What you need to know about your cough
Coughing is a normal reflex action that clears your throat of mucus or foreign irritants. Everyone coughs from time to time to clear their throat, but a number of conditions can cause coughing to occur more frequently.
A cough that lasts less than three weeks is called an acute cough. Most coughing episodes go away or at least improve significantly within two weeks.
If your cough lasts between three and eight weeks and gets better at the end of that period, it is considered a subacute cough. A persistent cough that lasts more than eight weeks is a chronic cough.
You should see your doctor if you are coughing up blood or have a barking cough. You should also contact him if your cough does not improve within a few weeks, as this could indicate something more serious.
Diagnostics
Given the wide range of diseases that can be a symptom of persistent coughing, it is important to conduct a full examination to understand the true cause of the problem. To do this, they first use subjective and objective examinations, studying the patient’s lifestyle and habits, as well as comparing other symptoms. Be sure to look at the intensity, frequency of coughing and even the sound that is heard. A barking cough often indicates a viral infection. If there are no other alarming signs (for example, no blood is produced with sputum), then the patient is diagnosed with a cold.
If there is a suspicion of a more serious illness, an x-ray and blood test, as well as sputum examination, are prescribed.
The cough can become chronic. In such cases, the patient is first referred to an ENT doctor, and a visual examination of the chest is also performed. If necessary, a sputum examination is prescribed (especially if the cough is wet and does not go away for a long time).
If cancer is suspected, bronchoscopy is performed. It is also necessary to rule out allergies and problems with stomach acidity. For this purpose, appropriate studies are also prescribed. Sometimes your doctor may recommend a trial course of treatment to see how your body reacts. Making a diagnosis is often difficult or time consuming. But it is better to start dealing with the problem quickly, and therefore, before receiving the test results, the patient may be recommended to take medications or certain procedures.
Bronchoscopy
During the diagnostic process, the patient’s bad habits must be taken into account. First of all, studies are carried out to exclude diagnoses caused by a person’s lifestyle.
Doctors always take into account the state of sputum. A productive cough produces mucus (especially during the daytime). It cannot be stopped, because the release of sputum indicates the healing process. It accumulates during sleep and a cough may occur in the morning. If sputum is not produced, the cough is called unproductive, and additional studies are carried out.
What causes a cough?
Cough can be caused by several conditions, both temporary and permanent.
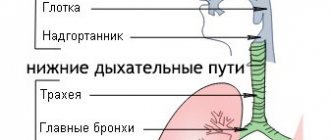
Clearing the throat
Coughing is a standard way to clear your throat. When your airways become clogged with mucus or foreign particles such as smoke or dust, coughing is a reflex response in an attempt to clear the particles and make breathing easier.
This type of cough is usually relatively rare, but the cough gets worse when exposed to irritants such as smoke.
Viruses and bacteria
The most common cause of cough is a respiratory tract infection such as a cold or flu.
Respiratory tract infections are usually caused by a virus and can last from a few days to a week. Infections caused by the flu may linger a little longer and may sometimes require antibiotics.
Smoking
Smoking is a common cause of cough. A cough caused by smoking is almost always a chronic cough with a characteristic sound. This is often called smoker's cough.
Asthma
A common cause of cough in young children is asthma. Typically, an asthmatic cough includes wheezing, which makes asthma easier to identify.
Asthma exacerbations are treated with an inhaler. Children can get rid of asthma as they grow older.
Medicines
Some medications cause coughing, although this is usually a rare side effect. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, commonly used to treat high blood pressure and heart disease, may cause coughing.
The cough stops after stopping the drug.
Other states
Other conditions that may cause a cough include:
- vocal damage cough
- stopping nasal drops
- bacterial infections such as pneumonia, whooping cough and croup.
- serious conditions such as pulmonary embolism and heart failure
Another common condition that can cause a chronic cough is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). In this condition, the contents of the stomach return to the esophagus. This backflow stimulates a reflex in the trachea, causing the person to cough.
Main types of cough
By nature, cough is divided into productive and non-productive. By timbre it can be:
- Silent.
- Voiced.
- Barking.
- Muffled.
- Short.
- Siplym.
By type of sputum discharged:
- With mucus (sputum is light or colorless).
- With admixtures of pus (sputum has a greenish tint).
- With bloody impurities (sputum is colored red or orange).
- With serous discharge (sputum has a greenish tint).
Dry
In most cases, a dry cough develops in the upper respiratory tract. It is loud, intrusive, and sometimes accompanied by whistling sounds. It comes from the throat, as opposed to a wet cough, which usually comes from the chest area. More often than not, a dry cough becomes productive after some time. If the mucus has a too viscous consistency, it is accompanied by the release of a small amount of sputum and does not bring relief to the patient. In the case of frequent episodes of dry cough, irritation of the walls of the respiratory tract occurs, which causes even greater discomfort.
Weak and insufficient amount of sputum is not able to remove the infection from the body, as a result of which germs can spread into the lower respiratory tract.
The occurrence of unproductive spastic exhalations does not always indicate the development of any disease. They may appear due to chemical irritants, smoke or allergens entering the respiratory tract, which may include:
- Wool.
- Pooh.
- Pollen.
- Dust.
- Strong odors.
- Food, etc.
Wet
Bronchospasms, accompanied by the release of a sufficient amount of sputum, bring relief to the patient, since sputum not only clears the airways, but also removes microbes from the body. If left untreated, a strong wet cough may become dry after a few days, and instead of leaving the respiratory tract, mucus stagnates in the bronchi. Therefore, it is very important to provide the patient with plenty of fluids and expectorants when the first signs of the disease appear with wet sputum discharge.
In children, the muscles of the respiratory tract are weaker than in adults, and their openings are narrower, so it is more difficult for them to cough. Severe bronchospasms with sputum in a child indicate the development of acute inflammation of the bronchi, alveoli or lungs. In adults, this symptom is also often a sign of a cold, and in smokers it can signal the development of a chronic disease - obstructive pulmonary disease.
COPD leads to the formation of irreversible processes in the lungs.
Barking cough
A barking cough occurs when the patient's mucous membranes in the back of the throat and vocal cords become inflamed. As a result, spasmodic exhalations are accompanied by a rough sound, reminiscent of a dog barking. Reflex spasms are paroxysmal in nature and are considered unproductive - when coughing, sputum does not come out and the airways are not cleared. The patient feels soreness and soreness in the throat, the voice often becomes hoarse or disappears altogether.
A barking cough appears in diseases such as whooping cough, laryngitis, false or true croup, compression of the trachea by a tumor, and attacks of hysteria.
Viral
A viral cough develops as a result of damage to the body by viral infections. Its characteristic feature is the rapid development and appearance of abundant sputum within 1-2 days after infection. After the viral disease is completely cured, it may bother the patient for several more weeks. Sputum during a viral cough is clear, fluid, and free of pus.
The following types of viruses can cause the disease:
- Rotaviruses.
- Influenza virus.
- Respiratory-sentential viruses.
After penetration into the nasopharynx, they move into the bronchi, after which the person develops symptoms of acute bronchitis. After the body produces antibodies to the virus, a gradual improvement in health is observed. As a rule, this occurs within 3-5 days after the onset of the disease.
An important feature of viral bronchitis is the lack of therapeutic effect when taking antibiotics.
Recovery occurs only when the body can independently produce protective antibodies. Therefore, treatment of viral diseases should include, first of all, measures to strengthen the immune system.
Allergic
The appearance of an unreasonable, obsessive cough may indicate an allergy. Incorrect diagnosis and treatment leads to aggravation of the situation, so it is important to promptly identify the exact cause of the problem.
Signs of allergic manifestations are:
- Paroxysmal, dry cough, swelling of the walls of the larynx and bronchial mucosa.
- Symptoms appear at certain times of the year. For example, if you are allergic to the color of some plants, the allergy occurs in spring or summer.
- Presence of skin rashes, itching.
- Weakness, irritability, apathy.
- Development of short-term runny nose, lacrimation.
- No signs of a cold: fever, migraine.
After taking antihistamines, the above symptoms quickly disappear.
Psychogenic
The appearance of bronchospasms without any apparent reason may be due to psychosomatic diseases. They can be identified by the following symptoms:
- Unexpected development.
- Stop after eliminating the cause of stress, as well as at night when the person is sleeping.
- Unproductive character, lack of sputum.
- The presence of other signs of emotional disturbance (for example, tics).
- No abnormalities during laboratory examination.
Cough after various illnesses
A lingering cough can be a residual phenomenon after an infectious or viral disease of the respiratory tract, or in the absence of proper treatment of the ENT organs. It can also be caused by the addition of the herpes virus after already cured bronchitis.
A persistent cough after bronchitis, especially in adults, requires re-examination for the development of complications. The most common complications that develop after acute bronchitis are pneumonia and asthma.
When does a cough require emergency care?
Most coughing episodes resolve or improve significantly within two weeks. If you develop a cough that does not improve over time, see your doctor—it may be a sign of a more serious problem.
If additional symptoms develop, contact your doctor as soon as possible. Among the symptoms, it is important to watch for the following:
- heat
- chest pain
- headache
- drowsiness
- confusion
Coughing up blood or difficulty breathing is a medical emergency.
Comparison criterion 3 - cough timbre
Dry cough is called barking
, similar, as one might imagine, to the loud barking of a dog. This situation is due to the fact that the sputum becomes viscous and is difficult or impossible to cough up.
Hoarse or hoarse cough
with dull and whistling sounds speaks of diseases such as laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia. With laryngitis and tracheitis, the cough is accompanied by a hoarse voice, and with bronchitis and pneumonia - chest wheezing.
Silent cough
may be associated with severe inflammation of the vocal cords. It sometimes occurs in patients with extreme malnutrition or heart failure.
Up to contents
How to treat a cough?
Cough is treated in different ways, depending on the cause. For healthy adults, most treatments will involve self-care.
Treating cough with home remedies
A cough may be caused by a virus that cannot be treated with antibiotics. But you can make it easier in the following ways:
- Stay hydrated by drinking more water.
- Elevate your head with extra pillows while you sleep.
- Use cough drops to soothe your throat.
- Regularly gargle with salt water to remove mucus and soothe your throat.
- Add honey or ginger to hot tea to relieve coughs and clear your airways.
- Use decongestant sprays to unblock your nose and make breathing easier.
Health care
Typically, medical care will include a doctor examining your throat. He will listen for a cough and ask about any other symptoms.
If your cough is likely caused by bacteria, your doctor will prescribe oral antibiotics. Medicines usually need to be taken for a week to completely cure a cough. Expectorant cough syrups or cough suppressants with codeine may also be prescribed.
If your doctor can't find the cause of your cough, he or she may order additional tests. These may include:
- chest x-ray to evaluate if your lungs are clear
- blood and skin tests if an allergic reaction is suspected
- testing sputum or mucus for signs of bacteria or tuberculosis
It's very rare that a cough is the only symptom of heart problems, but your doctor may ask for an echocardiogram to make sure your heart is functioning properly and isn't causing the cough.
Complex cases may require additional analysis:
- CT scan. A CT scan offers a deeper view of the airway and chest. It may be useful in determining the cause of a cough.
- Esophageal pH monitoring. If the CT scan does not show the cause, your doctor may refer you to a gastrointestinal specialist or a pulmonary (pulmonary) specialist. One test these specialists may use is esophageal pH monitoring, which looks for signs of GERD.
In cases where the above treatment is either impossible or extremely unlikely, or the cough should go away without intervention, doctors may prescribe cough suppressants.
Therapy
For colds and severe coughing, medications that have an expectorant effect are prescribed. The doctor may recommend taking vitamins, inhalations, mustard plasters and other measures that can stop attacks. Folk remedies are allowed only as an addition to the main therapy and with the consent of a specialist.
Drug treatment
If you have a hypertensive cough, you can ask your doctor to change medications, because stopping ACE inhibitors often helps eliminate chesty cough. After a week, you can check how you feel, and if symptoms persist, the problem may not be with the medications.
Acid cough needs to be treated with medications and proper nutrition. The patient needs to eat less fatty and salty foods and avoid alcohol and coffee for a while. It is also not recommended to have dinner too late. Food must have time to be digested in the evening, otherwise a night's sleep will be in jeopardy.
In cases related to cancer, tuberculosis and other dangerous diseases, surgery is prescribed.
It is very important to treat coughs during pregnancy immediately. The attacks provoke the tone of the woman’s uterus, and this threatens premature birth and loss of the child.
What happens if you don't treat your cough?
In most cases, the cough disappears naturally within a week or two after it first appears. Coughing usually does not cause long-term damage or symptoms.
In some cases, a severe cough can cause temporary complications, such as:
- fatigue
- dizziness
- headache
- cracks in ribs
But this happens very rarely and usually stops when the cough disappears.
A cough that is a symptom of a more serious illness is unlikely to go away on its own. If left untreated, this condition may worsen and cause other symptoms.
Preventive measures
Never getting sick is difficult, but in order for a person to avoid a cold cough, it is enough for him:
- eliminate cigarettes from your life;
- if possible, move to another area or city, change jobs if environmental conditions are assessed as difficult;
- do not drink cold drinks;
- avoid hypothermia;
- constantly inhale or take medications prescribed by a doctor if the disease is chronic;
- reduce stress levels.
Hypothermia must be avoided.
Coughing for no reason is a symptom that cannot be ignored. It can help diagnose a serious illness in a timely manner. Often it is late treatment that does not allow a person to cope with the disease. Paying attention to yourself will help protect you from dangerous diseases and live longer.
What preventive measures can be taken to avoid coughing?
Although coughing is sometimes necessary to clear the airways, there are ways to prevent other types of cough.
Quit smoking
Smoking is a common factor in the development of chronic cough. Smoker's cough can be very difficult to cure. Once you quit smoking, you will be much less likely to catch a cold or chronic cough.
Diet changes
A fairly old study from 2004 found that people who ate diets high in fruit, fiber and flavonoids were less likely to experience chronic respiratory symptoms such as cough.
Comparison criterion 4 - time of cough onset
Morning cough
occurs in chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. It is especially common for smokers. This type is caused by the accumulation of sputum during the night, which does not clear and provokes a cough in the morning.
Evening or night cough
occurs due to the fact that a lying person accumulates phlegm, which does not cough up for a long time during sleep. Moreover, sputum in a horizontal position can accumulate in the larynx, provoking attacks.
Up to contents
Cough in adults and children
In children, coronavirus is often mild or asymptomatic. If there is a cough but no fever, this does not mean that the child is sick with coronavirus. But if other symptoms appear, such as vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste and smell, then it is best to seek medical help.
Other symptoms in children include a severe, dry cough. There may be no signs of a cold.
An expectorant cough indicates inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. Compared to an adult, a child's chest muscles are weaker and their airways are narrower, making it much more difficult for them to cough up. The sputum is more viscous, making it difficult to leave the lungs.