Inflammation of the appendages, the treatment of which in women sometimes causes great difficulties, is a separate group of diseases of the ovaries and fallopian tubes that arise as a result of infection, hypothermia or previous surgical interventions. In gynecology they are also called “adnexitis” or “salpingoophoritis”.
Why do the appendages hurt and why does adnexitis occupy one of the leading positions among all gynecological pathologies? How and with what you can effectively cure inflamed appendages and what remedies are available for this, including folk remedies - we will talk about all this in this material. For all questions, we invite all women suffering from adnexitis to contact the doctors of our clinic - all services, from complete diagnosis to comprehensive treatment and prevention of relapse and chronicity of the process!
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendages in women
The symptoms of adnexitis will largely depend on the factor that provoked the development of the pathology, as well as the strength of the inflammatory process. Thus, in the acute form of the disease, pain and other accompanying symptoms will be clearly expressed, but in the case of chronicity, the signs will be erased.
The intensity of inflammation also depends on the type of pathogenic microorganism, if adnexitis is of infectious origin. The general state of the body’s defenses also plays an important role.
The acute course is accompanied by the development of the following clinical picture:
- tension in the lower abdomen;
- severe pain, sometimes spreading to the lumbar area or to the limb on the affected side;
- a significant increase in general body temperature - the indicator can reach or exceed 39°C;
- unscheduled menstruation or its delay;
- Uncharacteristic vaginal leucorrhoea - it may contain admixtures of pus, be green/yellow, or include foam.
In the absence of adequate therapy, chronic disease cannot be ruled out. In this case, the severity of the clinic depends on the current stage of the disease: now the patient is in remission or an exacerbation of adnexitis.
Typical for the chronic form of adnexitis are:
- disorders of the menstrual cycle (MC), sexual function;
- various diseases of the urinary system, cystitis is especially common.
Important! During the period of exacerbation of chronic adnexitis, the development of symptoms of the acute form of the disease is typical.
Symptoms of the chronic form
Chronication of the disease occurs due to the patient’s failure to receive the necessary drug treatment when diagnosing acute lesions of the appendages.
This type of disease is characterized by the constant presence of aching pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lumbar region. When trying to palpate the abdomen, the woman experiences tolerable pain.
Chronic adnexitis is accompanied by structural and functional changes in the ovaries, so a woman may notice MC disturbances - scanty/increased bleeding is noted. Menstruation becomes very painful.
Many women note a complete absence/significant decrease in sexual desire. Sexual intercourse itself is accompanied by pain.
What it is?
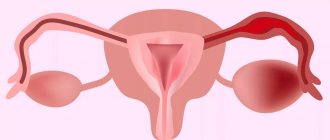
Inflammation of the appendages in women is a combined group of infectious and inflammatory diseases localized in the ovaries and/or uterine tubes. Adnexitis can be unilateral or bilateral.
The appendages and the uterus have a close anatomical and physiological connection, so the inflammatory process most often simultaneously develops both in the tubes (salpingitis) and in the ovaries (adnexitis or oophoritis). When the uterus is involved in the infectious-inflammatory process, the clinical picture of the disease is supplemented by signs of endometritis.
Answers on questions
Answers to frequently asked questions.
What is inflammation of the appendages
Inflammation of the appendages is a combined lesion of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. It can be left- or right-handed. In some cases, the inflammatory process forms in both appendages.
What are appendages
The appendages are the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Accordingly, they are right and left.
How the appendages hurt
With the development of adnexitis, a woman feels pain of varying intensity (it all depends on the strength of the inflammation) in the lower abdomen - the area of projection of the uterus and its appendages.
Why do the appendages hurt?
The cause of pain can be various reasons. But most often adnexitis develops against the background of hypothermia of the legs, but it can also be triggered by infections.
What to do if your appendages hurt
If you develop pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a gynecologist as soon as possible. Self-treatment can cause serious harm to health.
Where are the appendages located in women?
The female appendages - fallopian (uterine) tubes and ovaries are located in the pelvic area.
How is inflammation of the appendages treated?
Treatment of the disease is quite long. The treatment regimen largely depends on the cause that provoked it and the accompanying complications.
Causes of adnexitis
The main reason for the development of adnexitis is any type of microorganism. They are classified as opportunistic flora, which under normal conditions do not cause pathological conditions in humans, but at the same time, against the background of a decrease in protective forces, their pathogenicity manifests itself.
Most of them are staphylococci and streptococci. Among absolute pathogens, the most common pathogens are sexually transmitted infections. Among them are gonorrhea, chlamia and trichomonas.
In order for the development of pathogenic properties to occur, as well as the appearance of other pathogens, provoking factors must act:
- First of all, this is a decrease in immunity. It can be associated with hypothermia, various extragenital and genital diseases, and autoimmune pathology.
- In some cases, these may be malformations of internal organs , for example, facilitating the reflux of menstrual blood into the fallopian tubes to the ovaries.
- This also includes hypothermia, heavy physical exercise, and swimming in open water.
- Transmission of pathogens through the genitals , for example, during unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as promiscuity and a large number of sexual partners.
- Insufficient supply of nutrients, vitamins, microelements.
- Presence of intrauterine devices.
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages in women
Treatment of the disease is complex. Includes mandatory medication intake. A woman may be prescribed physiotherapy. The use of folk remedies is allowed.
Physiotherapy
Additionally, the patient is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapy. Good results in relieving the inflammatory process are shown by:
- electrophoresis with iodine and lidase (help in eliminating scars and adhesions);
- ultrasound (exposure to the affected area with ultrasonic waves);
- high frequency currents.
When the pathology becomes chronic, the following may be recommended:
- mud and paraffin wraps;
- sanitization of the vagina, application of mineral waters to the area of inflammation.
Drug treatment
The patient must be prescribed medications. Priority is given to drugs from the group of antibiotics.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the appendages
Prescribed drugs from the group:
- penicillins;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
They cope well with pathogenic microflora, capable of reproduction and survival in an acidic environment.
When diagnosing a pathogen that does not require oxygen, Metronidazole is used.
Suppositories for inflammation of the appendages
Suppositories are given in a course, the duration of which does not exceed 10 days. They are introduced at night.
During therapy the following can be used:
- Terzhinan. Has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effects. It has many side effects and disrupts the local microflora.
- Polygynax. A drug with antibacterial, antifungal and antimicrobial effects.
- Klin-D. Relieves inflammation of infectious origin. Does not cause dysbiosis.
- Pimafucin. Used in case of thrush. Can be used in pregnant and lactating women.
- Betadine. The main active component is iodine. Used as an antifungal agent.
- Ketoconazole. Used for fungal pathologies.
- Livarol. Effective against fungi, does not disturb vaginal microflora.
- Travogen. Belongs to a group of broad-spectrum drugs.
- Hexicon. Recommended for diagnosing diseases from the PPP group.
- Movalis. Relieves the symptoms of the inflammatory process, as well as relieves pain and helps reduce body temperature.
- Suppositories with indomethacin. They belong to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Folk remedies
Treatment with traditional methods should not exclude the drug regimen developed by a specialist, but only supplement it.
- Juniper berries (for bilateral inflammation). Pour boiling water (200 ml) over 15 g of fruits. Leave for 4 hours. Drink 1 tbsp. three times a day.
- Pour cinquefoil (2 tablespoons) with bubbling water (500 ml), leave for 60 minutes. Filter. Drink ½ glass 30 minutes before meals 4 times a day.
- Combine sweet clover, coltsfoot, centaury (20 g each). 1 tbsp. pour boiling water (200 ml) over the mixture and leave for 60 minutes. Drink 75 ml 6 times a day for a month.
- Combine rose hips and black currants. Pour 20 g of berry mix with boiling water (200 ml). Leave for 60 minutes. Squeeze the berries. Add a little granulated sugar to the drink. Drink 100...125 ml three to four times a day.
- Grind dry walnut leaves. Take 1 tbsp of the product and brew with boiling water (200 ml). Leave in a thermos for 4 hours. Squeeze. Drink the resulting volume throughout the day.
It is advisable to include pumpkin in your daily diet. It is advisable to drink fresh juice in the morning on an empty stomach.
Douching
To prepare solutions, you can use the following recipes:
- Pour 10 grams of bergenia root with water (200 ml) and cook in a water bath for 30 minutes. Filter the composition and let cool. Use every day.
- Pour boiling water (200 ml) over 3 grams of dried calendula flowers. Leave for 60 minutes. Strain. Apply every day.
- Stir St. John's wort (2 spoons) in cold water (1 l). Boil the mixture and cook for 20 minutes. Let cool. Filter off the sediment and use it to sanitize the vagina in the evenings.
Surgical therapy
Surgery is rarely practiced. The main indication is the formation of an abscess. Preference is given to the laparoscopic technique. In this case, the development of postoperative complications is almost completely excluded. The recovery period is also significantly reduced.
Important! Severe adhesive disease also becomes an indication for surgery.
Forecast
Adnexitis responds well to medication. With timely intervention on the pathological process, inflammation of the appendages can be eliminated in 7-10 days. But provided that the therapeutic course is completed completely and is not stopped at the first symptoms of improvement. If adnexitis has taken a protracted form and led to the formation of adhesions, the resulting neoplasms can only be removed surgically. In this case, the recovery period will take about a month, which has a number of restrictions related to nutrition and lifestyle.
Complications
In the absence of adequate drug therapy, the development of serious complications cannot be ruled out.
Tuboovarian formation
A tubo-ovarian formation is, simply put, an extensive abscess. May cause melting of the tissues of the tubes and/or ovaries, which causes the development of sepsis.
Pelvioperitonitis
The condition is an inflammation in which the pelvic peritoneum is involved. The treatment is surgical - a laparoscopic technique is used - since the patient needs drainage of the pelvic area.
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is an equally common complication of chronic adnexitis. The attachment of the fertilized cell occurs in the cavity of the fallopian tube, since due to the formed adhesions it is not able to reach the uterine cavity.
Incorrect attachment of the egg is a condition for a woman’s life that requires urgent surgical intervention. The growing embryo will still rupture the oviduct, causing massive bleeding.
Infertility
The inability to conceive is the most serious complication of adnexitis. It is formed as a result of obstruction of the oviducts caused by adhesive disease. The reason may also be the lack of ovulation due to the loss of the ovaries' functional abilities.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of adnexal lesions includes a gynecological examination, laboratory tests and ultrasound.
Gynecological examination
During an examination in a gynecological chair, when attempting to palpate the appendages, a woman experiences acute pain.
Laboratory research
The patient is required to study the blood and smear obtained during a gynecological examination. When deciphering the CBC, characteristic abnormalities in the composition of the blood are revealed.
Studying a smear helps in identifying the pathogenic agent that provoked damage to the appendages.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a mandatory procedure that helps to identify the characteristic signs of adnexitis - dilated, enlarged oviducts, cystic formations in the ovarian tissues.
Forms
Damage to the oviducts and ovaries can occur in different forms.
Latent form
The latent (hidden) course of the disease does not cause clear manifestations, but is the most dangerous form of the condition. It remains untreated, but constantly progresses. A woman may experience slight malaise and lethargy, which she attributes to normal fatigue.
Acute form of adnexitis
For the acute form of damage to the appendages, the development of vivid clinical symptoms is typical - severe pain in the lower abdomen (especially on the affected side), uncharacteristic discharge, high body temperature.
Subacute form of adnexitis
It should be considered as a transitional stage of the disease from acute to chronic form. Symptoms of the disease are present, but are subsiding.
Chronic form of adnexitis
The chronic course is characterized by alternating stages of remission and exacerbation.
Diet for adnexitis
Following the principles of dietary nutrition is justified only during acute inflammation, as well as relapse of chronic inflammation.
The diet excludes the consumption of potentially allergenic foods - dark chocolate, sweets, egg whites. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of sugar and salt.
The menu should include foods with high levels of vitamin C. These are:
- sweet red pepper;
- citrus;
- strawberry;
- cranberry;
- kiwi.
Lean varieties of meat/fish should be present.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease exists. To prevent the development of adnexitis, doctors recommend:
- go for a gynecological examination at least once every six months;
- refuse unplanned sex with casual partners or use condoms;
- try not to get too cold;
- treat all diagnosed diseases, preventing their chronicity.
Adnexitis is a rather unpleasant disease, which, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications, including the development of infertility. For this reason, if pain develops in the lower abdomen and accompanying symptoms appear, a woman should consult a gynecologist.
Preventive recommendations
In order to avoid such a diagnosis, it is necessary to follow some preventive recommendations.
- Observe basic rules of personal and intimate hygiene. Especially in public places.
- Avoid hypothermia, especially below the waist. To do this, you should dress according to the weather, regardless of fashion trends.
- Use barrier methods of contraception with a new or untested partner.
- Undergo annual preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
- Treat chronic diseases, especially the genitourinary system, in a timely manner.
- Do not overuse wearing thongs.
- When using anal, oral and vaginal sex, use a condom, and do not forget about the shower.
The state of the intestines also affects the vaginal microflora. Try to stick to proper nutrition, minimize stress factors and do not abuse medications. Take antibiotics only as prescribed by your doctor.