured at the side by ligaments, as a result of which the joint is immobile.
- The subtalar is a rather inactive joint in the hindfoot. Performs the function of the arch of the talus and calcaneus.
- The metatarsophalangeal is a low-moving, spherical, streamlined joint that is responsible for flexion and extension of the fingers.
- The talocalcaneal-navicular is a universal articulation of three bones with a specific axis of rotation. Rotational movements around the axis are performed inward and outward.
- The ankle is the largest joint, connecting three bones together. It is formed in the form of a block by the talus and tibia. The joint itself is attached to cartilage, and ligaments are located along the edges. Any rotational movements of the foot are possible thanks to the mobility of this joint. Takes on the entire main load.
This complex structure of the foot allows it to perform three main functions: supporting, balancing and springing.
The supporting function is due to the ability to withstand and prevent vertical loads. During walking, it turns into a pushing function - the most complex due to the combination of springing and balance. In the case of supporting dysfunction, a person experiences severe pain while jumping or running.
Balancing function - regulates the position of the body during movement. If the foot is anatomically normal, it is capable of spreading out, covering the underlying surface. Thus, a person feels the area where he places his foot.
Spring - smoothes shocks while walking, running or jumping. If the arch (instep) is at a low level, this provokes diseases of both the legs and the spine. In some cases, even internal organs can be regularly injured.
Classification of toe fractures
All causes of toe fractures are classified into two groups: traumatic and pathological. The first type includes chips and cracks of bones resulting from accidents, squeezing a finger with a heavy object, or a sharp blow from sharp objects. The second type of fractures includes injuries resulting from serious diseases of the skeletal system, such as tuberculosis or osteoporosis. Pathological fractures are formed under the influence of traumatic factors of insignificant force.
Depending on the number of chips and fragments formed as a result of the injury, there are two types of fractures: open and closed. The first type is characterized by serious damage to the skin, as a result of which the bone comes out. With a closed fracture, there is no violation of the integrity of the soft tissues.
As a result of injuries, displacement is possible, which is characterized by deviation of the bone from its normal position. In case of displaced fractures, open injuries are often diagnosed that violate the integrity of the soft tissues. All displaced fractures are divided into cracks with:
- longitudinal discrepancies are formed as a result of a violation of the integrity of the muscular and ligamentous apparatus;
- longitudinal overlap, in which bones and their fragments are displaced from a physiologically normal place and overlap each other; formed as a result of pinching of muscles and ligaments at the site of injury;
- angular shift, which are diagnosed more often in children, which is associated with insufficient formation of the periosteum on the child’s leg; as a result, a shift occurs from one side of the bone fragment to the other;
- the introduction of fragments occurs when fragments of bone tissue become wedged into a bone or joints.
Based on the nature of bone tissue destruction, cracks without fragments and with fragments are diagnosed. Comminuted fractures are classified into one-two-multi-comminuted, in which a corresponding number of fragments is formed.
Depending on the location of the injury, it can lead to a fracture of the big toe, index, middle, ring or little finger.
In addition, a crack may appear near the nail, middle or marginal phalanx of the finger.
Damage to the thumb and ring finger is diagnosed most often, which is associated with their greatest mobility during movement.
Diagnostics
The deformity is easy to visualize with a broken phalanx of the thumb. In other cases, minor fractures and cracks cannot be determined independently. The victim needs a professional examination by a traumatologist, during which the specialist will clarify the statute of limitations and the root cause of the injury, and also prescribe an x-ray. In order to identify the location of a crack or split as accurately as possible, the picture is taken in two projections. Based on its results, the type of fracture, its severity are determined and treatment options are prescribed.
How to identify a broken toe - symptoms
Timely detection of a toe fracture allows you to prevent complications and also speed up the recovery process.
All signs of bone cracks are divided into probable and reliable symptoms of injury to the leg.
The first group includes a clinic characterized by:
- The appearance of pain syndrome. Depending on the nature of the damage, the strength of the impact and other factors, the pain can be severe and can only be relieved with the help of painkillers. Less commonly, the victim may lose consciousness. Cracks that involve a break in one part of the bone may not cause pain. Depending on the location of the injury, the pain can be localized in the thumb, index, ring and middle fingers, and little finger. Acute pain syndrome occurs when the periosteum is damaged. Dull pain indicates bleeding and damage to soft tissues.
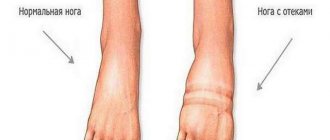
- Redness, swelling, and hematoma occur as a result of damage to soft tissues and blood vessels. An increase in local body temperature is often diagnosed against the background of excessive synthesis of histamine, serotonin and bradykinin. These biologically active substances cause hyperthermia, the development of inflammatory processes and expansion of the lumen of the vascular ducts, as well as the leakage of plasma outside the physiological channel.
- An increase in the size of the injured toe is another sign of a toe fracture as a result of tissue swelling.
The damaged finger becomes limited in movement or completely immobilized.
The second group of symptoms for a broken toe includes the so-called reliable signs:
- Separation of a section of bone tissue that can be felt during examination of the patient.
- Shortening of the finger is determined together with a violation of its mobility; as a rule, such a clinic is possible with a longitudinal fracture or crack with bone fragments intersecting each other. Shortening can be determined visually by comparing the damaged and healthy areas.
Often, when several toes are injured at the same time, the mobility of the entire foot is impaired.
Treatment
Treatment of a fractured toe can occur without applying a plaster cast; minor injuries can also be eliminated with the help of a timely applied tight elastic bandage that promotes immobilization. But in most cases, for a complete and quick recovery, the doctor applies a cast not only to the injured finger, but also to the nearest fingers. In some cases, a cast is applied to the entire forefoot.
Treatment of a broken toe can occur using three techniques, namely:
- Closed one-stage reduction;
- Skeletal traction;
- Open reduction.
Each treatment option is characterized by its own characteristics and results after recovery. In all cases, you need to trust only a professional specialist; independent treatment using such methods will be ineffective and dangerous.
Closed one-stage reduction
Treatment of a fracture of the nail phalanx of the big toe without displacement is carried out by closed simultaneous reduction. This manipulation does not require exposure of bones or skin incisions; it is performed manually using traction devices.
Each location of the fracture requires the use of its own type of reduction. The main feature of this method is the correct stretching of the limb segment along the axis, as well as the implementation of movements that are reversed according to the mechanism of injury.
The bone realignment procedure is painful, so it is performed only under internal or external anesthesia. It is performed the second or third time, since the displaced bones are quite small and not convenient for influencing them. After the reposition is completed, the doctor puts a plaster splint on the patient and a control x-ray is taken.
Skeletal traction
If it is not possible to perform a closed one-stage reduction, preference is given to skeletal traction. To do this, the doctor performs manipulations to pull back and support the distal fragments. They warn about divergence by a fragment.
The skeletal traction procedure requires the mandatory use of local anesthesia, which completely relieves pain and allows the patient to easily tolerate this manipulation. During skeletal traction, a nylon thread is passed through the skin, and its ends are tied together to form a ring. Next, a hook made of a special wire is fixed to the plaster, which holds this ring, providing skeletal traction.
After such manipulation, the patient walks with a cast for another 2-3 weeks until the bone completely heals. Skeletal traction is used in the most difficult situations, and mostly applies to extensive injuries to the extremities. But toe fractures can also sometimes be treated using this method.
Open reduction
In case of a comminuted or open fracture, treatment is carried out by open reduction. With this manipulation, you can quickly restore the integrity of the bone, as well as provide reliable fixation to the fragments using special metal devices.
To carry out internal fixation, screws, knitting needles, wires, and plates are used. Open reduction is a major procedure followed by immobilization for an additional 4-8 weeks.
What to do if a toe is broken - first aid
First aid for a broken toe involves a number of measures aimed at reducing pain, minimizing the risk of complications and the development of possible symptoms.
Do I need to call an ambulance?
What to do if a toe is broken is the main question asked by people who have suffered a phalangeal injury. First of all, you should call emergency help, even if the victim thinks that the damage is not serious. This need is due to the following factors:
- the first aid arsenal of medical personnel has all the necessary means to relieve inflammation and pain, as well as prevent infection;
- the ambulance team consists of people who have a medical education and have sufficient knowledge and skills to provide assistance to the victim to prevent complications;
- The ambulance transport is equipped with the necessary means for the safe transportation of the victim, as well as immobilization of the injured finger or toe, which eliminates the deterioration of the condition and complications.
What is the best position to hold your leg?
If a toe is broken, it is important to immobilize it and also prevent its contact with other fingers and surrounding objects. This will help prevent additional damage and complications.
During limb immobilization, it is important that the patient does not experience discomfort or pain. For this purpose, it is recommended to bend the affected foot, pointing the toes upward, while the main emphasis during movement should be on the heel. To transport the victim to a medical facility, he should be placed on a couch, and the limb should be fixed in an elevated position. This position helps improve blood flow, reduce swelling and pain.
A broken finger should only be secured with a splint if there is a suspicion of displacement or an open fracture. This should be done using a plate, pencils and a tight bandage.
Is it necessary to give painkillers?
Taking painkillers helps prevent the development of severe pain and discomfort after injury. In addition, medications in this group prevent deterioration of the psycho-emotional background.
As a rule, in any first aid kit you can find the necessary medications that have a targeted effect on the source of pain - these are Analgin, Spazmalgon, Paracetamol. Doctors recommend taking drugs from the group of anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs (NSAIDs) for injuries of this kind. These include Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ketanov, Nimesil, Diclofenac. Such remedies help not only relieve pain, but also reduce the risk of developing an inflammatory process and infection.
The choice of medication form depends on the patient’s age. It is not recommended to take the tablets for children under 3 years of age. Such young patients should be given drugs in the form of a powder for the preparation of a suspension or a ready-made suspension or syrup.
When a thumb or any other finger is broken, the victim is advised to take a double dose of painkiller according to age. If a fracture is diagnosed in children under 12 years of age, as well as in patients with gastrointestinal pathologies, it is not recommended to increase the one-time volume of medication, since a deterioration in the general condition, development of intoxication and exacerbation of chronic diseases is possible.
After taking an anesthetic, a decrease in the feeling of pain occurs after 15-20 minutes and lasts up to 2 hours, which is due to the absorption, action of the active substance and the rate of its elimination from the body.
Do I need to apply cold?
Cold helps prevent pain from increasing due to its cooling effect on nerve endings, which reduces the speed of transmission of nerve impulses from the injured limb to the brain. In addition to relieving pain, cold helps to cope with swelling and reduce the likelihood of hematoma formation.
However, it is not recommended to indulge in cold compresses with ice, as there is a high risk of frostbite on your fingers. To obtain the desired effect, it is enough to apply the bandage for 3 minutes every quarter of an hour.
First aid
If a fracture is suspected, the injured toe and foot need to be fixed in one position. If possible, apply ice to the damaged area.
If there is an open wound, the injured limb is bandaged with a sterile bandage to avoid possible infections from entering the bloodstream. Then a splint is applied to the foot and secured with a bandage. This fixation of the foot will help to avoid further trauma to the bones and soft tissues of the damaged area of the toe.
Watch the video where a traumatologist gives recommendations on how to act immediately after an injury in order to alleviate the victim’s condition and avoid complications in the future:
How to treat a fracture?
If a toe is broken, therapy is selected based on the results obtained during x-ray diagnostics about the condition of the soft and bone tissues, as well as the nature of the damage and the presence of complications. Today, three methods of recovery after injury are used in medical practice.
Closed reduction
One-stage closed reduction is the most commonly used method for treating displaced bone fractures, which involves smoothly pulling the bone and giving it a natural physiological position. Before the procedure, the patient is given local painkillers, such as Lidocaine or Procaine.
After repositioning the injured finger, a mobility test is performed on the joints of each phalanx of the finger, which helps determine the correct alignment of the displaced bones. If there is no normal mobility of the joints, the fragments of fragments are re-matched or treated in other ways.
If reduction is successful, a cast is applied to secure the bone in the correct position until a callus forms.
Skeletal traction
This method is used when one-stage closed reduction does not bring the desired result - bone fragments cannot be fixed in their natural physiological position. Skeletal traction involves maintaining fragments of damaged tissue in a taut position, which helps prevent re-displacement.
For this purpose, special medical nylon threads or pins are used, which are pulled through all tissues of the finger, including damaged ones, and are tightly fixed to the plaster using hooks.
The patient is placed in skeletal traction for a period of two to three weeks, during which the puncture site is treated twice daily with disinfectants (alcohol solution of iodine or brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, betadine, chlorhexidine or miramistin).
After 14-21 days, traction devices are removed from the injured toe, after which a plaster cast is reapplied to further heal the broken toe. Bones heal after traction, usually within a month.
Symptoms
A toe fracture is characterized by two types of symptoms - absolute and relative. Absolute signs indicate a fracture most clearly. Relative symptoms only indicate the presence of injury, in which a fracture may or may not be present.
Relative signs of a fracture:
- pain syndrome;
- swelling on the injured limb;
- hematoma;
- impaired finger functionality.
Symptoms are more pronounced if the main digital phalanx is injured. If your thumb is broken, swelling and bleeding tend to be more noticeable.
Absolute signs of a fracture:
- pathological mobility of the injured limb;
- unnatural finger position;
- a crunching sound when squeezing the injured area.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a toe is injured in the lower extremities, you should contact a trauma surgeon for help in the trauma department, who will help determine whether the toe is broken by visually examining the injured limb and questioning.
In addition to the presence of a specific clinic, to diagnose the condition, as well as differentiate between a bruise and a fracture of the toes, instrumental research methods are used, which are carried out in a trauma department. To confirm the diagnosis, as well as determine the nature of the crack, an x-ray is prescribed. If there is insufficient information, as well as to exclude possible complications and the nature of damage to soft tissues and ligaments, magnetic resonance or computed tomography is used.
An important step in the differential diagnosis of fractures and bruises is to conduct a test that allows you to hear a slight crunch of bone tissue.
Based on the data obtained, further prescriptions and recommendations regarding treatment and rehabilitation are given.
Prevention
To prevent a fracture, you need to follow these recommendations:
- Shoes should be comfortable and fit your feet;
- The diet should contain foods containing calcium. It is useful to eat fermented milk products, cabbage, beans, apples, etc. They will ensure normal functioning of the body;
- In addition to proper nutrition, take vitamins C, B12, D;
- Follow safety precautions in areas where there is a high risk of injury. These include sports grounds, hazardous industries;
- Regularly undergo medical examinations. They help detect chronic pathologies that can cause weakening of bones and sudden injuries.
Now you know what to do if you break your toe. If you receive a serious injury, you need to call an ambulance and subsequently follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Thanks to this, it will be possible to prevent dangerous complications and achieve rapid healing.
Is plaster always applied?
Is plaster necessary for such a seemingly minor injury? To heal and restore mobility of hard and soft tissue, complete rest for the finger is necessary. This is achieved with the help of plaster, which allows you to immobilize the limb and create favorable conditions for the growth of callus.
As a rule, immobilization of a finger with a bone fracture is carried out by applying a bandage treated in a plaster solution to the limb, thanks to which, when hardened, the bandage retains its shape. In modern medicine, dressings made of polymer materials are actively used, which:
- allow immobilization of the injured limb;
- retain shape;
- do not get wet, do not heat up or cool down;
- lightweight and easy to use.
The only drawback of this method of tissue immobilization is the high cost, which the medical policy does not cover. In addition, polymer products are not available in many clinics or are used only by pre-order.
Plaster and polymer dressings are not used for minor injuries to hard and soft tissues that can heal on their own. If the fracture has many fragments or does not heal well, the plaster cast is replaced with devices for external fixation.
How long to wear a cast?
For closed fractures without displacement or pinching of tissue, a fixing bandage is applied for 14-21 days, while restoration of the damaged finger’s functionality is possible after 30 days.
To form a callus, a cast is applied to the big toe in case of a comminuted or displaced fracture for up to one month, with functions restored only within 60 days.
In the case of an open injury or open reduction, the bone will take up to 1.5 months to heal, after which it will take another 30-50 days to return to full function.
Main Causes of Injuries
You can damage a joint not only at work or during physical activity, but also at home. The most common causes of fracture include:
- jump from a great height;
- neglect of safety precautions at work;
- sports activities;
- an object falling or a strong impact on a solid obstacle.
Regardless of the origin of the injury, timely diagnosis of the fracture will avoid unpleasant consequences and shorten the recovery period.
Why are the big toes most often injured?
The main difference between the phalanx of the affected toe and the rest is that it has two bones, instead of 3. During movement, the finger is subjected to significant pressure, supporting body weight and protruding slightly forward, making it more likely to be injured.
Swelling and blue discoloration can spread from the main phalanx to the entire leg and adjacent joints, making it difficult to move the foot or step on it. If the thumb is fractured, a cast is applied from the upper 1/3 of the tibia to the phalanx for 5 weeks.
Possible complications
How long it takes for a toe fracture to heal depends not only on the chosen method of treating the fracture, but also on the accompanying complications. The likelihood of the latter occurring is high, since most people, having been injured, do not rush to seek medical help.
Most often, lack of timely treatment leads to:
- the formation of a pathologically large callus or false joint;
- improper fusion of fragments;
- ankylosis (immobility of the joint in a bent position);
- osteomelitis (purulent-necrotic process of bone tissue and bone marrow against the background of infection);
- gangrene (tissue death due to prolonged oxygen starvation, with the addition of bacterial flora) develops rapidly and can cause amputation.
Rehabilitation period
Upon completion of treatment, the recovery stage begins. Its essence is to restore the functions of muscles and joints after prolonged immobility. Properly carried out rehabilitation guarantees a return to your normal lifestyle.
Photo 2. To fully restore the function of the foot, therapeutic exercises are required. Source: Flickr (kenga86)
How long does recovery take?
The average rehabilitation period is one month , if no complications arise. The latter include malunion, osteomyelitis, pseudarthrosis, and infection. Suppuration after surgery, for example, increases the recovery period by 2 weeks. In addition, as you age, bone tissue takes longer to heal than in youth.
Using fasteners
In order to reduce the load on the damaged finger, special orthopedic devices are used - therapeutic orthoses . These structures are made from durable but lightweight materials, securely fix the bone and thus prevent improper fusion.
Medicines and nutrition
Taking certain medications and optimizing your diet are designed to provide the body with substances that speed up recovery. Consuming dairy products, protein, and fruits and vegetables promotes bone mineralization and provides sufficient vitamins. Calcium supplements prescribed by a doctor also speed up rehabilitation.
Exercise therapy and exercises
To reduce muscle atrophy, you must regularly . The complex is selected by a doctor and includes flexion, extension, and grasping small objects with the toes.
Treating a fracture at home
At home, treatment is based on the doctor’s recommendations regarding:
- Bed rest - the victim should rest a lot, raising the injured limb upward.
- Moderate physical activity - any movement while wearing a plaster cast and for some time after its removal should be supported by crutches.
- Taking painkillers for severe pain. The duration of administration depends on the severity of the damage, but does not exceed 3 times per day, no more than 5 days.
- Taking vitamin-mineral complexes rich in calcium and calciferol: Calcium D3 Nycomed, Calcium Complivit, Calcemin. Drugs of this group are also indicated by their administration through electrophoresis.
Types of fractures of the joints of the foot
Depending on the condition and type of injury, it can be:
- Open fracture - the tissues are destroyed by bone fragments, a piece of the phalanx is visible through the damage. Such pathologies are accompanied by slight displacement of bones, tearing of the dermis, blood vessels and muscles.
- Closed – the skin has retained its integrity, the bone is not visible.
- With a slight displacement - injured phalanges can move to the side, pinching nerve endings, blood vessels or muscle tissue.
- No offset.
- Multiple fracture - with bone destruction in several or one place.
- Crack – with the appearance of a crack in the phalanx.
- A comminuted fracture is the appearance of fragments when a whole bone is crushed.
Comminuted fractures are often caused by injury with a blunt small object (hammer or stone).
Rehabilitation
After removing the plaster cast, the patient will need rehabilitation, which is necessary due to stiffness against the background of long-term immobilization of a finger or the entire foot. For this purpose, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage and therapeutic exercises are prescribed. Exercise therapy (physical therapy) is one of the most effective methods of recovery. Aimed at preventing restrictions in joint movement. During the exercises, all fingers are used except the injured one. The number of sessions varies from 10 to 15 procedures, the duration of which gradually increases from 5 to 15 minutes. The most effective activity is to move small elements, grab them and hold them with your fingers.
Muscle relaxation - warm baths with the addition of salt and/or soda help cope with pain after removing the fixing bandage, stimulate joint mobility and reduce the risk of developing inflammatory processes. Baths are prescribed in a course of up to 2 weeks with the duration of one procedure being 10 minutes.
During rehabilitation after a fracture, a special diet should be followed - the diet should be rich in dairy and fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables.