Heart pathology ranks first in the statistics of all diseases of Russians. Its widespread prevalence and high mortality rate make it necessary to pay attention to the main signs and symptoms of heart disease.
The list of heart diseases includes:
- Coronary heart disease, including the following forms: cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction, post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
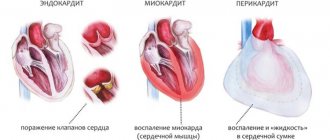
- Inflammatory diseases: endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis.
- Chronic heart failure.
- Tumors (myxoma) and metastases of malignant tumors of other locations.
- Cardiomyopathy (hypertrophic, dilated, restrictive).
- Traumatic injury (bruise, wall rupture).
- Toxic effects (antitumor drugs).
Introduction
Heart disease is a general term used to refer to a wide variety of heart conditions that can affect the heart muscle, valves, blood vessels, structure, electrical system, or coronary arteries.
Heart disease includes conditions such as cardiac arrhythmia, high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, valvular disorders and congenital heart defects. Although each disease affects the heart differently, the main problem with all types of diseases is that they can somehow interfere with the vital pumping activity of the heart.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in Russia for both men and women.
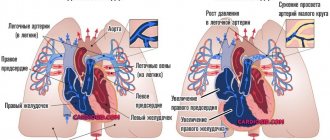
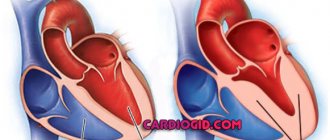
Congenital defects
The pathology is often diagnosed in the early stages in infants (immediately after birth, the child is subject to a thorough examination). Formed at the stage of intrauterine development. Main signs of heart disease:
- Change in skin color. They become pale and often acquire a bluish tint.
- Respiratory and heart failure are observed.
- There are heart murmurs.
- The child may be delayed in physical development.
In most cases, the main treatment method is surgery. Often it is not possible or not possible to completely eliminate the defect. In such circumstances, a heart transplant should be performed. Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms and preventing the development of chronic failure and arrhythmia.
According to statistics, in 70% of cases the first year of life ends fatally for the child. The prognosis improves significantly if the disease is detected early. The main prevention lies in careful planning of pregnancy, which means maintaining a correct lifestyle, eliminating risk factors, regular monitoring and following all recommendations of the attending physician.
The cardiovascular system
The heart is a powerful and tireless pump. It consists of muscular chambers that compress blood through the vascular system and a series of valves that ensure that blood moves efficiently in the right direction. There is a self-regulating electrical system that senses the heart rate and coordinates the sequential beating of the various chambers of the heart.
To do all this muscular work around the clock, the heart needs a large and continuous supply of oxygen-rich blood. Coronary arteries are vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle, making them extremely important to the heart and life.
List of heart diseases
The normal functioning of the heart and vascular system can be disrupted by a large number of different diseases. Several umbrella categories are often used, from which different types of diseases branch.
Atherosclerotic disease
While many disease processes can affect blood vessels, the term "cardiovascular disease" generally covers disorders of the blood vessels (arteries) that are associated with either atherosclerosis, hypertension, or heart disease.
Atherosclerosis is a disease in which plaque made up of fat, calcium, cholesterol and other substances builds up and hardens in the arteries, impairing blood flow.
There are different types of atherosclerotic diseases, including coronary artery disease, carotid artery disease, and peripheral artery disease.
Coronary heart disease (CHD), common in most parts of the world, can lead to heart attacks (myocardial infarction) and is the most common type of heart disease. In coronary artery disease, atherosclerotic plaques form in the lining of the coronary arteries, hardening and narrowing the arteries.
Atherosclerosis and high blood pressure (hypertension or hypertension) can lead not only to coronary artery disease, but also to carotid artery disease, which affects the carotid arteries on both sides of the neck, and peripheral artery disease, which can affect almost any other artery in organism.
Rhythm disorders
Causes: neuroses, obesity, poor diet, cervical osteochondrosis, bad habits, intoxication with drugs, alcohol or drugs, coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathies, heart failure, premature ventricular excitation syndromes. The latter are heart diseases in which there are additional impulse pathways between the atria and ventricles. You will read about these anomalies in a separate table.
Characteristics of rhythm disturbances:
| Name | Description |
| Sinus tachycardia | Rapid heartbeat (90–180 per minute) while maintaining the normal rhythm and normal pattern of impulse propagation throughout the heart. |
| Atrial fibrillation (flicker) | Uncontrolled, irregular and frequent (200–700 per minute) atrial contractions. |
| Atrial flutter | Rhythmic contractions of the atria with a frequency of about 300 per minute. |
| Ventricular fibrillation | Chaotic, frequent (200–300 per minute) and incomplete ventricular contractions. Lack of complete contraction provokes acute circulatory failure and fainting. |
| Ventricular flutter | Rhythmic contractions of the ventricles with a frequency of 120–240 per minute. |
| Paroxysmal supraventricular (supraventricular) tachycardia | Attacks of rhythmic rapid heartbeat (100–250 per minute) |
| Extrasystole | Spontaneous contractions out of rhythm. |
| Conduction disorders (sinoatrial block, interatrial block, atrioventricular block, bundle branch block) | Slowing down the rhythm of the entire heart or individual chambers. |
Syndromes of premature excitation of the ventricles:
| WPW syndrome (Wolf–Parkinson–White syndrome) | CLC syndrome (Clerc-Levy-Christesco) |
| Signs: paroxysmal (paroxysmal) supraventricular or ventricular tachycardia (in 67% of patients). Accompanied by a feeling of increased heartbeat, dizziness, and sometimes fainting. | Symptoms: tendency to attacks of supraventricular tachycardia. During them, the patient feels a strong heartbeat and may feel dizzy. |
| Cause: the presence of a bundle of Kent, an abnormal pathway between the atrium and ventricle. | Cause: the presence of a James bundle between the atrium and the atrioventricular junction. |
| Both diseases are congenital and quite rare. | |
Treatment of rhythm disturbances
It consists of treating the underlying disease, adjusting diet and lifestyle. Antiarrhythmic drugs are also prescribed. Radical treatment for severe arrhythmias is the installation of a defibrillator-cardioverter, which will “set” the rhythm of the heart and prevent ventricular or atrial fibrillation. In case of conduction disturbances, electrical cardiac stimulation is possible.
Treatment of premature ventricular excitation syndromes can be symptomatic (elimination of attacks with medications) or radical (radiofrequency ablation of the abnormal conduction pathway).
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms of heart disease depend on what condition the person has. However, the most common signs that occur during many different types of heart disease include chest pain or discomfort, rapid heartbeat, lightheadedness or dizziness, syncope, fatigue and shortness of breath.
Causes of heart disease
Because there are many types of heart disease, there are many different causes that cause it. Some causes are unclear, and some are obvious, such as a genetic abnormality, a birth defect, or as a result of certain underlying conditions or medications or drugs.
Many of the risk factors for heart disease are based on a person's lifestyle, such as diet, activity level, weight (obesity), smoking, and treatment and management of chronic diseases.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the possibility of developing atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease are identified. They can be divided into:
- Controllable - which can be influenced.
- Uncontrollable - which cannot be influenced, but they must be taken into account when developing therapeutic and preventive measures.
Controlled factors include:
- Bad habits – smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Stress.
- Arterial hypertension is a constant increase in blood pressure.
- Obesity.
- Physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle).
- Poor nutrition
- Diabetes.
- An increase in “bad” cholesterol in the blood.
Among the uncontrollable factors:
- Age: after 50-60 years, the risk of developing the disease increases significantly.
- Gender: In men, pathology occurs more often.
- Heredity – the presence of IHD in close relatives.
Diagnostics
To diagnose heart disease, your doctor will take a complete medical history, conduct a detailed physical examination, and choose from a variety of tests. Depending on what the doctor is looking for, these tests may include an electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, ambulatory monitoring, computed tomography (CT), cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study, stress testing, and electrophysiology testing.
Treatment
Treatment for cardiovascular disease is variable and depends on the type of disease.
For almost all types of heart disease, lifestyle changes such as healthy eating, daily exercise, weight loss, quitting smoking and stress management are key.
If these changes do not help, your doctor may prescribe medications. There are many options that can be considered, from ACE inhibitors to anticoagulants, from beta blockers to calcium channel blockers and many more.
There are also surgeries, special procedures and medical devices that can be used in severe or special cases.
If you have been diagnosed with any heart disease, rest assured that after long-term treatment, people are living longer than ever. Managing heart disease means making lifestyle changes, learning what symptoms to watch for, and possibly taking medications. Lifestyle changes that may be needed include quitting smoking, eating healthy, exercising regularly, losing weight and managing stress.
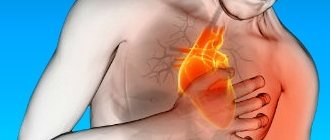
Myocardial infarction
A heart attack is a dangerous condition caused by blockage of a coronary artery by a blood clot. This causes disruption of blood circulation in the tissues of the brain and heart. The condition develops against the background of various cardiovascular pathologies and requires immediate hospitalization of the patient. If medication is provided within the first 2 hours, the prognosis for the patient is often favorable.
A heart attack causes acute pain in the sternum, a sharp deterioration in general health
Signs of a heart attack
A heart attack is characterized by pain in the sternum. Sometimes the pain is so severe that the person screams. In addition, the pain often spreads to the shoulder, neck, and radiates to the stomach. The patient experiences a feeling of tightness, a burning sensation in the chest, and numbness in the hands.
Important! A distinctive feature of myocardial infarction from other diseases is persistent pain at rest and after taking Nitroglycerin tablets.
Causes
Factors leading to the development of a heart attack:
- age;
- previous small-focal heart attacks;
- smoking and alcohol;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- high cholesterol;
- excess body weight.
The risk of developing a serious condition increases with a combination of the conditions described above.
Treatment
The main goal of therapy is the rapid restoration of blood flow in the area of the heart muscle and brain. For this purpose, drugs are used that help resolve blood clots, such as thrombolytics, heparin-based drugs, and acetylsalicylic acid.
When the patient is admitted to the hospital, coronary artery angioplasty is used.
Prevention
The most common forms of heart disease are largely preventable if you pay attention to your heart risk factors and take smart steps to reduce them. Ideally, you should work with your doctor to conduct a formal risk assessment, but you can also make a fairly accurate risk assessment on your own. If your risk is low, that's great.