Approximately every second man over 50 knows firsthand what prostatitis is. This disease is an inflammatory process that occurs in the tissues of the prostate gland. As a result, a malfunction of the genitourinary system occurs. The symptoms of prostatitis in men are quite specific. To prevent complications, people over 35 years of age are recommended to undergo regular medical examinations, which makes it possible to detect the disease at the initial stage.
What is prostatitis?
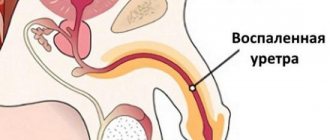
Prostatitis
is an inflammation of the prostate gland, which is called the prostate. The prostate gland is a minor part of the male reproductive organs. It is located under the bladder, around its neck. The fact is that the urethra passes through the prostate, that is, the prostate is located around the urinary tube. As a result, when the prostate enlarges, the urinary canal is compressed, which interferes with the passage of urine.
In men over 35 years of age, the prostate often becomes enlarged. This is a typical occurrence. Most of the diseases in men over 50 years of age are just a consequence of disruption of the genitourinary system, that is, as a result of inflammation of the prostate gland. We must remember that the larger the prostate gland, the more urine will be blocked, thereby the body will be increasingly poisoned by this urine.
The disease is quite common and is diagnosed in more than 80% of sexually mature men, of which approximately 30% are detected in the age category from 20 to 40 years. If we refer to statistical studies, we can say that prostatitis is detected in every 10 patients.
[Video] I.A. Izmakin, chief urologist at the Euromedica clinic, talks about what prostatitis is:
- What happens if prostatitis is not treated?
Prevention
The urologist will tell you the best way to treat prostatitis after examining the patient. But, like any other disease, it is easier to prevent prostatitis than to get rid of the consequences of the disease. To do this you need:
- To live an active lifestyle. Regular exercise prevents congestion in the pelvic area and improves blood circulation. The following have a good effect: swimming, race walking, dancing, fitness. At the same time, you should avoid strength sports.
- Provide yourself with proper nutrition. It is worth limiting the amount of fried, salty, fatty, spicy, pickled and smoked foods. The basis of the diet should be: fresh vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products, cereals. It is important to adhere to the drinking regime.
More information about nutrition for prostatitis in men can be found here.
Is there a way to prevent the disease and who needs it first? Borisov Vladimir Viktorovich, professor, doctor of medical sciences says:
- Avoid casual sex.
- Have a regular sex life. For a middle-aged man, the norm is to have sex several times a week. This promotes natural massage of the prostate gland, which significantly reduces the risk of the growth of various bacteria in it.
- It is important to avoid hypothermia.
- It is necessary to undergo an examination by a urologist annually.
After 35 years, every man is obliged to monitor his health, since during this period the risk of developing prostatitis increases. To prevent the onset of the disease, it is important to follow simple preventive measures and undergo regular medical examinations, which will help identify the pathology at the initial stage, when it is easily treatable.
Causes of prostatitis
The causes of prostatitis are the following:
- The main cause of prostatitis is impaired blood circulation, which leads to an enlarged prostate. The cause of poor blood circulation is a sedentary lifestyle, as well as excess weight.
- Another cause of prostatitis is infection. Often the infection can occur as a result of gonorrhea or urethritis, less often as a result of complications of sore throat, flu, or tuberculosis.
- Bacterial inflammation of the prostate
begins when infectious agents enter the prostate gland through the blood, lymph, during unprotected sexual intercourse, in other words, through biological fluids of the body. Various microorganisms that are constantly present on the human skin, or even in the abdominal organs, such as the intestines, can, under certain conditions, trigger the development of the disease.
- Injuries to the organs and soft tissues of the pelvis, and disruption of their blood circulation are often the cause of prostatitis. As a rule, this most concerns drivers whose work is associated with occupational hazards - constant vibrations, shaking, increased load on the perineal muscles.
- The development of the disease is also facilitated by frequent hypothermia and low physical activity, the presence of chronic genitourinary diseases or hormonal imbalance, urinary retention and irregular sex life.
With vigorous sexual activity, men quickly experience nervous and physical exhaustion, the functioning of the hormonal system and the secretions of the gonads are disrupted, leading to a gradual decrease in potency. Interrupted sexual intercourse also has a negative impact on men's health.
[Video] Program Live Healthy! “Is coitus interruptus good or bad?”:
- Sedentary lifestyle
affects the functioning of the endocrine, nervous and cardiovascular systems. There is a deterioration in the blood supply to the pelvic organs with congestion, oxygen starvation of prostate tissue - all this predisposes to the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which in turn can cause the development of prostatitis. All these factors are not the root cause of the formation of the inflammatory process, but serve as entry points for infection to enter the prostate gland.
- Presence of inflammation in the rectum
or the urethra often becomes the cause of secondary infection of the prostate gland - ascending type, if microbes rise upward from the external urethral canal, or descending type, when microbes enter the prostate from infected urine.
- Chronic constipation is a predisposing factor for the development of prostatitis. Constant bowel dysfunction can lead to inflammation in the prostate.
- The immune system plays an important role in the development of this disease. Due to bad habits, emotional experiences, poor nutrition, physical fatigue, the immune system weakens, and the human body becomes vulnerable to infectious agents of various kinds, including those that cause inflammation of the prostate gland.
- Among the causes of prostatitis are urological infections
and some past sexually transmitted diseases, such as gonorrhea or urethritis. Even such chronic diseases in the body as bronchitis, tonsillitis, untreated carious teeth can be the cause of this disease.
General symptoms of the disease
The first signs of prostatitis in men may be as follows:
- Decreased libido can be called the first symptom indicating the presence of inflammation in the prostate gland. A healthy man should have an erection every morning. Prostatitis may manifest itself in that it occurs irregularly or is completely absent. In this case, a man may notice that the penis is not able to become hard enough for sexual intercourse. The seminal fluid becomes thin and cloudy.
- Urge to urinate at night. A healthy man will not wake up at night to go to the toilet. The patient may be bothered by a feeling of incomplete emptying. This is how the disease can manifest itself at the initial stage.
- Pain experienced by approximately half of all patients with prostatitis. They are aching in nature and concentrated in the pelvic area. Pain may occur during urination or ejaculation. Any discomfort that a man experiences in this area is a reason to visit a doctor.
These are only the first symptoms of prostatitis, which are characteristic of each type of disease.
Other symptoms include:
- Unpleasant sensations during bowel movements.
- A burning sensation in the perineum and urethra (cutting in the urethra in men).
- Fast fatiguability.
- Psychological depression and depression.
- Mucus threads can be seen in the urine.
These symptoms are secondary and depend on the type and degree of prostatitis, which can have a variable clinical picture.
Review of the best methods for diagnosing prostatitis in men.
Signs of prostatitis
Signs of acute prostatitis
are an increase in body temperature and frequent urination, which is accompanied by pain and weak pressure. In addition, signs of prostatitis include burning of the perineum and pain in the rectum during bowel movements. In the stage of purulent inflammation, spontaneous opening of the abscess and leakage of pus from the urethra or rectum is likely.
A sign of chronic prostatitis
there is a burning sensation in the urethra and perineum, discharge of pus at the end of defecation or urination, increased fatigue and irritability of the body.
[Video] I.A. Izmakin, chief urologist at the Euromedica clinic, talks about the signs by which prostatitis can be identified:
Difficulty urinating with prostatitis is very dangerous, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to acute urinary retention.
Men should not ignore such indirect signs of the development of prostatitis as a complete or partial decrease in libido, accelerated ejaculation, sometimes painful, and prolonged erection at night. All these symptoms are characteristic of inflammation of the prostate gland, even in an uncomplicated stage and amenable to adequate treatment.
If we talk about manifestations visible even to a non-specialist, then in most cases patients notice clear or sometimes purulent discharge from the urethra, especially noticeable in the morning, and the presence of white flakes and threads in the urine.
Article on the topic
— how to improve potency at home?
Illness in young people
The main cause of prostate inflammation in young men most often lies in an unhealthy lifestyle: young people spend little time outdoors, do not play sports, and spend a lot of time sitting at the computer. This leads to the fact that by the age of 30, young men become regular patients of a urologist and treatment takes a long time. The cause of chronic prostatitis in young people can be constant stress and mental stress, especially for students. In addition, many young men who are busy with their careers do not yet have a family or a permanent sexual partner at the age of 30, and a promiscuous sexual life is also a provoking factor, which can lead to prostatitis. In adolescence (15-16 years), prostatitis can be triggered by hormonal changes in the young body, as well as reduced immunity, if proper treatment is not carried out.
There are many causes of chronic prostatitis, they vary depending on age, but at 30, 40, and 80 years old, at the first signs of the disease, you must consult a doctor and in no case self-medicate: do not take antibiotics, diuretics, etc. other tablets. This can lead to the most severe consequences, such as prostate dysfunction.
Symptoms of prostatitis
Acute form.
Like many diseases, prostatitis is divided into acute and chronic. General symptoms are characteristic of the manifestation of an acute form of the disease.
- The patient develops general weakness, obvious malaise
- Often accompanied by fever, headaches
- As a rule, pain in the perineum is pronounced, covers the groin area and intensifies during urination or defecation.
- The feeling of frequent urge to go to the toilet, which does not bring relief due to incomplete emptying of the bladder, leads to increased irritability and nervous excitability of patients. In severe cases, acute urinary retention develops.
Chronic form.
Unlike the acute form, the chronic form of prostatitis is asymptomatic and occurs latently (that is, without pronounced characteristic signs). The clinical picture is often blurred, with mild symptoms; patients do not pay due attention to the obvious discomfort and do not consider it necessary to seek medical help, confusing the symptoms of prostatitis with prostate adenoma, which is extremely dangerous. The principles of treatment for these diseases are completely different, as are possible complications with undesirable consequences.
Men often attribute deterioration in general well-being, problems with potency and nervous disorders to fatigue and lack of rest, that is, a person simply does not want to realize that he is sick and needs treatment. Annual preventive examinations play an important role in the timely detection of this disease, allowing diagnosis to be made at the earliest stages.
White flakes in urine. The chronic form of inflammation of the prostate is expressed in fast-passing, mild pain in the perineum, in the pubic and groin areas. As a rule, the duration of sexual intercourse changes, both in the direction of lengthening and vice versa and the brightness of sexual sensations. Discharge appears from the urethra, especially in the morning, or white flakes are visible to the naked eye in the urine (if you take it into a glass, you can see the flakes in the form of white smoke).
Poor urination. Since the inflammatory process leads to the narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, urination disorders occur, which men should pay attention to first of all: the stream of urine becomes weak, urination may be drop by drop or difficult at the beginning or at the end. Many patients experience a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder or uncontrolled leakage of urine.
Frequent urination. The inflammatory process irritates the nerve endings, leading to frequent urination, especially at night, usually in small portions. All these symptoms clearly indicate the development of a pathological process and require immediate consultation with a doctor. Only a specialist can establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. Unfortunately, these symptoms may hide a terrible disease such as prostate cancer.
[Video] Doctor Evdokimenko “Chronic prostatitis - lie or truth?”:
Types of prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland is usually divided into 4 categories:
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Asymptomatic chronic.
- Chronic prostatitis of bacterial origin.
The acute form is diagnosed quite rarely and is associated with a bacterial infection, which is always severe. The patient experiences acute pain, body temperature rises, and general weakness of the body occurs. Visual examination shows an increase in the size of the prostate. This type of disease requires urgent treatment, as it can cause various complications.
The chronic type of the disease is associated with constant pain that bothers a person for more than 3 months in a row. A urine test in this case will show the presence of pathogens.
The asymptomatic type of prostatitis has practically no characteristic signs and symptoms. It can be detected during a regular medical examination or when visiting a doctor about another disease.
Chronic prostatitis of a bacterial nature is most often associated with the active development of Escherichia coli. This can be facilitated by a decrease in the body’s defenses, operations of the pelvic organs, and the presence of a source of infection. This type of disease is characterized by a sluggish course, and its symptoms are similar to the manifestation of an acute form of inflammation.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
A urologist is involved in identifying prostatitis. It diagnoses the very fact of damage to the prostate gland. Based on the symptoms of the disease, the doctor can already determine the stage of its development during the first appointment. The man will definitely undergo a prostate ultrasound.
Possible diagnostic measures:
- Taking prostate juice and analyzing it is the main method for diagnosing prostatitis.
- Taking a smear from the urethra. The resulting secretion is sent for bacteriological testing.
- Submission of urine for analysis.
- PSA level assessment. It is a protein of the prostate gland.
If the data obtained is not enough to make a diagnosis, the patient is admitted to a hospital and a urodynamic examination is carried out in its conditions.
Cystoscopy is a method for diagnosing prostate diseases, during which the doctor can perform some therapeutic procedures. However, they rarely resort to it.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a urologist can determine the presence of prostatitis. After the examination, he may prescribe additional examination:
- Physical examination - palpation of the prostate, during which it is possible to determine the condition and size of the gland.
- Transrectal ultrasound.
- Analysis of a smear or prostate secretion for the presence of leukocytes and bacteria.
- Clinical analysis of urine, in which protein, leukocytes and bacteria can be detected.
- Ejaculate analysis.
We have written a detailed article describing how a semen analysis (spermogram) is carried out and how to prepare for the procedure.
- Cytological analysis of urine.
- Bacteriological urine analysis.
- PSA protein level analysis.
- Urodynamic study.
- Cytoscopy. It can be prescribed only if indicated, in case of injury or in preparation for surgery.
Treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis
Although a disease such as prostatitis has long been known and is widespread among men of all ages, it is quite difficult to treat.
Treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis directly depends on how severe the symptoms of the disease are. Sometimes the patient’s condition is extremely severe, which often occurs due to intoxication of the body.
The disease manifests itself acutely, the body temperature rises sharply, chills, pain in the pelvic area, lower back, and perineum appear. Nausea and vomiting may occur, disruption of the process of emptying the bladder with pain, burning sensation, etc. This condition is dangerous due to its complications. Possible addition of a bacterial infection, development of prostate abscess, septicemia and septicopyemia. Most often, complications arise against the background of existing chronic diseases, for example, in the presence of diabetes mellitus.
If the disease is acute, the man must be hospitalized in a hospital, in the urology department. If this is not possible, then the patient is assigned to the general surgical department.
There are general treatment tactics for managing patients with acute prostatitis:
- Maintaining bed rest.
- Prescription of antibacterial drugs.
- A ban on prostate massage even for the purpose of obtaining prostate secretions. The ban is due to the high risk of developing sepsis.
- Prescription of drugs aimed at normalizing blood microcirculation, increasing its fluidity and viscosity. For this, drugs such as Detralex, Pentoxifylline, Cavinton, Trental are administered intravenously. Thanks to the effect of these medications, it is possible to achieve the outflow of lymph and venous blood from the inflamed gland, reduce toxic manifestations and remove decay products from the body.
- Oral administration of NSAIDs: Ketoprofen, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Piroxicam. They are prescribed to reduce pain.
- It is possible to use other analgesics, for example, Nimesil, Nise, Tempalgin, Ketanov. In addition to reducing pain, these medications eliminate inflammation to some extent. In their practice, urologists and andrologists widely use rectal suppositories to provide analgesic effects and reduce inflammation. They contain the same components as tablet preparations, but thanks to local administration, the effect is enhanced. You can use suppositories for prostatitis with propolis.
- If the patient suffers from severe intoxication of the body, the administration of rheological solutions, for example, Hemodez or Neocompensan, as well as detoxification agents and electrolytes, including solutions of Disol, Trisol, Lactosol, Ringer's solution, potassium chloride solution with the addition of glucose, is indicated.
Surgery is necessary if the ability to empty the bladder independently is completely absent, or a prostate abscess has formed.
The use of antibiotics to treat bacterial prostatitis is mandatory. If the disease begins acutely and symptoms of intoxication are present, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed as quickly as possible; waiting for the results of tests for bacterial flora in this case is impractical and dangerous.
Treatment BEFORE receiving test results. Medicines are selected from the group of fluoroquinolones. This may be Levofloxacin (Eleflox, Tavanic), Ofloxacin (Zanocin, Ofloxin), Ciprofloxacin (Ciprobay, Tsifran, Tsiprinol). Such empirical therapy is due to the fact that fluoroquinolones are active against bacteria that most often provoke prostatitis - these are gram-negative pathogenic flora and enterococci. In addition, fluoroquinolones have a detrimental effect on gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria, as well as on atypical infectious agents, such as chlamydia. By introducing itself into the metabolic processes of protein metabolism of bacteria, the antibiotic destroys their nucleus, leading to the death of the microorganism.
However, a number of scientists are against prescribing fluoroquinolones until test results have been received. They point out that if bacterial prostatitis is caused by Koch's bacillus, this will lead to its resistance, mutations and the formation of a new, more pathogenic flora, which is very difficult to get rid of. Therefore, it is so important to make sure that there are no tuberculosis bacteria in the body.
Side effects. Depending on the clinical picture of the disease, fluoroquinolones can be prescribed either intravenously or intramuscularly. If the liver and kidneys are impaired, the risk of side effects is 3-17%. However, most often patients complain of disturbances in the digestive processes, and also experience certain disorders of the central nervous system. A drop in blood glucose levels, the development of photosensitivity (increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet radiation), heart rhythm disturbances - all these are infrequent complications from the use of fluoroquinolones and they occur in no more than 1% of cases.
Treatment AFTER receiving test results. When the results of laboratory tests are received, the therapeutic regimen can be reconsidered if the identified inflammatory pathogen is not sensitive to fluoroquinolones. This group of drugs must also be replaced if, after 24-48 hours from the start of taking them, the patient’s condition has not improved, or if he does not tolerate them well. The drugs of choice in this case are macrolides (Azithromycin, Sumamed), Trimethoprim, Doxycycline, antibiotics from the cephalosporin group (Cefepime, Cefotaxime, Kefzol, Cefazolin, Cefpirome).
If recovery does not occur after 14 days from the start of taking medications, then the treatment regimen should be adjusted again.
Leading Russian and foreign urologists have a common point of view regarding the timing of therapy. They claim that it cannot last less than 14-30 days. After completing the intake of antibacterial agents, a repeated, in-depth diagnosis with ultrasound of the prostate and taking prostate secretions for bacterial culture must be carried out. If the identified microflora can be controlled with the help of medications taken, and the patient feels well, then treatment is extended for another 14-30 days. As a result, the total period of taking antibiotics will be from a month to two. When it is not possible to completely relieve inflammation, it is advisable to change the therapeutic tactics.
Patients whose disease is severe are subject to hospitalization in intensive care wards.
Basic medications for the treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma
Next, we will describe in more detail the drugs that are most often prescribed by doctors for prostatitis and are the most effective in combating the disease.
Adenorm
Adenorm is a drug prescribed for the treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia (adenoma). Belongs to the group of alpha adenoblockers. Available in capsule form. The main active ingredient of the drug is tamsulosin hydrochloride. This component helps reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostate gland.
Adenorm does not apply:
- in childhood;
- with severe liver failure;
- with postural hypotension (decreased pressure when standing).
If taken uncontrolled and contraindications are not observed, the drug can lead to the following undesirable effects:
- dizziness;
- rhinitis;
- skin rash accompanied by itching and redness;
- asthenic syndrome;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- strong heartbeat.
The frequency of use of Adenorm is 1 time per day. The capsule is washed down with plenty of water. The dose should be taken in the morning before meals.
When taking the drug, especially in the first days, those who work with complex mechanisms and drive a car should be careful.
Bazetam
Basetam is prescribed for dysuric symptoms that are observed in the urinary tract during benign prostate hyperplasia. Available in capsule form. Belongs to the group of alpha-blockers. The main active ingredient of Basetam is tamsulosin hydrochloride. After taking the drug, the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostate and bladder decreases. Thanks to this, the normal process of urination is resumed and pain is eliminated.
Side effects caused by Basetam include dizziness, headache, lightheadedness, tachycardia, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Contraindications include severe renal and hepatic damage and the presence of postural hypotension.
Bazetam is taken in the morning, preferably before breakfast. Frequency of administration – no more than once a day. The course of treatment is 12-14 days.
Peponen Active
Peponen Active is a herbal preparation that contains pumpkin seed oil. Prescribed for the treatment of prostatitis and its prevention.
The main active ingredient restores the functions of the prostate gland due to its anti-inflammatory effect and improved microcirculation. In addition, the substances contained in pumpkin seed oil resist the production of the hormone dihydrotestosterone, which is responsible for prostate growth, improve kidney and liver function, and cleanse the intestines of waste and toxins.
Pepoten Active should be used 3 times a day, 1 capsule after eating. Capsules are washed down with plenty of water. The course of treatment is 1 month.
Side effects after taking the drug are rare. The reaction is mainly observed from the gastrointestinal tract - nausea, abdominal pain, heartburn. If the drug is taken for a long time, stool upset may occur.
Contraindications include ulcers of the gastrointestinal mucosa in the acute stage, cholelithiasis.
Peponen
Peponen is prescribed for functional disorders in the urethra due to prostate adenoma. The drug is available in capsule form. The main component of the medicine is pumpkin seed oil.
Peponen is well tolerated by patients. Only sometimes does an allergic reaction to the main active ingredient occur. In addition, in rare cases, when taking the medicine for too long, loose stools are observed.
The drug has no contraindications, except for individual intolerance to pumpkin seed oil.
Peponen should be taken three times a day, 1-2 capsules, regardless of meals. The duration of therapy is determined by the treating doctor.
Prostamed
Prostamed is a herbal preparation used to treat prostatitis in the chronic stage, prostatic hyperplasia, accompanied by urination problems. The composition of the medicine includes:
- pumpkin seed powder;
- goldenrod extract;
- aspen leaf extract;
- pumpkin globulin.
The drug is available in tablets. Prostamed is well tolerated by patients because it has a herbal composition. Only rarely can allergic reactions to the components of the medicine be noted.
Take Prostamed 3 times a day, 2-4 tablets. Duration of therapy is 12 weeks.
Prostate Plus
Prostate Plus is a biologically active food supplement for men suffering from prostate diseases. Available in tablet form. The product includes:
- pumpkin seed powder;
- selenium;
- zinc;
- citrus pectin;
- nettle extract;
- lycopene, obtained from tomatoes;
- African palm fruit extract;
- African plum bark extract.
Prostate Plus should be taken at the same time, once a day, during meals, with water. Duration of admission – 30 days. The medicine for prostatitis is well tolerated by men and does not cause side effects. In isolated cases, patients experience an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
Flosin
Flosin belongs to the group of alpha-blockers. The main element is tamsulosin hydrochloride. The medicine eliminates dysuric symptoms such as urinary retention, frequent urination, pain during urination, which are caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The main active component helps to relax the smooth muscles of the prostate, improve the outflow of urine, patency of the urinary tract, relieve spasm, pain and eliminate irritation.
The drug is taken once a day in the morning. The capsule is washed down with a glass of water and is not chewed. Flosin is taken after breakfast.
Side effects include:
- headache, nausea, dizziness, drop in blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- rhinitis;
- skin rash, urticaria;
- constipation;
- ejaculation disorder;
- asthenia.
Flosin is contraindicated for people with severe liver failure, orthostatic hypotension, or sensitivity to the active ingredients.
Homvio Prostan
Homvio Prostan is a herbal preparation prescribed for diseases of the prostate and genitourinary system in men. The product eliminates pain, relieves inflammation, and relieves spasms.
The main indications for use of the drug are:
- benign prostatic hyperplasia;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- chronic and acute urinary retention;
- enuresis, pyelonephritis;
- renal colic;
- urolithiasis disease.
Medicine for prostatitis is available in the form of drops. You need to take 5-15 drops at a time. The frequency of use of the drug is 3 times a day. The duration of treatment depends on the pathological process, but should be at least 6 weeks. Homvio Prostan should be drunk half an hour after or before meals, slowly dissolving in the mouth.
Contraindications include individual intolerance to the components of the drug and children under 12 years of age. As for undesirable reactions, they rarely appear and only in the form of allergies.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Treatment for chronic prostatitis directly depends on the stage of the disease. If the disease worsens, treatment is similar to that for acute bacterial prostatitis.
When the disease is in remission, a man will experience the following symptoms:
- Minor painful sensations that occur rarely but regularly;
- A feeling of heaviness in the prostate area, lumbosacral area, and genital area;
- In some cases, dysuric disorders are added: increased urge to urinate, pain during bladder emptying, etc.;
- There may be a deterioration in psycho-emotional well-being, depressive moods against which sexual failures occur.
As a rule, the chronic form of the disease is treated with the following recommendations:
- Prostatilen and Vitaprost help relieve swelling from prostate tissue, eliminate the leukocyte surge, reduce the risk of blood clots, and normalize blood microcirculation. There is research data conducted by Professor Tkachuk V.N. He notes that when taking Vitaprost and Prostatilen, pain in the vast majority of patients (97% of patients) becomes 3.2 times less pronounced. Urinary disorders are reduced by 3.1 times. In addition, the form of release of medicines in the form of rectal suppositories is very convenient. This allows them to be prescribed even to patients who have not been hospitalized. The course of therapy should be from 21 to 30 days.
- In addition, it is recommended to take herbal preparations, for example: Speman, Lycoprofit, Peponen.
- Regular physical activity helps strengthen the pelvic muscles and normalize blood circulation. It is best if it is a specially designed physical therapy complex. Physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect - rectal electrophoresis, transrectal microwave hyperthermia, UHF, magnetic laser therapy, etc. These procedures are very effective in helping to get rid of pelvic pain syndrome.
More details:
Medicines for prostatitis in men: list
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko “treatment of prostatitis is simple. Is it possible to cure prostatitis forever?
Specific treatment regimen
Treatment of chronic prostatitis is a long process and requires an integrated approach. Next, a method for getting rid of this disease will be presented. You should not put it into practice on your own, without medical advice. The fact is that such treatment will be effective only if the patient is diagnosed with congestive prostatitis, that is, the possibility of infection is excluded. You can verify this only after conducting a high-quality diagnosis with studying the secretion of the prostate gland, scraping the urethral epithelium (infectious prostatitis is diagnosed in 10-15% of cases).
It is important to remember that congestive prostatitis does not require antibiotic therapy. When inflammation of the prostate gland is infectious, antibiotics are prescribed for prostatitis.
Chronic congestive prostatitis is most often treated by doctors using rectal massage. The purpose of it is to improve blood microcirculation, normalize metabolic processes, and eliminate congestion. However, this technique often causes not only physical but also psychological discomfort in patients. Therefore, men deliberately delay going to the doctor and aggravate the course of the disease.
The technique presented below allows you to get rid of congestive prostatitis without rectal digital prostate massage.
In order to start therapy, you need to prepare in advance, for this you will need to purchase:
- The drug Prostatilen for intramuscular administration and water for injection. A full course will require two packages of the drug.
- Acoustic therapy device Vitafon.
- The drug Vitaprost in the form of rectal suppositories. One package will be enough.
- Wobenzym – tablets 90 pcs. A full course of treatment will require 2 whole packages and a quarter of a third.
- Five packs of capsulated vitamin E - “Viardot”.
- Speman tablets - packaging.
You should make a reservation in advance about the Vitafon device. This device will replace the doctor's finger, which he uses during a prostate massage, inserting it into the anus. The device does not need to be inserted anywhere; the therapeutic effect is achieved through the action of acoustic waves on the prostate gland. It is applied externally.
As for the price, on average it is 1,500 rubles. However, after spending one time, you can use the device for many years. It perfectly helps relieve inflammation during exacerbation of chronic prostatitis.
The device comes with instructions for use. This should be used as a guide when using the device.
Attention!
There is one important warning, although it is purely individual. The instructions indicate that during the first seven days of using the device, the stomach should be smeared with iodine to enhance the effect. In practice, it turns out that such an amount of iodine for the body turns out to be excessive and leads to its poisoning with vomiting and pain in the kidneys. Therefore, if unwanted symptoms occur, it is best to avoid iodine.
How to take medications?
Treatment begins from the day when all components are acquired:
- Prostatilen is injected into the buttock once a day. You need to dilute it like this: take 1-2 ml of water for injection for 2 ampoules of the medicine. If the injections seem very painful, you can dilute them with Novocaine. The course of injections is 10 days.
- Speman should be taken 2 tablets 2 times a day. The full course of treatment is 25 days, if you consider that there are 100 tablets in the package, then it will go away completely.
- Wobenzym take 3 tablets 3 times a day. This should be done 40 minutes before meals. The full course of treatment is 10 days. As for the number of tablets that will be required: there are 40 pieces in one package, that is, you need 2 full packs and 10 more pieces. You can ask the pharmacist to sell them separately, many of them will accommodate you halfway. If they refuse, then you can limit yourself to 2 packages, since the drug is quite expensive. If you drink it not for 10, but for 9 days, then nothing bad will happen.
- Viardot is taken 5 capsules with meals for 20 days.
- At night you need to insert 1 Vitaprost suppository. It’s great if the intestines are cleansed first. The course is 10 days.
- The Vitafon device must be used according to the instructions for use. It is advisable to conduct 2 to 3 sessions of acoustic therapy. However, you should not stop treatment in the middle of the session when there is a feeling of exacerbation of chronic prostatitis. This is the norm, as it should be. The course will end with recovery.
If you do not deviate from the proposed scheme, you will be able to get rid of the disease for a long time. However, you should avoid drinking alcohol. At the same time, sexual life will resume in full.
During treatment, the prostate must not be overcooled, so your pants should be warm and your coat long. You should avoid swimming in cold water during the summer months.
To improve blood microcirculation and get rid of stagnant processes, you need to move as much as possible. To do this, you should give up a sedentary lifestyle, start running, walking.
There are many treatment regimens for congestive prostatitis, and each practicing urologist uses his own technique. As a rule, they are all effective, the main thing is that the absence of infection in the prostate gland is confirmed. In this case, success is guaranteed.
Source:
https://hron-prostatit.ru/
Conservative treatment
The basis of treatment for prostatitis is taking medications and physiotherapy, including its latest techniques. To achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to use several treatment methods in combination.
Treatment with medications
Only a doctor can tell you how to cure prostatitis at any stage of its development after conducting the necessary tests and studies. When treating prostatitis, medications are always used:
- Antibacterial drugs. Their purpose is due to the fact that in most cases, the cause of the disease is the development of bacterial microflora. In this case, the doctor may prescribe: “Ceftriaxone”, “Cefepime”, “Cefatoxime”, “Urotractin”, “Tetracycline”, etc.
- Alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers are a group of drugs used to relax the muscles of organs in direct contact with the prostate (urethra, bladder). Medicines in this group include: Tamsulosin, Doxazosin, Terazosin. The method of their use is considered new, but it has already proven its effectiveness.
- Nonsteroidal drugs. Medicines can relieve pain and relieve inflammation. They must be taken simultaneously with antimicrobial drugs.
Urologist-andrologist of the highest category, chief physician of the Med Center Service clinic Vyacheslav Tsezarevich Skorobogaty talks about methods of drug therapy for pathology:
- Medicines that can eliminate congestion in prostate tissue: Venoruton, Escusan.
- Suppositories with anesthesin, belladonna or ichthyol help improve microcirculation.
- Curantil and Trental help restore capillary patency.
- To improve local immunity, the doctor may prescribe Raveron or Prostatilen.
- For prostatitis, hormonal drugs such as Organon can be prescribed. This is an analogue of male sex hormones.
Effective drugs
Is it possible to use any one remedy to treat a disease? This is impossible to do, because treatment of prostatitis requires an integrated approach, and only a doctor can prescribe medications, since what is suitable for one patient may not be effective for another. The most commonly used drug therapy is:
- “Prostatilen” is an extract obtained from the bovine prostate gland. The drug has an antibacterial and anti-edematous effect. The average price is 450 rubles.
- "Prostamol UNO" is of plant origin and is made from sabal palm. The cost of tablets is 850 rubles.
- "Vitaprost" relieves swelling and congestion in the prostate area. Price – 900 rubles. The drug is available in tablets and suppositories.
- "Prostan" is made on the basis of finasteride. The cost of the medicine is 300 rubles.
- The herbal preparation "Peponen" is made from pumpkin seeds. The capsules normalize urination, which often suffers during illness, increase a man’s potency and relieve pain. Price – 950 rubles.
We reviewed suppositories for prostatitis - the most effective and inexpensive drugs.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is widely used to treat prostatitis in men. With the direction of the attending physician, the patient can visit:
- Magnetotherapy. The procedure is aimed at improving cellular nutrition of the prostate, removing waste products from cells and stimulating local immunity. Thanks to magnetic therapy, antibacterial agents are delivered faster to inflamed areas and blood supply improves.
- Microwave therapy helps expand capillaries and improve nutrition of prostate tissue.
- Stimulation with low-frequency current using an electrode placed in the cavity of the urethra. As a result, stagnant secretions are removed from the gland.
Dermatovenerologist Makarchuk Vyacheslav Vasilyevich will give you a lecture on physiotherapeutic methods in the treatment of prostatitis:
- Laser therapy helps reduce blood viscosity and dissolve small blood clots.
- Vacuum therapy is used simultaneously with laser therapy. As a result of the procedure, the blood supply to the organ improves.
- Ozone therapy is used to treat prostatitis in men. During the procedure, a liquid with a high content of ozone is injected into the urethra.
The treatment regimen for prostatitis is selected strictly individually for each patient.
Prostate massage
Not so long ago, gland massage was added to the list of procedures that can be used to treat prostatitis. It is used to relieve congestion in the organ and remove metabolic products from the blood and lymph. Massage is used after eliminating the acute process and combating pathogenic bacteria.
To carry it out, a finger is used, which is inserted into the rectum. A doctor should perform the massage. As an alternative, vibromagnetic laser massage can be used, which combines vibration with the action of laser radiation and the creation of a magnetic field. This procedure is used to improve the flow of nutrients to the organ and drainage of its ducts.
Phytotherapy
It is known that herbal medicine is an alternative to the use of medications in the treatment of many diseases. Is it possible to cure prostatitis with its help? Very often, to improve metabolic processes in the prostate, doctors recommend the use of medicinal herbs (licorice, nettle, peony, plantain, St. John's wort, etc.). All these plants contain a lot of selenium and zinc. However, they should only be used as part of complex therapy. As a rule, decoctions of these herbs are used for baths.
We have prepared for you a separate article about the treatment of prostatitis with folk remedies.
Stem cell administration
A disease that has become chronic can be treated by introducing stem cells into the organ tissue. Thus, it is possible to replace damaged cells with healthy ones.
Acupuncture
Eastern medicine has successfully used this technique for many centuries to treat all kinds of diseases. Only specially trained acupuncturists can perform this procedure. After influencing certain points of the body, blood supply to the prostate gland increases.
Hirudotherapy
Treatment of prostatitis with the help of leeches, which release special substances that promote:
- Blood thinning.
- Relieving swelling.
- Restoring blood microcirculation.
For treatment, leeches are placed in the anus. The course of treatment for prostatitis using this method consists of 5 sessions, the break between procedures should be 3-4 days.
Surgical and other clinical treatments
Sometimes prostatitis cannot be treated without surgery.
This can be done in two ways:
- Transurethral resection.
- Prostatectomy.
Transurethral
resection.
Transurethral resection is a minimally invasive treatment method. A resectoscope is inserted into the body through the urethra under general anesthesia. A high frequency current is supplied through it. It is used to cut off altered gland tissue. If there is such a need, it can be removed completely. During the operation, bleeding does not develop, since the currents cauterize the blood vessels. After such an intervention, the prostate tissue stops putting pressure on the urethra, and the person can empty the bladder normally.
The man is no longer haunted by pain. The procedure itself takes place under video control. The image is displayed on the screen, on which the doctor can track all his actions.
[Video] Patient's story about resection (TUR):
Prostatectomy.
Prostatectomy is an abdominal operation. It carries a higher risk of complications. The recovery period will last longer than after transurethral resection. However, sometimes such a procedure is the only way to help the patient.
Other treatment methods include:
- Cryodestruction.
In this case, liquid nitrogen is used to treat prostatitis. Men have been treated this way for many years. Treatment and recovery are quite extended over time. Cryodestruction is indicated for those patients who cannot undergo surgery. Despite all the difficulties of therapy, it is possible to get rid of the symptoms of the disease.
- Transurethral
microwave therapy.
This method comes down to the effect of electromagnetic waves on the prostate gland. Under their influence, the inflamed tissues are destroyed, and the symptoms of the disease recede. The procedure is a minimally invasive technique, but it cannot be performed on all patients. Sometimes after such treatment the disease recurs. In addition, there is a possibility of complications. If we evaluate the effectiveness of such treatment, it is stronger than taking medications. However, it cannot be compared with surgery. - Ultrasound therapy.
Exposure of prostate tissue to ultrasound can eliminate the inflammatory process. The procedure can be carried out at home, but after a detailed consultation with a doctor.
It is prohibited to use ultrasound for cancerous tumors of the organ. If you use it as part of complex therapy, you will be able to achieve recovery.
- Treatment with leeches.
Hirudotherapy is one of the ways to treat prostatitis. With its help it is possible to achieve a good effect.
- Stenting
and balloon dilatation.
The procedure involves inserting an endoscope with a small balloon into the prostate. During the operation, the urethra is widened, after which a stent is placed in it. This allows you to normalize the flow of urine. The method is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic examination scheme is directly dependent on the complaints and signs with which the patient turns to a urologist or andrologist.
Diagnosis of prostatitis in men can be performed both at home and in a medical facility.
The initial diagnostic stage is collecting data for anamnesis. The doctor performs an external examination of the genital organs and listens to the patient’s complaints.
Based on the initial data, a scheme for further diagnostic examination of the sick man is developed.
During the collection of anamnesis, the doctor determines the duration of the symptoms that appeared, the presence of previous prostatitis, a list of past diseases by the patient, risk factors for the development of the disease, a possible list of past sexually transmitted diseases, the development of signs of the disease, the presence of sexual partners and sexual relations.
At the present stage of development of medicine, a list of questions is placed in a questionnaire that the patient fills out before visiting the doctor’s office. This saves patient and doctor time.
The first mandatory stage of examining a patient with signs of prostatitis is an examination of the prostate gland from the rectum.
The doctor determines the degree of enlargement of the inflamed organ, its density, uniformity of consistency or the presence of nodes or compactions, and the degree of pain during palpation.
Before palpation, an enema of the intestinal cavity is performed.
In the absence of an inflammatory process in the prostate, there is no pain, but with prostatitis, the intensity of the pain can be different, and its localization is felt in the groin, rectum, perineum, and sacrum. In this case, a number of procedures, for example, cystography, are contraindicated.
For microscopic examination of prostate secretions, the patient undergoes a prostate massage through the rectum.
If there is a desire to urinate before the end of the prostate massage, this cannot be done until a drop of prostate secretion from the urethral opening is taken for analysis.
The procedure ends with passing a microscope slide over the opening of the urethra, after which the smear is stained and microscopically analyzed for the following parameters:
- presence of leukocytes and counting their number;
- lecithin amount;
- activity of pathogenic microorganisms and their presence.
The detection of bacteria in the field of view of the smear indicates an infectious type of prostatitis.
The number of leukocytes in the field of view of more than 2 indicates an inflammatory process in the prostate.
For a reliable result of a microscopic examination, it is necessary to correctly take the sample for analysis and correctly stain the preparation.
The above tests are mandatory, additional examinations are prescribed by the doctor selectively, depending on the doctor’s suspicions about the nature of the inflammation.
Analysis of urethral secretions is performed with an instrument similar to a catheter. Cotton wool is wound over the metal coating.
Before taking the test, avoid urinating for 2-3 hours. Otherwise, the microflora is washed out into the external environment.
The doctor inserts a cotton swab approximately 4 cm into the opening of the penis and makes rotational movements. A swab from the urethra is examined for the presence of DNA residues and bacteria.
Urinalysis is a means of detecting blood cells: red and white blood cells, protein (normally absent or present in trace amounts).
If errors are made in the analysis of the urethral smear and symptoms of prostatitis, urine culture is prescribed for bacteriological analysis.
READ ON THE TOPIC: How to get tested for prostatitis.
The disadvantage of this method is the long wait for the growth of a colony of pathogenic microorganisms (up to 1 week).
Sowing is carried out using a comparative method after collecting three portions of urine (beginning, middle and end of bladder emptying).
A larger number of pathogenic microorganisms in one of the samples gives rise to the assumption of a localized focus of infection.
The detection of bacteria in the first part of urine does not provide grounds for confirmation of inflammation.
POPULAR WITH READERS: All about the prostate gland and its diseases
The second and third parts of urine with an excess of the number of detected microorganisms provide grounds for determining the localization of inflammation (in the urethra and bladder, respectively).
The degree of deviation of sexual function from the norm is checked by analyzing sperm for viscosity and other physical and chemical indicators of the environment, for the activity and viability of male gametes; a spermogram is rarely prescribed.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: Spermogram interpretation, norms.
The uroflowmetric method is used infrequently. If possible and to complement the picture of the changes occurring, a urodynamic examination of the urinary tract is performed.
Ultrasound examination clarifies the density of the diseased organ and other parameters obtained after a digital examination of the prostate through the rectum.
The prostate gland is viewed in two ways: transrectal ultrasound and ultrasound through the abdominal cavity.
If adenoma or prostate cancer is suspected, the doctor may prescribe an additional cytoscopic blood examination, the so-called PSA test.
A blood sample is taken from a vein, and a blood test establishes (rules out) the presence of the PCA protein, which appears in malignant tumors.
At home, a patient may suspect prostatitis based on the color and turbidity of the urine and the symptoms of the disease.
Complications and consequences
The inflammatory process of the prostate gland, with timely treatment, does not lead to gross disturbances in the sexual sphere. However, if untreated, it most often causes suppression of sexual desire and infertility in men of reproductive age. Among the fairly common complications of untreated prostatitis are various secondary urinary tract infections, and chronic renal failure can develop. No less dangerous are bladder stones and acute urinary retention.
The disease progresses and affects the bladder - due to deterioration of blood circulation, the outflow of urine is impaired and the walls become hardened; these pathological changes are irreversible.
How to prevent disease
The well-known general practitioner, Elena Malysheva, emphasized that the treatment of this disease lies in the right lifestyle. Prevention consists of following a set of measures:
- Eliminate emerging infections.
- Go to the toilet on time.
- Fight constipation.
- Use condoms during sex.
- Do physical exercises: gymnastics, brisk walking, running.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Eat more vegetables, dried fruits, vegetable fats.
- Take a vitamin complex once every six months.
- Avoid interrupting sexual intercourse.
Living with prostatitis is not easy. In the fight against prostate disorders, the combination of traditional medicine with folk methods gives positive results. You should not resort to independent choice of medications and health procedures. Timely visits to the urologist in the future make it possible to use more gentle therapeutic techniques.
Answers to some questions about methods of treating prostatitis
- What happens if prostatitis is not treated?
Any acute prostatitis without special treatment always becomes chronic. But in any case, without treatment, both acute and chronic prostatitis can cause prostate abscess, cystitis, pyelonephritis, vesiculitis and even prostate adenoma. And a little later, impotence and infertility will appear, which will be very difficult, time-consuming and expensive to cure.
- Is it possible to treat prostatitis with herbs?
Maybe. These can be plants such as St. John's wort, licorice root, echinacea, goldenrod. These herbs contain components that help with asymptomatic non-bacterial prostatitis. It is possible to purchase rectal suppositories that contain extracts of these herbs.
- In case of chronic prostatitis, is rectal massage of the prostate necessary?
The vast majority of urological clinics abroad have abandoned this procedure in favor of physiotherapeutic treatment, which is more effective. In addition to the fact that rectal massage causes physiological and psychological discomfort, it allows you to work exclusively on the lower part of the prostate. However, in Russia the vast majority of urologists practice this technique.
- Does hirudotherapy and acupuncture help?
If we take into account the theory of influence on energy fields and points, then we can say that this method works. However, there are no studies that could be cited in order to substantiate the effectiveness. The only thing that can be stated is a slight decrease in pain and a decrease in urinary disorders. Hirudotherapy helps relieve swelling from prostate tissue, normalize microcirculation in the organ, and reduce inflammation. This is possible thanks to the enzymes that are present in the saliva of leeches, according to V. A. Savinov and M. I. Kuznetsov. However, any alternative treatment methods should be discussed with your doctor. They cannot replace traditional therapy.
- Can chronic prostatitis cause prostate cancer?
It can be argued that prostate cancer is the cause of the development of prostatitis. Inflammation of the prostate gland causes complications such as urethral strictures, prostate abscess, and sclerosis of organ tissue. As for oncology, there is no such data. However, if a man is diagnosed with prostatitis, regardless of its form, he should be regularly examined by a urologist and, if necessary, undergo treatment.
Is it possible to cure prostatitis using traditional methods?
The Internet is replete with traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of prostatitis. What craftsmen - healers - do not promise. For example, in their opinion, inflammation of the prostate gland can be cured in 1 hour. Is this real? Of course not!
Chinese prostatitis patch, magic heating pads, monastery tea and similar methods can only worsen the condition. Traditional medicine does not deny that urological collection, decoctions of herbs with bactericidal properties, vitamins and minerals are useful for prostatitis, but only as a concomitant treatment, and not as a substitute for urologist’s prescriptions.
The same can be said about urological massage and physiotherapy. These methods are very effective, but only while taking antibiotics that destroy bacteria that cause inflammation of the prostate. Prostatitis cannot be treated with any methods other than medications!
Factors influencing the development of the inflammatory process
Inflammation is characterized by acute and chronic course. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by high fever, pain in the lower back and sacrum, and discomfort in the reproductive organs. Acute prostatitis begins suddenly. Its appearance is provoked by genitourinary infections:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- urethritis;
- STI.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli are the main pathogens that provoke the occurrence of the disease.
Calculous prostatitis
The most common urological disease that can occur in men is calculous prostatitis. During illness, stones appear in the area of the prostate gland, causing pain. The disease must be treated on time or the appearance of pus cannot be avoided, which will lead to infertility. Paraproctitis may occur, in which the tissue near the rectum becomes inflamed. Males can infect women during sexual intercourse, which will lead to gynecological diseases. This disease, when neglected, is irreversible!
Prevention of prostatitis
Preventive measures against prostatitis:
- Rational nutrition (balance of vitamins and microelements);
- Monitoring the health of the genitourinary system, timely elimination of infectious foci (including caries);
- Maintaining hygiene during sex (do not practice different types at the same time; the rectum and pharynx are a source of potential causative agents of prostatitis);
- Regular physical activity to avoid stagnation.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol abuse (important for vascular health and hormonal balance).
Prostate massage, Kegel exercises and ejaculation help empty the prostate ducts, so something from the list should be present in a man’s life on a regular basis.
Surgical treatment of prostatitis
Surgical intervention for prostatitis is resorted to in three cases:
- The need for urgent removal (drainage) of cavities with pus formed as a result of acute inflammation.
- A large volume of pathologically changed (sclerosed) tissues, difficulty urinating due to damage to the neck of the bladder or the prostatic part of the urethra.
- Multiple stones (calculi, calcifications) in the body of the prostate.
Cysts (“cold abscesses”) and abscesses are removed by puncture (through a puncture). The purulent masses are pumped out, the cavities are washed with antiseptics, tannins are introduced, and a vacuum is created to cause the walls to stick together. If necessary, open access is performed through an incision in the abdominal wall and bladder. After the operation, drugs for blood vessels (Trental, Venoruton), antibiotics and warming are prescribed.
Stones and sclerotic tissue are a consequence of chronic prostatitis. Surgical intervention is performed using endoscopic methods (TUR – transurethral resection). An instrument is inserted into the urethra, with which intracavitary manipulation is performed.
About how transurethral resection of the prostate is performed
In the presence of multiple stones (in chronic calculous prostatitis), a subtotal resection of the prostate is performed - all tissues are removed along with the stones. Various methods of dissolving and removing stones from the gland are ineffective (according to experts).
Transurethral electroresection of the gland is also performed for bacterial prostatitis to remove chronic inflammatory foci. The ducts are opened and the purulent contents are evacuated.
Surgery for prostatitis is used in extreme cases, when the discomfort from constant relapses exceeds that from postoperative complications. If conservative therapy gives a positive result, then surgical manipulations are not performed.
Chronic asymptomatic prostatitis: causes in mature men
The described chronic prostatitis does not belong to any of the listed groups. The cause of occurrence is the physiological features that occur in older men. The patient does not complain about the severity of symptoms. A person only learns about the presence of the disease through tests or surgery. It is less often diagnosed in patients whose age has exceeded the mark of forty years. Causes of chronic prostatitis:
- infections;
- pathogenic microbes.
Chronic prostatitis, which is caused by an infection, is very difficult to treat with medication. Congestive prostatitis occurs in young people due to irregular sex life, when the gland is most active. No reliable reasons for its appearance have been identified. Signs that distinguish congestive prostatitis:
- weakening of sexual desire;
- lack of vivid orgiastic sensations;
- weak erection;
- the desire to urinate is especially pronounced in the morning;
- Difficulty urinating is almost invisible.
The causes of prostatitis are still not fully understood. It is known that men who have somatic diseases more often suffer from the inflammatory process:
- intestinal diseases, stool disorders;
- chronic bronchitis, ARVI;
- the presence of lesions in other organs (caries, tonsillitis);
- previous STDs;
- immune pathologies.
Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate tissues and form stagnation. What are the causes of infectious diseases of the prostate gland? Factors that contribute to the spread of infection are:
- completeness;
- systematic drunkenness;
- smoking;
- uncomfortable, tight clothing;
- prolonged exposure to the cold;
- frequent car trips.