The study of material obtained from the cervix makes it possible to determine the characteristics of the cellular structure of this anatomical region, identify pathological changes and confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis.
Microscopy of a smear from the cervix
The most common type of cytological analysis in gynecology is the PAP test, or Papanicolaou test. It was developed at the beginning of the twentieth century for the early diagnosis of cervical cancer, and it continues to be used today. There are also the latest methods in this area - ThinPrep, or liquid-based cytology. This technique significantly increases the efficiency of the diagnostic search and allows you to make a timely diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Cervical cytology - what is it?
A cytological smear for morphologically changed cells is also called PCR analysis. It increases the chance of detecting atypical cancer cells; they indicate the onset of the oncological process. Also, this type of analysis reliably determines the presence of pathological microflora, human papillomavirus.
Early diagnosis of cancer makes it possible to preserve the health and sometimes even the life of a woman. This is due to the fact that the early stage is asymptomatic, and when the clinical picture of the disease makes itself felt, the disease is difficult to treat even with surgical intervention. Delayed diagnosis sometimes negate the use of radiation or chemotherapy.
Another advantage of early diagnosis of cancer is the ability to preserve the integrity of the genital organs and the possibility of the reproductive function of the body.
To prevent the development of undesirable consequences, it is necessary to undergo an annual examination by a gynecologist and undergo this type of analysis.
Sometimes this type of test may be called a PAP test.
Goals of oncocytology
Liquid oncocytology of the cervix is a screening examination to identify malignant tumors. This examination allows us to identify the development of pathology at an early stage, which allows us to prescribe adequate therapy and minimize the risk of possible complications.
Oncocytology is performed to identify the inflammatory process. Most often it occurs in the form of colpitis. Colpitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix. To determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process, cytological analysis may be required.
But most often liquid oncocytology is used to diagnose malignant tumors, since atypical cells are identified in this smear, which are a sign of malignancy.
Indications for cervical cytology
In addition to detecting modified cellular structures and determining a precancerous condition, this type of analysis can be used as a method for additional diagnostics of intracellular changes.
He is appointed:
- To identify abnormalities in cell development in body tissues.
- To determine the nature of pathogenic microflora.
- To determine the cause of changes in the cyclicity of menstruation.
- To identify pathologies caused by papillomavirus.
- In order to identify a woman’s inability to conceive a child.
- To determine the pathology of the epithelial layer of the cervix.
- To determine the cause of bloody vaginal discharge.
This type of analysis is also prescribed:
- Before a planned pregnancy.
- With frequent labor processes.
- If the birth occurred at an early age (the woman giving birth was under 18 years old).
- Before the onset of menopause.
- Before inserting a contraceptive device.
- If a woman has not contacted an antenatal clinic for more than 3 years.
- If a visual examination of the cervix using a vaginal speculum raises doubts about the health of this organ.
- With a positive test for HIV infection.
- With genetic burden (illness of close relatives with cancer).
If a cytological examination suspects the presence of a tumor, the patient must undergo this type of examination at least twice a year.
Atypical cells detected: what does this mean for the patient
Regular medical consultations are the key to the effectiveness of both treatment and prevention.
The gynecologist must conduct a detailed consultation, during which he will explain what it is in a particular case and explain the advisability of conducting an additional examination. Additional diagnostic search methods will allow you to correctly determine the most effective course of therapy.
For diagnosis when atypical cells are detected during a cytological examination in gynecology, the following are additionally prescribed:
- repeated cytological analysis of the cervical epithelium;
- colposcopy;
- biopsy;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- test for detecting human papillomavirus.
It is important to follow all medical recommendations and prescriptions; this will allow the pathological process to be identified and corrected in a short time. The effectiveness of the course of treatment should be regularly monitored using cytological examination. Therapy will be considered complete when cytology results confirm the healthy state of the cervical epithelium.
Examination of scrapings from the cervix is an important diagnostic procedure that should be carried out regularly for preventive monitoring of a woman’s health. An annual visit to a gynecologist for an examination and diagnosis of possible pathologies should be a rule of life for everyone, because early diagnosis of any disease is the key to timely initiation of treatment and its high effectiveness.
Unscheduled cervical cytology
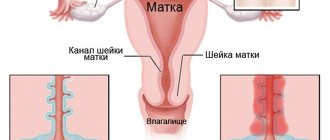
During colposcopy, two smears are usually taken:
- The material is collected directly from the cervical canal.
- A vaginal smear allows you to determine the presence of pathogenic microflora.
In some cases, an unscheduled appointment of this type of study occurs. It occurs in the following cases:
- If there is a suspicion of the presence of papillomavirus, or genital herpes.
- Vaginal discharge of unknown etiology.
- Disorder of menstruation, prolongation or delay.
- Heavy uterine bleeding.
- Suspicion of HIV infection.
- If a woman wishes to have an intrauterine device installed.
Where to go and what to do if there is a deviation in the results
After a cytology smear and receiving the results, you need to go to the doctor, who will correctly decipher the indicators and tell you what to do next. Depending on what cells were found, additional studies are performed to clarify the diagnosis and confirm it. If bloody discharge appears after taking a smear, this is normal for 1-2 days. If the discharge continues for more than 2 days, then this is a reason to consult a doctor unscheduled. In rare cases, untimely treatment threatens the patient with reactive changes in the body and rapid deterioration of the condition.
Cytological examination is never prescribed just like that, only for direct indications. After the results have been received, you should not decipher the text yourself, but seek help from a doctor. He will check all the indicators, correlate them with your medical history and complaints, and conduct additional studies if necessary. Then treatment will be prescribed. After its completion, it will be necessary to conduct a cytological examination again.
What does cytology show?
The result of cervical cytology can be divided into positive and negative:
- A positive analysis indicates that atypically altered cellular inclusions were found in the cervical tissue. They have a changed morphological structure, shape, and can be observed in different quantities.
- If the result is negative , no cellular changes are detected; this is a normal indicator.
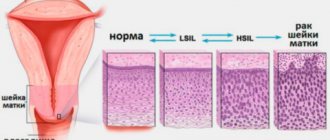
Changes in cell structure are divided into 5 stages:
- Stage 1 . The study picture is not alarming and is within normal limits.
- Stage 2 . The inflammatory process is within relative normal limits. The number of modified cells is relatively small. This serves as a reason for prescribing additional diagnostic measures.
- Stage 3 . The study may reveal cells with changes in the nucleus or cytoplasm. This result is not a deviation from the norm. Most often, it is a risk factor that a woman may develop cancer. In this case, a histological examination is mandatory.
- Stage 4 . Indicates the initial degeneration into an atypical form of a small number of cells. There is a pronounced change in the nucleus, chromosome, and cellular contents. Re-appointment of cytological and histological analysis is required.
- Stage 5 . It is characterized by a high level of modified cells, this is the reason for conducting a comprehensive examination and prescribing appropriate therapy.
Material for cervical cytology
Oncological diseases of the cervix (90% of all cases) affect the stratified epithelium; much less often, the glandular layer is involved in the pathological process.
In this regard, the following material is collected:
- Columnar epithelial cells in the area of the cervical canal (endocervical cells) are taken.
- Flat epithelial cells are collected from the vaginal side of the cervix (ectocervical cells).
- Cells that are formed at the junction of columnar and squamous epithelium will be taken and subjected to cytological examination.
Interpretation of research results
Indicators of normal cytological examination of the cervix
The normal balance of microflora and the absence of pathological changes when analyzing a smear for cytology confirm the healthy state of the cervical canal. When studying, the cells in the smear are compared with the morphological standards of the norm, that is, their size, shape, and structure should not have abnormal deviations.
The doctor confirms that the study results correspond to a healthy state in the following cases:
- Cytology smear includes cylindrical single-layer epithelial cells.
- When taking a smear from the transition zone or vagina, it is normal to detect stratified epithelial cells.
Even minor deviations in cell morphology are reflected in the laboratory report. Changes may confirm inflammatory diseases or the presence of benign abnormalities. Most often noted:
- inflammatory atypia;
- atypia due to the presence of HPV;
- mixed atypia;
- atypia of unknown etiology, which require further diagnostic appointments.
How to prepare for cervical cytology?
To achieve the reliability of the analysis, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparation activities before carrying out this procedure.
To do this you need:
- For 2 days, before the cytological examination, you need to prepare and completely avoid sexual contact.
- One day before the procedure, do not do hygienic washing and douching.
- Do not use the bathtub , but only use the shower.
- Avoid the use of hygienic sprays, gels, tampons, vaginal suppositories, and any tablet forms . Since their use may negatively affect the reliability of the analysis.
- Immediately before the procedure, do not urinate for 2 hours.
- For a few days, stop using antibacterial drugs , anti-inflammatory drugs, and contraceptives.
- If an infection is detected , you can take a smear only after complete recovery, after 10 days.
- This type of analysis is not carried out during menstruation , as it will be poor and will not show signs of the disease. It is prescribed 5 days before the onset of menstruation, or after 5 days after the end of the cycle.
What diseases cause deviations in results
A cytological report will not show an accurate picture and will not make a diagnosis. After receiving the results, they need to be taken to a specialist who will decipher the indicators not only taking into account cytology, but also based on other studies, examination, anamnesis and heredity.
A negative cytological analysis may indicate the presence of:
- Bacterial vaginosis;
- Inflammation in the urethra or vagina;
- Invasive or non-invasive cancer;
- Trichomonas, candida, herpes, coccal infection;
- Metaplasia;
- Hyperkeratosis, colpitis, metaplasia.
Many other diseases are also possible, which negative cytology will show. In some cases, the doctor will ask you to redo the study in the hope that it was performed poorly or an error was made during the collection of biomaterial.
How is cervical cytology performed?
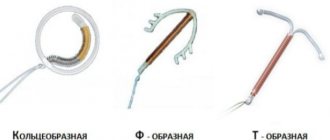
To carry out this procedure, only a sterile instrument is used.
For this purpose the following is used:
- Eyre's spatula . It is used to collect material from the vagina and upper part of the cervix.
- Endobrush . A special probe for collecting material from the cervical canal.
- Sterile brush.
- Anatomical tweezers.
- Gynecological speculum.
- Volkmann spoon for scraping the cervix.
Material is collected for cytological examination by a gynecologist.
For this:
- The woman lies down on the gynecological chair, having previously removed her underwear to the waist.
- For complete visualization, a vaginal speculum is inserted.
- A sterile brush is inserted into the lumen of the cervical canal, approximately 2 cm, to collect endocervical tissue. The taken material is placed on a special glass slide, which is assigned a specific code or number.
- Using an Eyre spatula, scraping is performed in the area of the transition of cylindrical to squamous epithelium. The contents are also placed on glass and labeled.
- To take material from the ectocervix site, you need to take a new sterile spatula. The biomaterial is placed on a separate glass slide.
- After this, the smears are treated with a special solution, dried, and sent for further laboratory examination under a microscope.
To conduct this type of study, 15-20 minutes are enough.
Technique
Liquid oncocytology of the cervix is performed in a treatment room by a gynecologist. Before the smear, an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is performed. Most often, a transvaginal ultrasound (through the vagina) is performed. After which the patient is examined on a chair in the mirrors and a smear is performed directly for oncocytology.
Oncocytology smears are performed using sterile instruments (spatulas, brushes). With their help, the doctor takes a sample of the mucous membrane of the cervix and cervical canal. After which the discharge is placed in a sterile container with a preservative and transferred to the laboratory.
Main indicators of cervical cytology
The cytological smear is subjected to microscopic examination.
This determines:
- The presence of pathogenic microflora.
- The number of red blood cells and leukocytes.
- Condition of the columnar epithelium.
If the number and shape of cells does not cause abnormalities, the study is considered negative, which is the norm.
When the analysis shows that morphological changes have occurred in the cells, with a violation of their structure, this result is considered positive. In this case, a repeat type of analysis is prescribed in combination with additional types of research.
How long to wait for results and expiration date
There is a slight difference in the time it takes to do a smear for flora and cytology at a paid research laboratory or at a antenatal clinic. In the first case, the conclusion can be received in hand in 1-4 days. If necessary, you can do an urgent study, which will be somewhat more expensive, but the result will be within two to three hours.
How many days the cervical cytology is done, if taken at a antenatal clinic, will depend on where the test is taken. The clinic usually does not have its own laboratory that can handle such research, among other things. Therefore, the material is prepared and transported to a laboratory that cooperates with the clinic.
You can check with the gynecologist after the test to determine how long the cytology test is done and when the results will be available, but usually this period reaches 8 working days. This time includes transportation of the biomaterial, the time at which the result will be prepared, and sending the results back to the clinic. Regardless of where the material is submitted, the result will be valid for three months. After this period you will have to retake the analysis.
Deciphering cervical cytology
When deciphering a cytological analysis, the following is considered to be the norm:
- Cells of unchanged columnar epithelium are detected.
- Multilayer vaginal cells without disturbing their structure.
- Small changes that may indicate the initial stage of inflammation are within normal limits.
- A small number of leukocytes (up to 15 units), acidity is 4.0-4.5. The main part of the bacteria is Doderlein bacillus.
- Small mucus impurities.
- Flat cell epithelium does not exceed 10 units.
- The degree of vaginal cleanliness is within the second stage.
Pathological changes are detected if the following deviations are observed in the smear:
- An increase in acidity over 5.0.
- The presence of trichomonas, Neisser gonococci, fungi of the genus candida, gardnerella, chlamydia, papillomavirus indicates the presence of an infectious pathology.
- The detection of several types of lactobacilli at once, against the background of an increase in acidity to 7.0, or if it becomes alkaline, may indicate the initial form of dysplasia. The degree of vaginal cleanliness can move into the third or fourth category.
- The complete absence of lactobacilli, the development of an alkaline environment, with a high concentration of columnar and squamous epithelial cells raise the suspicion of the probable development of a cervical form of uterine cancer. Such changes are most often observed against the background of an increased content of leukocytes, with large amounts of mucus, and a change in vaginal cleanliness to the fifth degree.
Atypical cells are considered to be when the following changes occur in the cellular structure:
- The volume of the core increases significantly.
- Its configuration and coloring are disrupted.
- Morphological abnormalities appear in the cytoplasm.
It should be noted that even significant deviations do not always provide grounds for making a diagnosis indicating the development of an oncological process.
To achieve a reliable diagnosis, prescribe:
- Repeated cervical cytology.
- Colposcopy in combination with biopsy.
- Diagnostic curettage.
- Complete blood test using tumor markers.
When the analysis shows that morphological changes have occurred in the cells, with a violation of their structure, this result is considered positive. In this case, a repeat type of analysis is prescribed in combination with additional types of research.
What to do if you receive a positive cervical cytology test result
When undergoing this type of study, a positive result is quite common. But this does not always mean that a woman develops cancer.
Very often, a positive result may indicate the presence of an infectious process, which can occur as a result of diseases of the genital area, erosion, or vaginal dysbiosis.
After treatment for sexually transmitted infections, repeated cytological analysis usually returns to normal.
If atypical cells or symptoms of dysplasia are found in the analysis results, this is also indirect evidence of the development of a malignant neoplasm. This happens because cervical cytology is not designed to detect the stage of the cancer process. It can only indicate the emergence of risk factors for this disease.
To establish a final diagnosis and exclude oncopathology, colposcopy, biopsy, and histology are required. A diagnostic curettage is required.
In addition to the above studies, the woman is prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy followed by cauterization of the affected areas. If the disease is viral, it is recommended that both partners undergo a full course of therapy. This will prevent re-infection.
After all treatment measures, it is recommended to undergo an annual cytological examination for the presence of cervical cancer.
What changes are possible?
Benign changes may include:
- Detection of trichomonas, candida fungi, coccal infections, anomalies caused by infection with the herpes virus.
- Cellular atypia provoked by inflammatory reactions: metaplasia, parakeratosis, keratosis.
- Atrophic changes in epithelial cells in combination with inflammation: hyperkeratosis, colpitis, metaplasia.
Dysplastic changes and atypia suggest the following conditions:
- Atypia of unknown origin (ASC-US).
- High risk of presence of cancer cells in the material (HSIL).
- Precancerous atypia: varying degrees of dysplasia.
If cancer cells are detected, it is necessary to prescribe additional examination methods and a subsequent course of therapeutic correction (conservative or surgical treatment) with constant cytological monitoring.
Flora smear in women: interpretation of results
Cervical cytology and pregnancy
This test is taken three times during pregnancy:
- An initial smear is taken during a visit to the antenatal clinic for registration.
- At week 30, testing is performed again.
- To avoid infection of the child during childbirth, cytology is performed at 37 weeks of pregnancy.
This frequency of this test is due to the fact that during pregnancy women may experience a hormonal imbalance, and as a result, this leads to changes in the vaginal microflora. A weakened immune system may be a favorable factor for the development of vaginal candidiasis and other undesirable consequences.
Pregnant women should be aware of the special importance of conducting this type of analysis, that this is a safe type of diagnosis, it is performed with a sterile instrument and cannot be a source of infection for the woman.
It is very important to take a PAP test before pregnancy. If during its passage an increased content of leukocytes, erythrocytes, and morphologically changed cells is detected, pregnancy should be postponed. Its planning is allowed after complex therapy, in the event that a repeat analysis is negative.
How often should you get a smear test?
Women over 18 years of age must have a smear test at least once a year. And after 40 years, oncocytology is recommended to be performed 2 times a year. If a woman has a hereditary predisposition to cervical cancer, cervical dysplasia, erosion, then in this case she needs to undergo testing at least 2 times a year. According to indications, liquid oncocytology can be performed more often, as a control for the treatment of the underlying disease.
Liquid oncocytology is a modern and safe method for determining pathological changes in the cervix. Thanks to this method, the percentage of efficiency in diagnosing precancerous diseases and oncology has significantly increased. Since this procedure is safe and painless, it is performed on all patients with suspected cervical pathology or as a preventive measure. This test must be taken once a year starting at the age of 18.
Liquid cytology of the cervix
This technique has become widespread in Europe and Russia since approximately 2004.
It is distinguished by a high degree of reliability and ease of implementation:
- To perform this, a special brush was developed. When performing cervical cytology, it is inserted into the area of the cervical canal. The gynecologist makes 3 rotational movements clockwise and two circular movements counterclockwise. This allows for the highest quality sampling of cervical contents.
- This procedure does not require anesthesia and takes no more than 15 minutes.
- After this, the contents along with the brush are placed in a special test tube-bottle. It contains a liquid composition that dissolves the material under study, turning it into a homogeneous mass. The tubes are sent to the laboratory for analysis.
- In laboratory conditions, the solution is filtered and centrifuged. After this, the resulting sediment is applied to a glass slide and stained using the Papanicolaou technique.
- Microscopic examination is carried out in a similar way as with a regular cytology test.
The result is normal if the smear contains, in small quantities, unchanged columnar epithelial cells. The analysis should not contain inclusions of fungal mycelium, papillomaviruses and other bacterial infections.
The decrypted result is usually issued on time, 7 or 10 days after taking the material for research.
This type of analysis should be performed at least once a year. It should be done after a woman begins a normal sex life. After 30 years of age, this type of examination can be done once every three years.
Advantages and disadvantages of liquid-based cytology of the cervix
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Complications
Liquid oncocytology is a safe procedure that does not cause negative consequences for the body. But despite this, a few hours after the procedure, discharge from the genital tract may be observed. The discharge may be the usual whitish color, mucous and brownish. But small amounts of bloody discharge may also be observed.
Vaginal discharge should not be profuse and cause discomfort in the woman, since this phenomenon is caused by a slight intervention on the mucous membrane of the cervix, so there is no need to worry. Vaginal discharge returns to normal within 2–3 days.
After oncocytology, minor pain in the lower abdomen may appear, similar to menstrual pain. It also involves medical intervention and speculum examination.
If a woman has increased sensitivity to pain, then as prescribed by a doctor, you can take an antispasmodic or analgesic drug. The pain syndrome goes away within a day.
Doctors' recommendations
All experts in the field of medicine (gynecology and oncology) argue that this type of analysis should be done once a year.
This will make it possible to identify cancer pathology at an early stage of development. Only timely detection of this disease will allow for a complete recovery.
Cervical cytology allows you to identify women who are at risk. Register them and carry out monitoring to monitor the progression of the oncological process.
Cytological examination in gynecology
Cytological analysis in gynecology refers to microscopic examination of samples taken from the vagina and cervical canal to determine the typical cellular composition. This diagnosis allows doctors to draw conclusions about the presence of inflammatory processes, precancerous diseases or cancer in the patient’s reproductive organs.
Unlike histological examination, the cytological method is non-invasive. That is, when taking biological material there is no need to perform a biopsy or puncture, and the integrity of the tissue is not compromised at all. Samples taken using a fingerprint or swab are analyzed. To obtain accurate results, you must carefully follow the rules for preparing for the examination. It is also very important that the analysis is deciphered by the woman’s attending physician, who will take into account her complaints and data from other diagnostic methods.
Cytological analysis usually takes no more than a day to complete. If a precancerous condition or an oncological process is discovered, invasive diagnostic techniques are used to clarify the diagnosis - biopsy.
Cytology is especially important when biopsy is contraindicated and when examining a large number of patients (when it is necessary to identify women at risk for developing malignant pathology).
Rules for preparing a woman for analysis
The preparatory stage should begin 2-3 days before the procedure.
During this time you must refrain from:
- any sexual contact;
- douching;
- use of vaginal contraceptives, suppositories, tablets;
- hygienic toilet of the genitals using soap;
- taking baths, swimming in pools, ponds;
- use of antibiotics.
The analysis should be taken on days 6-12 of the menstrual cycle. During bleeding, biomaterial is not removed. Blood distorts the result data.
In the case of a gynecological examination or colposcopy, the Pap test is postponed for 72 hours. The test is not prescribed during an acute inflammatory process of the genital area. A smear for oncocytology is carried out after the symptoms of the disease disappear. 2 hours before the test you should refrain from going to the toilet.