MCV in a blood test is a measure that describes the average red blood cell volume, which is how large the red blood cells are in the body.
The measurement is carried out automatically. As a rule, the results are considered in negligible units - femtoliters. Some laboratories use absolute values, microns.
The MCV study shows not only anemia, but also other diseases. True, the technique must be used in a system with other diagnostic measures.
There are deviations, both larger and smaller. Almost always they relate to pathological processes, although exceptions are possible.
What does the patient need to know about this laboratory indicator?
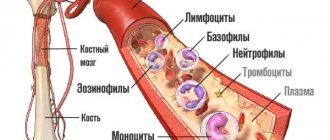
Red blood cells and their function in the body
Red blood cells are a cellular unit of blood, the main purpose of which is to saturate the body with all components of the inhaled air. They carry oxygen molecules from lung tissue to internal organs, as well as other parts of the body.
In the opposite direction, red cells remove carbon dioxide from the body, formed after absorbing air. Oxygen delivery is carried out by hemoglobin proteins, which make up 98% of the total mass of protein compounds in red blood cells.
When hemoglobin concentration decreases, the transport function of blood cells is disrupted. Therefore, these indicators must be constantly monitored.
Changeable cells
Red blood cells are constantly working. Their task is to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to all organs. MCV data carries important information. It indicates the constant work of red blood cells. Their normal volume affects the normalization of pH, the removal of antibodies and toxins.
Red blood cells in normal quantities control the formation of clots and dissolve them. Pathology in their number, shape, size indicates the onset of the disease or the presence of a congenital anomaly. Therefore, it is so important to monitor the morphological indicators of red blood cells, to know your erythrocyte index, and blood functions.
MCV in blood test - what is it?
MCV in a blood test is a determination of the qualitative indicators of the material being studied. It displays the average size of red blood cells and is included in the list of indicators that are required to be identified during a general blood test (CBC).
MCV parameters are included in the list of erythrocyte indices. Performing an MCV analysis allows the doctor to establish quantitative characteristics of the condition of the cells, and then perform a comparative analysis, determining the norm, deficiency of cellular material, or excess of the average volume of erythrocyte units.
What is the average red blood cell volume?
The normal shape of a red blood cell is a biconcave disc.
The average volume value is one of the most common in blood tests. It can be calculated both for routine diagnostics and to identify possible anemia and its causes.
There are red blood cells of varying sizes in the bloodstream, but most of them should be of normal, correct size. This suggests that the cells are able to optimally perform their functions. Under the pressure of various factors, the percentage of abnormally large or small volumes can increase significantly. Analysis of the average volume will show which cell sizes predominate and will allow you to prescribe a treatment regimen.
Normal MCV values in adults
MCV as part of a blood test is an indicator that tends to change under the influence of age-related changes in the body of a person donating blood for biochemical research.
The following factors may also affect diagnostic results:
- taking medications belonging to the pharmacological group of antidepressants;
- a hearty breakfast before donating blood;
- prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- malfunctions of medical equipment.
In young men, the optimal MCV parameters are from 80 to 90 fL. For representatives of the female half of the population, the normal size of red blood cells is from 80 to 95 fl. In women, the MCV rate is slightly higher, which is due to the physiological characteristics of the female reproductive system and monthly blood loss.
Age-related changes in MCV in adults
MCV in a blood test is a determination of qualitative indicators of the cellular composition of the blood, during which age-related changes in the body are taken into account. Below are the erythrocyte indices that are normal for men and women who belong to a specific age group:
| Age | Age-related changes in men (unit fl) | Age-related changes in women (unit of measurement fl) |
| From 14 to 18 years old | 78-94 | 79-99 |
| From 19 to 45 years old | 80-98 | 82-101 |
| From 46 to 65 years | 82-102 | 83-103 |
| Over 66 years old | 84-103 | 84-104 |
When performing a study on MCV parameters, adjusted for age-related changes in body tissues, the factor of the presence of concomitant diseases in the patient being examined, his lifestyle, working conditions, quality of nutrition, addiction to addictions (alcohol, smoking, drugs) are taken into account.
Norm
Average volume of red blood cells in children under 6 months, table of norms.
| Age | MCV (fl) |
| in the fetus | 98 — 118 |
| first 3 days | 95 — 121 |
| 4 – 7 day | 88 — 126 |
| second week | 86 — 124 |
| month | 85 — 123 |
| 60 days | 77 — 115 |
| 3 months – 6 months | 77 — 108 |
MCV standards for children, adolescents and adults, table.
| Age | MCV values | |
| men | women | |
| from 6 months. up to 2 years | 70 — 99 | 72 — 89 |
| 3 - 6 years | 76 — 89 | 76 — 90 |
| 7 l. 12 liters each | 76 — 81 | 76 — 91 |
| from 13 years old - 19 | 79 — 92 | 80 — 96 |
| 20 years to 30 | 81 — 93 | 82 — 96 |
| 30 l. - 40 years | 80 — 93 | 81 — 98 |
| 40 l. – 50 l. | 81 — 94 | 80 — 100 |
| 50 l. 60 l each | 82 — 94 | 82 — 99 |
| 60 years 65 l. | 81 — 100 | 80 — 99 |
| after 65 years | 78 — 103 | 80 — 100 |
As the body ages
MCV in a blood test is a determination of the qualitative indicators of the test material, which change throughout the entire life cycle, but not significantly. The only thing that is observed in both men and women is a slight increase in the average cell size.
This is explained by the fact that with age, body weight increases and intracellular metabolism deteriorates. To provide more tissues with the necessary level of oxygen, the body increases the average size of the red blood cells synthesized.
Indications for analysis
MCV blood test is not the only one. To clarify the diagnosis, the therapist may require a retake or refer it for additional tests.
MCV is informative in two cases:
- in order to diagnose one of the types of anemia;
- to determine the type of water-salt imbalance. People are often sent for such an analysis if they have various intestinal infections, acute respiratory diseases and ARVI.
Other, no less serious, reasons for getting tested may be:
- failure of the hormonal system;
- metabolic problems;
- overweight;
- increased blood sugar or diabetes;
- a sharp and causeless decrease in the level of the immune system.
MCV analysis results often help identify such deviations:
- anemia of normochromic type. It is fixed when pathologies appear in the bone marrow, sometimes caused by chronic diseases;
- macrocytic type anemia. It is characterized by an excessive increase in mcv. Red blood cells increase in size due to insufficient amounts of vitamin B and folic acid;
- microcytic anemia. In this case, the disease occurs due to a lack of iron in the blood.
Normal MCV values in children by age
At all stages of development of the child's body, changes in MCV parameters are observed. The table below shows the optimal average sizes of red blood cell units in children, taking into account the age group.
| Age | Normal level (measurement value fl) |
| In infants | Up to 140 |
| From 1 month up to 1 year | 71-84 |
| From 2 to 5 years | 73-85 |
| From 5 to 10 years | 75-87 |
| From 11 years and older | 80-100 |
MCV in a blood test is a determination of the qualitative indicators of the test material, which play a key role in the diagnosis of blood diseases in children of all age groups. Therefore, if a child is prescribed OAC, then identifying the normal average size of erythrocyte units is a prerequisite for diagnosis.
What is anisocytosis?
Anisocytosis on blood smear
Red blood cells are disc-shaped blood cells that can compress and bend to move through the thinnest capillaries. When their size exceeds the norm, they can no longer deliver oxygen to all tissues; when their size is smaller than normal, accordingly, less oxygen is delivered. Depending on the size they are divided into 4 groups:
- microcytes - < 6.2 µm;
- normocytes - 6.2 - 8.2 µm;
- macrocytes - 8.2 - 12 µm;
- megalocytes - > 12 µm.
In this case, normocytes, that is, cells of the correct size, should make up about 70% of the total number of red blood cells. About 15% are divided between cells of large and small sizes. When an increase in the ratio of cells of abnormal size to normal size is detected in the patient’s blood, anisocytosis is detected.
Anisocytosis is the general name for a high number of cells that are different in size from normocytes. There are 3 types of anisocytosis:
- microcytosis - predominance of microcytes;
- macrocytosis - predominance of macrocytes;
- mixed - both large and small cells exceed the permissible ratio.
The level of distribution of abnormally sized blood cells is recorded in the analysis by the RDW value. The RDW rate (in %) is:
- for adults - 11.5 - 14.5;
- for newborns - 14.9 - 18.7;
- for children from 6 months - 11.6 - 14.8.
How is the MCV blood test performed?
To determine the MCV level, you need to visit a laboratory that specializes in determining quality blood parameters, or take tests at a local clinic.
To obtain the most accurate diagnostic results with minimal risk of data errors, you will need to follow the rules for preparing for the donation of biological material, undergo the blood sampling procedure and wait for the test results.
Preparation
Includes the implementation of the following recommendations, which allow you to maintain the cellular composition of the blood at an optimal level without provoking its sudden changes.
The patient who will be tested will need to follow the following rules:
- 3 days before blood sampling, do not drink alcohol;
- take the test in the morning (preferably before 10-00);
- 2 days before diagnosis, exclude physical activity, do not engage in strength sports, do not lift heavy objects;
- have breakfast only after blood sampling, so that the stomach is empty (the best option would be to eat wheat, rice, pearl barley, barley porridge with vegetable salad).
It is recommended not to smoke 8 hours before donating blood. In the evening the day before the test, you should not overeat. All food consumed before laboratory testing should be light and not burden the digestive system.
Blood collection
A mandatory condition for submitting biological material for testing for MCV levels is taking blood on an empty stomach.
This procedure is performed using two methods, namely:
- ring finger bundle - pierced with an automatic pen with needles or a metal scarifier (about 1-2 ml of blood is taken by a laboratory assistant);
- ulnar vein — collection of biological material is carried out with a disposable syringe, which is filled with 5-10 ml of blood.
In order to obtain the most accurate research results, it is advisable to perform simultaneous collection of capillary and venous blood. This will allow for a comparative analysis of the selected samples, eliminating the possible occurrence of inaccuracies and errors in the operation of medical equipment.
How long to wait for answers
Modern medical equipment allows you to obtain laboratory test results for the MCV level within 15-20 minutes.
after delivery of biological material. In most cases, determining the average size of red blood cell units is only 1 of more than 20 parameters of the cellular composition of the blood that laboratory specialists need to determine.
If the staff of the clinic where the collected blood is tested uses automatic analyzers, the diagnostic process is significantly accelerated.
In laboratories that are not equipped with modern medical equipment and use microscopic research techniques, you will need to wait from 1 to 2 hours. In this case, the laboratory assistant performs an independent blood test, establishing the average volume of red blood cells using a microscope.
It is believed that the microscopic diagnostic method carries a greater number of errors, because there is a human factor involved. In order to save personal time and obtain the most accurate diagnostic results, it is recommended to donate blood in laboratories that are equipped with automatic analyzers.
Additional diagnostic techniques
To specify the pathology, one blood test is not enough. We need auxiliary methods. Diagnosis is carried out under the supervision of a hematologist.
- Interview and anamnesis collection. Primary measures are aimed at identifying the cause and essence of the phenomenon.
- Biochemical blood test. They also study the concentration of iron, micro and macroelements.
- Genetic consultation. If there is a suspicion of a hereditary pathological process.
- Ultrasound of the liver and pancreas. Abdominal organs in general.
- Sugar control. Specific techniques such as plotting a graph (curve). Tests for diabetes.
- Blood tests for hormones. Different profiles. Thyroid gland, adrenal glands, etc.
- If there is a suspicion of dangerous processes in the bone marrow, a puncture is indicated. The sample is studied in the laboratory.
- MRI if there is a risk of cancer.
The study of mean erythrocyte volume (MCV) allows us to say a lot about the state of the hematopoietic system: the technique reveals hypoxia, ischemia, and disorders of the bone marrow. This is a routine but useful diagnostic method.
Comparative study
To ensure a comparative study on MCV, simultaneous sampling of capillary (ring finger) and venous blood is performed.
The laboratory specialist places both samples into the analyzer and, based on the diagnostic results, checks the data obtained. This research method makes it possible to eliminate the factor of incorrect operation of medical equipment and minimize the likelihood of obtaining a false result.
Reasons for increasing MCV
A violation of the MCV norm in the direction of an increase in the average cell size may indicate the occurrence of blood diseases or indicate a pathological condition of internal organs.
The following reasons for increased MCV in the bloodstream are identified:
- intoxication of the body with antibacterial drugs or medications included in the group of antidepressants;
MCV in blood tests increases with illness - bacterial infection that caused extensive inflammation;
- uncontrolled use of steroid drugs or contraceptives based on synthetic hormones;
- severe liver diseases in the form of cirrhosis, viral or intoxicating hepatitis;
- long-term use of strong alcoholic drinks;
- autoimmune pathologies, which are expressed in disruption of the process of red blood cell synthesis;
- prolonged contact with chemicals of toxic etiology, the compounds of which saturate the blood;
- iron and iodine deficiency in the body caused by poor diet or other factors;
- diseases of the thyroid gland associated with insufficient or excessive synthesis of hormones.
Most patients with MCV levels exceeding the norm experience characteristic symptoms in the form of causeless pain in the abdominal cavity, pale skin (if liver pathology is present, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes is possible), increased heart rate, and shortness of breath.
At risk are people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, as well as those with a genetic predisposition.
Reasons for the decrease in the indicator
A decrease in the average size of erythrocyte units is no less dangerous than an increase in blood cell parameters. The internal organs and tissues of the body begin to experience an acute lack of nutrients, oxygen starvation of cells and premature death occurs. A person quickly loses weight, and dysfunction of internal organs and systems develops.
The reasons for the decrease in MCV are the following factors:
- porphyria or a hereditary predisposition to the body producing defective cells;
- heavy metal poisoning (most often a similar clinical picture occurs in people who have been in contact with lead vapor);
- the presence of cancer of the blood or internal organs;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- long-term use of medications, the side effect of which is a decrease in the average volume of red blood cells;
- anemia of all types.
People who have a low MCV complain of constant fatigue, loss of physical strength, become absent-minded, cannot concentrate, and the thought process is disrupted.
The nervous system exhibits symptoms such as increased irritability, depression, rapid mood swings, and memory impairment. If these signs appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Classification and causes of microcytic (MCV lowered) anemia
Anemia is a group of diseases of the human circulatory system, which is expressed in a decrease in hemoglobin levels, as well as a reduction in the average volume of red blood cells.
This pathology is classified according to the causative factors that provoked its development, namely:
- allastic - caused by systemic dysfunction of the bone marrow, as a result of which the process of synthesis and maturation of blood cells is disrupted;
- iron deficiency - there is a decrease in the rate of hemoglobin production, since the patient’s body does not receive enough iron;
- thalassemia is a hereditary type of anemia that occurs due to the fact that the body is not able to form sufficiently strong polypeptide bonds in the protein compounds of hemoglobin;
- hemolytic - develops when the level of dead cells exceeds the number of new red blood cells.
A type of microcytic anemia is taken into account by the attending physician when making a diagnosis, as well as during the formation of a therapeutic course. Eliminating the pathological causes of the disease is a prerequisite for successful treatment.
Cell Variability
Under the constant influence of a number of environmental factors, the occurrence of biochemical and physiological adaptation of blood cells cannot be ruled out.
Variability in the average volume of red blood cells is possible under the following conditions:
- prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages (alcohol addiction);
- daily contact with toxic substances;
- eating excess amounts of protein foods;
- deficiency of foods containing iron and vitamin B12.
Sooner or later, physiological variability of cells leads to the development of diseases of the blood, as well as tissues of internal organs that suffer from an increased or decreased MCV. Most often, the pathological state of cells leads to the development of blood cancer.
Reasons for the downgrade
If the average volume of red blood cells is reduced, this means that microcytosis has developed. As is the case with an increase in the indicator, there is a high probability of a pathological origin of the disorder. Doctors should find out what's what.
There are also quite a few factors for the decline in MCV.
Burdened heredity
Some forms of pathology are genetically determined. This includes diseases that, upon a quick assessment, cannot be called dangerous for the hematopoietic system. For example, Down syndrome, Morphan syndrome, etc.
There are also purely myeloproliferative disorders that affect only the bone marrow. A hematologist should figure out what's what. According to need, geneticists are involved.
Treatment involves only symptomatic correction. It will not be possible to radically influence the situation.
Some drugs
Taking certain medications causes a drop in the average volume of red blood cells. This includes drugs from several groups.
- For example, birth control pills. With prolonged and indefatigable use, red blood cells become smaller in volume.
- Or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs also reduce MCV. This is a temporary phenomenon. As soon as the concentration of active substances decreases, everything will return to normal.
Treatment. It is enough to abandon the drug or reconsider the approach to therapy. The doctor decides the issue. It is strictly prohibited to arbitrarily exclude medications.
Advanced anemia
The types already mentioned above. Iron deficiency, megaloblastic. Hereditary forms are especially dangerous. For some time, the body is actually able to compensate for the pathological process. It increases the size of red blood cells, filling them with more useful content.
But this is temporary. As the pathology, the primary diagnosis, progresses, more and more oxygen is required. The body is no longer able to make up for the deficiency and red blood cells decrease. This is the result of the body's processing.
Attention:
If nothing is done, there is a real risk of death from hypoxia.
Therapy. Standard, as described above. Anemia must be treated as quickly as possible. Iron supplements, vitamins, etc. Genetic forms require the participation of a specialized specialist.
Cancer
Any localization except bone marrow and cerebral structures. Oncological processes can provoke a decrease in MCV.
As a rule, the problem is the disintegration of a large tumor or metastasis. In the first case, severe intoxication is observed. The organ responsible for the synthesis of formed cells also suffers.
In the second case, individual cells spread into the bone marrow. This first provokes microcytosis. And then there are fewer red and white blood cells altogether.
Treatment. Detect the tumor as early as possible and remove the neoplasia. Radiation and chemotherapy are prescribed as needed. Strictly under the supervision of specialists.
Many forms of cancer can be eliminated. Moreover, it’s quite simple. Advanced neoplastic processes can no longer be treated.
Blood loss
Especially plentiful. The volume of red blood cells decreases as a result of the physical loss of some formed cells. Patients with coagulopathies, such as hemophilia, are especially at risk in this regard.
There are other, no less dangerous conditions: injuries, acyclic bleeding of gynecological causes, etc.
Treatment. Give the transfusion as quickly as possible. It is important to replenish the red blood cell mass to prevent hypoxic complications from developing.
The procedure is carried out strictly in a hospital setting. The patient is observed for several days. Only then are they discharged when they are convinced that the threat to life has disappeared.
Gestation
Pregnancy. A complication such as a decrease in MCV is especially common in women of thin build.
Because the fetus develops quickly, problems occur. More oxygen needs to be carried. This means that at an early stage there is an increase and then a decrease in the average volume of red blood cells.
Treatment. No special therapy is needed. You need to see a gynecologist or obstetrician. Visit a hematologist as needed.
Correlation of MCV with other erythrocyte indices
When determining the MCV indicator, a prerequisite for a blood test is the establishment of other erythrocyte indices.
The average volume of red blood cells correlates with the following indicators:
- MCH - displays the average mass of hemoglobin in each individual red blood cell (normal values are from 27 to 31 pg), and the comparative analysis takes into account the ratio of “hemoglobin level/numerical number of red blood cells”;
- ICSU — shows the average level of hemoglobin not in whole blood, but only in the erythrocyte mass (the norm is from 320 to 360 g/l).
Medical practice shows that a violation of at least one of the listed erythrocyte indices affects other characteristics of the cellular composition of the blood. All of the above indicators make it possible to determine the level of hemoglobin and promptly prevent its decrease and the development of blood diseases.
What to do if the indicator deviates from the norm
If the results of a general blood test show a deviation from the norm in the average size of erythrocyte units in the direction of increasing or decreasing their size, the following steps must be taken:
- together with your doctor, try to establish the causative factor influencing the change in red blood cells;
- streamline the daily routine, balance the diet, saturating it with foods containing a sufficient amount of iron, iodine, vitamin B6, B12 (veal, nutria meat, rabbit, turkey, legumes, nuts, ocean fish, seaweed, shellfish, crustaceans);
- take medications that will be prescribed by your doctor;
- completely stop using alcoholic beverages, tobacco products and drugs;
- Avoid a sedentary lifestyle, engage in cycling, athletics, and swimming.
MCV as part of a blood test is an indicator that tends to change under the influence of environmental factors. Therefore, in order for the average cell volume to reach optimal levels, an integrated approach is required using drug therapy, compliance with the instructions of the attending physician and dietary standards.
Article design: Mila Friedan