The human immune system is capable of not only independently fighting various diseases, but also remembering pathogenic microorganisms and “harmful agents” that it has encountered. As a result, specific proteins appear in the blood serum, which in professional language are called antibodies.
One of the most informative examinations is a blood test for antibodies, which allows you to determine what diseases a person has previously encountered and what he is suffering from now. In addition, the examination helps to identify the general level of the immune system and disruptions in its functioning.
What are antibodies? And how to decipher the results of the analysis?
Antibodies are proteins that the immune system produces in response to infection. In laboratory diagnostics, it is antibodies that serve as markers of infection. The general rule for preparing for an antibody test is to donate blood from a vein on an empty stomach (at least four hours must pass after eating). In a modern laboratory, blood serum is examined on an automatic analyzer using appropriate reagents. Sometimes a serological test for antibodies is the only way to diagnose infectious diseases.
Tests for infections can be qualitative (they answer whether there is an infection in the blood) or quantitative (they show the level of antibodies in the blood). The level of antibodies for each infection is different (for some there should be none at all). Reference values (normal values) of antibodies can be obtained with the test result. In the online laboratory Lab4U you can take a set of tests for all TORCH infections at one time and with a 50% discount!
Immunoglobulin G is reduced
Immunoglobulins G can penetrate the placenta into the blood of the fetus; over time, the fetal body begins to produce immunoglobulins G on its own. Often the development of an infectious process in a pregnant woman is associated with a drop in the level of immunoglobulins at a certain stage of pregnancy. The receipt of immunoglobulins by the fetus from the mother provides protection for the newborn’s body throughout the first half of the year after birth. In people with acute and chronic infections, the blood is checked for the level of serum immunoglobulins; treatment for immunoglobulin deficiency is carried out with the help of gamma globulins. Immunoglobulin G is reduced in the following cases:
- in case of poisoning by petroleum or coal products;
- tumors of the lymphatic system;
- congenital muscular dystrophy;
- when the body loses protein as a result of burns, exfoliative dermatitis and other diseases;
- with long-term treatment with immunosuppressants;
- after irradiation (radiation sickness or treatment with radiation);
- after removal of the spleen;
- hypogammaglobulinemia is observed in babies in the first half of the year after birth; it refers to the physiological characteristics of the body and is considered the norm.
Various classes of antibodies IgG, IgM, IgA
Enzyme immunoassay determines infectious antibodies belonging to various Ig classes (G, A, M). Antibodies to the virus, in the presence of infection, are detected at a very early stage, which ensures effective diagnosis and control of the disease. The most common methods for diagnosing infections are tests for IgM class antibodies (acute phase of infection) and IgG class antibodies (sustained immunity to infection). These antibodies are detected for most infections.
However, one of the most common tests - hospital screening (tests for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B and C) does not differentiate the type of antibodies, since the presence of antibodies to the viruses of these infections automatically assumes a chronic course of the disease and is a contraindication, for example, for serious surgical interventions. Therefore, it is important to refute or confirm the diagnosis.
A detailed diagnosis of the type and amount of antibodies for a diagnosed disease can be done by taking an analysis for each specific infection and type of antibodies. Primary infection is detected when a diagnostically significant level of IgM antibodies is detected in a blood sample or a significant increase in the number of IgA or IgG antibodies in paired sera taken at an interval of 1-4 weeks.
Reinfection, or repeated infection, is detected by a rapid rise in the level of IgA or IgG antibodies. IgA antibodies have higher concentrations in older patients and are more accurate in diagnosing ongoing infection in adults.
A past infection in the blood is defined as elevated IgG antibodies without an increase in their concentration in paired samples taken at an interval of 2 weeks. In this case, there are no antibodies of classes IgM and A.
When is the study ordered?
AT are studied to identify the autoimmune nature of the pathology in the following cases:
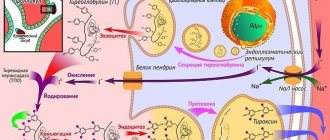
- any dysfunction of the thyroid gland: if TSH is higher than 4 mU/l and hypofunction of the gland is detected or an enlargement of the organ is observed with normal or reduced function;
- when it is necessary to prescribe medications such as amiodarone, interferon, lithium for treatment, since carriers of immunoglobulins have a high risk of developing pathology induced by these medications;
- when TSH is above 2.5 mU/l during pregnancy (carriers of AT-TPO are prescribed L-thyroxine and monitoring of thyroid function after pregnancy is recommended), as well as in the presence of postpartum depression;
- sometimes - in the differential diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis, after determining the level of ATrTSH;
- in the presence of any autoimmune diseases of other organs and systemic diseases.
The analysis is also prescribed for irradiated people under 20 years of age and women over 60. In all other cases, an ATTPO study is not necessary. ATTG, as already written above, is studied only when monitoring patients after treatment for differentiated thyroid cancer.
The study allows us to make an accurate diagnosis of the following autoimmune diseases:
- like Hashimoto's thyroiditis;
- Graves' disease;
- as autoimmune thyroiditis;
- hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism of newborns.
In newborns, a study is carried out to identify disorders if the mother had elevated thyroid antibodies to thyroid peroxidase or was diagnosed with postpartum thyroiditis.
IgM antibodies
Their concentration increases soon after the disease. IgM antibodies are detected as early as 5 days after onset and reach a peak between one and four weeks, then decline to diagnostically insignificant levels over several months, even without treatment. However, for a complete diagnosis, determining only class M antibodies is not enough: the absence of this class of antibodies does not indicate the absence of the disease. There is no acute form of the disease, but it may be chronic.
IgM antibodies are of great importance in the diagnosis of hepatitis A and childhood infections (rubella, whooping cough, chickenpox), easily transmitted by airborne droplets, since it is important to identify the disease as early as possible and isolate the sick person.
IgG antibodies
The main role of IgG antibodies is the long-term protection of the body from most bacteria and viruses - although their production occurs more slowly, the response to an antigenic stimulus remains more stable than that of IgM class antibodies.
Levels of IgG antibodies rise more slowly (15-20 days after the onset of illness) than IgM antibodies, but remain elevated longer, so they may indicate a long-standing infection in the absence of IgM antibodies. IgG may remain at low levels for many years, but upon repeated exposure to the same antigen, IgG antibody levels rise rapidly.
For a complete diagnostic picture, it is necessary to determine IgA and IgG antibodies simultaneously. If the IgA result is unclear, confirmation is carried out by determining IgM. In case of a positive result and for an accurate diagnosis, a second test, done 8-14 days after the first, should be checked in parallel to determine the increase in IgG concentration. The results of the analysis must be interpreted in conjunction with information obtained in other diagnostic procedures.
IgG antibodies, in particular, are used to diagnose Helicobacter pylori, one of the causes of ulcers and gastritis.
Treatment methods
With the development of autoimmune damage to the cells of the thyroid gland in combination with the inflammatory process, hyperfunction of an important organ is initially observed, and thyrotoxicosis develops. With pathological changes in tissues and progression of thyroiditis, the production of thyroid hormones decreases, doctors diagnose hypothyroidism.
Look at a selection of effective methods for treating pancreatitis at home using folk remedies.
Learn about the cases in which surgery to remove the thyroid gland is performed and the possible consequences of surgery from this article.On the page https://fr-dc.ru/hormones/testosteron/produkty-dlya-povysheniya.html read about how to increase testosterone in men with the help of food.
Important points:
- Treatment methods depend on the type of pathological process. In most cases, in the absence of severe forms and suspicion of a malignant process, drug therapy is prescribed,
- In case of autoimmune thyroiditis, the course of treatment is long; doctors do not always select the optimal name of the hormonal drug on the first try. There are no specific medications; it is often necessary to use two or three types of drugs in turn,
- For replacement therapy, a synthetic analogue of the hormone levothyroxine is used. The endocrinologist selects the dosage of Levothyroxine (L-thyroxine) individually for each patient,
- in case of damage to the heart muscle, pressure fluctuations, the doctor additionally prescribes beta-blockers,
- when the autoimmune form is combined with subacute thyroiditis, the use of Prednisolone, a drug of the glucocorticosteroid category, is required,
- with a high titer of autoantibodies, compositions in the NSAID category give a positive result,
- To strengthen the body's defenses, the patient uses vitamin formulations, dietary supplements, and adaptogens. It is important to eat nutritiously to exclude acute iodine deficiency,
- for maintenance therapy throughout life, the doctor determines the minimum permitted dosage for one day. The norm is individual: the amount of L-thyroxine for each patient varies depending on a set of factors,
- with active proliferation of thyroid tissue and tracheal stenosis, surgical treatment of goiter is prescribed. After the operation, the patient receives hormone replacement therapy.
Antibody analysis in the diagnosis of TORCH infections
The abbreviation TORCH appeared in the 70s of the last century, and consists of capital letters of the Latin names of a group of infections, the distinctive feature of which is that, while relatively safe for children and adults, TORCH infections during pregnancy pose an extreme danger.
The blood test for TORCH infection is a comprehensive study, it includes 8 tests:
— Determination of antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1,2 IgM and IgG
— Determination of antibodies to cytomegalovirus IgM and IgG
— Determination of antibodies to the rubella virus IgM and IgG
— Determination of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii IgM and IgG
Often, infection of a woman with TORCH complex infections during pregnancy (the presence of only IgM antibodies in the blood) is an indication for termination.
What does human blood consist of?
If you have ever looked at a drop of blood through a child's microscope, then even in this way you may have noticed that it is not uniform.
The composition of blood can be divided into two components :
- Plasma;
- Shaped components.
Plasma is a liquid that flows out when a small scratch occurs. It has no color, but is extremely important for our body. It contains and delivers to all cells of our body:
- Protein;
- Carbon dioxide;
- Oxygen;
- Useful microelements;
- Glucose and other vitamins necessary for the quality functioning of organs and systems.
Shaped components include:
- Red blood cells are the same molecules that color the blood. Their main task is to transport carbon dioxide and oxygen. These cells look like bulging discs. Their lifespan is 4 months, after which they are destroyed;
- Platelets are cells designed to fight vascular damage. They instantly react to injury to the vessel wall and, sticking to each other, clog the site of the lesion;
- Leukocytes are particles involved in the formation of immunity and capable of penetrating into tissues from the blood channel. When an infection arises in your body, they strive to destroy it, for which they produce antibodies and various cells that can absorb pathogenic formations.
Initially, blood is a sterile substance, but it is susceptible to viruses no less than other organs of our body.