Arthritis is a medical term used to describe an inflammatory, metabolic or degenerative pathology that affects one or more joints. The causes of acute or chronic disease include trauma, respiratory, gastrointestinal, urogenital infections, endocrine and immune disorders, and osteomyelitis. Arthritis of any etiology is clinically manifested by pain, swelling of the joint, and limited mobility. With purulent pathologies, symptoms of general intoxication of the body occur.
To diagnose inflammatory pathology, instrumental studies are carried out - ultrasound, thermography, radiography, CT, MRI, arthroscopy. Biochemical and serological tests can determine the cause of arthritis, determine the type of infectious agents and their resistance to medications. Treatment is conservative - a course of medications, exercise therapy, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, and, if necessary, immobilization of the joint. Severe lesions of the articular structures become indications for surgical intervention.
Types of arthritis
Practicing rheumatologists and orthopedists use several classifications of inflammatory joint diseases in their work. However, the most extensive classification is one that partially provides for the causes of this disease. According to which, arthritis is divided into main and secondary (complications of other diseases).
The term “arthritis,” introduced by Hippocrates, was used in subsequent centuries to refer to any joint pathology. Starting from the end of the 15th century, scientific medical luminaries began to gradually identify separate forms of the disease.
Thus, Bayu identified rheumatism among arthritis. At the beginning of the 17th century, Sydenham described gout and rheumatoid arthritis as independent forms. Several decades later, infectious specific arthritis was united by Bouchard under the general name “infectious pseudorheumatism.” In the 19th century, Muller made the first attempt to classify joint pathology. He clearly distinguished inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) from dystrophic diseases (arthrosis). This division remains important to this day.
Forecast
Rapidly progressing rheumatoid arthritis can shorten a patient's life expectancy from three to twelve years. The disease itself is not so much dangerous as its complications.
Women with this disease are more susceptible to obesity and the development of pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
The general prognosis for such arthritis depends on the degree of neglect of the pathology and the therapeutic measures taken. The sooner therapy is started, the higher the chance of stabilizing the condition.
Primary forms
- Osteoarthritis – the cartilage tissue of the joints is affected, resulting in complete deformation.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a connective tissue disease affecting small joints.
- Septic arthritis (infectious) – a fungal or bacterial infection affects large joints, such as the knee or hip. Then all joints are involved in the inflammatory process.
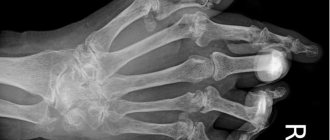
- Gout is a metabolic disease characterized by growths of uric acid salts. A lump near the thumb is a manifestation of this type of arthritis.
- Still's disease is a form of rheumatoid arthritis that is very difficult to diagnose. The vast majority of cases occur in children under 16 years of age.
- Spondylitis is an infection in the vertebrae, mainly caused by bacteria. There are several forms of the disease - spinal osteomyelitis and tuberculous spondylitis.
Disturbances in body systems
Due to the fact that this form of arthritis is an autoimmune disease, it negatively affects the functioning of all body systems. A person's kidneys and liver may be affected, leading to the development of hepatitis.
In the digestive system, disruptions occur during treatment with NSAIDs. Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and the formation of erosions on the gastric mucosa are possible.
Abnormalities in the nervous system may occur in the form of decreased sensitivity and paresthesia.
Additional disorders as the disease progresses:
- redness of the eyes;
- brittle nails;
- amyotrophy;
- flatulence and colitis.
Because there are so many possible symptoms, rheumatoid arthritis can be difficult to diagnose. To do this, the patient needs to undergo a full list of diagnostic procedures.
Arthritis, which is a complication of other diseases
Arthritis of the joints, which develops secondary to other diseases, requires a separate diagnosis, because in this case it is their symptoms that come to the fore.
For example, systemic lupus erythematosus, in addition to damage to small joints, is characterized by fever and the “butterfly” symptom: redness of the facial skin in the cheeks and nose, shaped like the wings of a butterfly.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is a disease of connective tissue and its derivatives.
- Purpura is small-spotted capillary hemorrhages in the skin, under the skin or in the mucous membranes.
- Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic, progressive joint disease that occurs during psoriasis.
- Reactive arthritis is an inflammatory disease affecting the joints that develops after suffering certain infections (genitourinary, intestinal, nasopharyngeal).
- Hemochromatosis is a hereditary, genetically determined disease, manifested by a violation of iron metabolism with its accumulation in tissues and organs.
- Hepatitis is an inflammatory disease of the liver, usually of viral origin, often spreading to the joints.
- Granulomatosis is an inflammation characterized by the formation of granulomas (nodules) resulting from the transformation of cells capable of phagocytosis.
- Borreliosis is the most common tick-borne disease in the Northern Hemisphere. The bacteria are transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Ixodid ticks. The musculoskeletal system is primarily affected.
Accurate classification greatly facilitates correct diagnosis and further therapy.
Symptoms of joint arthrosis
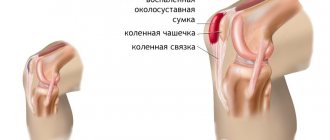
The development of arthrosis of the joints is based on a violation of the nutrition of the articular (epiphyseal) ends of the bones. As a result of changes in the patency or damage to the vessels through which nutrition is provided to the bone, aseptic necrosis occurs, which aggravates lesions in the joint.
Arthrosis is progressive. First of all, painful changes affect the internal (so-called synovial) membrane of the joint capsule, then they capture the cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of the articulating bones. As a result, there is a gradual destruction of the cartilage, which entails exposure of the bone. In some places the bone tissue is thinned out, in others it becomes denser, and bone spike-like outgrowths form. In most cases, the development of arthrosis occurs in the hip, knee and first metatarsophalangeal joints.
Do your knee joints hurt? We recommend that you seek their treatment at Dr. Bubnovsky’s centers in St. Petersburg: https://www.bubnovsky-spb.com/uslugi/lechenie-sustavov/kolennye/
Symptoms of joint arthrosis include pain. They are characterized by periodic occurrence, exacerbation after sudden physical exertion or after being at rest for a long time. Due to the presence of painful sensations, mobility in the joint is limited. Arthrosis accompanies inflammation of the tissues that surround the joint and nerve trunks. The functional purpose of the joint also suffers due to protective muscle tension.
Causes of the disease
Arthritis is a complex and diverse disease. Its development is due to many reasons. In medical classification, it is customary to distinguish several main groups:
- Infectious provocateurs – the presence of viral and bacterial diseases.
- Traumatic causes - the damaged joint was not fully restored, which subsequently caused an inflammatory process.
- Immunological factors - poor diet, lack of vitamins, bad habits, including abuse of caffeine-containing drinks, increase the risk of the disease.
- Genetic predisposition. The disease can be inherited. If you have close relatives who suffer from joint inflammation, your chances of getting sick increase.
A very wide range of people are at risk. In addition to the obvious reasons, there are circumstances that give a powerful impetus to the disease:
- Female. Statistics show that women are much more likely than men to seek help from rheumatologists. There is a completely logical explanation for this. The natural but difficult process of pregnancy and childbirth deprives the body of many beneficial vitamins and minerals. Carrying a child means an increased load on the entire musculoskeletal system and possible complications in the form of arthritic diseases.
- Chronic diseases.
- Fractures, sprains, dislocations and other injuries.
- Surgical operations under general anesthesia.
- Any types of allergies.
- Complications from vaccination.
- Other joint diseases. For example, arthrosis, bursitis, and Bequeira's cyst almost always cause complications.
- Advanced age. Over time, joints tend to wear out if a set of measures is not implemented.
To summarize, it can be argued that anyone, including small children, may be at risk.
Symptoms
The main indicator of the disease is pain in one or more joints. Many people don't take this seriously. Brief discomfort does not cause any particular inconvenience. Unpleasant symptoms are quickly relieved by massage or taking simple painkillers.
Over time, symptoms become more difficult to ignore. The pain intensifies and becomes wave-like. The disease worsens when moving and at night.
During this period, obvious symptoms appear:
- Morning stiffness;
- Swelling accompanied by redness of the skin;
- Increased temperature in the area of inflammation;
- Restricted mobility due to severe pain;
- Joint deformation noticeable to the naked eye.
Symptoms may vary depending on the species. Using the most common diseases as an example, you can create a general picture of the symptoms:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by symmetrical damage to the joints; noticeable nodules appear in the flexure areas. An exacerbation of the disease is observed in the early morning, by the afternoon the symptoms practically disappear. If the disease is in an acute stage, the patient has a high fever, the limbs go numb, severe pain appears when inhaling, the lymph nodes are enlarged, blinking is accompanied by sharp pain.
- Reactive arthritis – against the background of general symptoms, inflammation of the urinary tract, the appearance of cystitis, and urethritis are observed. Increased tearing, pain in the eyes, complications such as conjunctivitis.
- Infectious – chills, fever, severe headaches, general weakness, swelling of tissues in the affected joints. The type of infection that caused the disease is determined using tests.
- Gouty – the joints of the hands and feet become very swollen. The first joints of the big toes are most often affected. But, gouty arthritis can appear in the elbows, knees, and fingers. The areas of inflammation turn red. The pain syndrome is cramping - from very strong, tugging, to weak, spreading.
- Psoriatic – small joints of the toes and hands increase in size, causing general swelling of the extremities. It is not symmetrical in nature, unlike rheumatoid. The skin of the affected fingers acquires a purplish-bluish tint, as if after a blow. Complete or partial lack of mobility. The pain is very strong. It is impossible to do without taking strong anesthetics.
- Osteoarthritis – symptoms appear slowly, gradually, as the disease progresses. The first alarming sign is the crunching of the limbs and spine. Depending on the form of the flow, it may be in a stage of regression for many years. Extremely dangerous due to its small symptoms and large scale of damage.
- The traumatic - inflammatory process makes itself felt by the appearance of crunching in damaged joints, as with osteoarthritis. Pain and swelling may not appear soon. Therefore, you should not ignore the primary signs.
Stiffness
It is also one of the most characteristic symptoms that distinguishes arthritis from other joint pathologies.
Stiffness manifests itself in the morning - after sleep. Most often, the disease first affects the joints of the hands and fingers.
Already at the initial stage, the so-called symptom of “tight gloves” appears - severe stiffness in the hands, a feeling that they are wearing something that prevents them from moving them. As other joints are affected, a similar feeling appears in them.
When the pathological process affects the intervertebral discs, “corset syndrome” appears - a feeling of constriction and stiffness in the back.
Characteristics of symptoms at different stages:
| Stage | Symptom severity |
| 1 | There is either no morning stiffness or it lasts no longer than 30 minutes |
| 2 | The duration of the symptom is from 30 minutes to 3 hours after waking up |
| 3 | A person feels stiff for more than 3 hours after sleep |
Diagnostics
The wide range of causes and symptoms make diagnosing joint arthritis challenging. Only an experienced and highly qualified doctor will be able to collect all the components of the disease into a single picture. While common types can be diagnosed fairly quickly, rare types caused by other chronic pathologies are not easy to detect. For example, rheumatoid arthritis of the joints still remains a mystery to rheumatologists - the reasons for its appearance are not sufficiently substantiated.
To prescribe an effective course of therapy, a final diagnosis is made along with an indication of the underlying causes.
To achieve this, a wide range of medical measures are carried out:
- A complete medical history is collected;
- Laboratory tests are carried out (general blood biochemistry, determination of sugar levels, PCR testing, urine analysis, etc.).
- Infectious, allergic, traumatic, bacterial and other connections are excluded until a provocative one is determined;
- Research using diagnostic equipment - radiography, ultrasound, MRI;
- Biopsy of the synovial fluid filling the joint cavity.
- Arthroscopy. A more modern way to examine joints and collect synovial fluid. The method provides accurate data and, as a rule, does not require repeated procedures.
- A complete clinical picture of the disease is compiled.
All sequential diagnostic steps are extremely important for determining joint disease. Complex hardware research does not exclude, but complements each other.
As noted above, making a correct diagnosis is a difficult task. Therefore, any diagnostic methods cannot be ignored or replaced. Therapy and further prognosis of the disease completely depend on this.
Arthritis treatment
Treatment of arthritis occurs in several stages. At each of them, therapy is set with its own goals and objectives, which are implemented using certain techniques. If at the initial stages conservative, standard schemes are used, then at subsequent stages surgical intervention is already indicated, up to the removal of the affected joints.
The goals of any therapy are the same:
- Relieve pain syndrome;
- Stop the progression of the disease;
- Restore the functionality of the joint;
- Eliminate possible complications.
To achieve results apply:
- Drug therapy. First of all, it is aimed at relieving excruciating pain and resuming a normal lifestyle - sleep, work, movement, performing daily activities. Anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed (for example, Diclofenac, Baralgin, Ketorol), which cannot cure the disease, but will eliminate the pain syndrome. Chondroprotectors that are capable of restoring cartilage tissue. Antibiotics of different spectrum of action, to relieve severe inflammation and abscess.
- Physiotherapeutic activities. They include ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis with painkillers, phonophoresis, massage, mud therapy, warming, wraps, hydromassage, therapeutic baths. After a week's course, the patient's condition improves significantly. In combination with drug treatment, any type of arthritis becomes practically asymptomatic. The patient’s quality of life improves, and he will be able to begin his daily duties.
- Therapeutic exercise and balanced nutrition. Treating arthritis requires a complete overhaul of your diet. A large amount of fresh vegetables and fruits must be introduced into the diet, fatty meat is replaced with fish and seafood, fried, salty, spicy foods and all kinds of seasonings are completely excluded. All food is only boiled and stewed without adding oil. Dietary nutrition will ensure the supply of necessary minerals and vitamins to the body and, in particular, to the affected joints.
Physical activity is also subject to adjustment. A state of rest and constant bed rest will only aggravate the patient’s condition. Depending on the severity of the disease, exercise therapy is prescribed individually by the attending physician. The complex should be performed regularly, without skipping, taking into account all medical recommendations.
As an example, here are a number of exercises for ankle arthritis:
- smooth rolling from toe to heel;
- walking on the inside of the foot;
- jumping on your toes;
- walking on heels;
- into a sitting position, pulling your toes towards you.
For severe cases, many exercises can be performed in water, where the load is reduced and exercise therapy is more comfortable. The use of an exercise bike is also shown.
Therapeutic massage reduces joint tension and swelling. Definitely included in the general process of treating arthritis. A visit to a sanatorium-resort establishment will help achieve maximum results.
In any case, all therapeutic measures, physical therapy exercises and medications are prescribed only by the attending physician, based on the diagnosis.
Traditional methods of treating arthritis
All methods are good in the fight against disease. Traditional medicine offers many recipes that have been tested on no one person. The most popular of them:
Pine baths. Pour boiling water over the spruce branches, leave for 10 minutes, and lower the legs into a container with pine needles for 30 minutes. After the procedure, immediately go to bed. Can be repeated daily until relief occurs.
Heat flax seeds in the oven or in a dry frying pan, place in a fabric bag and apply to the sore joint.
Fresh cabbage is famous for its anti-inflammatory effects. Apply warm sheets to arthritic areas, previously smeared with any kind of honey. Wrap the compress with cling film and a warm scarf. It is advisable to do this at night.
Mix a raw chicken egg thoroughly with two tablespoons of table salt, apply the mixture to a clean cotton cloth and wrap the sore spot. As it dries, apply a new portion of the mixture.
Mix kefir with crushed chalk to form thick sour cream. Apply the compress overnight. Relief will not be long in coming.
Despite the effectiveness of traditional methods, it should be remembered that self-treatment can end very badly. Without traditional methods, the positive results will be temporary and the arthritis will return very quickly.
The combination of several methods, folk and traditional medicine gives a stable, long-lasting effect and reduces the risk of relapse.
Prevention
The prognosis for all types of arthritis is usually favorable. In most cases, the disease is completely curable within 6-9 months. During this period, it is important not to give up on a full life, but to adapt to it as much as possible. Following simple recommendations and rules will improve the general condition of the patient:
- Reduce stress on joints;
- Perform stretching exercises;
- Strict compliance with all recommendations of the attending physician;
- Full sleep;
- Eating a balanced diet.
Health depends entirely on self-control and compliance with the rules. It's a small price to pay for a complete cure for arthritis. It is only important to adhere to preventive measures to prevent relapse.
- Healthy and proper nutrition should become a good habit for life. This will not only help prevent the return of arthritis, but will also have a beneficial effect on the general condition of the body.
- Completely eliminate alcohol and smoking. Bad habits have never contributed to good health.
- Avoid infectious diseases. To do this, take immunomodulatory drugs and carefully treat even a runny nose.
- To live an active lifestyle. Long walks and vigorous exercise should become a daily responsibility.
- Avoid strenuous physical activity to minimize the risk of injury.
- Before going to bed, do a preventive massage.
Only by completely reviewing your lifestyle can you avoid a relapse and prevent arthritis from developing with renewed vigor. If the disease returns, ignoring even seemingly insignificant symptoms at first glance is a direct path to the surgical table and possible disability.
Epidemiology
Arthritis is a widespread disease in the human population. In the United States alone, more than 42 million people suffer from arthritis, and one in six are disabled as a result of the disease. It should be noted that among the causes of disability in this country, arthritis ranks first. Arthritis has “about the same effect on the U.S. economy as a moderate economic downturn,” with the disease costing Americans more than $64 billion annually, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports. These losses are associated with treatment costs and decreased productivity. In developing countries such as Brazil, India, Indonesia, China, Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, the Philippines and Chile, according to studies cited by the World Health Organization, arthritis and similar diseases cause “no less harm there than in rich countries.” countries."
Over time, the number of people suffering from arthritis is gradually increasing. In Canada, it is believed that the number of patients will increase by 1 million over the next ten years. [ source not specified 3183 days
] Although arthritis is not as widespread in Africa and Asia as in Europe, the number of people suffering from this disease is growing rapidly in these parts of the world. Due to the prevalence of arthritis, the World Health Organization declared the period from 2000 to 2010 the “Decade to Fight Bone and Joint Diseases.” During this time, doctors and healthcare workers are focusing their efforts on making life easier for those suffering from musculoskeletal diseases, including arthritis.