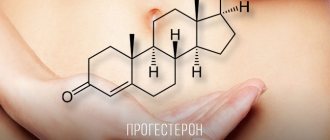
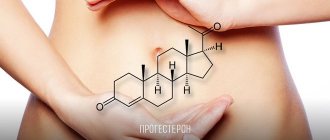
Progesterone is an important hormone for the female body, because it is responsible for the fertilization process and the favorable course of pregnancy.
Under the influence of a number of factors, a disruption in the production of the hormone may occur; in such situations, the use of medications that help increase its level becomes a salvation. Progesterone is a representative of this group of drugs.
Compound
1 ml of Progesterone 1% injection solution contains 0.01 grams of the active substance, as well as benzyl benzoate (Benzylii benzoas) and refined olive/peach oil (Oleum Olivarum/Oleum Persicorum).
One milliliter of injection solution Progesterone 2.5% includes 0.025 grams of the active substance, benzyl benzoate (Benzylii benzoas) and refined olive/peach oil (Oleum Olivarum/Oleum Persicorum).
Progesterone 1% and 2.5% is available in 1 ml ampoules, packaged in packages of 5 or 10 pieces.
The composition of the gel and capsules varies depending on which pharmaceutical company produces these dosage forms.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Progestogen is a steroid hormone that is produced in the body by the corpus luteum of the ovaries .
The mechanism of action of progesterone drugs is associated with their ability to interact with specific progestin receptors, which are located on the surface of target cells.
By binding to them, the substance penetrates the cell nucleus, activates deoxyribonucleic acid and stimulates the synthesis of ribonucleic acid.
The effect on a woman’s body is that the drug:
- stimulates the transition of the endometrium (the mucous layer of the inner mucous membrane that lines the body of the uterus) from the proliferative phase, which coincides with the ovulatory and follicular phases of the ovarian cycle, to the secretory phase;
- creates optimal conditions for embryo , reduces the sensitivity of the uterus and fallopian tubes to the action of oxytocin and has a tocolytic effect;
- stimulates lipoprotein lipases ;
- increases body fat reserves;
- helps increase the level of induced and basal (background) insulin glucose utilization ;
- enhances the accumulation of glycogen in the liver;
- stimulates the synthesis by the adrenal cortex of the mineralocorticosteroid hormone aldosterone ;
- provokes hypoazotemia ;
- increases the excretion of nitrogen-containing metabolic products in the urine;
- suppresses the production of a number of hypothalamic factors for the release of luteotropin (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and, accordingly, the biosynthesis of pituitary gonadotropic hormones ;
- reduces the permeability of the capillary wall in the tissues of the mammary glands;
- reduces swelling of the connective tissue framework, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle ;
- suppresses the proliferative and mitotic activity of ductal epithelial tissue (in the case when progesterone is used in the form of a gel).
When taken orally, intravaginally using the drug in capsules, or injecting an injection solution under the skin and into the muscle, the substance is quickly absorbed. When applied to the skin in gel form, it is almost not absorbed and does not enter the systemic circulation.
The maximum plasma concentration when taking the tablet orally is observed after 1-3 hours; with intravaginal application, this figure is achieved after 2-6 hours.
protein binding (mainly albumin (approximately 50–54%) and 43–48% corticosteroid binding globulin ).
In the liver, the substance is biotransformed into inactive metabolites (mainly pregnanediol and pregnanolone ).
From 50 to 60% of the substance is eliminated by the kidneys , more than 10% - with bile ; Progesterone metabolization products excreted in bile intestinal and can undergo enterohepatic recirculation .
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is quickly absorbed, being converted in the liver into pregnanediol, pregnanol and pregnandione. The maximum amount of active substance in the blood is observed after 8 hours. The half-life lasts several minutes. The excretion process is carried out by the kidneys (50-60%).
Pharmacodynamics
It has a gestagenic effect, it stimulates RNA synthesis, this occurs due to the penetration of the substance into the nucleus and activation of DNA. The influence of the hormone contributes to the successful implantation of the egg.
In addition, it suppresses the contractility of the muscle fibers of the uterus and its tubes, as well as:
- stimulates the process of fat deposition;
- promotes glucose utilization;
- produces aldosterone production;
- helps regulate pituitary hormones;
- responsible for the excretion of nitrogen.
Indications for use
Progesterone: What is it for in oral capsule form?
Taking capsules is indicated for premenstrual syndrome and if a woman is diagnosed with fibroadenomatosis (fibrocystic disease).
As a progestational component, the drug is prescribed for HRT ( hormone replacement therapy ) in the period preceding menopause , immediately during menopause (including if menopause is premature ), as well as in the postmenopausal period .
Capsules for intravaginal administration: indications for use
Capsules for intravaginal use are indicated:
- if it is necessary to prescribe HRT to a woman in case of ovarian dysfunction accompanied by a lack of progesterone ( oocyte donation );
- to maintain the luteal phase during preparation for IVF ;
- to maintain the luteal phase in the induced or spontaneous menstrual cycle .
For prophylactic purposes, the drug is prescribed to prevent habitual and threatening spontaneous abortion caused by gestagen insufficiency ; for endocrine infertility ; to prevent the development of fibroids and endometriosis .
Indications for use of the oil solution
Since progesterone causes menstruation (if their delay is associated with a deficiency of this hormone), it is prescribed to correct various types of menstrual irregularities .
Thus, the use of an oil solution is advisable for amenorrhea (absence of menstrual bleeding for several cycles) and oligomenorrhea (that is, a delay in menstrual bleeding for more than 40 days).
In addition, injections are prescribed for:
- algomenorrhea (painful periods) associated with insufficiency of the gonads
- anovulatory metrorrhagia (uterine bleeding not associated with ovulation);
- endocrine infertility (including those caused by insufficiency of the corpus luteum);
- threat of spontaneous abortion ;
- diagnostic procedures, the purpose of which is to determine the level of estrogen+ .
When menstruation is delayed, progesterone can be used both in tablet form and in injections. However, more often an injection solution is prescribed, since the effect after it is noticeable much faster than after taking tablets.
Indications for use of the gel
Applications using Progesterone in gel form are prescribed for mastalgia and mastopathy .
secondary amenorrhea associated with progesterone deficiency , as well as in reproductive programs if a woman needs to compensate for the lack of progesterone during oocyte donation .
Names of medications
The following two drugs are in greatest demand:
- The drug "Duphaston", the main active component of which is synthetic progesterone, produced in the laboratory. This drug has passed all clinical trials, confirming its high effectiveness. The drug "Duphaston" can help if the level of this hormone has not fallen too low. The drug is available in the form of tablets and also in the form of vaginal suppositories.
- The drug "Utrozhestan" is an analogue of "Duphaston", but at the same time it differs significantly from it. The difference is that this product is made on a plant basis. It is because of this that it is considered preferable, since it has fewer contraindications and adverse reactions. Like Duphaston, Utrozhestan can be taken orally or vaginally.
Despite these benefits, all previously mentioned medications are systemic. That is, they require a long reception time. If there is a threat of miscarriage, which is caused by a sharp decrease in progesterone levels, such medications will not be able to help. This is when Progesterone injections can demonstrate their effectiveness and reliability.
The active substances of the solution quickly spread throughout the body, gradually break down and relieve dangerous symptoms. It has been proven that one hour after intramuscular injection, the amount of progesterone stabilizes. The maximum concentration of the hormone is reached after six hours. It is also important to emphasize that the injection of this substance is painless, unlike antibiotics or antiviral drugs.
How to administer Progesterone injections according to instructions?
Contraindications
All dosage forms of Progesterone are contraindicated:
- in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- in the presence of serious impairment of renal function and/or hepatic function ;
- if the patient is diagnosed with hepatitis ;
- in the acute form of inflammation of the venous walls , as well as in acute thromboembolic diseases ;
- patients who have an increased risk of blood clots ;
- vaginal (vaginal) bleeding of unknown origin;
- missed miscarriage;
- incomplete abortion;
- porphyrin disease.
Additional contraindications to the use of an oil solution are:
- the presence of a malignant tumor of the mammary gland or genital organs (for breast carcinoma, exceptions are cases when progesterone is prescribed as part of complex therapy);
- pregnancy (starting from 14 weeks).
Side effects
Treatment with progesterone drugs can cause the development of allergic reactions.
The effect on a woman’s body of the drug in capsule form is in some cases accompanied by:
- increased drowsiness;
- dizziness that occurs 1-3 hours after taking the tablet;
- various types of menstrual cycle disorders (for example, a reduction in its duration or the appearance of intermediate bleeding).
The most common side effects of injections:
- acute blockage of the lumen of blood vessels by a thrombus;
- thrombophlebitis (thrombosis accompanied by inflammation of the venous wall);
- thrombosis of retinal blood vessels;
- increased blood pressure ;
- the appearance of edema ;
- chronic cholecystitis , characterized by the formation of stones in the gallbladder (calculous cholecystitis);
- increased drowsiness ;
- headache;
- apathy;
- visual impairment;
- hair loss ( alopecia );
- decreased libido ;
- hirsutism (male pattern hair growth in women);
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- deterioration of appetite and, as a result, loss of body weight;
- menstrual irregularities;
- cholestatic hepatitis;
- depression;
- dysphoria (gender identity disorder);
- release of milk from the mammary glands not associated with breastfeeding ( galactorrhea );
- enlargement, tenderness and tension of the mammary glands;
- local reactions (redness of the skin and pain at the injection site).
What is the function of progesterone?
Progesterone travels through the blood to tissues where there are progesterone receptors. The hormone attaches to receptors to produce actions in the body. Estrogen and progesterone are responsible for the release of eggs from the ovaries during ovulation. Then progesterone:
- Prepares the uterine lining for implantation of a fertilized egg
- Supports the endometrium throughout pregnancy
- Prevents further release of the egg until the pregnancy is terminated
- Prevents more than one egg from being fertilized at a time, although sometimes more than one egg is released
- Stops muscle contractions in the fallopian tubes after egg transport
- Plays an important role in fetal development during pregnancy
- Stimulates breast tissue for lactation
- Strengthens the pelvic wall muscles in preparation for childbirth
In case of hormonal imbalance, an artificially created progestin option can help.
Instructions for Progesterone (Method and dosage)
Progesterone injections: instructions for use
Progesterone injections are given into the muscle or under the skin.
For dysfunctional uterine bleeding, daily administration of 0.5-1.5 ml of a one percent solution is indicated for 6-8 days. If the patient has undergone a uterine cavity curettage procedure, the course of injections begins after 18-20 days.
If curettage is not possible, the drug can be administered even during bleeding. When using Progesterone during bleeding, bleeding may temporarily increase (usually for 3-5 days).
For this reason, patients with moderate or severe forms of anemia are recommended to first transfuse 0.2-0.25 liters of donor blood. If bleeding has stopped, do not interrupt the course of treatment before 6 days. If the bleeding has not stopped after 6-8 days of treatment, it is considered inappropriate to continue administering the solution.
For algodismenorrhea (painful periods), treatment begins 6-8 days before the start of menstruation. Patients are advised to administer 0.5 to 1 ml of a one percent solution daily for 6-8 days. The course of treatment can be repeated several times.
For preventive purposes, to prevent spontaneous abortion, 0.5 to 2.5 ml of a one percent solution is administered daily or every other day. Injections continue to be given until the threatening symptoms disappear completely. In case of habitual miscarriage, the drug should be administered until the fourth month of pregnancy.
The maximum single and daily dose for adult patients when Progesterone is administered into the muscle is 0.025 g.
Progesterone to induce menstruation: how to inject when menstruation is delayed
For hypogonadism, amenorrhea , as well as to induce menstruation in case of delay, treatment begins with the prescription of estrogenic drugs. The goal of therapy is to achieve sufficient proliferation of endometrial cells . Upon completion of the course using estrogenic drugs, the patient is prescribed Progesterone injections.
Treatment involves administering 0.5 ml daily or every other day 1 ml of a one percent oil solution (in some cases, Progesterone 2.5% may be prescribed to induce menstruation). Typically, 5 to 10 injections are required.
Instructions for Progesterone in tablets and gel form
The tablets are taken orally (without being tied to the time of meals) or used intravaginally, the gel is used as a local remedy. The dosage regimen, optimal dosage form and duration of treatment are determined depending on the indications and characteristics of the course of the disease.
As a rule, the daily dose is from 200 to 400 mg of progesterone. To maintain the luteal phase during IVF, the patient is prescribed a dose of 600 mg of progesterone, with a frequency of applications 3 times a day (200 mg every 8 hours).
One application requires 2.5 g of gel (equivalent to 25 mg of progesterone). The gel is applied using a special dispenser applicator to the skin of the mammary glands once or twice a day daily (until completely absorbed) or in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (from the 16th to the 25th day). Treatment is usually carried out over 3 cycles.
A repeated course is possible according to indications.
Girls' comments
There are a lot of reviews about Progesterone injections on various gynecological forums. Women write that the injections helped them cope with the problem of missed periods, which sometimes occurs after childbirth. It is noted that in this case only one course is enough. Other patients praise Progesterone injections for their help in case of delay due to hormonal imbalances. This drug came in handy. Women also write that with progesterone deficiency, injections help with severe pain during menstruation.
Often in reviews, injections of this drug are praised by pregnant women who also experienced progesterone deficiency while pregnant. It is noted that after a course of injections, the amount of pregnancy hormone stabilizes even if its content was far from normal.
Interaction
Reduces the intensity of the action of anabolic steroid drugs , oxytoxic drugs (that is, agents that stimulate the contractile activity of the uterus gonadotropic hormones synthesized in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland . Reduces the lactogenic effect of oxytocin .
When used simultaneously with diuretics , bromocriptine ; drugs that reduce high blood pressure ; systemic coagulants , immunosuppressants Progesterone enhances the effect of these drugs.
When taking the drug in combination with barbiturates , a decrease in its pharmacological activity is observed.
Progesterone reduces the effectiveness of anticoagulants.
special instructions
Use with caution and under constant monitoring for diseases of the heart and blood vessels , epilepsy , mild or moderate renal dysfunction , for the treatment of diabetics, patients suffering from bronchial asthma and migraines .
Progesterone is also prescribed with caution to patients with a history of mental disorders . When the first signs of depression occur, treatment is stopped. You should also pay attention to early signs of thromboembolism . Their appearance is a reason to discontinue the drug.
Patients with diabetes mellitus during treatment with Progesterone should constantly monitor blood glucose levels .
Since steroid hormones are metabolized in the liver, progesterone is not prescribed to patients with impaired liver function .
Treatment with progesterone drugs may be accompanied by a weakening of concentration, so care should be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other activities that require a high speed of psychomotor reactions or pose a potential threat to health and life.
Long-term use of increased doses of Progesterone can cause cessation of menstruation.
The drug in gel form is applied without rubbing it into the skin of the mammary glands or massaging them. After applying the cream, you should not be in direct sunlight.
Analogs
Matches by level 4 ATX code:
Iprozhin
Utrozhestan
Crinon
Prajeesan
Progestogel
Progesterone-containing drugs are Utrozhestan , Iprozhin , Crinon , Prajisan , Progestogel , Endometrin . A multicomponent analogue of the drug - vaginal capsules Triozhinal .
Use of Progesterone during pregnancy
Tablets and injections during pregnancy are indicated only in cases where it is necessary to prevent spontaneous miscarriage. There are no reliable data on the safety of using the drug in gel form during pregnancy.
During breastfeeding, you should refrain from using Progesterone tablets and injections. The gel is prescribed when there are no alternative treatments and the benefit to the mother potentially outweighs the risk to the baby.
There is an opinion that the drug helps get rid of an unwanted pregnancy, which is why the questions often arise: “How to disrupt an early pregnancy with the help of Progesterone?”
However, this is impossible, since progesterone, on the contrary, helps strengthen pregnancy (for this reason, the drug is prescribed to women who have been diagnosed with infertility, as well as to women who are about to undergo IVF). But a deficiency of this hormone can lead to miscarriage.
How to give a progesterone injection
To avoid pain after injections, you need to learn how to do them correctly. First, you need to hold the ampoule in your clasped hand so that it warms up a little.
If a crystalline suspension is observed inside, it is heated using a water bath until the contents become homogeneous. Next, the medicine is cooled to human body temperature.
Injections are given intramuscularly or under the skin. The first method is less painful; as a result of subcutaneous injections of progesterone, bumps often appear.
Reviews about Progesterone
The largest number of reviews about the drug can be found on special forums dedicated to the problem of female infertility.
Most women who have had difficulty conceiving and bearing a child note the effectiveness of Progesterone, even in cases where the patient suffered several miscarriages before starting a course of using this drug when another pregnancy occurred. That is, in some cases, Progesterone is the only chance to save a pregnancy.
However, there are also negative reviews about the drug. They are associated with a fairly large number of side effects of the drug and the presence of contraindications to its use. In addition, some of the women treated with Progesterone did not notice any effect from the prescribed therapy.
Be that as it may, as is the case with other medications, self-medication with progesterone preparations is unacceptable. You can begin a course of use only after a comprehensive examination and based on test data.
Menstrual cycle and injections
This hormone is considered one of the main ones, which, together with estrogen, regulates the cycle in women. During ovulation, a mature egg is released from the follicle, after which progesterone begins to act very actively. The hormone prepares, activates and increases the secretory functions of the endometrium to receive an egg if conception has occurred. In addition, it gives cervical mucus properties that facilitate the transportation and preservation of ingested male semen.
If conception has taken place, this hormone creates conditions for the development of the fetus: thanks to it, the contractile function of the uterine muscles decreases. It is in this regard that the balance of hormones is so important for the healthy functioning of a woman’s reproductive system.
Progesterone price, where to buy
The price of injections in Russia is from 105 rubles for a package of ampoules with a one percent solution and from 360 rubles for a package of ampoules with a 2.5% oil solution. You can buy tablets for an average of 180 rubles (the price depends on the place of purchase, the manufacturer of the drug, the concentration of the active substance in one tablet and the number of tablets in the package).
In Ukrainian pharmacies the price of Progesterone in tablets is on average 45 UAH. The cost of ampoules with a 1% solution is from 12 UAH, ampoules of 2.5% cost an average of 32 UAH.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Oxyprogesterone capronate 125 mg/ml 1 ml No. 10 (PVC 2x5) JSC Dalkhimfarm
998 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Progesterone (amp. 1% 1ml No. 10) DHF JSC
RUB 285 order
- Progesterone (amp. 2.5% 1ml No. 10) DHF JSC
936 rub. order
- Oxyprogesterone capronate (amp. 12.5% 1ml No. 10) DHF OJSC
RUB 1,062 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Progesterone 1% 1 ml No. 10 solution TOV FZ Biopharma, Ukraine
68 UAH order - Progesterone 2.5% 1 ml No. 10 solution TOV FZ BIOPHARMA, Ukraine / PrAT Biopharma, Ukraine
75 UAH order
- Oxyprogesterone capronate 12.5% 1 ml No. 10 solution for injection TOV"FZ "Biopharma", Ukraine
114 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Oxyprogesterone capronate ampoule Oxyprogesterone capronate solution d/in. 12.5% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Biopharma CJSC
114 UAH order
- PROGESTERONE ampoule Progesterone solution oil. d/in. 2.5% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Biopharma CJSC
57 UAH order
- PROGESTERONE ampoule Progesterone solution oil. d/in. 1% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Biopharma CJSC
59 UAH order
show more