The metabolism carried out in the human body is a series of successive chemical reactions. The constantly occurring transformation of energy and various substances is the basis for the normal functioning of the body.
Any doctor to whom the patient has approached can safely report metabolic disorders, since all diseases, to one degree or another, occur with metabolic disorders.
Metabolic disorders in the body can be of a protein, carbohydrate, fat, mineral, etc. nature, but this division is conditional and is based on the prevailing pathogenetic process - all types of metabolism are interconnected and significantly influence each other. The pathogenetic basis of metabolic disorders is a change in the harmonious interaction of substances involved in metabolism, an excess or deficiency of these substances, as well as disturbances in transformation reactions leading to the accumulation of intermediate products and the disproportionate formation of final metabolic products.
The causes of metabolic disorders are varied, the leading role among which is played by heredity and pathologies of organs and systems that regulate metabolic processes.
What is metabolism?
Metabolism can be divided into 2 important processes that occur in the body in parallel:
- Anabolism (assimilation, plastic metabolism).
- Catabolism (dissimilation).
Anabolism is the synthesis of substances within the body, which expends energy. Assimilation includes the biosynthesis of proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and fats. The most active process of plastic metabolism occurs in a growing organism.
Catabolism is the process of decomposition of substances into simpler elements, due to which the body stores energy that is used to maintain life. The simplest example is getting nutrients from food. It happens like this:
- Substances entering the body with food.
- Absorption from the digestive tract.
- Assimilation.
- Removal of breakdown products unsuitable for absorption.
For the normal functioning of the body, the balance of these two processes is important. When it is violated, various pathologies arise.
The following types of metabolism may be disrupted:
- Belkovoy.
- Carbohydrate.
- Water.
- Lipid (fat).
- Mineral.
Treatment options
Combating the causes and consequences of metabolic disorders is a responsible and complex matter. Congenital metabolic diseases require constant medical monitoring and regular therapy.
Acquired diseases can usually be stopped in the early stages of their development if you seek help in a timely manner. Many diseases without treatment develop into very problematic forms.
However, even without doctors, victims of metabolic disorders have something to do. The main attention should be paid to diet and diet. The amount of carbohydrates and animal fats consumed should be reduced and constantly monitored. Fractional meals are an opportunity to reduce the amount of food that comes in at one time. This maneuver responds with a shrinkage of the stomach and a gradual decrease in appetite.
It is equally important to get your sleep schedule in order.
The state of the nervous system is of great importance. You should avoid stressful situations and learn to respond adequately to those that do occur.
Without regular physical activity, it is almost impossible to achieve one, two and three - physical education should become a part of life.
But the basic and obvious points should in no case stop you on the way to a specialist - the doctor will tell you how to treat metabolic disorders in the body. The question is, who should we run to?
Causes of metabolic disorders
The main causes of metabolic disorders include:
- Stress.
- Genetic predisposition (congenital deficiency of certain enzymes).
- Unbalanced diet.
- Intoxication.
- Frequent diets.
- Bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol.
- Malfunctions of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives and other medications.
- Worm infestations and other parasitic infections.
- Viral diseases - influenza, measles, chickenpox.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Drug therapy
Metabolic disorders (symptoms in women require the help of a therapist, and, if necessary, other specialists) in some situations are provoked by congenital pathologies or various diseases.
After diagnosis, the doctor will establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe medication:
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Thyroid drugs | "Iodide", "L-thyroxine" | Drugs are prescribed for dysfunction of the thyroid gland. Take 1 rub. per day, washed down with milk or juice. The duration of therapy is 3-6 months. |
| Hormonal drugs | "Actovegin", "Amarin" | Medicines help restore hormonal imbalances. The standard dosage is 1-2 tablets. 3 r. per day for 4-6 weeks. |
| Insulin | "Insuman", "Levemir" | Medicines are selected for people with diabetes. The average daily dosage ranges from 0.5 to 1 IU/kg. |
| Enzymes | "Trypsin", "Lidaza", "Ranidaza" | The adult dosage is 5 mg 1-2 r. per day. Before the injection, the medicine is diluted with saline solution (0.9%). The course of treatment includes 20 injections. |
| Amino acids | "Glycine", "Methionine" | The drug is prescribed 1 tablet. (100 g) 2-3 r. per day for 14-30 days. The medicine eliminates disorders and restores metabolism, reduces emotional stress and promotes mental performance. |
| Antimicrobial agents | "Aspirin", "Dipyridamole" | The drugs eliminate pain and stop inflammatory processes. Prescribed 100 mg 3 times. per day. Therapy continues for 7-10 days, unless an adverse reaction occurs. |
To restore impaired metabolism, taking into account the provoking factor and the characteristics of pathological processes, antidepressants and drugs that accelerate or slow down metabolism are also prescribed. In some situations, homeopathic remedies are used.
Medicines are prescribed by the doctor after a complete diagnosis based on the results obtained. Many drugs cause side effects, which should be taken into account and self-therapy should be avoided.
Restoring metabolic disorders in a woman’s body is a long process. You will need the help of a general practitioner who, based on complaints and existing symptoms, will select the most effective solution. Therapy is carried out comprehensively, starting from a correct lifestyle and ending with medications if the disorders are complicated.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Congenital metabolic diseases
Congenital pathologies can be divided into 3 large groups. These include violations:
- Metabolism of small molecules (failures in the metabolism of carbohydrates, neurotransmitters, neuromodulators) - diseases that cause failures of intermediate metabolism.
- Energy metabolism – insufficient energy production and consumption.
- Metabolism of complex molecules - pathologies that interfere with the production of complex molecules.
Sports activities
Metabolic disorders (symptoms in women that appear at an early stage will help identify the disease and take action) can be restored with regular physical activity.
Sports activities have a positive effect on the general condition of the body, thereby supporting proper metabolism:
- increase energy costs;
- accelerate metabolic processes;
- increase the activity of the glands;
- increase the tone of the central nervous system;
- restore motor-visceral reflexes responsible for the metabolic process.
A specialist will help you select exercises, taking into account the woman’s condition and the individual characteristics of her body. For the first time, it is recommended to give preference to a simple gymnastics complex.
Along with playing sports, if there is a metabolic disorder, you should regularly take walks in the fresh air, walk, and run. It is important to devote at least 1 hour a day to active physical activity. Slow metabolism requires heavy loads and movements with high amplitude. It is recommended to run slowly and at intervals.
Metabolic disorders: symptoms
Common signs of metabolic failure are:
- Unhealthy skin color.
- Labored breathing.
- Sudden weight gain or loss without objective reasons.
- Joint and muscle pain.
- Deterioration in the quality of hair, nails, skin.
- Thermoregulation disorders (increased sensitivity to cold and heat).
- Sleep problems.
- Changes in blood pressure.
- Edema.
- Prolonged increase or decrease in body temperature.
- Frequent urination.
- Bowel problems: diarrhea or constipation.
- Memory impairment.
- Mood swings.
- Skin rashes.
- Tooth decay.
Symptoms of metabolic disorders in women include infertility and menstrual irregularities (the most common manifestation is scanty discharge).
Also, failures of different types of exchanges may have their own signs, identified by the results of laboratory tests. If carbohydrate metabolism is disturbed, the following may occur:
- Changes in the concentration of glucose in the blood (therefore, a common consequence of a failure of carbohydrate metabolism is diabetes mellitus - a violation of the absorption of glucose).
- Presence of glucose in urine.
Symptoms of lipid metabolism (its disturbance is usually associated with deterioration in the digestion and absorption of fats) are:
- Steatorrhea (presence of lipids in stool).
- Development of cholesterolosis (deposition of cholesterol in cell membranes or on the walls of blood vessels).
Signs of protein metabolism disorders are:
- Content of uric acid in the blood.
- Presence of amino acids in urine.
- Increased bilirubin levels in the blood.
Protein metabolism disorders
Proteins, as is known, are the main building material for the human body and play a leading role in its vital functions. Without exception, all pathological processes occur with a violation of protein metabolism, which is possible at any stage of its transformation in the body:
- Disturbances in the processes of protein absorption, which lead to nutritional deficiency (dystrophy of intestinal tissue, starvation, unbalanced composition of food in terms of the amino acid component).
- Disruption of the processes of protein synthesis of an acquired and hereditary nature, leading to a change in the amount of synthesized protein or to the formation of a protein with an altered molecular structure (hormonal changes, dysfunction of the nervous and immune systems, genomic errors).
- Disorders of amino acid metabolism, leading to an imbalance in the processes of transamination (formation) and oxidative deamination (destruction) of amino acids (pregnancy, treatment with sulfonamides, fasting, severe liver disease, pancreatitis, myocardial infarction, hypoxia, fasting, trauma).
- Disturbances in the terminal stages of protein metabolism, leading to the accumulation of nitrogenous breakdown products and a slowdown in their removal from the body (liver and kidney diseases, hypoxia, leukemia, genomic errors).
- Disorders of the protein composition of the blood, leading to a change in their total quantity or an imbalance in the ratio of their fractions (almost all pathological conditions, congenital abnormalities of protein formation, fasting, blood loss, loss of proteins in the urine).
Consequences of metabolic disorders
Metabolic disorders can lead to the development of the following diseases:
- Diabetes mellitus is the body’s inability to absorb glucose due to a failure in the synthesis of the hormone insulin.
- Coronary heart disease – acute or chronic damage to the heart muscle (myocardium) due to a violation of its blood supply.
- Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease in which narrowing of the lumens of blood vessels occurs due to deposits on their walls (atherosclerotic plaques).
- Obesity is an increase in body weight due to pathological fat deposits.
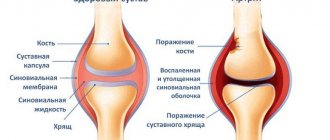
- Gout is an inflammatory disease of the joints.
Metabolic disorders can also cause:
- Deterioration of bones and muscles.
- Delayed growth and development in children.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system.
In children, the consequences of metabolic disorders can be:
- Rickets is a disorder of bone formation.
- Anemia (anemia) is a lack of erythrocytes (red blood cells that transport oxygen).
Water metabolism disorders
Water is an essential and essential fluid for homeostasis, making up slightly more than half the body weight of an adult. Normal water balance means approximately the same amount (about 2.5 liters) of water entering the body and leaving the body.
Violation of water metabolism can occur in the form of dehydration and pathological fluid retention in the body. Both conditions are dangerous and seriously affect human health: for example, with dehydration, blood thickening occurs, all organs and tissues suffer, especially the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract; with edema, the function of the excretory system is disrupted, cardiac output decreases and pressure increases.
| Dehydration | Water retention in the body |
If there is insufficient fluid intake into the body:
| For water poisoning:
|
With a lack of electrolytes:
| For swelling:
|
| With hyperventilation of the lungs - hyperventilation syndrome in children | |
For polyuria:
|
Diagnosis of metabolic disorders
To diagnose a metabolic failure, you need to consult a therapist. He will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis and refer the patient for studies, including:
- Blood and urine tests (general, biochemical, glucose).
- Glucose tolerance test.
- Blood cholesterol level test.
- Lipid profile.
- Computer tomogram.
- ECG.
Also, depending on the symptoms, instrumental studies (primarily ultrasound) of the kidneys, liver, pancreas, and organs of the endocrine system can be performed.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is recommended to discuss the use of recipes from witch doctors and healers with your doctor to prevent possible side effects. Many components can provoke an allergic reaction or worsen health conditions. There are also certain contraindications that you should pay attention to before starting treatment with folk remedies.
Effective alternative medicine recipes:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Herbal tincture | Mix chamomile, knotweed, birch buds, St. John's wort and immortelle, 100 g each. Grind the components well. Before use, pour 15 g of the resulting mixture with hot water (500 ml). | The tincture is consumed 35 minutes before meals; you can add a spoonful of honey for taste. |
| Blooming Sally | Pour boiling water (500 ml) over 30 g of herb. Leave for 30 minutes and strain. | The product is taken in 70 ml 4 times. per day before meals. |
| Dandelion root tincture | Grind the roots (20 g) and pour vodka, or alcohol (1 tbsp.). Infuse for 14 days in a dark place. Strain the medicine and take it according to the schedule. | In case of impaired material metabolism, it is recommended to drink 35 drops of the tincture. 3 r. per day before meals. |
| Garlic tincture | Grind the main product (350 g). Add vodka (200 ml), leave in a cool, dark place for 10 days. Strain the resulting tincture, squeeze and take according to the scheme. | The medicine is taken for 11 days. The dosage is gradually increased from 2 to 25 drops. |
| Walnut leaves | Pour 2 tsp. leaves with hot water (1 tbsp.). Leave for 2 hours, then strain. | The product is taken 100 ml before meals, 4 rubles. per day. |
To restore the metabolic process, it is also recommended to consume dandelion leaves in a salad or juice obtained from them. The leaves of this plant can also be brewed and drunk instead of tea.
Treatment
The tactics for treating metabolic disorders depend on the complexity and causes of the pathology. Minor glitches can be resolved by:
- Nutrition corrections.
- Lifestyle changes - maintaining a daily routine.
- Prescriptions of vitamin-mineral complexes.
- Physical education classes.
The type of diet depends on the nature of the disorder. In most cases, split meals are recommended: small portions, every 2-3 hours. Also exclude fried, pickled, salty, spicy, fatty foods. Limiting carbohydrates and animal fats may be necessary.
If the disorders are caused by enzyme deficiency or diseases, appropriate treatment is carried out. So, for diabetes mellitus, insulin therapy can be prescribed (if required), for thyroid diseases - hormonal medications. In some cases, surgical intervention is required (in the presence of goiter, pituitary adenoma).
Also, in case of metabolic disorders, sanatorium-resort treatment can be prescribed.
If you have symptoms of metabolic failure, you should consult a doctor. First, to fix a problem, you need to know its cause. This is impossible without diagnostic studies. This means that the patient will act according to intuition, which not only will not give the desired result, but can also aggravate the disorders. Secondly, self-medication often means taking vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements. Again, not knowing exactly what substances the body lacks can increase the imbalance. And an excess of vitamins and minerals is no less dangerous than their deficiency.
Treatment of metabolic disorders requires an integrated approach. The patient may need the help of several specialists at once, for example, an endocrinologist, nutritionist, or psychotherapist. A psychotherapist will help you get rid of stress and sleep problems.
Diseases associated with metabolic disorders
Metabolic failure is associated with a disruption in the normal processing of fats by the liver. At the same time, there is less low-density lipoprotein in the blood and the body begins to form reserves. A person's blood vessels suffer, which over time will lead to stroke and heart disease. Metabolic disorders are often accompanied by other diseases, including:
- Gierke's disease. A congenital metabolic disorder in which glycogen accumulates excessively in tissues. The pathology manifests itself in infants as stunted growth, enlarged liver, and protruding abdomen. The only way to treat Gierke's disease is diet. With age, the patient's condition improves.
- Phenylketonuria. This is a hereditary pathology characterized by slow mental development. It occurs due to a deficiency of the enzyme responsible for converting phenylalanine to tyrosine.
- Alkaptonuria. The disease is caused by a genetically determined deficiency of an enzyme that is involved in the metabolism of homogentic acid. As a result, arthritis develops. For therapy, a diet is prescribed that involves avoiding foods with tyrosine and phenylalanine.
- Albinism. This is a congenital absence of the black skin pigment melanin (characteristic of albinos).
- Gout. A chronic disease caused by impaired metabolism of salt and endogenous uric acid. Gout is characterized by the deposition of minerals in the kidneys, joints and cartilage, which causes the formation of painful inflammatory swelling.
- Hypercholesterolemia. The body's inability to break down lipoproteins and zolesterol, which leads to the accumulation of these substances in tissues. The disease causes atherosclerosis.
Prevention
Prevention of metabolic failures includes:
- A balanced diet with a limit on fatty, starchy, sweet foods and the inclusion of fruits, vegetables, lean meat, and dairy products in the diet.
- Avoiding overeating and fasting.
- Maintaining vitamin and mineral balance in the body (to control it, preventive blood tests should be taken).
- Developing stress resistance and avoiding emotional shocks.
- Quitting bad habits - alcohol reduces the production of testosterone, which is necessary to maintain the quality of muscle mass, and when smoking, toxins enter the body, which is why energy is spent on detoxification.
When developing a diet, it is recommended to consult a nutritionist. He will take into account all the needs of the patient’s body and develop an individual diet that allows him to maintain metabolic processes in optimal condition.
Also, the prevention of metabolic disorders is a timely visit to a doctor. You should make an appointment as soon as you notice at least a few symptoms of metabolic failure.
Treatment
Therapy should begin with eliminating the causes that caused it. To do this, adjust the diet and diet, reducing the amount of carbohydrates and fats consumed. Patients regulate the regime of wakefulness and rest, strive to avoid stress, play sports, due to which energy metabolism increases and the body becomes toned. The listed measures help eliminate metabolic disorders that are not complicated by genetic or other factors.
If the problem is neglected, you cannot do without medical help. If the pathology has already affected the functioning of the organs, the patient needs to undergo a course of treatment, including:
- hormonal drugs (for hormone imbalance);
- thyroid medications (for thyroid dysfunction);
- insulin (for diabetes).
Drugs
Reduced or increased metabolism requires complex treatment carried out under the supervision of a physician. Drugs that help correct metabolism are divided into the following categories:
- Hormones. Products based on biostimulants that normalize metabolism. Prescribed exclusively after diagnosis.
- Vitamin complexes. Preparations containing active compounds that take part in all vital processes, including fermentation, energy storage, production of necessary substances, tissue development, etc. Vitamins are taken regularly according to the schedule and dosage prescribed by the doctor.
- Enzymes. Products that neutralize the viscous consistency of hyaluronic acid.
- Medicines that control hemostasis. Anthrombiotics, erythropoiesis stimulants, hemostatics, etc.
- Amino acids (glycine, methionine). Means that compensate for the deficiency of these substances in the body, improving the state of energy resources, establishing hypothalamic-pituitary activity, etc.
- Biostimulants. They improve the condition of the nervous system, activate the body’s protective properties, and eliminate hypoxia. These drugs slow down or speed up metabolism, bringing it back to normal, and have a reparative effect.
After examining the patient and determining the causes of the pathology, doctors prescribe certain medications. As a rule, several of the most effective drugs are prescribed, for example:
- Reduxin. This drug is suitable for patients whose metabolic failures have led to gluttony and constant hunger. The components included in Reduxin give a feeling of fullness and help slow down the absorption of food, improving digestion. As a result, a person eats a normal amount of food and gradually gets rid of the extra pounds gained during illness.
- L-thyroxine. The medicine has a similar effect to thyroid hormone and is prescribed for pathologies caused by its dysfunction. After taking the drug, the functioning of the gland improves, the metabolism returns to normal.
- Glucophage. The medication normalizes the functioning of the pancreas, preventing the release of excess insulin into the blood, which is often observed with improper metabolism.
Diet
Deviations in metabolism require mandatory adherence to a diet. For adults, the doctor prescribes food No. 8 according to Pevzner. Nutrition for overweight and obesity is suitable for almost all people with impaired metabolism. The principle of creating a menu is not to reduce calories, but is aimed at restoring the function of systems and organs. A key sign of the effectiveness of a diet for metabolic disorders is a state of feeling slightly hungry.
The daily calorie content of the proposed diet is 2000 kcal, while the weight is normalized gradually and without harm to health. Basic diet rules:
- bread can only be made from wholemeal flour, no more than 150 g per day;
- You should eat vegetables every day (at least 200 g), with the exception of potatoes, beets, carrots;
- the patient's menu includes liquid soups with lean broth, but twice a week first courses with pieces of lean meat or meatballs are allowed;
- It is necessary to avoid spicy, salty, pickled foods;
- it is allowed to eat pasta made from durum wheat 2 times a week (serving no more than 150 g);
- lean meat should be in the diet daily, no less than 150 g (can be replaced with fish);
- eggs are allowed, but no more than 1 per day;
- Only vegetable oil is allowed;
- tea and weak coffee are drunk without sugar;
- consumption of fruits is mandatory, with the exception of bananas and grapes;
- low-fat dairy products are allowed;
- Baked goods and sweets are prohibited;
- be sure to drink 1.5-2.5 liters of water per day;
- Animal fats, rice, legumes, alcohol, store-bought sauces, smoked meats, semolina, and sausages are prohibited.
Folk remedies
If you have problems with metabolism, you should definitely consult a specialist, otherwise there is a risk of worsening your own condition. In addition to the prescribed treatment, it is allowed to use traditional methods of therapy. The following are considered effective:
- Infusion of walnut leaves. Four teaspoons of dry leaves are poured into 400 ml of boiling water and left for an hour. The decoction is taken in ½ tbsp. 4 times a day before meals.
- Horsetail tea. 1 tsp. The herbs are brewed with a glass of boiling water and left for 15 minutes. Drink tea 3 times a day, ¼ tbsp.
- Garlic tincture. 350 g of the product is grated, then the lower part of the mass (where there is more juice) is poured with 200 ml of alcohol and placed in a cool, dark place for 10 days. Afterwards, the liquid is filtered and drunk daily: first 2 drops, but every day increasing the dosage by another 2 drops. The duration of the course is 11 days.
Diseases
In medicine, metabolic disorders are listed under the ICD-10 code (E70-E90). This means that this phenomenon is a serious disease that requires full treatment. Moreover, it is so multifaceted and large-scale that it covers more than 50 individual syndromes and pathologies. For the most part, these are hereditary disorders, although there are also acquired ones. The most common ones are presented in the list below.
BUT (metabolism disorder) of aromatic amino acids:
- alkaptonuria;
- albinism;
- hypertyrosinemia;
- hyperphenylalaninemia;
- ochronosis;
- tyrosinemia;
- tyrosinosis;
- phenylketonuria.
BUT fatty acids and branched chain amino acids:
- adrenoleukodystrophy;
- acidemia;
- hypervalinemia;
- hyperleucine-isoleucinemia;
- deficiency of ACADs and muscle carnitine palmityl transferase;
- leucinosis.
Other BUT amino acids:
- argininemia;
- argininosuccinaaciduria;
- Hartnup's disease;
- hydroxylysinemia;
- hyperammonemia;
- hyperhydroxyprolinemia;
- hyperlysinemia;
- hyperprolinemia;
- glutaric aciduria;
- homocystinuria;
- methioninemia;
- sulfite oxidase deficiency;
- non-ketone hyperglycinemia;
- lactose intolerance;
- ornithinemia;
- excess cystine;
- sarcosinemia;
- Lowe and Fanconi syndromes;
- cystathioninuria;
- cystinosis;
- cystinuria;
- citrullinemia.
BUT carbohydrates:
- galactosemia;
- glucosuria;
- deficiency of galactokinase, sucrose, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, pyruvate, liver phosphorylase;
- oxalate nephropathy;
- oxaluria;
- pentosuria;
- cardiac glycogenosis;
- fructosuria.
BUT sphingolipids and lipids:
- gangliosidosis;
- diseases of Kufs, Fabry, Batten, Sendhoff, Woman, Gaucher, Tay-Sachs, Bielschowsky-Jansky, Krabbe;
- leukodystrophy;
- Faber syndrome;
- cerebrotendinous cholesterosis.
BUT glycosaminoglycans:
- mucopolysaccharidosis;
- Gunther and Hurler-Scheie syndromes.
BUT glycoproteins:
- aspartylglucosaminuria;
- Mannosidosis;
- mucolipidosis;
- α-L-fucosidase deficiency.
BUT lipoproteins:
- hyperglyceridemia;
- hyperlipidemia;
- hyperlipoporteinemia;
- hyperchylomicronemia;
- hypercholesterolemia.
BUT of purines and pyrimidines:
- hyperuricemia;
- xanthinuria;
- problems with uric acid synthesis.
BUT bilirubin and porphyrin:
- acatalasia;
- Gilbert's syndrome;
- erythropoietic porphyria.
BUT minerals:
- Menkes and Wilson's diseases;
- hemochromatosis;
- hypercalcemia;
- hypercalciuria;
- hypermagnesemia;
- hypophosphatasia;
- hypophosphatemia;
- enteropathic acrodermatitis.
Amyloidosis:
- nephropathy;
- polyneuropathy;
- Mediterranean fever.
Reduction of fluid in the body:
- hypovolemia;
- deficiency of extracellular fluid;
- plasma deficiency;
- dehydration.
Acid-base balance disorders:
- alkalosis;
- acidosis;
- hypervolemia;
- hyperglycemia;
- hyperkalemia;
- hypernatremia;
- hyperosmolarity;
- hypoinsulinemia;
- hypokalemia;
- hyponatremia;
- hypoosmolarity;
- hypoparathyroidism;
- hypopituitarism;
- hypothyroidism;
- parathyroid tetany.
Metabolism is a complex, branched system that cannot fully function with the slightest damage to at least one of its elements. As soon as there is a shortage or excess of all these bilirubins, amylases, lipoproteins, purines, one of these diseases is diagnosed. And such a signal indicates only one thing: a metabolic disorder.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to independently understand that the metabolism is disturbed based on individual symptoms, because they relate to the clinical picture of a dozen other diseases. So, at the first suspicion, it is better to undergo a series of laboratory diagnostics. At your appointment with an endocrinologist you will find:
- examination, survey: familiarization with medical history, height, weight, physical development, blood pressure, calculation of BMI and the amount of visceral fat;
- blood test for triglycerides, T3 and T4 hormones, lipoprotein, adiponectin, homocystine, HDL and LDL cholesterol, C-peptides, HbA1c, microalbumin, creatinine;
- Analysis of urine;
- Dopplerography of the carotid arteries;
- CT;
- Ultrasound of the pancreas, bile, kidney and liver;
- ECG.
First of all, an examination and interview of the patient is carried out, but often this does not allow us to accurately determine at what level the violations occurred and what substances they affected. Therefore, laboratory diagnostic tests are prescribed to see which organs have failed.
Preventing metabolic problems
To prevent the occurrence of metabolic imbalance, follow simple guidelines:
- eat rationally, form healthy eating habits;
- do not overeat, do not starve;
- replenish vitamins and minerals;
- regulate work and rest schedules;
- lead an active lifestyle, train, do gymnastics;
- are not exposed to stress;
- strengthen the immune system;
- do not drink alcohol, drugs, or smoke.
To normalize your metabolism, eat regularly and nutritiously
An imbalance of substances can prevent proper nutrition, the absence of bad habits, an active lifestyle, and strengthening the immune system. Energy is released during carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Proteins are essential for tissue repair and formation. Diseases of impaired metabolism disappear with adequate therapy with drugs and folk remedies.
How to restore a child's metabolism. First birthday
Did you know that for a full metabolism a child needs more than 70 of these same substances? And they are exchanged at different speeds and are absorbed in different ways. The circulation of substances in the body is, without irony, a real miracle of nature, a complex system of checks and balances. Even scientists have not yet figured out all the connections of this system, but they have already figured out the most important thing - and what mom definitely needs to know. What is this?
What does a mother need to know about metabolism in order to be calm about the health of her child? In the most general form, metabolism in children, like adults, consists of two large processes. On the one hand, complex nutrients are broken down into simple ones. On the other hand, complex ones are synthesized from simple ones and become building materials for the tissues of the body itself. And all this can only happen if there is a continuous supply of oxygen. In total, cells contain about 70 chemical elements that form two main types of chemical compounds in the body: organic and inorganic substances. And in the body there are constantly processes of synthesis and decay, and in order to ensure this continuity, the body needs substances that it receives along with food. And each of the substances - proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals - has its own role in metabolism. Russian scientist Ilya Arshavsky supplemented this theory with another principle - excess recovery. This principle goes like this: in order to enrich yourself with additional energy resources, you need to spend the ones you already have. Naturally, the question arises: why does nature need such altruism?
It's simple, Arshavsky says that body growth and metabolism depend not only on the absorption of nutrients, but also on physical activity.
He compares the body to a spring, which throughout life not only unwinds, but also twists, constantly feeding itself. And this happens only thanks to movement. As an example, the scientist cites the results of a study conducted with puppies during milk feeding - if puppies are given milk, but not allowed to move, then development and growth are sharply delayed. That is, when we move, it’s as if we are constantly winding up our clockwork. And for proper movement, you just need proteins, fats and carbohydrates. These are two sides of the same coin.
How to improve metabolism and lose weight
Metabolic disorders often cause excess weight. Fat deposition and muscle gain are similar anabolic processes. They differ from a catabolic point of view. Accelerating breakdown is beneficial for losing weight, but becomes an obstacle to building muscle.
Therefore, athletes are recommended to slow down their metabolism, and those who want to lose weight, on the contrary, need to speed it up. Help with this:
- warming up before the first meal;
- intense aerobic exercise throughout the day;
- drinking large amounts of water;
- adding spices to food;
- drinking green tea;
- relaxing activities to reduce stress.
Sometimes, to restore shape, it is enough to correct metabolic processes. This will help you lose weight without health-destroying diets and extreme stress. However, this will work for a healthy person.
Drugs that speed up metabolism
Let us note right away: you should not try to establish metabolism through medication without the help of an endocrinologist. All drugs are somehow related to hormones. Uncontrolled use can upset the balance.
By prescribing drugs that improve metabolism, the doctor seeks to cure the disease that slowed it down (hypothyroidism, calcium deficiency, iodine deficiency, and others). There is also a group of medications that stimulate metabolic processes - metabolic drugs:
- anabolic steroids – stimulate protein synthesis;
- hypoglycemic agents – promote the breakdown of glucose;
- lipid-lowering drugs – regulate cholesterol and phospholipid levels.
This group also includes enzymes and antienzymes. Their intake replenishes the deficiency or reduces the increased concentration of catalysts necessary for metabolic processes.
Causes
More than 30 different substances are involved in metabolism, with the synthesis, breakdown and absorption of which a variety of problems can arise. They lead to disturbances in metabolic processes. Scientists are still studying the factors that provoke such failures, but they are not yet ready to answer why this happens. They give only approximate reasons:
- age;
- genetic mutations;
- slagging, intoxication of the body;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland;
- heredity;
- poor nutrition;
- birth injuries and intrauterine hypoxia;
- refusal of healthy lifestyle;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- passive lifestyle;
- stress, depression, prolonged nervous tension, severe emotional stress;
- postpartum disorders, when a woman’s hormonal levels cannot recover after pregnancy and childbirth.
This is probably not a complete list of reasons, but scientific research is still underway in this direction. Perhaps very soon we will find out exactly why a failure occurs in this or that case. After all, if the provoking factor is not eliminated, the disease will remain untreated.