Almost everyone has encountered this situation: a neighbor, relative or work colleague was taken away in an ambulance with a heart attack. The patient was subsequently diagnosed with a heart attack, severe arrhythmia, or aortic aneurysm. However, all these cases have a common pattern - the patient’s serious condition and a real threat to life.
It would be good if people were near such a patient and called an ambulance. During a heart attack, time is literally counted in minutes; death can occur suddenly. That is why everyone should know the first signs of a heart attack, what is necessary and what is strictly forbidden to do in this case.
General information
Heart attack - this is the concept most often used to describe sudden, acute pain in the heart area. The term is rather colloquial in nature and is used to describe an episode ischemia . Practicing cardiologists and general practitioners in their professional activities use another concept - acute coronary syndrome . This diagnosis is established temporarily and, after examinations, is clarified to myocardial infarction or exertional angina . Every year, 17 million people worldwide die from ACS.
Heart or panic?
Having a heart attack or panic attack is definitely an unpleasant experience for anyone. And for some people, a heart attack can additionally cause feelings of panic. It's not entirely common for a panic attack and a heart attack to occur at the same time in the same person, but it is certainly possible. Although panic attacks are not considered to be the direct cause of heart attacks, both are linked to stress. Chronic stress over time certainly increases the risk of heart attack. And since the symptoms can be extremely similar, at the moment it is difficult for the patient himself to distinguish them from each other. Both panic and heart attacks occur with pain, shortness of breath, sweating, palpitations and dizziness. Therefore, doctors can distinguish them based on examination data.
Pathogenesis
A heart attack is caused by a decrease in blood flow to a specific area of the myocardium. First, an ischemic due to poor nutrition and then they talk about angina pectoris . If the cause is not eliminated, then ischemia turns into necrosis - damage to the heart muscle, and then they talk about myocardial infarction . Most often, these processes are formed as a result of blockage or due to significant narrowing of the lumen of the coronary artery by a thrombus or atherosclerotic plaque . With even a slight spasm of the coronary artery, the blood supply is severely impaired due to the presence of a plaque on the wall of the vessel, which aggravates the situation.
The nature of local changes in the myocardium at the stage of ischemia formation is indistinguishable from the angina attack itself. However, myocardial infarction is formed only if it was not possible to restore adequate blood supply to this area of the myocardium in time. And then irreversible damage to the heart muscle occurs - myocardial infarction.
Classification
The main criterion is the nature of the pathological process. It has already been mentioned in passing that a heart attack is a simplified name for two phenomena.
Which ones:
Angina pectoris
Usually unstable form. Its essence lies in disruption of the normal nutrition of the heart muscle. But the volume of the lesion is not yet enough to cause extensive destruction of cardiac structures.
This form is characterized by constant, smooth or spasmodic progression without signs of improvement even with full therapy.
Recovery requires lifelong medication without any guarantees. Effective treatment is possible only at stages 1-2.
Heart attack
The second option is coronary insufficiency. Develops in response to critical narrowing or blockage of the arteries supplying the heart.
The essence is approximately the same - the death of muscle structures, only the volume of destroyed cells is greater. A heart attack occurs immediately, like an avalanche, in contrast to angina, when the development of the same condition may take more than one year, this is the main difference.
Treatment in intensive care, and then in the cardiology department. The prospects are vague. The prognosis depends on the quality of first aid and the area of involvement in the destructive process.
Causes
The main prerequisites for the development of a heart attack are various diseases of the cardiovascular system, endocrinological disorders and other chronic processes in the body:
- cardiac ischemia;
- arterial hypertension , hypertensive crises;
- tendency to thrombosis and other abnormalities in the blood clotting (thrombophilia);
- chronic heart failure;
- blockage of veins and arteries with blood clots (coronary artery thrombosis, pulmonary embolism );
- decompensated diabetes mellitus , caused by a long-term lack of adequate therapy;
- changes in blood circulation caused by fatty and cholesterol deposits on the walls of large and medium-sized vessels ( atherosclerosis );
- rhythm disturbances ( extrasystolic arrhythmia , atrial fibrillation );
- dissecting aortic aneurysm.
The risk group includes older people, which is due to age-related changes in vascular elasticity and the condition of the myocardium. Heart attacks most often occur in men. The patient's standard of living also influences the likelihood of a heart attack. At risk are people who are obese and cannot get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages).
Recently, a disappointing trend has emerged - heart attacks are becoming “younger”. Heart attacks are becoming more common in people under 40 years of age. In medical practice, there are cases of myocardial infarction not only in 25-year-olds, but also in 16-18 year olds. Causes of myocardial infarction at a young age:
- genetic predisposition;
- violation of coagulation, hemostatic system;
- drug use;
- emotional overload;
- high susceptibility to stress;
- atypical course of atherosclerosis .
The risk of developing angina and myocardial infarction is also quite high in pregnant women suffering from chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system. During pregnancy, the load on the heart, which works for two, increases, hypoxia and lack of oxygen increase, and the total blood volume increases.
A negative role is also played by:
- excess weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- presence of bad habits;
- stressful situations;
- age over 50 years.
An attack can also be triggered by long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in large dosages.
How to recognize an emergency?
It’s not easy to do this without qualifications. A distinction is made between the main types of coronary insufficiency; it is also necessary to distinguish the described disease from intercostal neuralgia, perforated gastric ulcer, pneumonia and other phenomena.
What characterizes heart pain:
- Lack of response to breathing. Inhalation and exhalation do not affect the intensity of the syndrome. The same cannot be said about signs of non-cardiac discomfort.
- No changes when moving. If you stand up, sit down, lie down, the power of manifestation will be the same. This is the trait of heartache.
With intercostal neuralgia, the pain intensifies with inhalation and movement.
A perforated ulcer is defined by a sharp, cutting sensation in the abdomen and epigastric region. It is this nature of pain that makes it possible to distinguish the condition from others.
Pneumonia causes predominantly respiratory symptoms.
Diagnosis falls on the shoulders of doctors. There is no point in guessing on the coffee grounds. The brigade should be called. An attack can be recognized by the nature of the pain, its duration, and additional manifestations.
Heart Attack Symptoms
Most often, attacks occur in the morning and are accompanied by severe pain. The patient experiences tightness in the chest, difficulty breathing and cannot take a full independent inhalation/exhalation. The pain syndrome may be accompanied by a tingling or burning sensation. Similar symptoms may occur with heartburn . The pain can radiate and radiate to the lower jaw, left shoulder, arm, neck. The radiating pain is stabbing in nature. The duration of the pain syndrome can last from half an hour to three hours. Signs of an impending heart attack may appear long before it occurs. This period may be more than 20 days.
How to recognize a heart attack?
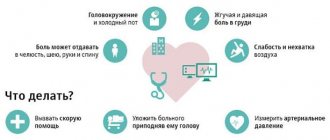
It is not difficult to recognize a heart attack, because... spasm of the coronary arteries gives clear symptoms (to say “spasm of the heart muscle” is incorrect, because only the vessels supplying the myocardium spasm, which leads to changes in the heart muscle). Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following signs:
- pressing pain behind the sternum, feeling of tightness in the chest;
- feeling of lack of air, feeling of discomfort in enclosed spaces;
- apnea, the appearance of snoring during sleep;
- heartburn, nausea, pain in the epigastric region;
- dizziness;
- a feeling of numbness in the left arm from the shoulder to the little finger;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- changes in sleep and wakefulness patterns;
- excessive anxiety;
- excessive fatigue even with minimal physical activity.
A timely visit to your doctor if you notice the above signs will help prevent a cardiovascular disaster and stop the attack without consequences. In addition to the main symptoms of difficulty breathing and pain, the patient may have other signs that can help identify a heart attack:
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea syndrome);
- vegetative symptoms ( hyperhidrosis , cyanosis of the skin, cold feet, pallor);
- nausea accompanied by belching, heartburn, feeling of food stuck in the anterior abdominal wall;
- instability of body temperature (sharp rise and fall, accompanied by heat and fever);
- feeling of rapid heartbeat;
- feeling of pulse instability;
- blurred vision up to loss of consciousness, dizziness;
- psycho-emotional instability: excessive anxiety, panic attacks, internal shaking, trembling in the body.
Symptoms of a heart attack differ slightly by gender. Women experience heart attacks much later in life than men.
Symptoms of a heart attack in women
The endurance of the cardiovascular system in women is determined by biological characteristics. The female body has adaptive mechanisms provided by nature for bearing and giving birth to a baby. The frequency of attacks in both sexes levels off after menopause, but women have fewer complications and experience a heart attack more easily. Very often, women suffer an attack “on their feet.” The signs of a heart attack in women are identical to those of the stronger sex, but may be slightly less pronounced.
Symptoms of a heart attack in men
Men experience myocardial infarctions earlier and experience them much more severely. The frequency of deaths among representatives of the stronger half is higher. Cardiovascular diseases in men are diagnosed late, already in an advanced state due to ignoring symptoms and not recognizing oneself as sick. The symptoms in men are almost the same as in women, only more pronounced.
Panic attack: what is its essence?
A panic attack occurs when you suddenly experience intense fear, anxiety, or discomfort that peaks within a few minutes. The attacks may be triggered by a stressful event, such as public speaking, a large presentation, or being fired from work. But some people have no obvious reason for developing a panic attack. The most likely and typical symptoms:
- Chest pain
- Interruptions in heart function, tachycardia,
- Sweating,
- Fear of death,
- Worry about developing madness and loss of self-control,
- Dizziness,
- Nausea,
- Chills,
- Paresthesia (feeling of numbness or tingling).
Women are known to experience panic attacks more often than men. They most often occur between the ages of 18 and 25. For most women, they may be isolated or occur rarely, while for others they occur regularly. People with panic disorder experience multiple attacks and fear recurrence. If you're having a panic attack and suspect you're having one, there are a number of things you can do to shorten the duration or stop the attack altogether.
- Deep breathing with concentration within yourself will help,
- Simple exercises can relieve an attack,
- Talking to friends and family helps
- Meditation or listening to soothing music can help.
These actions will help you take your mind off panic and calm down. If you have been diagnosed with panic disorder, you may be prescribed antidepressants and other medications to prevent additional attacks or reduce their intensity. In addition, some lifestyle changes can help you gain control over your anxiety or panic disorder:
- You need to get plenty of rest and good sleep
- Proper nutrition is important
- Regular sports and gymnastics in the morning
- Stress management
- Talking to someone about fears and worries
- Personal time for yourself, doing what you love
- Maximum exclusion of trigger situations
Most panic attacks last between 20 and 30 minutes, but there may be some exceptions. And some people may experience panic attacks that last several days.
Tests and diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis and determine further treatment tactics, the patient, after admission to the hospital, undergoes laboratory and instrumental examination, which includes:
- blood test for cardiac enzyme levels;
- electrocardiogram;
- EchoCG;
- R-graphy of the chest organs;
- coronary angiography to assess the state of patency of the heart vessels, identify plaques and determine further treatment tactics: stenting, bypass surgery, drug therapy.
Based on the results of the examination, a revised diagnosis is made and the future fate of the patient is decided.
Necessary examinations
Upon admission to the department, diagnostics are carried out urgently. Usually, results are not expected; urgent measures are indicated to bring basic vital signs back to normal. Then more careful work is needed.
Approximate list of events:
- Oral interview with the patient and collection of anamnesis. What matters is the number of attacks and how often they occur (if they have happened before).
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate.
- Daily monitoring. Registration of the same indicators within 24 hours using a Holter monitor. Can be carried out repeatedly to clarify conditions. The study answers the question about the dynamics of blood pressure and heart rate throughout the day, depending on circadian phenomena.
- Electrocardiography. Shows even slight arrhythmia. All functional deviations are clearly visible.
- Echocardiography. Demonstrates defects and the degree of destruction of cardiac tissues. This visual technique is essentially a version of ultrasound.
- General blood test, biochemical and hormone tests.
Treatment
Treatment of a heart attack is carried out in a hospital setting. The timing depends on the severity of the condition, complications, concomitant pathology and age. On average, treatment takes 2 weeks in the absence of complications and operations.
Patients with myocardial infarction spend the first 3 days in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit; after stabilization, they are transferred to the general cardiology department. It is not recommended to stop therapy early and leave the walls of the medical institution. If you are irresponsible about your health, the risk of a recurrent attack increases significantly, and complications may develop.
conclusions
Under a heart attack with characteristic symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid rhythm or pulse, many pathological conditions can be hidden. Pain in the heart does not always indicate a heart attack. The cause of deterioration in well-being may be an exacerbation and transition of angina to an unstable form, vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), malignant arrhythmia, thromboembolism or heart failure. Therefore, if characteristic signs and complaints occur, you should immediately consult a doctor and call an ambulance. This will minimize the risk of cardiac complications and save lives.
Medicines
The patient is advised to take medications to avoid recurrent heart attacks and angina attacks. Treatment is carried out comprehensively and includes taking drugs from several groups at once:
- Beta blockers . Reduces the load on the heart, blood pressure levels and normalizes heart rhythm ( Concor , Egilok , Carvedilol ).
- Antiplatelet agents . Prevents thrombus formation, thins the blood ( Aspirin Cardio, Cardiomagnyl, ThromboASS ).
- Statins. cholesterol levels , reduce the volume of plaque in the vessel ( Liprimar, Rosuvastatin, Simvastatin ).
- Diuretics. They unload the heart muscle by removing excess fluid and eliminating swelling ( Indapamide, Veroshpiron ).
- Cardioprotectors. Helps restore the heart muscle ( Mildronat, Preductal ).
Procedures and operations
There are several methods of surgical treatment aimed at restoring normal blood circulation in the heart muscle:
- Coronary angiography followed by balloon angioplasty or stenting of the coronary arteries. Balloon angioplasty involves widening a vessel narrowed by plaque by inflating a balloon. The operation allows you to get rid of the consequences of ischemia, but does not eliminate its causes. To maintain the shape of the vessel, a stent is inserted into it - a special device made of thin material that fixes the width of the vessel using a spacer.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting and mammarocoronary bypass grafting. Blood flow is restored by suturing a shunt and creating a bypass path for blood circulation. Own veins taken from the lower extremities act as a shunt.
First aid for a heart attack
The danger of a heart attack lies in its transition to myocardial infarction. Help must be provided immediately to avoid death. A heart attack can happen at the most inopportune moment: while driving a car, while flying on an airplane, on the way home. What to do if you have a heart attack if you find yourself at home alone:
- take a comfortable body position, stop any physical activity, behave calmly and do not fuss;
- Call an emergency medical team, to do this, dial the number “103” on your cell phone, describe your condition in detail and follow the instructions.
Before the ambulance arrives, place a Nitroglycerin and chew Aspirin . Acetylsalicylic acid prevents the formation of blood clots, thins the blood, which prevents myocardial infarction from progressing and does not increase the area of necrosis in the heart muscle. If you have already encountered similar situations before and your attending physician gave you certain recommendations, then it’s time to take advantage of them.
Measure your pulse and blood pressure if you have a blood pressure monitor at home. Under no circumstances should the patient be given Corvalol , Validol , Valocordin , because These drugs depress the nervous system, which can make it difficult to diagnose the patient's condition. Coughing helps stimulate blood circulation in the chest. Take a deep breath, then cough as loudly as possible for 2 seconds as you exhale. Proper first aid can save a person's life. Indirect cardiac massage in the absence of breathing and pulse in the patient can also save life.
First aid provided by the ambulance crew
Doctors who arrived at the scene provide first aid to the patient, after which they take him to the hospital for further treatment. Basic measures:
- oxygen therapy (use of a special oxygen mask);
- Heparin injection to reduce blood clotting and improve hemodynamic parameters;
- the use of neuroleptics and analgesics in the form of a dropper can relieve pain ( Droperidol, Fentanyl ).
In rare emergency cases, a defibrillator to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation. An electrical discharge can restore the normal rhythm of the heart and prevent it from stopping. First aid for a heart attack in women includes identical measures and manipulations.
Action tactics
If you suspect a heart attack, you should act immediately. First of all, you need to provide rest to the patient, stop performing any exercise, take a half-sitting or half-lying position, which will make breathing easier. You also need:
open a window or provide ventilation to the room;- free your neck, throat and chest from tight clothing;
- breathe steadily, taking deep, calm breaths in and out;
- if chest pain occurs, take a nitroglycerin tablet, placing it under the tongue (not recommended for pressure below 110/70 mmHg;
- if the pain lasts for more than 7–10 minutes, or if it intensifies or worsens, call someone for help, call an ambulance;
- for arrhythmia (rapid, uneven pulse and heartbeat), washing with cold water, a compress on the face or forehead can help;
- in case of dizziness and a state close to loss of consciousness, it is necessary to raise the position of the legs, which will ensure better blood flow to the upper body;
- if vomiting or nausea occurs, do not lie down to avoid aspiration (choking) of vomit;
- While waiting for a doctor, you should not take other medications or attempt self-medication.
Emergency care algorithm
In case of a prolonged attack of angina with chest pain or atypical symptoms lasting more than 5–15 minutes, medical intervention is necessary, otherwise there is a high risk of developing the most acute stage of a heart attack.
In the event of a heart attack, an emergency medical technician or a hospital emergency department doctor urgently provides the following measures:
If the pain syndrome persists, the patient is given one dose of Nitroglycerin, in a tablet, capsule or aerosol under the tongue. The drug is contraindicated in case of a sharp drop in blood pressure, hypotension or collapse.- Another necessary remedy is Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin Cardio or an analogue) in a dosage of 325 - 300 mg.
- At the same time, an electrocardiogram is taken to identify signs of myocardial ischemia (insufficient blood supply) to the heart area, confirming or refuting the diagnosis of unstable angina or heart attack. And an oxygen mask is put on to prevent hypoxia.
- In case of a heart attack with severe chest pain, the patient can be given an intravenous painkiller (Analgin 2.0 - 4.0 50% solution or Promedol, Morphine in a dosage of 1.0 - 2.0 ml 1%).
- For high blood pressure, medications to lower blood pressure are indicated: Propranolol 10-30 mg per day, or Metoprolol 50 mg.
In a hospital setting, the issue of further treatment of the patient is decided. If a heart attack is confirmed and an attack is detected in the first hour, the specialist may prescribe diagnostic coronary angiography or stenting at the Cardiology Center for Vascular Surgery. These minimally invasive surgical techniques are carried out with the aim of identifying a clear area of blockage of a heart vessel, expanding it with the help of a stent to restore patency, blood flow and nutrition of the heart muscle.
In the absence of signs of a heart attack and confirmation of unstable angina, inpatient treatment is required for a period of 10–14 days and subsequent prophylaxis to prevent complications.
Prevention
To prevent the development of a heart attack, you must adhere to certain rules:
- Monitor your diet and weight. Avoid consuming salty and fatty foods and maintain proper drinking regimen. Completely avoid foods and drinks that can increase your blood pressure. Try to eat foods rich in B vitamins, magnesium and potassium.
- Give up such a bad habit as smoking. Nicotine not only provokes the progression of atherosclerosis, but also thickens the blood, causing blood clots.
- Walk in the fresh air, do exercises, and do not neglect therapeutic exercises. Maintain an appropriate level of physical fitness for your age. Regular physical exercise helps stimulate blood circulation and maintain vascular tone, which helps avoid an attack.
- Monitor your blood pressure levels by measuring them twice a day and regularly taking antihypertensive medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Every 6 months, consult a doctor for preventive purposes.
- Do breathing exercises, relaxation and relaxation exercises. Try to avoid stressful situations, or find your own way to put your emotional background in order (yoga, meditation).
Heart attack in men
In representatives of the stronger half of humanity, a heart attack often occurs with complications due to prolonged ignoring of all symptoms. In men, the pain syndrome may be more pronounced.
Heart attack in women
In women, a heart attack is less likely to cause complications. The main symptoms are the same as in men. First aid is provided as standard.