This article describes everything about gonorrhea, its signs and treatment, complications and prevention. This disease is one of the most famous sexually transmitted infections. Symptoms are more severe in men than in women.
The second name of the disease is gonorrhoea. It is difficult to treat, since the causative agent of gonorrhea constantly mutates and also gradually gets used to different antibiotics. Because of this, therapy may take months.
Is it possible to become infected with tripper?
The only cause of tripper is infection from an infected person. That is, of course, you can become infected with it. Moreover, you cannot get gonococcal infection without contracting it from someone else. After all, infections do not arise from the air, they are only transmitted from another person.
If a woman gets tripper, most likely she had sexual contact with a sick man. Conversely, males become infected from their girlfriends.
The pathogen is transmitted through sexual intercourse. Other methods of infection are extremely rare. The infection can be transmitted during any sex. This is not only a classic contact in which penetration of the penis into the vagina occurs.
Gonococci can infect the pharynx and rectum.
Therefore, they become infected with triper during oral and anal sex. Any sexual contact without a condom with an active stage of infection is highly likely to result in the partner getting sick. There are other routes of transmission. But they are implemented much less frequently. These include:
- Household way.
Sometimes the infection enters the human genital tract without direct intergenital contact. For example, if the discharge gets on common hygiene items. This could be soap or a washcloth.
If a healthy person washes himself with the same soap that contains bacteria for a short time, he can become infected. This route of transmission of infection exists more in theory than in practice. It has been reproduced in experiments. In addition, isolated cases of such infection have been reported. But doctors encounter them very rarely.
Very often, patients try to explain to their spouse the fact that they have gonorrhea not by adultery, but by domestic infection. But in reality this is unlikely.
- Infection during childbirth.
The mother can infect the child. When born, it passes through the birth canal. Therefore, he may get an infection. Most often it occurs in the form of inflammation of the eyes. Neonatal ophthalmopathy occurs in 40% of children born to mothers with untreated triper.
- Autoinoculation.
This is an independent transfer of infection from one part of the body to another. Most often, a person spreads the infection from the genitals to the eyes with their hands. This is possible if a person scratches his private area and then rubs his eyes.
Bacteria enter the mucous membrane and cause inflammation. This form of infection is more difficult to treat than urogenital triper. It requires the use of higher doses of antibacterial drugs.
Disease prevention
Infection with gonorrhea is most often possible through unprotected sex. To prevent infection, it is necessary to avoid promiscuity. Condoms must be used during sexual intercourse. If a man or his partner is sick, they should not have intimate relations until they are completely cured.
Personal hygiene must always be maintained. Prevention of gonorrhea involves antibacterial treatment of the genitals after unprotected sex. In this case, the man should immediately thoroughly wash the urethra and penis with soap. Then treat the genitals with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or Miramistin. This drug will reduce the risk of infection tenfold. It is easier to follow prevention recommendations than to treat gonorrhea.
Tripper is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in men. The advanced form of gonorrhea is very difficult to treat. The urethra most often suffers from gonococci. Bacteria are getting used to antibiotics more and more easily. As a result, treatment becomes even more complicated. Refusal of treatment or starting it in late stages can lead to infertility.
Triper incubation period
After transmission of the infection, the first symptoms of tripper do not appear immediately.
First there must be an incubation period. During this time, the pathogen accumulates. How long it takes for a man to experience tripper depends on a number of factors:
- immunity status;
- age;
- the amount of bacteria received from the partner;
- condition of the mucous membranes of the urogenital tract;
- recent infections;
- recently taken medications (antibiotics prolong incubation, immunosuppressants or glucocorticoids can shorten this period);
- the presence of concomitant infections of the urogenital system.
In general, men have a short incubation period. It lasts only 2-4 days. For women it is longer and lasts 5-7 days.
Often, tripper symptoms do not appear in girls at all. Then they talk about a subclinical form of the disease. In this case, only objective symptoms of triper disease are observed. That is, the patient does not have any complaints. And the doctor can detect signs of the disease only during examination. Often the disease is detected by chance during tests for preventive purposes.
Treatment of gonorrhea
It is best to start symptoms and treatment of gonorrhea in men at an early stage. Therapy is aimed at exterminating gonococci. A dermatovenerologist treats gonorrhea. First, the causes of the disease are established. Then a treatment regimen is developed. Therapy takes a long time, as bacteria quickly become accustomed to antibiotics.
Because of this, drugs are prescribed only after the results of bacterioculture. The most commonly prescribed are Bicillin, Ceftriaxone and some other antibiotics. During treatment, two drugs are used simultaneously. Azithromycin is considered the best antibiotic for treating gonorrhea. The drug "Sumamed" is used if the sensitivity of gonococci to the group of macrolides is detected.
Additionally, microenemas with antibacterial solutions are given. To restore the strengthening of the immune system, vitamins (rating of the best vitamin complexes) and restorative drugs are prescribed. Additionally, medications are used to maintain the functioning of the heart, kidneys, and liver.
During treatment for gonorrhea, the patient should drink a lot of water. Diuretics help flush out gonococci, pus, and infected areas of mucous membranes from the body. If there are additional diseases, then their treatment is carried out simultaneously.
After starting therapy, the patient undergoes repeated tests after 10-14 days.
Based on the results, treatment of gonorrhea in men is adjusted. Other medications may be prescribed or the dosage of previous medications may be changed. The following tests (smear, blood, urine) are taken only after 4 weeks. Even if gonorrhea is completely cured, a man should be examined every 6 months for two years.
Treating gonorrhea at home
Treatment of gonorrhea in a hospital is indicated only in case of relapse of the disease, complications or additional infection. In other cases, treatment is carried out at home. In addition to prescribed medications, folk recipes are also used.
To enhance treatment, infusions and douches of herbs are used. Chamomile provides effective assistance in therapy. It has wound healing, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. An infusion is made from chamomile, which is used for lotions and baths. The liquid is also poured into the urethra using a pipette.
How to treat gonorrhea with burdock? The roots of the plant are used for this. A decoction is made from them, which is similar in healing properties to chamomile infusion. Baths for the scrotum and penis are made from a product based on burdock roots.
Ginseng tincture is used to enhance the functioning of the immune system. You need to drink it in the morning, before meals, 5 drops. Ginseng helps improve blood circulation and strengthens mucous membranes.
Many vegetables and fruits have an antibacterial effect. A man should eat parsley, celery, wild berries (especially viburnum, blueberries and lingonberries) every day. The listed recipes, herbs, vegetables and fruits help speed up recovery.
The first sign of a tripper
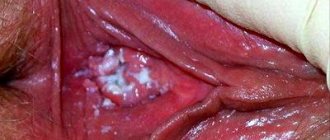
In most men, the first sign of tripper appears quite early. This is discharge from the urethra. They are usually purulent and quite abundant. They are released constantly, in drops. Over several hours, quite a lot of discharge accumulates. They can have an unpleasant odor and stain your laundry.
According to the clinical course, they are distinguished:
- fresh;
- chronic;
- hidden.
In turn, fresh is divided into acute, subacute and torpid.
In the acute form of the disease, a lot of pus is released from the urethra. On examination, significant swelling and redness of the urethral sponges is noted.
The subacute form is characterized by mild symptoms. There is little discharge, and redness and swelling are minimal.
With a sluggish or torpid form, there are almost no symptoms. There may be minor discharge, which often goes unnoticed. Such patients often do not seek medical help. They are the most dangerous epidemiologically because they spread the infection among partners without knowing that they are sick.
Types of gonorrhea
There are two types of gonorrhea. The acute form is accompanied by the rapid appearance of pronounced symptoms. They do not go away, but get stronger over time. Bacteria can be destroyed in the first two hours after infection, then the infection begins to develop rapidly.
Very rarely, chronic gonorrhea manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. At times they disappear completely. Men decide that the disease has gone away on its own and are in no hurry to see a doctor. However, the disease progresses further, so chronic gonorrhea is the most dangerous. It can lead to serious consequences.
Symptoms of triper in women
In general, the symptoms in women are similar to those in men. They also have discharge. There may be redness of the genitourinary organs and their swelling. Sometimes subjective signs in girls include itching and pain during sexual intercourse. But often the gonorrhea in women is weakly expressed. They feel only minor discomfort and do not always consult a doctor. Discharges are subtle. They can be perceived by women as harbingers of ovulation or menstruation, the result of sexual arousal, etc.
Sometimes the inflammation spreads to the inner thighs. In this case, redness of the skin in this area is noted.
Upon objective examination it is observed:
- infiltration of the walls of the urethra;
- hyperemia and edema;
- discharge of a purulent or mucopurulent nature;
- erosions may appear on the cervix;
- the doctor may notice discharge in the cervical canal.
Symptoms of tripper in men
Let's discuss in more detail how tripper manifests itself in men. It can affect various structures of the genitourinary system.
Typically, gonococci cause anterior urethritis. Only the distal urethra becomes inflamed. But inflammation can also spread to its posterior part. Then total urethritis develops.
If inflammation spreads to the bladder, urethrocystitis is diagnosed. It is manifested by severe dysuric disorders. Men complain that it hurts to urinate. Strong urges arise. Then the patient must urgently empty the bladder, otherwise urinary incontinence may occur. Pain during urination intensifies at the end. It can be sharp and painful. In this case, the amount of urine released may be small. The reason is frequent urination. When inflammation spreads to the bladder, blood may be released in the urine. It usually occurs at the very end. This type of hematuria is called terminal. In general, inflammation of the lower urinary organs in men is not accompanied by general intoxication symptoms. Although sometimes fever and malaise are possible.
The presence of pus in the urine is another manifestation of tripper in men. It often occurs if the entire length of the urethra is affected, involving the bladder.
Chronic tripper
Sometimes the first symptoms of tripper in men do not prompt the patient to see a doctor.
Improper treatment is characterized by the development of a chronic form of pathology. This type of tripper manifests itself as focal inflammation. Individual fragments of the mucous membrane or gland become inflamed.
Subjective signs of tripper may be completely absent. Sometimes they are weakly expressed. There are almost no allocations. Only a small amount of discharge on underwear in the morning indicates that a man has gonorrhoea. Bonding of the urethra is also possible.
Inflammation of the posterior region may cause discomfort during ejaculation. Often there is more frequent urination than normal. It may be painful in the end.
In some men, gonorrhea causes sexual disorders:
- decreased sex drive;
- premature ejaculation;
- decreased sensations from orgasm;
- weakening of erection.
A man may notice blood or pus in the ejaculate. There is no discharge from the urethra during the daytime. Although they may intensify somewhat after:
- physical activity;
- alcohol;
- sex;
- long walk.
In the chronic form, the signs of tripper in men are hardly noticeable. Therefore, laboratory tests are crucial in diagnosis.
What is gonorrhea
Unprotected contacts can lead to various consequences.
If a person discovers suspicious symptoms, he often wonders what gonorrhea disease is. The branch of medicine that deals with this and similar diseases is venereology. And it is a venereologist who should be contacted in case of suspicion. Gonorrhea is a disease caused by gonococcus, in other words, gonorrhea. Gonococcus is a type of gram-negative diplococcus, differing from others in that they are round in shape and arranged in pairs. The targets most often are mucous membranes, but these cocci can settle in other places. In reality, gonorrhea is the same triper, it’s just a common second name. The causative agent is diplococcus - Neisseria gonorrhoeae or gonococcus.
Wanting to find out what triper disease looks like, people turn to the Internet or specialized literature. And they find out that gonorrhea and tripak are one and the same thing. But Trichomonas and Tripak are completely different phenomena. The first is caused by protozoa, the second by cocci.
Since gonorrhea and triper are the same thing, they are treated in the same way. Therefore, the question of what tripper is and how it is treated is within the competence of venereologists. After all, it is a sexually transmitted disease that has many negative health consequences. It is often confused with trichomoniasis, since both diseases are characterized by strong discharge, often of a discolored color.
Often visitors to medical forums ask whether the signs of gonorrhea are really different from syphilis, and how this manifests itself. These are two different diseases, but syphilis is more dangerous, it is more difficult to treat and is more easily transmitted. At the same time, a clear manifestation is a characteristic formation on the skin that appears after a few weeks - a chancre.
We can say that the same disease, which is called by different words, is gonorrhea or triper. Gonococcus can immediately manifest itself in an acute form and remind of itself with copious discharge. Syphilis in the initial stages usually does not manifest itself in any way and only causes aesthetic discomfort. In the early stages of this disease, many patients do not know what the appearance of mucus on underwear and pain in the reproductive organs means. At the same time, for gonococcal infection such manifestations are normal within a week after sex with a carrier.
What is the difference between triper and gonorrhea - nothing. It’s just that gonorrhea is a scientific name, and the other name is a common, outdated one. It just so happens that this venereal disease is called by different words. Also, “tripper” is the official name for this STD in Germany.
Symptoms in men with complications
Sometimes tripper in men causes complications. Basically, they develop if the patient ignores the first signs of tripper and does not consult a doctor.
The most likely complications may be inflammatory processes of structures located in close proximity to the urethra. These include:
- tizonitis – abscessation of the foreskin;
- balanitis or balanoposthitis - damage to the head of the foreskin;
- phimosis is the result of an inflammatory process when it is not possible to expose the head;
- paraurethritis – damage to the paraurethral ducts;
- littreitis - inflammation of the alveolar tubular glands located in the urethra;
- Morganitis – inflammation of Morgagni lacunae;
- cooperitis - inflammation of the ducts of the bulbo-urethral glands.
Inflammation in various glands often goes undetected. But it is still quite dangerous. Because it can lead to the formation of an abscess. This is a cavity with pus.
The disease manifests itself with severe symptoms. There is severe pain, swelling, and general symptoms of intoxication appear. Body temperature usually exceeds 38 degrees.
Pathology may require surgical treatment. With a long course of chronic tripper, urethral strictures may develop. They can be either single or multiple. The length of these strictures is on average 1 cm. They prevent emptying of the bladder.
The main symptom remains a sluggish stream of urine. What tripper looks like in men with inflammation of the testicles and prostate. The spread of the disease to the internal genital organs is not uncommon. This is a consequence of the lack of adequate and timely treatment. Most often the epididymis becomes inflamed. Then the symptoms of triper disease are as follows:
- groin pain;
- increase in body temperature, sometimes up to 40 degrees;
- redness of the skin of the scrotum and its tension;
- enlargement of the epididymis;
- pain upon palpation.
Subacute or chronic epididymitis is also possible. Then the symptoms are the same, but less pronounced. The infection spreads into the epididymis from the urethra. There are two possible ways:
- through the vas deferens - due to their antiperistaltic movements caused by inflammation of the seminal mound;
- through lymphatic vessels.
The risk of developing epididymitis against the background of triper increases with physical activity and sexual intercourse. The pathological process rarely spreads to the testicle. However, orchiepididymitis of gonococcal etiology also occurs. Then there is severe pain in the scrotum. It intensifies when trying to palpate. The skin is tense and hyperemic. The testicle is increased in size.
Only the membranes may be damaged with the development of purulent periorchitis. In this case, the epididymis is not determined by palpation. When exudate accumulates, a fluctuating formation may be detected. This is a phenomenon in which vibrations of fluid inside an organ are determined.
In men, tripper can affect the prostate. In this case, gonococcal prostatitis is diagnosed. He can be:
- catarrhal;
- follicular;
- parenchymatous.
The disease is often accompanied by vesiculitis.
The catarrhal form of prostate inflammation in triper is diagnosed if the pathological process is limited to the excretory ducts. He usually has no symptoms. If lobules of the prostate are involved, it is follicular prostatitis. Then a pronounced clinical picture arises. Signs may be:
- feeling of warmth in the perineum;
- pain at the end of urination;
- fever and weakness.
Pseudoabscesses may form in the prostate. During a digital rectal examination, the doctor detects lumps. They may be painful. But the gland itself is usually not enlarged.
The most severe symptoms are accompanied by parenchymal prostatitis. A man feels pain in the pubic area. He develops a fever and exhibits severe symptoms of intoxication. There may be difficulty urinating. On palpation, the prostate is enlarged and painful.
The disease is dangerous because triper often causes an abscess with purulent melting of prostate tissue. In this case, acute urinary retention is possible.
Gonococci can provoke chronic, sluggish inflammatory processes in the prostate. They are accompanied by mild dysuria.
In the end, after urine is released, prostate secretion may be released. This symptom is called voiding prostatorrhea. If prostate secretion comes out after defecation, it is defecatory prostatorrhea.
With chronic prostatitis, sexual function disorders often occur. Symptoms include:
- erectile dysfunction;
- decreased sex drive;
- premature ejaculation.
Diagnostics
Only a venereologist can make a correct diagnosis for this pathology based on the examination results. Diagnosis of gonorrhea includes a set of laboratory and instrumental procedures, on the basis of which the presumptive diagnosis is confirmed and adequate treatment is prescribed.
During the initial examination of the patient, the clinician needs to:
- to determine the mechanism of infection, familiarize yourself with the patient’s life history;
- perform a digital rectal examination;
- examine and palpate the external genitalia;
- conduct a survey of the patient - clarify when the first signs of the disease appeared, determine the degree of their severity.
Laboratory tests to help identify pathology:
- General blood and urine analysis. The patient undergoes a standard test.
- Urethroscopy. A positive result from this examination indicates the presence of changes in the structure of the epithelium.
- Bacteriological culture. This examination allows you to accurately distinguish gonorrhea from other sexually transmitted diseases. For research, a sample of mucus is taken from the urethra or anus. The specifics of this analysis prohibit before performing the act of urination, performing hygienic treatment of the genitals using disinfectants, and also taking any antibacterial drugs.
- Sensitization method. This is based on the introduction into the body of a protein drug created on the basis of a gonococcal allergen. The results of the examination will be known within a day.
- Immunofluorescence analysis. This study is considered one of the most reliable and fastest methods. The analysis is based on examination of venous blood, which makes it possible to determine the presence of antibodies against gonococci.
Thanks to the results of such a comprehensive diagnostic course, the specialist creates an individual treatment regimen for the patient.
In some cases, the patient is additionally prescribed the following instrumental procedures:
- urethroscopy;
- fluoroscopy;
- ultrasonography of the pelvic organs.
When examining a patient, it is very important to differentiate gonococcal infection from the following diseases:
- trichomoniasis;
- candidiasis;
- chlamydia;
- syphilis.