Chlorine is actively used in production and in everyday life; it is present in the form of compounds in any body. Chlorine ions ensure water metabolism, maintain the internal environment of the body, and affect the activity of nerve cells. The daily intake of the substance is 0.8 g and is provided mostly through the intake of table salt.
Being a simple substance, chlorine has a pungent odor, a metallic taste and a yellow-green color. It is highly soluble in water and finds its application in the following areas:
- disinfection of water in waste water;
- fabric bleaching;
- extermination of rodents;
- production of pure metals and plastics;
- production of food additives;
- creation of medicines.
Chlorine is highly toxic, which is why its use in industrial production is prohibited or limited in many countries.
The substance must be used with caution, since burning waste that contains chlorine releases a dangerous poison. In residential premises, the permissible concentration of chlorine is 0.1 mg/m3, in production workshops - 1 mg/m3.
How does chlorine poisoning occur?
Most often, chlorine poisoning occurs in the following cases:
- inhalation of gas vapors;
- if a concentrated aqueous solution comes into contact with the skin and mucous membranes;
- accidental consumption of chlorine-containing liquids or toxic chemicals;
- taking chlorine-containing substances for the purpose of suicide;
- work in production with violations of safety regulations;
- visiting the pool (if the disinfection regime is incorrect).
Household chemicals and chlorine-containing insecticides or pesticides pose a particular danger to children, who may ingest them while playing. Such poisonings in pediatric practice often lead to death.
The use of chlorine and its characteristics
Chlorine is widely used in industry:
- chlorine is used to disinfect water in swimming pools and plumbing;
- chlorine is used to bleach various materials;
- chlorine is used in metallurgy;
- in the production of plastics, rubber;
- for the production of glue, solvents;
- in chemical production in the production of bertholite and other salts, lime, insecticides, household chemicals.
The element is part of table salt, necessary to maintain electrolyte balance and correct blood pressure levels.
The human body contains the element - 0.25%, this is part of the gastric juice, an ion necessary in the formation of blood pressure. Professional swimmers have an increased rate. Since they are in a pool with disinfected water for a long time, the element penetrates into the bloodstream.
Healthcare facilities use chloramine to disinfect disposable and reusable medical products. The popular Domestos gel for disinfecting plumbing fixtures, liquid bleaches for fabrics, and antifungal compounds contain the element.
The gas is part of the chemical chloroacetophenone, the basis of tear gas. Chlorine was previously used as a personal protective equipment for household needs. The police fired gas to disperse the demonstrators. Now, due to the danger and consequences, the composition is being replaced by others.
Cyanogen chloride is a gas that was first used during the First World War as a chemical warfare agent. It is characterized by the fact that it is not sorbed by the coal gas mask charge, i.e. even standard precautions do not save from death.
Chlorine is considered a toxic substance when released in its natural form. Chlorine is extremely toxic; even minimal concentrations of chlorine cause serious health problems.
Since chlorine is heavier than air, when there is a leak, chlorine spreads in a yellow-green mist near the floor and collects in sloping places.
Symptoms of poisoning
Depending on the concentration and time of exposure, there are 3 degrees of poisoning: mild, moderate, severe. At extremely high concentrations of chlorine, a fulminant form of damage can develop.
In case of mild poisoning, the victim makes the following complaints:
- hyperemia of the conjunctiva, oral mucosa;
- sore throat;
- sneezing, dry cough;
- lacrimation, discharge of clear discharge from the nose (rhinorrhea);
- burning in the eyes.
Symptoms of moderate to severe intoxication:
- severe general weakness;
- depression of consciousness;
- hoarseness of voice;
- frequent shallow unproductive breathing;
- short-term pauses in breathing, suffocation;
- annoying painful cough, initially dry, then wet, with foamy pink sputum;
- chest pain that gets worse with coughing;
- decreased blood pressure (blood pressure), decreased heart rate;
- headache, dizziness;
- convulsions;
- nausea, vomiting.
In the clinic of moderate and severe chlorine intoxication, 3 periods can be conventionally distinguished: a latent period (maximum up to 1 day, on average 4-6 hours), a period of pulmonary edema and resolution (3-4 days), ending with recovery or worsening of the condition due to the addition of a secondary infections.
The fulminant form of chlorine intoxication develops within 5-30 minutes: a persistent spasm of the larynx occurs with a narrowing of the glottis, leading to respiratory arrest, cyanosis, swelling of the veins in the face and neck, loss of consciousness, convulsions, involuntary urination and defecation. With this form of poisoning, as a rule, the death of the victim occurs.
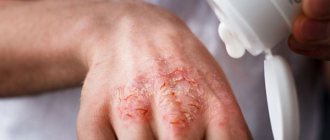
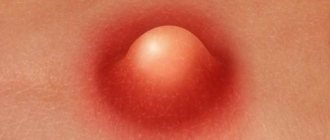
If a concentrated chlorine solution comes into contact with the skin, acne and contact dermatitis (redness and peeling of the skin, intense itching at the site of contact) may occur.
If poisoning is caused by ingestion of chlorinated water, abdominal pain and loose stools occur.
Source: depositphotos.com
Diagnostics
Chlorine poisoning, the symptoms and treatment of which is most often diagnosed and initiated by the ambulance doctor or paramedic who first arrived to the victim, is necessarily determined in several ways.
Inspection and collection of information
The primary determination of the causes of poisoning in the patient’s body is carried out as a result of examining the victim and interviewing witnesses who help determine the degree of poisoning.
If the enterprise has a medical worker, he can begin to provide emergency care and help the emergency doctor in determining the diagnosis. After diagnosis, the doctor immediately provides first aid to the victim, and then takes the patient to the intensive care unit.
In the department, the diagnosis of poisoning is confirmed by an examination by a toxicologist and an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. For further treatment, a pulmonologist or neurologist may be invited to the patient for consultation.
Doctors use the following indicators as the main signs of chlorine poisoning:
- rapid pulse more than 90 beats/min;
- pale skin
- increased agitation and breathing disorders;
- wheezing when breathing;
- lowering blood pressure in severe poisoning.
Additionally, the department conducts an examination of the victim, which includes:
Blood analysis
- A blood test can detect electrolyte imbalances and low (less than 7.3) pH levels. The doctor notes a reduced amount of oxygen and a large amount of carbon dioxide in the patient’s blood. The patient's blood becomes viscous and its coagulability increases. A blood test from a vein is performed in the intensive care unit or sent to a medical laboratory. Its cost is 700 rubles.
Spirography
- A spirograph allows you to determine respiratory failure and its degree.
The device allows you to use a nozzle to measure inhalation/exhalation volume, lung capacity and other breathing features in a hospital setting. The study is carried out on special equipment in a hospital or medical center. Its cost is from 1500 rubles.
Pulse oximetry
- Such a study allows you to determine the level of saturation with liquid blood gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide). If less than 94% oxygen is present in the blood, respiratory dysfunction is diagnosed. To establish the oxygen level, an external pulse oximeter is used, which, thanks to the analysis of capillary blood, allows you to evaluate the indicators within 3-5 seconds. A saturation study is carried out in a hospital to speed up the examination process, but in a medical laboratory the cost of such an analysis is 300 rubles.
ECG
- An ECG allows you to determine a change in cardiac function: an increase in heart rate or a slowdown; there may be disturbances in the pulse rhythm. The RR interval sharply decreases with the development of tachycardia, or, on the contrary, its increase is noted with bradycardia or partial AV block. An ECG is performed by an ambulance crew at the scene of an accident or in a hospital. The cost of the procedure is 600 rubles.
First aid for chlorine poisoning
In case of chlorine poisoning, it is necessary to evacuate the victim from the source of the lesion or interrupt contact with the toxic substance, and then call an ambulance, and only then begin providing first aid.
- Provide access to oxygen by opening a window and unbuttoning tight clothing.
- Wash your eyes, nasal passages, rinse your mouth with a 2% solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon of soda per 200 ml glass of water) or plenty of running water.
- Give alkaline drink (mineral water, milk).
- Inhale with baking soda.
- Apply Vaseline or olive oil into your eyes.
- Provide physical and psycho-emotional peace.
- If poisoning is caused by drinking chlorine-containing liquid, it is necessary to rinse the stomach (to do this, drink 1–1.5 liters of warm water and induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue).
Video: what happens if you drink bleach
Read further:
List of the best antibiotics for food and alcohol poisoning
Oxygen cocktail: benefits and harm for the body of children and pregnant women
Solvent vapor poisoning - first aid
Soda poisoning - how to treat, proper preparation of soda solution for children and adults
How to properly detoxify the body?
Article rating:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Share with friends:
You may also be interested in:
Arsenic poisoning - symptoms and causes, first aid and consequences
First aid for carbon monoxide poisoning for children and adults
Poisoning with heavy metal salts - symptoms and treatment
Poisoning with FOS - is there an antidote, first aid for intoxication?
When is medical attention required?
If there is a suspicion of chlorine poisoning, it is necessary to seek qualified help in 100% of cases.
Since it is not always possible to assess the degree of poisoning by clinical manifestations in the first hours, the victim should be under round-the-clock medical supervision for the first 24 hours. This is necessary to promptly prevent the development of life-threatening complications.
Treatment of chlorine poisoning is carried out in a hospital setting. The victim is provided with oxygen supply, hemodynamics are stabilized, vital functions are supported - breathing, cardiac activity, metabolic processes. Prevention of complications and symptomatic therapy are carried out.
How can you get poisoned by bleach?
Poisoning with chlorinated substances can have a very serious effect on the body. Moreover, in the absence of help or in case of severe intoxication, everything can end in the death of the victim.
You can be poisoned by bleach for several reasons:
- after inhaling its toxic fumes,
- in case of accidental ingestion (if the solution ends up in the hands of a child),
- when intentionally ingested (for the purpose of committing suicide),
- in cases of poison penetration through the skin.
Unintentional ingestion of chlorine can also occur in a swimming pool if the content of this disinfectant in the water significantly exceeds the norm. For the same reason, you should not drink raw tap water, especially if it gives off a distinct smell of chlorine.
You can inhale chlorine fumes if cleaning or disinfection is carried out in a room without ventilation, and if the rules for preparing the working solution are violated. Neglecting protective equipment can also cause bleach intoxication.
Possible consequences
Complications with mild poisoning are usually absent, symptoms persist for up to several days, and health is completely restored.
In moderate to severe cases, the following complications may develop (both acute and subsequently becoming chronic):
- conjunctivitis;
- diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract (pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, tracheobronchitis, bronchitis);
- bronchiectasis;
- toxic pneumonia;
- toxic pulmonary edema;
- emphysema, pneumosclerosis;
- paralysis of the respiratory and vasomotor centers;
- acute heart failure.
Treatment
An antidote to chlorine-containing products has not yet been invented, so treatment for bleach poisoning will be carried out in other ways:
- intravenous hormones (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone),
- blood oxygen saturation,
- stabilization of blood composition,
- antibacterial therapy for mucosal lesions,
- restoration of acid-base balance,
- if necessary - mechanical ventilation,
- relieving pulmonary edema.
All these actions are carried out in the intensive care or toxicology department of the hospital and are aimed at improving the patient’s condition, as well as reducing the risk of consequences.
Prevention
To prevent chlorine poisoning in enterprises, it is necessary to comply with workplace safety requirements.
At home:
- When using chlorine-containing detergents, ensure adequate ventilation and do not work with them indoors;
- do not come into contact with concentrated chlorine solutions without gloves;
- treatment with insecticides and pesticides should only be carried out while wearing a protective mask and goggles;
- store pesticides out of the reach of children;
- When visiting the pool, do not swallow water.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Chemical properties
Chlorine is a yellow-green, asphyxiating gas with a strong, pungent odor. Easily liquefied and mixed with water. In liquid form, the substance is highly corrosive.
Chlorine can be used for the following purposes:
- bleaching fabrics and paper;
- production of disinfectants and insecticides;
- production of plastics, synthetic fibers, dyes, solvents;
- disinfection of drinking water.
In the human body, chlorine-containing compounds are present in small doses in the form of macroelements that participate in many biological processes.
Is a chemical element responsible for the development of cancer?
After the end of World War II, scientists conducted research on this topic for three decades. It has been proven that chlorinated liquid promotes the accumulation of carcinogenic substances, which have a lethal delayed effect on the body.
Harm can be caused in two ways: inhalation of vapors and absorption of carcinogens through the skin. It is believed that overuse of hot showers is as dangerous as drinking chlorinated liquid. Volatile organic toxic substances released during bathing are inhaled by humans in very high concentrations. Most of all, patients suffer from cancerous tumors of the liver, lungs, digestive organs, and bladder. Therefore, it is very important to know how to get rid of chlorine in tap water. Below we will give recommendations on this issue; you can also use traditional methods. But this is considered a long-term event. You can use an alternative method and install a filter in your house or apartment for cleaning from someone competent in this field. Specialists will help you in choosing equipment and installation.
How to remove chlorine from tap water - removal methods
We present to your attention step-by-step instructions, following which you can neutralize the negative impact of the reagent.
Getting rid of the smell
Rub your hands with any citrus juice (lemon, orange, grapefruit) or a tomato slice. Wait about a minute, so the liquid will be better absorbed into the pores of the skin, and then rinse off.
If the problem cannot be solved, then make an exfoliating scrub using baking soda or coffee in a 1:1 ratio. Apply the cream to your brushes and massage them for 2-3 minutes.
We carry out moisturizing
Coconut, olive, almond, flaxseed oil or natural soap based on these ingredients are suitable. Apply a few drops of the composition or soap your hands. Remove excess oil with a dry cotton swab and rinse off the soap. This way you will get rid of the unpleasant odor and at the same time moisturize your hands.
People's Councils
Choose the product that you have on hand. It could be:
- Flower petals rich in aromatic oils: rose, peppermint, lavender, rosemary, geranium. In a private home, fragrant plants can be an alternative to flowers: parsley, currant leaves.
- A slice of lemon will also get rid of the smell.
- If there is no damage to the skin (cuts, abrasions, hangnails), then try toothpaste.
- Cow's milk is a gentle remedy. Place your hands in the milk product bath for a few minutes and then rinse them.
AMETHYST - 02 M Residential building for up to 10 people or up to 2 cubic meters/day.
Aeration unit AS-1054 VO-90
Main table dispenser AquaPro 919H/RO (hot and cold water)
How to use chlorine products correctly
If you trust the old disinfection method, proven over the years, rather than modern drugs, then try to protect yourself and others:
- Make the solution in a well-ventilated area.
- Clean with doors and windows wide open.
- Wear rubber gloves on your hands and protect your nasopharynx with a respirator.
When the first symptoms of poisoning appear (dizziness, nausea, watery eyes, rapid heartbeat), do not self-medicate, but go to the hospital.
How to neutralize chlorine and how to purify water from it at home
We warn that without special equipment it is unlikely that it will be possible to get rid of the reagent 100 percent. You can only significantly reduce its concentration. This can be done by installing stationary cleaning equipment for household use. We offer several model options designed for different purposes.
Normal carbon content
If the liquid supplied to your apartment or house does not have a strong odor and the color does not bother you, then most likely its concentration complies with the standards adopted in our country. However, in this case it is worth playing it safe and installing an additional filter.
It could be:
- Jug.
- Built-in system under the kitchen sink.
- Attachment on the crane.
We recommend that you do not buy the first model you like, but first do a laboratory analysis of the drinking resource. Please contact specialists from competent companies with the results of your research. Our managers will select the appropriate option.
How to remove and remove chlorine from tap water if its concentration is prohibitive
Strong chlorination is immediately visible; the liquid from the tap will be white and have a repulsive odor. In this case, you will have to “chip in” with your neighbors at the entrance and install a common house filtration system that works on the principle of reverse osmosis. There is no other option!
Other cleaning methods
Unfortunately, in the Russian Federation there is no other alternative to chlorination. Of course, this method neutralizes viruses and bacteria, but ultimately causes irreparable harm to human health. There are two simple ways to minimize negative impacts at home:
- Boiling. An electric kettle is not suitable for this purpose, since boiling occurs rapidly, which does not entail the death of all pathogenic microorganisms. It is better to use a gas burner and a regular metal kettle. Important: re-boiling is prohibited; the remainder must be poured down the drain.
- Advocacy. Any container of various sizes with a wide neck is suitable for this. There is still debate about how long it takes for water to settle from bleach. It is advisable to wait about six hours. Half of the liquid is suitable for drinking; carefully pour it into a new container and discard the rest.
How to protect yourself and remove chlorine from water - cleaning methods
Since the problem is not being solved at the state level, we will have to act independently.
The negative impact of the reagent can be reduced by the following methods:
- Shower heads are sold in specialized stores. They significantly reduce chloride concentration levels.
- After taking hygiene procedures, use softening oils and creams.
- Bath small children in a liquid with the addition of a solution of soda ash or milk of lime (you can ask the pharmacist for the recipe).
The effects of chlorine on the body
Constant exposure to even small doses of chlorine (the physical state can be any) on the human body threatens people with the following:
- Pharyngitis.
- Laryngitis.
- Bronchitis (acute or chronic form).
- Various skin diseases.
- Sinusitis.
- Pneumosclerosis.
- Tracheitis.
- Deterioration of vision.
If you have noticed one of the ailments listed above, provided that you have been constantly or once (cases of visiting a swimming pool also include) exposed to chlorine vapor, then this is a reason to contact a specialist as soon as possible! The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive diagnosis to study the nature of the disease. After studying its results, he will then prescribe treatment.