Tinnitus, which in medical terminology is called tinnitus, is characterized by some atypical sound in the head. For treatment with prescription drugs, the patient first has to undergo diagnostics to find the causes of the pathology. It’s not worth figuring out what to do on your own when a patient has constant noise in one or both ears at the same time, but it’s better to trust an experienced doctor.
Attempts to determine why this condition occurred through reviews on thematic forums and therapy with folk remedies usually blur the overall clinical picture. Even for an experienced doctor, it is difficult to diagnose ringing, crackling, humming, or congestion in the ear canal if there are no external manifestations of the disease. Adding to the complexity is the fact that the sound is a subjective assessment of the patient.
Sound conduction pathologies
According to statistics, the most common cause of hearing loss accompanying tinnitus is cerumen. This pathology is sometimes accompanied by ear pain and discomfort, aggravated after water procedures. It interferes with the normal conduction of sound. Sometimes the presence of a plug leads to an inflammatory process.
The second most common cause is otitis media. Inflammation can occur in the middle, outer, or inner ear. Otitis media is more common. Fluid accumulates in the ear cavity, formed due to the inflammatory process. As a result, extraneous noise occurs. Sharp pain in the ear, discomfort, and decreased hearing occur.
Standard noise classification
If frequent attacks of strange sounds are repeated during a cold or after the flu, then you should seek help from an ENT specialist. It is likely that a person has a complication in the form of otitis media - inflammation of the middle ear. During epidemics of diseases that are activated when it is cold, in addition to the respiratory organs, the eyes and ears suffer, where a secondary infection usually settles if the treatment is insufficient the first time.
Schematically, all sounds that make themselves felt when bending over, or just in the evening, are divided into two categories:
- monotonous;
- complex.
In the first case, we are talking about whistling, as happens with gusts of wind, wheezing, buzzing, ringing, and squeaking. The second option involves voices, music, and the ringing of a bell, which are considered to be the consequences of drug intoxication, psychopathology, and auditory hallucinations.
In addition to the fact that doctors use schematic degrees of severity of the disease to diagnose, they first have to figure out whether the symptom relates to:
- objective;
- subjective.
The objective format provides the doctor with the opportunity to hear the sounds that disturb the patient during the examination. This happens if an insect gets into the ear canal and buzzes or squeaks, trying to get out. Here, only a doctor can tell you how to get rid of a foreign body right on the spot. The faster the foreign object is removed, the higher the chances of successful recovery.
A doctor will be able to recognize initially hard-to-hear noises if their source is a failed hearing aid.
The subjective version is more common, appearing after anesthesia, when you go to bed and hear the movement of blood through the artery, immediately after sleep. In this situation, no plugs or exercises help. The source of why the periodic noise appeared may include psychosomatics. It is characterized by the manifestation of only sound effects, when at the same time there is no darkness before the eyes, no clenching of the jaw, no tingling along the spine, no drowsiness, no fatigue. When all of the listed types of unfavorable symptoms occur, this signals a serious deterioration in well-being at the acute stage.
Another separation format according to medical terminology involves sorting into two groups:
- vibration;
- non-vibrational.
The vibration format provides mechanical sounds that are produced by the auditory organ or its structure. We are talking about neuromuscular, vascular structures that can be heard even by a stranger. It will be possible to figure out treatment for this clinical picture quite quickly, even if the disease was chronic in adults.
But non-vibrational variations are more common, which are caused by irritation of nerve endings:
- central auditory pathways;
- inner ear;
- auditory nerve.
With non-vibrational genesis with subjective perception, patients even complain of a peculiar breathing sound, noting that the knocking appears as suddenly as it disappeared. Constant background music provokes irritability and insomnia.
Pathologies of sound perception
The most common is labyrinthitis, an inflammatory process affecting the structures of the inner ear. Due to the structure and physiology of a person, the inflammatory process often negatively affects the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, which leads to the appearance of additional symptoms such as dizziness and nausea.
Another possible cause is a pathological condition in which too much fluid collects in the inner ear. As a result, the functioning of receptor structures is disrupted. Associated symptoms: hearing loss in one ear, dizziness, which occurs and goes away spontaneously.
Hearing loss caused by damage to nerve pathways or auditory receptors also falls into the category of sound perception pathologies. Accompanied by severe hearing impairment in combination with noise.
Most common sources of noise
In most cases, noise complaints come from people who have tried to independently treat inflammation of the hearing aid by pouring in oil, decoctions of medicinal herbs, and garlic juice. The mentioned factors, along with many others, provoke blockage of the ear canal. This option is indicated by damage to only one ear.
The patient is haunted by a faint noise, which is often supplemented by:
- congestion;
- soreness;
- decrease in the quality of perception of the environment.
The problem begins with dust and foreign objects getting inside, which is especially typical for small, curious children. Adults experience discomfort after a holiday at sea, when it seems as if something is constantly gurgling, because drops of salt water have gotten inside.
If you do not take care of personal hygiene, then the likelihood of the formation of sulfur plugs increases, which rapidly grow against the background of an abnormally large release of the substance due to disease or a narrow ear canal. No methods will help here, and in order for the irritating symptom to disappear, you will have to rinse the cavity with a special solution and special tools. It is prohibited to remove wax on your own, as you can accidentally hit the eardrum and damage the activity of the auditory nerve.
In the latter case, a person can lead himself to sensorineural hearing loss through attempts at self-medication, or provoke a tumor. The disorder can make itself felt both slowly and suddenly after a stroke or surgery. The health-threatening syndrome develops due to damage to the nerve cells that are responsible for converting sound vibrations into impulses for transmission further. The exact degree of the anomaly will be determined by a neurologist, who, based on the examination and test results, will tell you about the necessary treatment to improve the condition.
The leaders in the ranking of the root causes of hearing loss are a couple of types of hearing loss:
- professional;
- senile
The first occurs as a result of working in hazardous production conditions. Here you can get many other diseases along the way. The main ways to protect yourself from the effects of occupational hearing loss include earplugs and taking vitamins.
Senile hearing loss manifests itself in old age. For some women it begins during menopause. The main danger is that the failure of receptors is almost always irreversible. To understand how far the disease has progressed, doctors send their patients for examination.
One of the most dangerous diseases, the name of which is neurosyphilis, occurs more clearly, starting rapidly. The deviation affects not only the auditory nerve, but also the meninges, even reaching the roots of the spinal nerve.
Against this background, the patient is faced with:
- skin dystrophy;
- paresis;
- loss of sensitivity;
- constant noises.
Some ordinary people confuse its symptoms with oncological tumors of a malignant or benign nature localized in nervous tissue, for example, neuroma. Its typical warning sign is a perverted perception of loudness.
Other pathologies
This includes diseases not related to the hearing aid. Thus, the cause of tinnitus can be cervical osteochondrosis, a disease that is characterized by damage to the cervical vertebrae and leads to prolonged compression of the arteries that supply blood to the ear.
Atherosclerosis is another disease that, when developed, leads to damage or narrowing of blood vessels. This means that the hearing organs do not receive enough blood.
Diseases associated with an increase or decrease in pressure, despite different mechanisms of development, can manifest themselves with the same symptoms on the part of the hearing organs.
Diagnostics
To detect the cause of the noise, a comprehensive examination is necessary, which should begin with a visit to the otolaryngologist. This doctor will analyze your complaints and medical history, examine the outer ear and eardrum, perform audiometry and make a conclusion about the condition of the hearing organ.
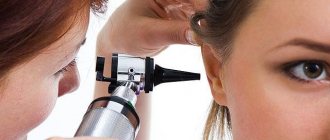
Otoscopy
This is an important examination that helps identify:
- blockage of the ear canal (wax or foreign body);
- presence of external/otitis media;
- boil in the ear canal cavity;
- myringitis;
- exostosis.
Using a special device (otoscope), the doctor can examine all the structures of the hearing system, right down to the eardrum. If the cause of tinnitus is associated with pathology of this part of the ear, then diagnosis, as a rule, does not cause difficulties.
Pure-tone threshold audiometry
This research is based on the brain's ability to selectively perceive the loudest sounds. The amplitude of the noise heard by the patient is measured by playing different noises in frequency and volume and asking the patient to indicate what they hear. By compiling an audiogram in this way, you can determine the patient’s hearing threshold:
| Diseases with a reduced hearing threshold | Diseases with an increased hearing threshold |
|
|
Auscultation of the temporal region
To diagnose the presence of noise, it is necessary to auscultate the skull with a phonendoscope:
- If the noise manifests itself as pulsation, then it is a vascular noise, as a consequence of a possible arterial aneurysm, tumor, arteriovenous malformation, and other diseases requiring surgical intervention.
- If it’s a clicking sound, then it’s a muscle noise created by contractions of the soft palate and middle ear. For such convulsive contractions, treatment with anticonvulsants is indicated.
Additional diagnostic methods
If, using the above methods, the doctor was unable to detect the cause of tinnitus, other diagnostic methods should be used. The presence of vertebrobasilar insufficiency, CNM and mastoiditis should be excluded.
| How is it carried out? | What can you find? |
X-ray of the temporal areasAn x-ray is taken in two projections - anterior and lateral. | Mastoiditis - in this case, focal darkening will be noted on the image. |
X-ray/MRI of the cervical spineX-rays are performed in a sitting position, with the head straightened, in two projections. MRI is a more accurate and expensive examination. It is performed in a lying position, without any preliminary preparation. | Osteochondrosis – the presence of deformation of the intervertebral discs or displacement of the cervical vertebrae indicates the possible presence of VBI. |
Examination of the patency of the auditory tubeThe auditory tube (which opens in the mouth) forces air into the middle ear. The presence of protrusion of the eardrum when examined with an otoscope is considered normal. | Eustachitis - due to swelling of the auditory tube, air will not be able to pass into the middle ear cavity and displace the eardrum. |
Angiography of cerebral arteries and vertebrobasilar regionA special instrument (catheter) is inserted through the subclavian artery and advanced to the mouth of the vertebral artery under X-ray control. A contrast agent is injected through the catheter, and the arteries of the vertebrobasilar and medullary areas are visualized. | CNMK and VBN - on angiography, narrowing of certain areas of the arteries is noted. |
Vestibular function studyUsing simple tests, the patient's coordination functions are assessed:
| Damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve – in this part of the ear, the vestibular and auditory parts work together. Vestibular dysfunction coupled with tinnitus suggests inner ear/nerve pathology. |
Increased body temperature
If the noise appears along with an increase in body temperature, an infectious process can be suspected.
In most cases, the body is able to cope with viruses or bacteria on its own. A doctor's help is required in the following cases:
- General weakness has appeared, there is intoxication.
- Symptoms are accompanied by loss of appetite and nausea.
- There is insomnia or drowsiness.
- A headache occurs.
- There are visual impairments.
A sharp increase in body temperature is also considered dangerous - if within 2-3 hours it rises above 38.5 degrees.
You should also consult a doctor if the temperature is low, but lasts longer than 3 days in a row.
“Which ear is it buzzing in?”
People usually associate this symptom with high blood pressure and vascular problems. However, this is far from the most common cause of tinnitus.
In general, in all patients this symptom manifests itself differently: the noise can be loud or quiet, on one side or both at once, constantly or from time to time. The noise can be of the same frequency or of different frequencies (for example, intermittent or pulsating). It is important for the otoneurologist to know all the characteristics of the ear noise of a particular patient, as well as its triggers (the causes of occurrence and factors that change the nature of the noise) in order to direct the diagnosis in the right direction.
Mandatory tests for tinnitus include audiometry, an auditory tube function test, and a study of the “reflexes” of the middle ear muscles. It is also advisable to conduct noise metry to clarify the frequency and volume of noise. But ultrasound of the neck vessels, so beloved by patients, is unlikely to provide meaningful information. MRI and CT are also performed according to strict indications and are not always required.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain that is accompanied by tinnitus may indicate serious poisoning or inflammation of the appendix. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor immediately. It is especially dangerous if the pain does not go away within an hour and is not relieved by painkillers. Sometimes, such symptoms do not require help - for example, on the first day of the menstrual cycle or in the presence of chronic problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In other cases, calling a doctor is required. In this case, you need to inform the specialist about taking analgesics - since the absence or masking of pain syndrome may interfere with the diagnosis.
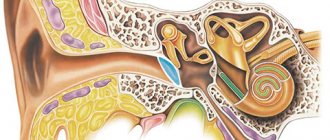
Diseases of the outer, middle, inner ear
It is quite normal if unpleasant clicking sounds occur when the nose is stuffy due to ARVI, or after anesthesia. But it is completely unacceptable to ignore disorders of the outer ear, which is represented by the concha itself and the immediate auditory canal. As soon as a barrier forms in them, a person ceases to normally perceive the sounds of the environment.
The most common diseases of these two parts of the hearing system include:
| Name | Description |
| Otitis externa | Inflammation of the skin due to infection with infectious pathogens such as streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus. It is characterized by pronounced noise, which is complemented by severe pain and periodic purulent discharge and redness. If help is not provided as soon as possible, the infection quickly spreads to the eardrum. It is usually diagnosed among ordinary people with reduced immunity, which is typical for those taking hormonal drugs, HIV-infected people, and those who live under the yoke of constant stress. |
| Furuncle | The boil always needs to be removed, as it quickly causes complications in the form of septicemia. This is signaled by a rise in body temperature, weakness, loss of appetite, and dehydration. |
| Mycosis of the outer ear | The lesion involves a fungal infection. During laboratory diagnostics, it becomes clear that the primary source was mycosis, due to which milky-white liquid constantly oozes from the hole. |
| Exostosis | Overgrowth of bone tissue in the ear canal where it should not be. Deviation is quite rare, but if the problem is ignored, it always results in the hole becoming so narrow that it can no longer pass the wave. |
In order not to reach the point where prolonged noise causes irreversible consequences in the outer ear, blaming all psychosomatics, it is necessary to promptly treat conditions such as runny nose and sinusitis. Otherwise, secondary infection may reach the ear canal, bringing with it the sensation of a short-term echo.
But much more often the middle section becomes the source of various deviations, which is explained by its physiological structure. The zone is not protected by a muscle layer, but only by a thin membrane. As soon as it becomes inflamed due to various negative influences, health begins to deteriorate. Adding to the complexity is the fact that the department is directly connected to the oral cavity. This explains why when you have a sore throat, you often have to deal not only with a cough, but also with unbearable pain in the ear.
For various advanced colds and viral diseases, therapy almost always also involves instillation into the ear to eliminate the spread of pathogens. The situation worsens with diabetes, heart disorders, after childbirth, when the body is still being rebuilt, with unstable intracranial pressure. It all ends with the patient developing otitis media in one of two forms:
- acute;
- chronic.
No homeopathy or propolis will help correct the situation if an otolaryngologist has not previously been consulted. When the doctor confirms that it was not poisoning, but otitis media, and assesses the extent of the damage, he will be able to prescribe a course of treatment at home. But if hospitalization is required due to a sharp deterioration in health, when the applicant simultaneously experiences chills, sweating, and abdominal pain after or before meals, then there is no need to resist it.
The acute stage of otitis is activated after suffering “on your feet”:
- tonsillitis;
- nasopharyngitis;
- laryngitis.
The characteristic noise is an unpleasant shooting sound when you stand up or when walking. If you start the acute form, trying to independently find what to drop into the affected ear, you can add a diagnosis of chronic otitis to your medical record.
Some of the most difficult clinical cases are disorders of the inner part of the ear, as they affect the vestibular apparatus. When such a deviation is found in adolescents, the sound will almost always haunt them throughout their lives, even with successful treatment.
The situation is aggravated by hereditary predisposition, which is especially dangerous in otosclerosis, when the auditory ossicles of both hearing organs are fixed or the nervous system of the inner ear is damaged. Many relatives of patients who have already been diagnosed with otosclerosis develop panic fear against the background of constant anticipation of the development of the disease. Moreover, you should not think that after drinking alcohol, which is used as a sleeping pill at night, the situation will improve.
Labyrinthitis is infectious in nature. There, the lesion literally knocks, “emits” other signals, disrupts coordination of movements, and provokes nausea. If you try to eliminate labyrinthitis by pouring fir oil inside or using other strange folk methods, this will lead to rapid damage to the cochlear apparatus.
Contusion, which is often temporary, and Meniere's disease are considered separately. Both clinical cases require careful diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Cerebrovascular accident
The most serious thing that noise in the ear can indicate is a violation of blood circulation in the brain. If typical symptoms appear, it is better to consult a doctor within a few days, especially if there are no prerequisites for the occurrence of the disease. Very often, typical symptoms appear in those who abuse alcohol or smoke a lot, use aspirin for a long time, do not monitor the amount of salt in their food, or consume excessive amounts of coffee and energy drinks. The main signs of cerebrovascular accident are dizziness, severe loss of coordination of movements and tinnitus. If symptoms do not go away within half an hour or progress, you need to call an ambulance.
Tinnitus in neurological diseases
Neurological pathologies cause tinnitus along with ENT diseases. Let's consider the most common causes of tinnitus, which fall under the competence of neurologists.
Tinnitus due to arterial hypertension and hypertensive crisis
With a significant increase in blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg), blood flow to the inner ear becomes uneven. As a result, the nerve endings inside it are excited, and tinnitus occurs. With arterial hypertension, this most often occurs during a hypertensive crisis - an attack of a sharp increase in pressure.
Other manifestations of hypertensive crisis:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the heart area;
- nausea and vomiting;
- convulsions;
- disturbance of consciousness.
During a hypertensive crisis, the patient requires emergency assistance. It is necessary to reduce blood pressure as quickly as possible, otherwise its jump can lead to myocardial infarction, stroke and other serious complications.
If arterial hypertension is accompanied by a chronic disorder of cerebral circulation, then the patient is almost constantly bothered by tinnitus.
Cerebrovascular accident
The most common cause of impaired blood flow in the vessels of the brain is atherosclerosis. This is a disease in which cholesterol plaques form on the walls of the arteries, partially or completely blocking their lumen.
Other causes of cerebrovascular accident:
- arterial hypertension (the main cause of which is also often atherosclerosis);
- increased blood viscosity and blood clot formation;
- diabetes mellitus (with this disease, the vessels of the brain, eyes, and kidneys are primarily affected);
- consequences of traumatic brain injury;
- intracranial tumors, hemorrhages.
The main symptoms of chronic cerebrovascular accident: headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, flashing “spots” before the eyes, increased fatigue, drowsiness, impaired memory and attention. Constant oxygen starvation does not leave its mark on the brain. Nerve cells gradually die, which over time can lead to the development of dementia.
The effect of increased intracranial pressure on noise in the head and ears
Tinnitus as a result of increased intracranial pressure occurs with hydrocephalus, intracranial tumors and hemorrhages, after traumatic brain injuries and infections (meningitis, meningoencephalitis).
Headache and tinnitus - characteristic manifestations of increased intracranial pressure - usually occur in the morning, after a person has been in a horizontal position for a long time. During the day the symptoms disappear. The vertical position of the body helps the excess amount of intracranial fluid flow away and its pressure decreases.
Diseases of the cervical spine
The vertebral arteries, vessels that play an important role in the blood supply to the brain, run along the cervical spine on the right and left. They are not just located on the sides of the spine, but pass through holes in the lateral processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Often, pathological changes in the spine - inflammation, displacement of the intervertebral disc, bone growths that form on the vertebrae - lead to impaired blood flow in the vertebral arteries and neck pain. Blood flow to the head decreases. The brain and other organs experience oxygen starvation.
This condition is called vertebral artery syndrome. Its main manifestations:
- constant burning pain in the back of the head, temples, which intensifies after sleeping in an uncomfortable position, traveling by transport;
- hearing loss and tinnitus;
- blurred vision, “fog before the eyes”;
- dizziness, loss of balance when turning the head suddenly;
- loss of consciousness;
- sleep disturbances, the patient does not feel sleepy and rested, in the afternoon there is severe fatigue and drowsiness.
Tumors
Acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor that leads to tinnitus and other symptoms: decreased hearing on one side, pain and impaired movements of the facial muscles of half the face, and speech impairment. For acoustic neuroma, the doctor prescribes surgical treatment or radiation therapy.
Many intracranial tumors lead to impaired cerebral circulation and increased intracranial pressure. Therefore, tinnitus can also be one of the symptoms of such pathologies.
Multiple sclerosis
This is a chronic disease that most often occurs between the ages of 15 and 40 years. All nerve fibers in the human body are covered with a special myelin sheath. It is necessary for the normal transmission of nerve impulses. In multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheath is destroyed, resulting in slower neuromuscular transmission.
The symptoms of multiple sclerosis are varied. In some people, the disease manifests itself in the form of numbness in a certain part of the body, for example, a limb, while in others severe paralysis develops, including breathing problems.
One possible symptom of multiple sclerosis is tinnitus.
Depression and neuroses
Under certain conditions of the nervous system, the hearing organ becomes hypersensitive to sounds and becomes irritated. This is often caused by depression, neuroses (neurasthenia, hysterical neurosis), and nervous breakdowns. The patient comes to see a doctor and complains of constant tinnitus, but during examination and examination no objective abnormalities are revealed.
For psychogenic tinnitus, psychotherapy and appropriate medications are prescribed.
Taking medications for tinnitus
Some medications are ototoxic—they can harm the nerve endings in the inner ear and cause tinnitus. This side effect is most pronounced with the following drugs:
- antimalarials (quinine) and some antibiotics (for example, streptomycin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (including aspirin);
- antipsychotics (haloperidol);
- antidepressants;
- digitalis preparations;
- furosemide
If you begin to experience tinnitus while taking one of these medications, you should stop taking it and consult a doctor immediately.
Only a doctor, based on the results of the examination and examinations, will determine what disease led to the occurrence of tinnitus. It is necessary to begin proper treatment of this symptom for any pathology as early as possible - this will help eliminate its root cause and prevent serious complications.
The Yusupov Hospital employs experienced neurologists, therapists, cardiologists, and has all the necessary equipment. This allows us to provide patients with modern, high-quality medical care.
Treatment
If there is noise in the right ear, how to treat it? First, the cause is determined. Without identifying the disease or conditions that led to discomfort, it will not be possible to cure such manifestations. An integrated approach consists of using medications that relieve anxiety, restore the condition of organs, and eliminate inflammation.
Pulsatile noise in the right ear or another type of noise is treated with different remedies based on the main ailment. Doctors usually prescribe:
- Antibiotics. Their use is associated with inflammation or infection that is localized in the ear. Antihistamines are also used to relieve swelling and reduce exudative discharge from the ear. Effective ones include Fenkarol, Hydroxyzine, Promethazine.
- Cerebral circulation stimulants. They are prescribed to normalize blood flow. The best products are Betagistin, Cinnarizine, and Cavinton.
- Nootropic medications. Their use will help achieve positive dynamics in combating noise manifestations. Mexidol, Cortexin, and Phezam are usually prescribed.
- Vitamin complexes. They strengthen vascular walls and restore nerve endings.
You should not choose medications on your own; this can lead to side effects, lack of effect and complications. These medications can only be taken if prescribed by a doctor. Whatever drug is prescribed, the dosage and duration of treatment must be observed.