Immunological studies Other tests
05/12/201801/24/2019 Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova) 1840 Views immunology, ttg
Today we’ll talk about antibodies to TSH receptors, what they are, and when analysis is needed. Determination of the norm of antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is carried out if diffuse toxic goiter or autoimmune thyroiditis is suspected. The criterion is a clinical and laboratory marker due to its high specificity.
The relevance of the study is also important when assessing the effectiveness of the treatment and the risk of relapse of the disease.
Method: chemiluminescence immunoassay. Price for private laboratories: 1100 rubles. Time to obtain results: up to 5 days, excluding the day of collection of biomaterial.
- 1 What is TSH?
- 2 Antibodies to TSH receptors - what are they?
- 3 When should you get tested for TSH antibodies? 3.1 Test for antibodies to TSH for pregnant women
- 5.1 Reasons for increased AT to thyrotropin
Symptoms
In the early stages, the symptoms of all autoimmune diseases are very similar:
- You may suspect an increase in antibody activity if you constantly feel tired, pain and aching muscles, elevated temperature, rash, thinning hair, swelling, numbness in the limbs, hearing deteriorates, the skin becomes dry, and the tone of your voice changes slightly.
- With Hashimoto's thyroiditis, for example, inflammatory processes, a constant craving for sleep, and decreased performance are observed.
- With a goiter (hardening of the thyroid tissue), a person sweats a lot, is easily irritated, and has a rapid heartbeat.
Symptoms do not last forever and may appear and disappear.
Prevention
It is impossible to prevent the synthesis of antibodies to TSH target cells. But in most cases, specific immunoglobulins arise under the influence of external factors. To reduce the likelihood of autoimmune thyroid diseases, you should:
- give up bad habits;
- avoid exposure to radioactive substances;
- eat a balanced diet;
- be examined by an endocrinologist every six months;
- limit consumption of carbonated drinks and fast food;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes;
- avoid excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Some endocrinologists are confident that autoimmune disruptions in the body often occur against the background of chronic foci of infection. Therefore, they recommend timely treatment of indolent diseases of the ENT organs - rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis.
Treatment
If the test results are negative and your body contains antibodies that are warring against you, do not panic and undergo additional examination. Do not rush to make any terrible diagnoses yourself.
Doctors often talk about situations where a person, without any particular reason, was recommended to take an antibody test and the antibodies turned out to be slightly elevated, which is why this unfortunate person was sent to an endocrinologist and recommended to take another half a million tests. Very often in the future such patients begin to seriously worry that something is wrong with them, although in fact everything is fine with them.
It is necessary to consult an endocrinologist, find out the TSH level, and do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. In addition, an additional examination of the joints is carried out. After this, the doctor decides what treatment to prescribe to the patient.
Today, medicine does not have safe and working methods for reducing the amount of antibodies if it is higher than normal, however, there are ways to work with diseases caused by increased antibodies to TPO.
- The doctor may prescribe hormone replacement therapy, which includes drugs such as L-thyroxine, Eutorix.
- For heart problems, beta-blockers are prescribed. In order to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, the patient undergoes tests periodically.
- In some cases, glucocorticoids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
- In addition, vitamins and adaptogenic drugs are additionally taken.
- For severely enlarged thyroid glands, doctors recommend surgery.
If we talk about treatment with folk remedies, then in general it also has a place, although self-medication is extremely dangerous. Even if you are planning treatment with any traditional methods, it is better to discuss this with your doctor.
- Herbal mixture and persimmon tinctures are used here. You can find many recipes on the Internet.
- Also, in order to restore the functioning of the thyroid gland, you need to get a sufficient amount of iodine, maintain yourself in a good mood, take a competent approach to the treatment of viral diseases, give up alcohol and smoking if possible, eat right and normalize your daily routine as much as possible.
- Some doctors may recommend avoiding wearing jewelry around the neck, as metals can affect the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Is it possible to lower antibody levels?
Before reducing the AT gland content, the cause of autoimmune disorders is identified. Depending on the indications, patients are prescribed:
- Antithyroid drugs (Tyrozol, Mercazolil) - interfere with the synthesis of iodine-containing hormones. Used for thyrotoxicosis, hormonally active tumors in the gland.
- Thyroid hormone substitutes (Euthirox, L-Thyroxine) – compensate for the lack of T3 and T4. Used for hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's thyroiditis in the hypothyroid phase.
- Glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone) - reduce inflammation in the gland. Used only for simultaneous autoimmune and subacute thyroiditis.
- Iodine preparations (Iodinol, Iodine Active) – stimulate the production of thyroid hormones. Used in complex therapy of hypothyroidism.
To lower antibodies in the blood, it is necessary to identify and eliminate provoking factors. If conservative therapy does not give the desired effect, a thyroidectomy is prescribed - removal of the thyroid gland.
An increase in AT of the thyroid gland is a consequence of incorrect functioning of the immune system. Specific proteins damage the organ, which leads to endocrine pathologies - Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, hypothyroidism, toxic goiter, etc. Before reducing the AT level, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is performed. Based on its results, drug treatment is prescribed. If it does not help, the gland is removed.
Rules for treatment with thyreostatics
The use of the drug should be constantly monitored by the attending physician; thyreostatics should not be taken in the initial volume (as in the first phase of treatment). This leads to cessation of thyroid function and increased production of TSH in the pituitary gland, which in turn increases the synthesis of thyrocytes. An increase in the production of thyroid cells (thyrocytes) leads to bloating, even after stopping thyroid drugs. There is a risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Carbimazole and thiamazole give a good therapeutic effect; the drugs are taken orally. Treatment with drugs begins with maximum doses that provide a therapeutic effect, then the dose is gradually reduced to the minimum. Usually carbimazole or thiamazole is taken for a year or two, once a day.
To confirm the therapeutic effect of thyreostatics, the endocrinologist will ask you to take a test for the level of T4 and T3 in the blood serum. Normal hormone levels indicate overcoming thyrotoxicosis. The TSH hormone level remains reduced for some time after the normalization of T3 and T4.
As hormonal levels normalize, physical activity is gradually restored.
Taking thyreostatics does not require the introduction of a special diet, however, the diet must contain sufficient quantities of proteins, fats, vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
Nutritionists advise eating frequently, in small portions, during treatment to prevent weakening of the body. It is recommended to include foods rich in carbohydrates (pasta, bread, fruits) in the diet; lean varieties of meat, preferably boiled, squid, seaweed and other seafood will be beneficial.
To reduce the risk of osteoporosis, you should take additional calcium supplements, and also put dairy products, fish and legumes on the table more often.
If taking hormonal medications causes weight gain, you should limit your consumption of sweets, fatty meats, sugar and foods rich in trans fats.
When hormonal metabolism is normalized, you should move more and exercise. What loads to choose and in what volume will the endocrinologist or physiotherapist recommend.
When is it recommended to take an anti-pTTH test?
This kind of tests is usually prescribed in case of suspicion of improper functioning of the thyroid gland, its enlarged state upon palpation. A person may also tell the doctor about what has been bothering him lately and complain about:
- insomnia;
- increased irritability or sentimentality;
- sudden weight loss or unjustified weight gain;
- increased fatigue.
An increase or decrease in TSH in the thyroid gland can negatively affect all systems of the body.
In what cases does a patient need to have an ATP TSH test:
- If you suspect hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis (increased activity of the hormonal production of the thyroid gland). Based on the analysis, the doctor will draw up a treatment plan that will be effective for the patient.
- The presence of Graves' disease or Graves' disease is a direct indicator for screening a person for anti-p TSH. By studying the patient’s research indicators, it will be possible to monitor the decrease in the hormone. In this way, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions about how effective therapy to reduce AT is.
- In the last stages of pregnancy. In case a woman had some difficulties with the functioning of the endocrine glands before pregnancy. The analysis will help to identify the level of TSH in the blood of women, and to avoid the development of thyroid pathology in the unborn baby.
- If the new mother had antibodies to rTSH, then it is necessary to diagnose the newborn in order to prevent serious diseases that may further affect the development of the child (physical, mental).
Rules for taking the analysis
If you plunge into the physiological characteristics of the human body, it becomes clear that the concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone is not the same at different periods of the day.
TSH is maximally elevated at 4 am. The lowest value of normal indicators of this substance is typical for 7 pm. It is recommended to take blood samples to study anti-TSH levels in the morning. Before taking the test for antibodies to TSH, it is recommended to avoid eating food, smoking and drinking any liquid, with the exception of ordinary water.
The last meal on the eve of the test should be taken at least 8 hours before. For laboratory research, biological material is collected from a vein. You can get the finished result the very next day.
Why does TSH increase?
If TSH is elevated even slightly, this means that the thyroid gland has reduced the synthesis of iodine-containing hormones. Why this happened needs to be found out as soon as possible, before their lack disrupts metabolism throughout the body. Among the reasons why the thyroid gland has decreased its activity and the level of TSH has increased in women, men, and children are the following ailments:
- hypothyroidism – the thyroid gland has reduced the production of hormones;
- tumors of the thyroid gland or pituitary gland;
- removed gallbladder;
- heredity;
- problem with the adrenal glands;
- overdose of iodine-containing drugs;
- antibodies to the thyroid gland, TSH receptors;
- gestosis – complications during pregnancy;
- stress, insomnia;
- poor nutrition.
Having discovered the cause, treatment must be started immediately, otherwise it can provoke serious problems in the body of women, men, and children. For example, hypothyroidism, antibodies to TSH receptors and other problems in the mother's body can greatly affect the child. In an infant, the thyroid gland may be so small that it will lead to growth retardation and cause cretinism. Therefore, if a newborn child has been diagnosed with hypothyroidism, antibodies to TSH receptors and other problems associated with the functioning of the thyroid gland, treatment should be started immediately, in the first two weeks of life. Otherwise, hypothyroidism in a child will lead to irreversible consequences.
Therefore, after the cause is discovered, it is imperative to follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor: on your own, without the help of medications, the thyroid gland rarely recovers, and ignoring the problem leads to death. The consequences are especially serious if the problem is caused by a tumor.
During therapy, the patient will have to undergo tests more than once. This should be done to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. This means that if therapy for hypothyroidism or another ailment is successful, deciphering the results will let the doctor know that you can stop taking the medications. Particularly good results can be achieved if hypothyroidism, antibodies to TSH receptors and other ailments were detected at a stage when the level of thyrotropin has risen, but the concentration of other hormones has not yet changed.
In some cases, lifelong therapy is prescribed. In this situation, the analysis should be done regularly, at the same time, and TSH values should range from 0.3 to 3 µIU/ml. Such monitoring will allow the doctor to timely adjust the treatment regimen if indicators change.
Preparation for the procedure
The level of TSH can be affected by changes in the circadian rhythm: a decrease in TSH is observed when sleep is disturbed or when working at night. The highest level of the hormone is recorded from 2 a.m. to 6–8 a.m., while it decreases in the evening.
The TSH test must be taken in the morning, after a full night's sleep.
Three days before the test, you must stop drinking alcohol, fatty and spicy foods. Taking biomaterial (blood) for analysis is carried out on an empty stomach (permissible 4 hours after a light snack), at the same time during a dynamic TSH study (for example, to monitor the effectiveness of treatment).
Analysis transcript
After performing a laboratory blood test for antibodies to specific TSH receptors, the norm is interpreted as follows:
A result of less than 1.5 m/l means a negative result;
From 1.5 to 1.76 m/l - questionable results;
More than 1.76 m/l - the analysis is considered positive.
If a negative test result is obtained, we can say that the person does not have functional and organic disorders in the thyroid gland. In some situations, even a negative result is not a guarantee of complete well-being. If there is any doubt, a medical specialist recommends additional examination methods.
What does an increased indicator mean?
A high level of antibodies may indicate the presence of a number of pathologies in the patient:
- With a high degree of probability - 85-95%, we can say that the patient has Graves' disease, in other words, he has an enlarged thyroid gland;
- Hashimoto's autoimmune thyroiditis - this disease is much less common;
- Thyroiditis – can occur in women after childbirth.
To provide a more accurate analysis, additional research will be required, since each of these diseases has its own treatment methods.
increased antibodies to TSH
Found (85 posts)
endocrinologist September 6, 2013 / Anastasia... / Moscow
...were diagnosed with primary hypothyroidism as a result of AIT. TSH
- 3.65 (norm up to 4.0), T4 St - ... .3 (norm from 9 to 18).
Antibodies
also elevated - 255 (normal is up to 5).
... please, is it really necessary to lower TSH
to less than 2, because it doesn’t work for me ... open
endocrinologist August 11, 2013 / Natalya / Engels
Good afternoon ! In February I was diagnosed with signs of diffuse nodular formations of the thyroid gland. right lobe - width 2.0 thickness 1.6 length - 4.5 left lobe 2 x 1.8 x 4.7 V glands - 15.2. In the right lobe... open
August 13, 2013 / Anonymous
It may be a secret to your doctor, but these antibodies
no need to check or reduce.
It is enough that TSH
.
These antibodies are elevated
in 10% of healthy people. Eutirox is not used to treat nodes. Benign according to...
endocrinologist May 25, 2013 / Alexander... / Alatyr
Hello, I have been treating diarrhea for 5 years; I gave birth to a child 1.5 years ago and took propicil. I didn’t take anything for 4 months, then the doctor prescribed 1 tablet. I passed Mercazolil on the day... open
June 1, 2013 / Alexander
...the method of choice will be surgery. However, according to your two indicators ( TSH
, T4 sv) it is not clear in absentia whether there is now a relapse of DTZ.
You can donate
thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor
antibodies Now, if they are elevated
, this is an indication for...
endocrinologist May 9, 2013 / Alexandra... / Vladivostok
MRI: Endosellar location of the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is enlarged, measuring 11x7.9x8.8. Asymmetry of the upper contour of the pituitary gland tissue. This is fine? open
May 10, 2013 / Anonymous
TSH increased several times
antibodies
were previously
elevated , but prolactin is slightly elevated. I feel terrible, and my vision has dropped significantly over the past year. By the way, an MRI in December showed that everything...
endocrinologist March 6, 2013 / Inna
... (I have had this since childhood). Took hormone tests: TSH
-thyroid-stimulating hormone and free T4 are normal - 1.13 and 1, ... from 0 to 40. I am 23 years old.
Antibodies
to peroxidase are also
elevated
- 97. Ultrasound doctor's conclusion - diffuse changes in the thyroid gland. Knot? Plot … open
endocrinologist March 5, 2013 / Olga / Samara
..., took tests because the TSH
decreased, free T3 and T4 are normal.
... 16.44 (normal 9.01-19.05) Antibodies
to thyroglobulin 21.1 ABOVE NORMAL (norm less than ... 13 weeks of pregnancy? Why can
antibodies
elevated , why is this dangerous for ... open
endocrinologist February 18, 2013 / Tatyana / 0
… thyroid. I got tested.
Antibodies
to thyroglobulin (4435 IU/ml) and thyroid peroxidase (1610 IU/ml)
are highly elevated hormones TSH
, T3 and T4 are normal, thyroglobulin is reduced (less than 0.2 mg/ml). Some… open
endocrinologist October 16, 2012 / Natalya / Moscow
My husband has monocular diplopia of unknown etiology. Ultrasound shows enlargement of the extraocular muscles. MRI of the brain, Ultrasound of the thyroid gland - normal, thyroid hormones - normal, general neurology -... open
October 16, 2012 / Alexander
Hello. If we are talking about endocrine ophthalmopathy, then it will cause increased
antibodies
to the
TSH
. Unfortunately, I cannot make a diagnosis in absentia. There are quite clear recommendations for diagnosis and treatment...
endocrinologist October 15, 2012 / Tatyana / Moscow
... I was diagnosed with stage I-II DTZ. The gland is not enlarged, there are no nodes. T3 and T4 were elevated
,
TSH
was not detected,
antibodies
were 2.3 when the norm was 1. Pulse up to 120, pressure reached 170/110. They prescribed Mercazolil with 20 mg, ... open
endocrinologist August 18, 2012 / Sveta / Kyiv
Hello, Doctor. My baby is almost 3 months old. (born May 24, 2012). On January 1, 2011, she began treating DTZ by taking Tyrozol. After 8 months got pregnant (not planned). At the 6th week. pregnancy... open (6 more messages)Last 5:
August 20, 2012 / Alexander
... when the hormones return to normal and you will need to decide whether to stop treatment or not. Antibodies
TSH
receptors return to normal more slowly than hormones.
...whether there will be a relapse of the disease or not. While they are elevated
, you cannot stop treatment, otherwise there is a risk of relapse...
Reasons for increasing values
As mentioned earlier, an increased level of antibodies to TPO means a militant attitude of the immune system towards the body’s cells. The main reason for this is a “breakdown” of the thyroid gland, due to which thyroid peroxidase enters the bloodstream.
TPO is necessary for the body, because it plays a significant role in the synthesis of iodine. If the amount of antibodies against TPO increases, less iodine is synthesized because the level of TPO decreases. Iodine is required by the body to produce the hormones T3 and T4, which, accordingly, are now also poorly produced. Problems begin with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, blood vessels, nervous and respiratory systems.
The causes of elevated markers of autoimmune diseases are:
- diseases such as diabetes, thyroiditis, hereditary immunity disorders, rheumatism, thyroid injuries;
- various viral diseases, inflammation, iodine deficiency or excess.
In addition, the amount of antibodies is affected by:
- ecology;
- stress;
- viral diseases;
- long-term treatment with hormonal drugs.
Antibodies may be slightly elevated if the patient had radiation therapy before donating blood.
With a normal TSH level, increased AT to TPO relative to the norm is not yet a pathology.
Causes of elevated TSH levels in the blood
The following reasons may cause an increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone:
- benign, less often malignant neoplasms in the pituitary gland (pituitary tumor);
- hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism is a pathology of the production of hormones by the thyroid gland;
- surgery to remove the gallbladder;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- autoimmune thyroiditis (also called Hashimoto's goiter);
- intoxication due to lead poisoning;
- excess iodine in the body;
- genetic pathologies;
- In women, an increased analysis of antibodies to TSH may occur with gestosis in late pregnancy.
If an increased level of TSH in the blood is initially detected, it is worth taking the test again, but prepare for it more carefully. Distortion of results can occur if measures are not taken in preparation for analysis. For example, the patient did not inform the doctor about the medications he was taking.
AT to TG
The following can increase the level of these substances:
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- diffuse toxic goiter;
- treatment of papillary and follicular thyroid cancer.
This indicator is of particular importance in the diagnosis of cancer. In papillary and follicular cancer, the resulting tumors begin to produce thyroglobulin in large quantities. After surgery to remove the thyroid gland, its level decreases sharply (equal to zero). If after removal of tumors this indicator is high, we can talk about relapse of oncology.
In some patients, antibodies to TG bind to thyroglobulin molecules and significantly change their shape and structure. As a result, they become invisible to laboratory analyzers. Therefore, determination of the level of these substances should be carried out together with an analysis for thyroglobulin. It should also be remembered that this type of diagnosis of cancer is only permissible for patients who do not have a thyroid gland. In a healthy person, the level of AT to TG should not exceed 40 IU/ml.
The role of anti-rTSH in the body
The production of any autoantibodies is considered a pathology and leads to a negative reaction from the body. In most cases, these compounds negatively affect the functioning of its systems, causing their hypofunction.
If the AT to TSH receptors is increased, everything happens exactly the opposite: the antibodies independently combine with receptors on the surface of thyrocytes, causing not a decrease, but an increase in the production of thyroid hormones and the development of thyrotoxicosis.
Pathogenesis of the development of DTZ
Thus, anti-rTSH can be considered one of the important laboratory markers of such a disease as DTG (diffuse toxic goiter).
Important! The mechanism of development of autoantibodies to thyrotropin receptors is not fully understood, but the influence of genetic factors can be traced in the development of thyrotropin.
Antibodies to TSH receptors
Antibodies to TSH receptors (AT-rTSH) are such would-be protectors. These are immunoglobulins of class G. For them, the target organ is the receptors that attach the TSH molecule to the surface of the thyrocyte.
Regulation of the production of thyroid hormones is carried out precisely through this receptor. The receptor that attaches TSH helps the latter penetrate inside the cell and stop the production of excess hormones.
AT-rTSH attach to these receptors and prevent TSH from acting on thyrocytes. Since there is no restriction on their activity, thyrocytes begin to produce thyroid hormones in large quantities. The TSH level becomes lower and lower, but the activity of the thyroid gland does not decrease.
Why determine the level of antibodies to TSH receptors?
- Diagnostics – it is the determination of the AT-rTSH level that is necessary to make a diagnosis. If the indicator is higher than normal, the diagnosis of diffuse toxic goiter is beyond doubt.
- Determination of treatment tactics - treatment of thyroid cancer begins with the use of antithyroid drugs that block the function of the thyroid gland. AT-rTSH decrease - treatment with these drugs continues.
- Prognosis and probability of relapse - if after a certain period of treatment a state of euthyroidism is achieved, but the level of AT-rTSH remains as high as before treatment, the probability of relapse of DTG is very high. In this case, surgical treatment is recommended.
AT-rTSH and pregnancy
Determination of this indicator during pregnancy is indicated when a low TSH level is detected, which may be a variant of the norm. If the indicator is not increased, there should be no worries. Pregnancy is proceeding normally.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptors are membrane structures of thyrocytes. They specifically bind pituitary TSH and ensure the implementation of its biological action. An increase in the level of Antibodies to the TSH receptor (AT to rTSH) is observed in Graves' disease (diffuse toxic goiter).
A test to determine antibodies to TSH receptors is an important step in the diagnosis of Graves' disease - diffuse toxic goiter (autoimmune hyperthyroidism).
Indications for determining Anti-TSH p antibodies:
- Identification or exclusion of autoimmune hyperthyroidism and its differential diagnosis with autonomous ectopia of the thyroid gland. The detection of Anti-TSH p antibodies in patients with thyrotoxicosis indicates that the disease is of an autoimmune nature. Since the course of treatment for Graves' disease differs from that of other forms of hyperthyroidism, it is clear that before starting treatment for a patient with thyrotoxicosis, it is necessary to test for antibodies to the TSH receptor.
- Monitoring therapy for Graves' disease and assessing the likelihood of relapse in patients. The amount of Anti-TSH p antibodies decreases with successful therapy. A significant drop in titer or disappearance of these antibodies means the patient is in remission of the disease, and based on this fact, the end of the course of therapy can be planned.
- Determination of Anti-TSH p antibodies should be carried out in pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy. Since these antibodies belong to the class of IgG antibodies, they can cross the placenta and lead to thyroid disease in infants. In patients with a history of thyroid disease, testing for antibodies to TSH receptors in the third trimester of pregnancy is mandatory. This will allow us to identify and assess the risk of developing thyroid pathology and the fetus.
How to reduce thyroid-stimulating hormone (treatment methods)
If it turns out that antibodies to TSH receptors are highly elevated, treatment is carried out by an endocrinologist. Most likely, conservative therapy will be prescribed. Surgery is extremely rarely required.
The patient is prescribed cytostatics. The most common are Mercazolil and Methylthiouracil . Under the influence of these drugs, cells divide more slowly, and antibody activity decreases. The level of antibodies to TSH receptors returns to normal.
Radioiodine therapy may also be prescribed . This method has become increasingly common lately. The effectiveness of therapy lies in the fact that radioactive iodine I-131 destroys antibodies that the body recognizes as foreign. The disadvantage of radioiodine therapy is that such iodine also irradiates healthy cells. Only the thyroid gland is exposed to irradiation, since the effect on the skin is no more than 0.2 cm.
Preparation for radioiodine therapy is mandatory. The patient must exclude:
- medications containing TSH - a month before therapy;
- products containing iodine - a week before manipulation;
- fast food, canned food, dairy and seafood products, eggs, greens and beans - two weeks before radioiodine treatment.
Pregnant women cannot use this type of therapy, so they are prescribed the medicine Propylthiouracil .
Pathologies of the thyroid gland in pregnant women
In women, during pregnancy, AT can penetrate the placenta, subsequently causing congenital pathologies of the thyroid gland in children. Patients registered with an endocrinologist should undergo an AT test during pregnancy to eliminate the risk of problems with the thyroid gland in the newborn.
An antibody test in a pregnant woman helps identify the following diseases:
- Graves' disease;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- diffuse toxic goiter.
Uncompensated thyrotoxicosis, caused by the production of antibodies to TSH, leads to the following deviations from the norm in a woman’s physical well-being:
- placental abruption;
- miscarriage;
- arterial hypertension;
- anemia;
- thyrotoxic crisis;
- heart failure
Congenital thyrotoxicosis leads to:
- intrauterine developmental delay;
- improper structure of internal organs;
- physical disabilities.
Deviation from the norm in the results of an AT test is not a reason to perform an artificial termination of pregnancy. Thyrotoxicosis requires compensatory therapy with hormonal drugs. To relieve symptoms of thyrotoxicosis and normalize the physical condition of pregnant women, propylthiouracil is used, a drug that does not pass into breast milk and the blood of newborns. If problems are identified during pregnancy that require radical intervention, surgery or radioactive iodine, their solution is postponed to the postpartum period.
The initial dose is 200 mg/day, it allows you to maintain normal T4. The level of T4 hormone production should be monitored every month.
During pregnancy, hormone levels gradually normalize and propylthiouracil is usually discontinued in the third trimester.
A few months after giving birth, the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis may return; it is necessary to donate blood again for hormones and, if necessary, start taking thyreostatics. Taking small doses of the drug by the mother is safe for breastfed children, however, if high doses are prescribed, it is recommended to stop feeding.
Normalization of elevated AT
To reduce the activity of the thyroid gland, a specialist may prescribe the drugs Methylthiouracil or Mercazolil. These drugs reduce the activity of antibodies on thyroid receptors. Radioactive iodine treatment is also used.
In case of diffuse thyrotoxic goiter, it is sometimes necessary to resort to surgery. But in order not to bring the matter to the operating room, it is better to prevent the disease.
If the amount of antibodies is more than 10 IU/l, a serious illness is likely that requires immediate treatment. To prevent Graves' disease, it is necessary to promptly treat infectious viral diseases. In addition, it is necessary to constantly eat iodine-containing foods. It is worth, for example, switching to using exclusively iodized salt.
To make a correct diagnosis, it makes sense to consult with an immunologist who knows everything about antibodies. Self-diagnosing and treating yourself without a doctor’s prescription is dangerous.
What does this hormone mean?
Everyone knows why a person needs immunity. It protects the body from harmful viruses and bacteria that can harm health. Defenders are various antibodies, which consist of proteins that can detect the “villain”.
But this mechanism does not always work smoothly and correctly; a failure, already described above, may occur - antibodies will begin to fight with healthy cells of the body.
The abbreviation AT to TPO stands for Antibodies to Thyroid Peroxidase.
Thyroid peroxidase is an organic substance consisting mainly of protein produced by the thyroid gland, which is involved in the hormonal synthesis of organic compounds.
For various reasons, the immune system may consider this enzyme an enemy and try to get rid of it. Because of this, AT to TPO increases, as a result of which the synthesis of many important hormones is disrupted.
Normal indicators
In order for a doctor to correctly assess the condition of the thyroid gland, the patient must undergo a test, the material for which is taken from venous blood.
There are international standards that are used to make things easier to understand. For all people, the norm of AT to TPO depends on age.
In adult women and men, it looks on average like this:
- up to 50 years – not higher than 30 IU/ml;
- after 50 years – not higher than 50 IU/ml.
During pregnancy, the norm of antibodies to TPO should be 5.6 units/ml.
It is worth noting that an increase of twenty units is still the norm, but this should still be monitored in order to prevent problems.
In a child, depending on age, the number of antibodies changes:
- in newborns – 1.1 – 17.0 mIU/l;
- up to two and a half months – 0.6 – 10.0;
- up to two years – 0.4 – 7.0;
- up to five years – 0.4 – 6.0;
- up to fourteen – 0.4 – 5.0.
Physiological values
Based on the above, it becomes clear that the less autoantibodies are detected in the blood, the better. And indeed it is. And how is the study of antibodies to TSH receptors interpreted: the interpretation of the analysis is indicated in the table.
Table: Interpretation of anti-rTSH values:
| Result | Index | A comment |
| Negative | less than 1.5 IU/l | The absolute norm of antibodies to TSH receptors, found in healthy people |
| Intermediate | 1.5-1.75 IU/l | This indicator means that a controversial (doubtful) result was obtained. You should retake the test in a few days |
| Positive | more than 1.75 IU/l | Is a laboratory confirmation of the development of DTZ |
Note! Elevated anti-TSH values are observed in approximately 85% of patients with diffuse toxic goiter. In some cases, the disease may proceed without a positive autoantibody level.
Specific signs of DTZ
Characteristics of the hormone
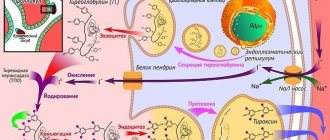
Thyrotropin (other names: TSH or thyroid-stimulating hormone) is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland to regulate the functioning of the thyroid gland. It has an effect on iodine-containing thyroid hormones, thyroxine and triiodothyronine, acting on thyroid receptors, stimulating or reducing their production. Thyrotropin is produced by the pituitary gland, an endocrine gland located in the sella turcica - a bone pocket in the wedge-shaped part of the skull, and attached below to the brain.
The activity of the pituitary gland is controlled by the hypothalamus, one of the parts of the brain. As soon as it detects an increase or decrease in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, it sends a signal to the pituitary gland, which, in order to reduce the production of thyroid hormones, increases the synthesis of TSH, in order to increase it, it decreases.
In order for the body to function correctly, without failures, thyrotropin and iodine-containing hormones must interact well with each other. Together they influence the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates in the body, regulate the cardiovascular, reproductive, digestive and nervous systems of humans. Therefore, their quantity in the blood is completely interrelated.
Antibodies and receptors
Receptors are associations of nerve endings, neurons and formations of intercellular substance. They ensure the transformation of internal or external environmental factors into nerve impulses. TSH receptors respond to T3 and T4 and promote their production.
Antibodies are proteins that combine with certain types of molecules (immunoglobulins or globulins). This is how the immune system reacts. If any malfunction occurs in the immune system, then it produces antibodies to the hormone, which stop its action and begin to stimulate the thyroid gland.
As a result, the level of two hormones increases significantly, which provokes the development of hyperthyroidism. When the opposite condition occurs, thyroid hormones are poorly produced or quickly destroyed, hypothyroidism occurs.
But it is almost impossible to find out which TSH ATr are synthesized by analysis; the test only helps to see the ratio of antibodies to thyrotropin receptors.
Article on the topic: TSH hormone (thyroid-stimulating): the norm for women of different ages
What to do if your AT level increases
How can you lower the level of antibodies that are produced to thyroid cells? In some cases, this is not necessary, since a minor deviation is not considered a pathology. A reduced rate is also considered a variant of the norm.
If the analysis reveals very high values, which are combined with symptoms of thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism (enlarged thyroid gland, fatigue, excessive sweating, etc.), the following treatment is carried out:
- use of thyroid drugs. They replenish the deficiency of thyroid hormones;
- glucocorticoid therapy;
- removal of the thyroid gland;
- use of selenium preparations.
If the functioning of the thyroid gland is maintained, the prognosis for patients is favorable. If treatment is not applied, severe heart failure occurs, atherosclerosis and dementia develop.
Bibliography
- Rudnitsky, Leonid Diseases of the thyroid gland. Pocket guide / Leonid Rudnitsky. - M.: Peter, 2015. - 256 p.
- Sinelnikova, A. 225 recipes for thyroid health / A. Sinelnikova. - M.: Vector, 2013. - 128 p.
- Sinelnikova, A. A. 225 recipes for thyroid health: monograph. / A.A. Sinelnikova. - M.: Vector, 2012. - 128 p.
- Uzhegov, G.N. Thyroid diseases: Types of diseases; Treatment with traditional medicine; Medical / G.N. Uzhegov. - Moscow: Russian State University for the Humanities, 2014. - 144 p.
- Khavin, I.B. Diseases of the thyroid gland / I.B. Khavin, O.V. Nikolaev. - M.: State Publishing House of Medical Literature, 2007. - 252 p.
Who should be tested and why is it carried out?
- The test is most often prescribed for people who have problems with the thyroid gland. Such people may not find the cause of the disease for a long time, and it is this test that can clarify the picture and clarify the diagnosis.
- Pregnant girls. It is very important to monitor TSH levels, since the fetus does not yet have its own functional thyroid gland and is completely dependent on the mother. An increased level of antibodies can break through the placenta and cause irreparable harm to the entire hormonal system of the unborn child.
There are several symptoms that should you see a doctor and get checked:
- Sudden change in body weight towards weight loss or weight gain;
- Irritability and general malaise appeared;
- Frequent headaches and tachycardia;
- Feeling overheated and excessive sweating, even in comfortable conditions.
increased antibodies to TSH
Found (85 posts)
endocrinologist February 11, 2015 / Ksenia / Moscow
… . I take oral contraceptives Regulon, because your menstruation cycle is irregular. My
antibodies
to TPO
elevated TSH
= 9. I was prescribed l-thyroxine 100 mcg.
I drank for 5 months. now I have ttg
= 0.01. T3 is slightly above normal, T4 is ok... open
endocrinologist January 10, 2015 / Semenova…
...
antibodies
increased , and in this analysis they are normal, but
antibodies to TPO
were increased TSH
was ... 198/110.
Now I have received the result: TSH
has become even lower - 0.012 (already... remains? For what reason can
TSH
continue to decrease after stopping eutyrox?... open
endocrinologist November 28, 2014 / Irina / Kursk
... Diagnosed with AIT, tested TSH
0.51 t4 16.6
antibodies
to TPO 322
are increased
, female hormones are normal, male testosterone and free.
... changes occur with hyperprolactinia and is it necessary to reduce the hormone antibodies
to TPO? Doctors tell me I don’t need it ... open
endocrinologist November 16, 2014 / Irina / Chelyabinsk
... makes a diagnosis: nodular non-toxic goiter, grade 0-1, against the background of AIT. All tests are normal: TSH
, T4 St., T3 St.
Only antibodies
are elevated - last time it was 220. I get examined every year. No treatment ever...open
endocrinologist November 6, 2014 / Tatyana
Good afternoon.. Please tell me whether antibodies
for pregnancy they
are elevated
as much as 735.
TSH
, TTs are normal. I recently had an hCG test and my hCG began to drop. Perhaps this is due to increased antibodies...? Which one can... open
endocrinologist August 23, 2014 / Natasha / Omsk
Hello, doctor! This is the situation: increased
antibodies
to TPO-68.81; T4-16.15;
TSH
-1.95; Of the sex hormones, FSH-18.11 is elevated... these test results, I’m very worried that
antibodies
elevated , I read that this can... open
endocrinologist May 24, 2014 / Ksenia / Novosibirsk
... scheme, up to 15 mg for a long period. During analysis: ttg
=0.004 mU/l and t4 sv =28.3 pmol/l.
Antibodies
to the
TSH
were also
elevated
.
In the month of May, tests showed: ttg
= 19.8 and t4 st = 8.9. I also found out about pregnancy, 1-2 weeks. Tell me... open
endocrinologist April 10, 2014 / Irina / Moscow
... in February 2014 there was a curettage of 69ХХХ triploidy. I am undergoing examination of thyroid hormones T3, T4, TSH
normal, slightly
elevated
ATTPO antibodies I took female hormones on the 5th day of the cycle, on an empty stomach. The result is all hormones... open
endocrinologist December 25, 2013 / Anna / Saratov
Hello, I’m planning a pregnancy, a gynecologist-endocrinologist prescribed a blood test for TSH and AT for TPO, and said that if the tests are normal, I should take iodomarin... open
December 30, 2013 / Alexander
Iodomarin will not harm you even with elevated antibodies and is needed regardless of TSH
.
TSH
, by the way, is needed below 3.0.
There is simply a greater chance that levothyroxine will be needed during pregnancy if antibodies are elevated
.
endocrinologist December 3, 2013 / Elena / St. Petersburg
...hormones, analysis showed that TSH
increased, T4 decreased and
antibodies
also
increased
.
I went to an endocrinologist, she... (a couple of years later) decided to get tested again: TSH
– 26, T4 slightly lowered,
antibodies
very
elevated
. I went to the medical center to see an endocrinologist, they did ... open
Reasons for increased Ab to TSH receptors during pregnancy, what should be done
TSH is an abbreviation that stands for thyroid-stimulating hormone. This is a biologically active substance synthesized in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The activity of its production directly depends on the level of hormones produced by the thyroid gland - thyroxine and triiodothyronine. The higher their content in peripheral blood, the lower the TSH value and vice versa.
During immune failures, the body synthesizes specific antibodies to thyroid-stimulating hormone, which affect its own tissues. Women are more prone to developing autoimmune diseases. And the pregnancy period requires especially careful monitoring. How to identify a deviation and what to do will be discussed further.
Radioiodine therapy
Treatment involves taking radioactive iodine preparations. Iodine is a well-known fighter against antibodies; he perceives them as foreign agents and actively works against them. In this case, there is no negative effect on the thyroid gland itself. This treatment is also not dangerous for other organs.
This method of treatment gives good results, so doctors often resort to it, but this technique is not applicable to pregnant women. About a month before treatment, you should completely avoid taking medications based on thyroxine and triiodothyronine. During this time, all drug residues should be completely removed and not interfere with further treatment.
To achieve the best result, the patient will have to follow a special diet before starting the therapeutic course. Its essence is to completely eliminate iodine-containing foods from the diet. You will have to adhere to this diet not only during the course of medication, but also for another two weeks after completing the medication.
The diet involves complete abstinence from:
- Greenery;
- Canned products, both meat and fish;
- Fast foods;
- Soy;
- Any dairy products;
- Chicken eggs;
- Seafood;
- Beans.