An inguinal hernia is the most common type of all hernias. In men, this location accounts for 90% to 97% of all cases. In women, inguinal hernias are detected relatively rarely, which is primarily due to the anatomical features of the structure of the anterior abdominal wall. Treatment is carried out only by surgery.
- Classification of inguinal hernias
- Reasons for appearance
- How is an inguinal hernia diagnosed?
- Treatment
- Rehabilitation period
What is an inguinal hernia
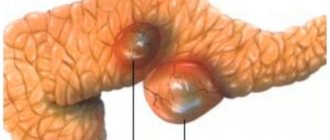
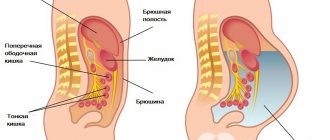
An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of part of the intestine or a fold of peritoneum (omentum) into the inguinal canal (an elongated cavity through which the testicle descends from the peritoneum into the scrotum). The development process occurs as follows:
- First, the so-called hernial orifice is formed. During this period, while running, jumping and other physical activities, a man feels a tingling sensation in the lower abdomen on the left or right side. At first the pain is minor, but gradually it intensifies (as the tissues diverge under the pressure of the intestine).
- The intestine, protected by a thin film of peritoneum (hernial sac), penetrates the resulting hole. Actually, this is already an inguinal hernia. From the outside, it looks like a thickening, a soft tumor in the pubic area closer to the thigh.
- Next, the loop of intestine descends lower into the scrotum, causing it to become asymmetrical. Such a hernia is called inguinoscrotal.
Development of inguinal hernia
The term "obliterated" means "overgrown." The vaginal process is the internal lining of the inguinal canal. Normally, it heals after the testicle descends into the scrotum. Otherwise, a congenital inguinal hernia is formed. Its main difference from the acquired one is the location of the testicle. In the congenital form of the pathology, it is located in the hernial sac.
Congenital and acquired inguinal hernia
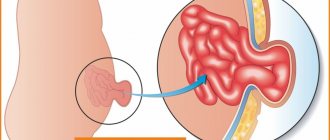
The intestine makes its way into the scrotum through the inguinal canal
Inguinal hernia in the photo
Photo 18+ of the appearance of various types of inguinal hernias:
- This is what an inguinoscrotal hernia looks like - https://prntscr.com/s40gv7.
- Extensive bilateral irreducible inguinoscrotal hernia - https://prntscr.com/s40hqt.
Inguinal hernias should be distinguished from femoral hernias. The latter are found predominantly in women. They represent a protrusion of the intestine into the anatomical opening - the femoral canal. The tumor is located on the thigh away from the scrotum.
Location of hernias
Femoral canal (superficial ring)
What does a hernia look like?
The basic sign that can tell about this disease is the appearance of a certain tubercle in the groin area, which sometimes changes in size. If a man lies in bed, it may even disappear as if nothing had happened. But when the position of the body changes, bloating occurs again. The same can be said when a man goes to the toilet, does exercises, or even just coughs. The dimensions of the tubercle can be insignificant - like a nut. There are bigger ones too. If desired, a photo of a large hernia can be found on the Internet.
Classification
Inguinal hernias vary in origin, location and phases of development. The main types are presented in the table below.
Depending on the place of exit, the hernia can be direct or oblique. Direct is always acquired, characteristic of the elderly, and often develops on both sides. The intestine exits through the medial inguinal fossa. It may remain within the inguinal canal (incomplete hernia) or protrude beyond its boundaries (complete hernia). It never descends into the scrotum. Such a protrusion is extremely rarely infringed. Dimensions do not exceed 10 cm.
An indirect hernia is diagnosed when the intestine comes out in the area of the deep inguinal ring. It can move the spermatic cord (plexus of veins, artery and vas deferens) to the side or penetrate into the thickness of its elements. This protrusion is prone to pinching. The size can reach from 4 to 40 cm.
Direct and oblique inguinal hernia
A very rare type is a supravesical hernia. In this case, the intestine is pressed through an opening called the supravesical fossa. A rare form is also a false hernia - loss of part of the organs under the skin due to rupture of the peritoneum.
Supravesical hernia
When several forms of protrusion are combined, a combined hernia is diagnosed. The combination of oblique and straight is called pantaloon.
When choosing a method of surgical correction, doctors are guided by the classification proposed in 1993 by LM Nyhus, according to which all inguinal hernias are divided into the following types:
- Oblique with a normal size of the inguinal ring. The hernial sac does not touch the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. This type usually occurs in children and young men.
- Oblique with deformation of the inguinal ring. It is displaced or expanded. The intestine does not descend into the scrotum.
- The third type consists of several subgroups: A - direct hernias, B - oblique with an extended inguinal ring, pantaloon and scrotal hernias, C - femoral.
- This group includes all recurrent hernias. Subgroups: A – straight inguinal, B – oblique, C – femoral, D – combined, combined.
Classification according to Nyhus
Sometimes hernias in the groin develop against the background of a postoperative scar. They are called ventral. As a rule, such formations occur after an urgent operation, when doctors make technical errors: they overstretch the peritoneum, use low-quality suture material. The cause may be postoperative complications in the form of hematomas, suppuration or suture dehiscence.
A dangerous form of inguinal hernia is sliding (floating), when an organ acts as one of the walls of the hernial sac. It is easily damaged during surgery.
Types of sliding hernias
Treating a hernia with surgery
Only surgery can completely heal an already developed hernia. Conventional therapy will not remove it. Only a skilled surgeon can do this. The operation, as already mentioned, can be performed in two ways - standard surgery and laparoscopy. Yes, the latter option can be called a more advanced method of getting rid of this uncomfortable pathology, but open surgery is still used most often.
It is done as follows:
- Local anesthesia is injected into the spinal cord;
- To gain access to the organs, the soft tissues of the anterior abdominal wall are opened;
- The hernial sac is carefully isolated from the tissues around it and carefully opened using incisions made parallel to the inguinal ligament;
- The contents of the pouch are delicately tucked into the peritoneum;
- The necks of the hernial sac are stitched and bandaged;
- Excess peritoneum is removed;
- The hernial orifice is eliminated, and the walls of the cavity are strengthened.
Reasons for development
Factors that provoke the appearance of an inguinal hernia:
- Severe chronic cough;
- Weak abdominal tissue (genetic feature);
- Diseases that cause increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, frequent constipation;
- Lifting heavy objects, especially carrying them in front of you;
- Sudden significant weight loss, resulting in the formation of voids pressing on the peritoneum;
- Excess weight.
The most common cause is heavy lifting. Athletes and loaders are in the high-risk zone.
Why does a hernia appear?
As mentioned earlier, in men an inguinal hernia, the symptoms of which can be completely invisible, is either acquired or inherited. In the first case, it grows due to the fact that the muscles of the peritoneum have begun to weaken. Among the signs of an acquired inguinal hernia it is worth highlighting:
- Age-related changes in muscle tissue;
- Relaxation of muscles as a result of systemic diseases;
- Consequences of various operations on the peritoneum;
- Sedentary pace of life;
- A state of constantly elevated intra-abdominal pressure during activities related, for example, to carrying heavy loads. The case may also be associated with constipation, excess weight, or a persistent cough for a long time.
In the second option, such a pathology begins to arise during the growth and development of the baby in the womb.
Symptoms
An inguinal hernia can interfere with walking, periodically ache (pulling pain), increase with strong physical stress and decrease when lying down. Some men are even able to push the bulge back into the inguinal canal (a reducible hernia), but not for long. At the same time, a characteristic intestinal rumbling is heard. This is possible if the hernia has appeared recently - there are no adhesions between the prolapsed intestine, the hernial sac and the surrounding tissue.
A small hernia may not manifest itself in any way, but as it grows larger, it begins to put pressure on surrounding organs. Because of this, nagging pain occurs in the abdomen and lower back. The part of the intestine located in the hernial sac is compressed, which significantly complicates the passage of feces. For this reason, various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract begin: rumbling, constipation, diarrhea. Sometimes part of the bladder gets into the hernial sac, and then urination may be disrupted: pain, burning sensations will appear, and the urge will become more frequent.
Surgeon Izmailov Murad Isaldibirovich on the causes, types, symptoms and treatment of inguinal hernias
If the protrusion is tense, painful, and does not change size in any position or when coughing, then pinching has occurred. This condition requires immediate medical intervention.
Signs of a strangulated hernia:
- The protrusion is painful and elastic.
- Bloating, constipation.
- Vomiting, nausea.
- Cardiopalmus.
If you have pain in the hernia area and constipation, you should not drink laxatives or self-medicate.
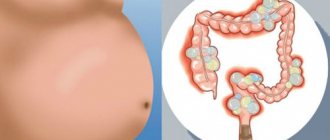
Irrigoscopy
The method for determining the inguinal growth is irrigoscopy. It is used when a sliding hernia with mild symptoms is suspected.
This hernia is difficult to diagnose. Therefore, X-ray examination comes to the rescue.
During irrigoscopy, the colon is examined and X-rays are taken.
Before the study, bowel cleansing is recommended, which will increase the quality of the diagnosis. To do this, a diet without fruits and vegetables is prescribed for several days. Meat becomes the main product. Before the procedure, the next dinner and breakfast are excluded. You are only allowed to drink still water.
During irrigoscopy, a special substance is injected into the colon, followed by an X-ray contrast apparatus. This method provides a way to study the intestines and diagnose its defects and diseases.
For a sliding hernia, it is permissible to use cystoscopy, cystography, and ultrasound of the bladder.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of an inguinal hernia can be easily made by a surgeon by visual examination and palpation with the patient standing and lying down. The doctor evaluates the size of the protrusion, its location, and reducibility. To do this, the man is asked to push and cough. It is important to differentiate a hernia from other neoplasms: lymphocele, hydrocele, hydrocele of the spermatic cord, femoral hernia, enlarged lymph nodes.
The following instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the inguinal canals. Allows you to determine the exact size and structure of the hernial sac. The contour of the hernia will be hyperechoic (outlined dark), and the contents will be hypoechoic (light), since it contains gas and liquid.
- X-ray with contrast. Evaluates the contents of the protrusion, the size of the hernial orifice, and the condition of the inguinal canal.
- Laparoscopy. Used in difficult cases. It is performed under anesthesia. Thin instruments are placed into the abdominal cavity through punctures to examine the hernia from the inside.
Laboratory methods may require a general and biochemical blood test.
Indirect inguinal hernia on ultrasound
Health training
In the case of an inguinal hernia, this exercise focuses on strengthening the abdominal muscles. But there is still a drawback - it can restrain the development of the disease only temporarily. It won't be possible to straighten it out at all. Although doctors advise walking, running or swimming. Training must be carried out in a bandage. There are plenty of photos and videos of such training programs on the Internet.
Here is a list of some exercises that can strengthen the abdominal cavity:
- Bike. You need to lie on your back and bend your knees. Then begin to make movements as if turning bicycle pedals. One cycle should last from half a minute to a minute.
- Scissors. You need to lie on your back and raise your legs thirty centimeters. Then start crossing them like scissors. You need to do three approaches ten times.
- Squeezing the ball. Starting position: lying on your back. You need to bend your legs and keep your feet firmly on the floor. A small ball is placed between the knees. It must be squeezed with your knees and released within one minute.
Treatment
An inguinal hernia can only be cured surgically. There is a lot of information on the Internet about various conservative methods, but at best they are auxiliary. It is impossible to radically solve the problem with their help.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
You can do without surgery only if the hernia is in its early stages and does not cause any discomfort. It's quite possible to live with her. Preventive measures will help prevent development:
- Wearing a bandage.
- Special exercises to strengthen the abdominal wall.
- Prevention of constipation.
It is sometimes possible to straighten a protrusion without surgery, but this method only works in young children. In adult men, it will come out backwards, since the gate has already been created.
There are situations when surgeons are in no hurry to operate even on a large, unstrangulated hernia. For example, in the case of elderly patients, for whom anesthesia can cause more harm than the protrusion itself.
Treatment without surgery at home
If you experience nagging pain, you can take antispasmodics. The safest remedy is No-Spa. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are effective in relieving discomfort, but they cannot be taken long-term due to side effects. In addition, these drugs can dull the pain that is a sign of impingement, which can have serious consequences due to lost time.
In order not to provoke complications, it is important to monitor timely bowel movements. The diet must contain fiber: fruits, raw and stewed vegetables, cereals, herbs. Apples promote regular bowel cleansing. They should be eaten on an empty stomach 20-30 minutes before the main meal. It is better not to overuse cabbage and legumes to avoid flatulence. It is also undesirable to eat a lot of animal protein and baked goods - this can lead to constipation.
Surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences Viktor Nikolaevich Kosovan talks about the treatment of inguinal hernia without surgery using massage and gymnastics
To strengthen the abdominal wall, you can perform special exercises while lying on your back:
- Place a load weighing 1-2 kg on your stomach, breathe through the peritoneum without raising the sternum;
- Raise straight legs to an angle of 30˚;
- Place your hands behind your head, supporting the back of your head with your palms and lifting the shoulder girdle;
- Bend your knees, hold the ball between them and squeeze it.
For any load, you need to wear a support bandage. You don’t need to do it all the time, otherwise your abdominal muscles will weaken. Important note: a bandage is only permissible for reducible hernias and if there are contraindications to surgery. Otherwise, it may compress the protrusion, which will lead to complications.
Bandage
Cold should not be applied to the protrusion, so as not to provoke a spasm. It is also impossible to purposefully warm it up.
Traditional medicine offers local therapy as supportive measures, for example:
- Pour a tablespoon of crushed oak bark into 0.5 liters of water, boil for 15-20 minutes, leave until cool. In the resulting broth, moisten gauze folded in several layers and apply it as a compress to the protrusion. Keep for 2-3 hours.
- Compress with sauerkraut juice.
- Dilute 4 tablespoons of apple cider vinegar (natural) in 0.5 liters of water. Make lotions for half an hour.
- Ointment recipe: take onions, plantain leaves and golden mustache plants in equal proportions. Pass through a meat grinder, add pork fat as a binder.
With a large hernia, treatment with conservative methods is not only useless, but also dangerous.
Surgeries to remove inguinal hernia
There are more than 300 surgical techniques for removing an inguinal hernia. The general gist is this:
- First, the soft tissues are cut, the prolapsed organ is returned to its place (or, according to indications, its strangulated part is excised - a hernia repair is performed).
- Then the weak area of the abdominal wall, where the hernial orifice was, is strengthened using the patient’s own tissue (tension method) or a synthetic mesh (tension-free hernioplasty, or alloplasty).
- The mesh gradually fuses with the surrounding fiber and becomes part of the body.
Operations last on average from 30 to 60 minutes. In complicated cases, the process may take 3-4 hours.
Disadvantages of tension methods:
- Increased risk of suture divergence and improper scarring;
- Long and painful rehabilitation period;
- Relatively high relapse rate.
Currently, tension-free hernioplasty is predominantly used. Advantages: risk of relapse no more than 3%, accelerated rehabilitation period. The only negative is the high cost of the mesh.
Plastic surgery can be performed using open or laparoscopic access. Absolute indications are strangulated protrusion, recurrence or likelihood of rupture of the hernia, inflammation of the area around it, adhesions, and intestinal obstruction.
Strengthening the peritoneum with mesh
Incisions can be made either with a regular scalpel or with a laser. In the latter case, the operation proceeds without blood loss, and the risk of wound infection is significantly reduced. The procedure takes 20-30 minutes and does not require hospitalization. The postoperative scar completely disappears after 3-4 months. Relapses are excluded. Immediately after the operation, you can carry out your normal activities, with the exception of heavy physical activity for 2 weeks.
Laparoscopic surgery
The laparoscopic method of hernia removal (endoscopic hernioplasty) is considered the most gentle. Endotracheal anesthesia and complete muscle relaxation are required. The intervention is performed through small incisions in the abdominal cavity, into which instruments and a video camera are immersed. The cavity is filled with gas for better visualization.
Diagram of the arrangement of instruments for laparoscopic hernia removal
The laparoscopic method is used to treat small hernias. It is technically inconvenient to work with large protrusions using this approach. Some surgeons consider this method to be traumatic: the formation of urinary tract fistulas due to implant pressure sores, damage to large vessels, and the development of intestinal obstruction are possible.
Plastic surgery according to Liechtenstein
Hernioplasty according to Liechtenstein is considered the gold standard for the treatment of hernias. Suitable for all types of protrusions. Surgeons prefer to perform the operation under local anesthesia, but epidural or general anesthesia can be given if the patient wishes. Access is made through a small incision just above the inguinal fold.
Scheme of hernioplasty according to Lichtenstein (the spermatic cord going into the testicle is held at the top)
Mesh flap
Suturing the mesh to the inguinal ligament
Summing the mesh to the internal oblique muscle
End result: an internal inguinal ring is formed from the two ends of the mesh (reconstruction)
Video of hernioplasty (animation)
Operation video
Examples of tension methods
Tension methods are used for small hernias that have arisen for the first time. A classic example is Bassini's plastic surgery. Access is made through an inguinal incision up to 8 cm long. The peritoneum is not dissected. The surgeon cuts the inguinal cord, finds the hernia, pushes it back into the gate, then sutures the rectus abdominis muscle to the inguinal ligament.
Reduction of the hernial sac according to Bassini
The Postempsky technique involves eliminating the inguinal canal. The surrounding tissues are sutured in such a way as to move the spermatic cord and create a new inguinal canal for it.
Folk remedies
An inguinal hernia in women, the symptoms of which are clearly expressed, cannot be completely cured using traditional methods, especially if the hernia has complications.
Medicines made according to folk recipes can:
- relieve inflammation;
- soothe pain;
- slightly slow down the development of the disease.
They are also used during the postoperative period.
For a higher effect, it is necessary to choose products that provide:
- Muscle recovery.
- Improving blood circulation in the perineum and pelvis.
- Restoring good functioning of the entire digestive system.
- Pain relief.
Most often, preference is given to herbal medicine. During treatment, herbs affect the disease itself and other internal organs. Inguinal hernia in women is treated using herbal teas that effectively affect the symptoms of the disease.
| Anti-inflammatory. |
|
| To improve digestion. |
|
| Astringents. |
|
| Painkillers. |
|
| From dropsy, as well as edema. |
|
| Herbs that eliminate congestion. |
|
During illness, constipation may occur.
You should take infusions of plants:
- glacium;
- castor bean;
- alyssum;
- Colchicum autumn columbine;
- European euonymus.
Ointments made from animal fat are widely used in treatment. The course of treatment with them is 1 month. The ointment is applied in the morning and evening. Camphor oil helps relieve inflammation and soothe pain. It is applied with light movements to the site of the hernia. This procedure is carried out once a day. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Apple cider vinegar is often used instead of camphor oil. Before use, it must be diluted in water. The ratio of ingredients should be 1:10. Rub this product once a day. Compresses are also used to improve overall well-being. Gooseberry herb helps with inflammation.
- Prepare the medicine in a double boiler for 10 minutes.
- Then the product is crushed and applied to the area where the hernia is located.
- The compress is fixed with a bandage and adhesive tape for more comfortable wearing.
- The procedure takes 40 minutes. 1 time per day, 2 weeks.
Shepherd's purse herb is used to relieve pain. For one procedure, 2 leaves of the plant are needed.
- The herb is steamed for 10 minutes.
- The sheets are wrapped in a bandage and carefully applied to the sore spot.
- It is necessary for the compress to remain on the hernia for 2 hours.
The duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
Rehabilitation after removal of an inguinal hernia
Features of rehabilitation depend on the method of performing the operation. The man spends 1 to 3 days in the hospital.
After classical hernioplasty (according to Liechtenstein):
- The drainage is removed on day 2.
- You can eat and move immediately after surgery.
- An enema is sometimes required to activate the intestines.
- Sick leave is issued for 1-2 weeks.
- The stitches will be removed in 7-10 days. Before this, they are processed daily and kept dry.
Full recovery will take from 2 months to six months. In the first weeks, it is very important to follow a diet, eliminating foods that cause constipation, diarrhea and gas formation. You cannot play sports or lift more than 5 kg for 2-3 months. Jumping, running, turning, bending are excluded. Sex is allowed after 2 weeks. To restore the abdominal muscles, the doctor will prescribe exercise therapy, which includes breathing exercises.
Surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences Viktor Nikolaevich Kosovan talks about the recovery period after surgery to remove an inguinal hernia in men.
Diet after hernia repair
A proper diet will speed up recovery. For the first few days, it is better to eat only liquid and pureed food in small portions. On day 4-5 you can go back to your normal diet.
You need to eat as many foods rich in protein and fiber as possible. The diet should include:
- lean boiled meat (chicken, beef);
- seasonal vegetables (raw or steamed);
- dairy products, especially cottage cheese;
- fruits and berries;
- various porridges (buckwheat, millet, oatmeal, pearl barley);
- Fish and seafood;
- nuts and dried fruits.
It is better to exclude alcohol and coffee from your diet, as well as smoking.
Complications after surgery
The likelihood of developing a complication depends on the type of hernia, surgical technique, and the presence of concomitant diseases. If the patient follows the rules of rehabilitation, then they practically do not occur.
Main complications:
- Postoperative wound inflammation;
- Mechanical damage to the nerves, vessels and organs surrounding the protrusion (if blood vessels are damaged, testicular atrophy is possible);
- Excessive tension, at which the threads begin to tear the fabric;
- Mesh displacement or rejection (very rare);
- Hydrocele of the testicle;
- Damage to the spermatic cord (fraught with infertility);
- Neuralgic pain;
- Hematomas and seromas;
- Adhesive disease.
In all cases, except inflammation, surgical intervention will be required.
Urgent Care
When determining a strangulated inguinal hernia, emergency care is as follows:
- if severe abdominal pain occurs, the patient is purposefully examined for the presence of a hernial protrusion;
- the patient is urgently hospitalized in a surgical hospital if there is a suspicion of infringement or if a pathology has arisen. Delivery to the hospital should be carried out in a supine position on a stretcher;
- you should not try to forcefully reduce a strangulated hernia;
- the patient should not take baths, painkillers, or apply cold or heat.
Recurrence of inguinal hernia
Relapse is possible after any hernioplasty method. The patient may have a genetically weak peritoneum, the slightest pressure on which provokes organ prolapse. For some, the corners of the mesh are coming off and the seams are coming apart.
With tension-free hernioplasty, the likelihood of relapse is low. According to general statistics, after removal of an uncomplicated hernia, relapses occur in 10% of cases. After removal of giant, pinched or sliding protrusions, the likelihood of the pathology returning increases to 30%. After laparoscopic hernioplasty, the risk of relapse is less than 1%.
The first signs of re-formation of a hernia are tingling, nagging pain in the operated area. A protrusion forms in the same place and becomes noticeable.
Light (diet) food
The basic goal of this diet is to prevent bloating or constipation.
As well as weight loss and replenishment of vitamins and minerals in the body. To deal with a hernia, you need to eat often, but in small portions. Up to approximately five times a day. It will be better to plan your diet in advance so as not to skip meals. What you can eat and drink:
- Jelly;
- Porridge;
- Vegetables and fruits without heat treatment;
- Omelette;
- Lean meat and fish;
- Rosehip decoction.
- Various broths;
- Juices.
What you should absolutely not eat or drink:
- Fried, fatty, spicy and salty foods;
- Floury and sweet;
- Vegetables and legumes - they can cause constipation (cabbage, peas and others);
- Alcohol;
- Strong coffee and tea.
Why is an inguinal hernia dangerous?
An inguinal hernia can prolapse at any time when a strangulation or injury occurs. This condition is fraught with complications in the form of necrosis (death) of intestinal loops or peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity). Acute appendicitis may occur due to malnutrition of the appendix due to compression of the vessels in the inguinal ring. In some cases, when the tissue becomes thinner, the hernia bursts, the tissue ruptures, and the contents spill out. In such cases, peritonitis also develops. The condition is fatal.
An inguinoscrotal hernia can have a negative effect on sperm because it increases the temperature in the scrotum and impairs blood circulation in the testicle. As for potency, in most cases it does not suffer. The erection remains intact, as does libido. Problems can only begin with a very large protrusion.
Do you need a bandage?
A bandage is a medical device for holding a muscle corset. This product is used during the recovery period after surgery. The bandage holds the muscles in the groin area under slight tension. This prevents the hernial sac from protruding. When the bag is large, the bandage prevents its further growth.
The device has several varieties: waist and in the form of swimming trunks. There are single-sided and double-sided bandages. The first type ensures that the bag is fixed on only one side. Double-sided bandages are suitable for women who lead an active lifestyle.
For a large hernia, it is necessary to use a bandage in the form of swimming trunks. Belt bands are necessary for girls to prevent the appearance of a hernia. The belt is comfortable to use. It is attached with adhesive tape, which allows you to adjust the pressure.
For pregnant girls, a corset in the form of a ribbon is best suited. This device can be adjusted.
The attending physician determines which bandage should be used. It is necessary to give preference to devices made from natural fabrics. The size of the bandage should correspond to the circumference of the hips. The small size greatly compresses the tissues and leads to poor circulation. A large bandage simply will not perform its functions.
FAQ
- Do they take you into the army with an inguinal hernia? – The commission will pay attention to its size, location, and the likelihood of infringement. Category D (unfit) is assigned for large recurrent protrusions that have a negative impact on other organs. Category B (limited fitness, can be called up for training or military action) is assigned for moderate recurrent hernias, which manifest themselves during physical stress. In other cases, they will be drafted into the army. They may provide a deferment for the duration of surgical treatment.
- Is it possible to go to the bathhouse? - Can.
- Is it possible to ride a bicycle? – Moderately possible, if the hernia is not scrotal, otherwise it can be strangulated.
- Is it possible to have sex with an inguinal hernia? - Can.
- Is it possible to pump up the abs and play sports? – Abdominal stress provokes an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which will aggravate the pathology.
Doctors' opinion on physical activity and baths:
Prevention
The disease can be prevented by avoiding excessive physical activity and lifting heavy weights. It is important to take care of the stable functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, because constipation provokes hernias. You need to lose excess weight and do physical therapy. You should strengthen your abdominal wall by performing abdominal exercises and “bicycle” exercises. Therapeutic gymnastics should be given at least 20-30 minutes a day.
It should be noted the importance of maintaining a competent diet. You need to eat often, but little by little, and no alcohol. Instead of fatty and spicy foods, flour and confectionery products, you need to eat vegetables, fish and meat, boiled or steamed.
Reviews from men about treatment
On forums, mostly hernioplasty with mesh is praised. Performance is restored quickly, relapses are rare. Reviews below.
Doctor's opinion about the rehabilitation period:
What happens during infringement
After pinching, a closed area with pinched organs appears. Blood circulation in organ tissues is disrupted. If the intestine is pinched, venous stasis and, as a result, swelling will most likely develop. In parallel with these processes, hemorrhage begins in nearby tissues, feces decompose, releasing toxic substances that poison the body. Hernial fluid appears in the cavity, which changes color and becomes dark red.
Surgical intervention
Before surgery, the patient should empty the bladder and bowels as thoroughly as possible. Depending on the severity, the type of anesthesia is selected, but local anesthesia is most often used.
The operation in this case is more complicated than conventional surgery. In addition to removing the hernia, the surgeon also needs to free the pinched organs. The main thing is that their contents do not enter the body.
In cases where the organs are too damaged, resection and plastic surgery of the hernial orifice are performed.
A favorable outcome is possible with timely surgery. The longer a patient delays going to the hospital, the greater the risk that everything will end very badly, even death.
After the operation, all therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating provoking factors.
You will need to strengthen your abdominal muscles and properly distribute physical activity. It will be necessary to cure all diseases that may be accompanied by a lingering cough or constant constipation. You will have to give up bad habits and, if present, cure obesity.