A virus differs from a bacterium in its structure. It includes:
- DNA or RNA cells;
- a protein shell called a capsid;
- lipid layer.
A distinctive feature of viral microorganisms is their inability to survive outside human cells. The spread of viral infections (flu, colds, sore throats) occurs in most cases by airborne droplets. Penetrating into the mucosa, pathogenic cells prepare for the “implantation” of viral RNA or DNA.
The spread of the virus leads to intoxication of the body, which manifests itself in:
- soreness and pain in the larynx;
- increased temperature (low-grade fever);
- deterioration of health;
- muscle and bone pain.
Indications for use
The medicine is recommended for the prevention and treatment of influenza, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial virus, herpes, adenovirus, etc. Arbidol has shown excellent action in the fight against acute viral infections of the gastrointestinal tract such as rotavirus and entrovirus and prevention.
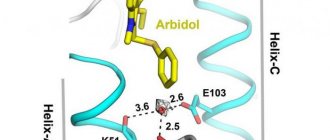
The main difference of Arbidol is the ability to restore the missing interferon in the body during the initial stages of the disease, which reduces their severity and shortens the treatment period.
Many parents are interested in: at what age is the drug approved for children? Previously, it was prescribed to children from the age of two, but currently its use is allowed only from 3 years. It is believed that taking medication in tablet form is difficult for a child under this age. The effect of the drug is to block the protein of the viral shell, which prevents the further development of the virus and its penetration into the cell. This is especially effective for cells of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract. Then the body’s immune system is stimulated, which, combined with the first effect, reduces the likelihood of complications and makes the course of the disease mild.
Within 90 minutes after taking the medicine, the maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is reached. And within 24 hours, 90% of the drug is eliminated from the body, with 40% of it leaving unchanged. The liver processes about 39% of the drug, and the kidneys, in turn, 21%. Arbidol is a slightly toxic drug; its lethal dose is 4 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, the maximum dosage is a condition that cannot be neglected.
Overdose
The drug very rarely leads to an overdose. This usually worsens allergy symptoms. Large spots appear on the body. At the initial stage, they are white and protrude above the surface of the skin. As the condition progresses, the spots become red, accompanied by severe itching and burning.
If at this stage the patient does not receive treatment, the symptoms may worsen, lacrimation, rhinitis and general condition worsen. In addition, the rash can spread to large areas of the skin of the body and even the face.
The condition may be aggravated by swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat. This leads to difficulty breathing, which often turns into suffocation. This condition threatens the patient’s life and therefore requires immediate treatment in a hospital setting. Since Arbidol does not have a specific antidote, medications are used depending on the symptoms of overdose.
In a hospital setting, the patient undergoes a gastric lavage procedure. Additionally, antihistamines, enterosorbents and oral rehydration agents are used to help avoid dehydration.
Instructions for use
Arbidol is available in the following forms:
- Powder for making syrup for children. Syrup is the only form of medicine approved for use in children over 2 years of age.
- Biconvex tablets with a white or cream-colored shell. Contains 100 or 200 milligrams of the main substance.
- Yellow gelatin capsules. They contain 50 or 100 milligrams of the main substance.
The tablets are enclosed in a blister, located in a cardboard package, and capsules are in polymer jars. The type of packaging and release form depend on the organization of the manufacturer of the medicinal product.
Pills
When treating the disease, from 12 years of age you should take four 200 mg tablets per day. It is better to take the medicine 30 minutes before meals. For prevention, you need to take one tablet a day before meals. Children aged 6 to 12 should take 100 mg four times a day for treatment. For preventive purposes, take one 100 mg tablet daily. Children over 3 years old are recommended to take half a 100 mg tablet four times a day, and for the prevention of viral diseases - half a tablet per day.
Capsules
Persons over 12 years of age are allowed to take no more than 2 capsules of 100 mg or 4 pieces of 50 mg at a time. Children aged 6 to 12 – 1 capsule of 100 mg or 2 pieces of 50 mg, from 3 to 6 years – 1 piece of 50 mg. The dosage of the drug in capsules does not differ from the dosage of the drug in tablet form, that is, the dosage regimen is the same.
Suspension
To prepare the syrup, you need to pour about 30 ml of boiled water at room temperature into a bottle of powder, close the lid and shake it thoroughly until a homogeneous mixture is obtained. Then add another 100 milliliters of water and stir. Before use, it is better to shake the bottle so that the suspension becomes homogeneous. The finished syrup can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 10 days. Dosage is made easier thanks to the included measuring spoon.
For ages 2 to 6 years, a single dose is 10 ml; for ages 6–12, it is 20 ml. For adults and children over 12 years of age, the maximum dose is 40 ml. When treating diseases, it is necessary to take the maximum single dose of the medicine 4 times a day. For prevention - maximum dose 2 times a week. The drug is taken 30 minutes after a meal and washed down with a small amount of boiled water.
The maximum course of treatment with Arbidol is 5 days. After which it is better to reduce the medication to once a day for 28 days. This regimen is used for treatment with any form of the drug.
If the drug is taken for the purpose of prevention in case of contact with a carrier of a viral disease, then it is better to adhere to a single daily dose of the drug for 2 weeks. During a surge in epidemics of viral infections, you should use the medicine 2 times a week for 3 weeks. It can be combined with other medications; the instructions do not prohibit this.
How can I tell if I have the flu or a cold?
- The temperature is not higher than 38.5 degrees.
- Headache.
- Stinging in the eyes.
- Runny nose.
- A sore throat.
- Cough.
- Chills.
- Weakness and drowsiness.
- Temperature from 38.5 to 40 degrees.
- Severe headaches.
- Severe pain in the eyes.
- Runny nose.
- Severe sore throat and cough.
- Severe chills, muscle pain.
- Increased sweating.
- Abdominal discomfort, vomiting, diarrhea.
Side effects and contraindications
It is not recommended to take Arbidol during pregnancy and lactation and for children under 3 years of age (the suspension is allowed from 2 years of age). In case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, it is also necessary to limit its use. The instructions suggest using with caution in case of renal and liver failure, lactose intolerance and diseases of the cardiovascular system. When used, the dosage must be observed.
Apart from possible allergic reactions to the components included in the drug, no other side effects were identified, even if the permissible dosage was exceeded.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators are recommended to be taken after a course of antibacterial treatment and antiviral drugs. During this period, the child’s body is weakened and susceptible to various infections.
They will also help in the event of the development of purulent tonsillitis, because will reduce the likelihood of developing all kinds of systemic complications.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p5VQ4lNEAy8
The most famous immunostimulating drugs for children include:
- Immunal,
- Imudon,
- IRS-19,
- Ribomunil, etc.
Analogs
On the pharmacological market there are various drugs, both domestic and imported, that can replace Arbidol. The most popular of them are the following:
- Ingavirin. Strong drugs aimed at combating influenza A and B viruses. More effective compared to Arbidol, but also much more toxic. Before using the medicine, consult a doctor.
- Kagocel. Used for the prevention and treatment of diseases caused by viruses. Activates the body's production of natural endogenous interferon in large volumes, which helps fight infection. As the instructions say, the drug can only be taken from the age of 3 years.
- Aflubin. The homeopathic remedy does not have an antiviral effect, but helps in the production of interferon in the body of an adult and a child. In addition, it reduces swelling, thins sputum, has a weak antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect and relieves intoxication of the body. The most common suspension is approved for use in children under one year of age.
- Remantadine. The drug does not have an immunostimulating effect, but it fights microorganisms well. It is quite effective, but it affects the liver, so people with impaired function of this organ need to take the medicine with caution. Contraindicated for children under one year of age.
- Ferrovir. The drug is quite effective in the treatment of various viral diseases. Restrictions on use include childhood and pregnancy. May cause a slight increase in temperature. For childhood diseases, it is better to replace this drug with analogues.
- Immunal. Used to strengthen immunity and prevention. Promotes rapid recovery from the disease and prevents the virus from entering the body's cells. The instructions do not describe any contraindications for use, except for individual intolerance. The closest analogue of Arbidol, but can be used in children under one year of age.
- Tamiflu. It is often prescribed to children and has quite strong antiviral effects. But there is a whole list of side effects, such as vomiting, diarrhea, nausea and abdominal pain. Capsules and suspension are available for sale. As an analogue of Arbidol, it must be taken with caution and should not be given to children under one year of age.
- Ergoferon. A modern antiviral drug with anti-inflammatory effect. Additionally activates the body's immune system.
- Anaferon. Used in the prevention and treatment of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections. It is a homeopathic remedy with antiviral action. Reduces the risk of complications.
It is necessary to consult a specialist before using medications. Many drugs have side effects and are contraindicated for certain groups of patients.
Arbidol for children - video
In this video, using the example of the effect of the influenza virus on the body, the principle of operation of the drug Arbidol at the cellular level is shown.
Arbidol is a popular and quite effective antiviral drug for children. It is very often used not only for viral infections, but also for colds in a child as an immunomodulator. Thanks to its action, the medicine helps the body successfully overcome the disease and complications that arise.
It is difficult to say how much better Arbidol works in contrast to Anaferon for children or other antiviral agents. In this matter, doctors often focus on the individual characteristics of the baby’s body. Therefore, the issue of prescribing and using the drug should first of all be discussed with specialists.
Do you use Arbidol to prevent viral diseases in your child? Which form of the drug do you prefer? If you have ever given Arbidol to your baby, share your experience and results with us in the comments!
Price
Arbidol and its analogues have similar effects and are used for the same diseases, but the price of these drugs varies significantly. In particular, it depends on where and by whom exactly the analogue was produced. The cheapest medications include Immunal and Anaferon, but they are homeopathic drugs, and many doctors claim their weak effectiveness, although they are much cheaper than Arbidol.
The most common forms of Arbidol release are capsules. The price for a package of 20 capsules is on average 450 rubles, while 10 pieces costs about 250. The suspension is much more expensive, and besides, it has a short shelf life - only 10 days and can only be considered as an analogue of capsules if the child is young.
Kagocel, in turn, is produced in only 10 tablets per package, and its price is almost equal to the cost of 10 capsules of Arbidol, and it can easily replace it. Ergoferon is cheaper than Arbidol, but is an unequal analogue of this medicine.
What should I not do if I have the flu?
- Use antibiotics. These are drugs that fight bacteria, that is, microorganisms that sometimes cause various infections. For example, streptococcal sore throat, cystitis, syphilis and others. Antibiotics have no effect on viruses, and colds and flu are viral infections against which antibiotics are useless.
- Use homeopathic remedies. Homeopathy is a method of treating a disease with a drug that causes its symptoms, but in incredibly small quantities. As a result, after all the dilutions, not a single molecule of the original substance will remain in the test tube and such “medicines” are useless. These include the well-known “Aflubin”, “Kagocel”, “Anaferon”, “Mastodinon”, “Arbidol”, “Ocillococcinum”, “Remens” and others.
- Self-medicate. Garlic, echinacea and vitamin C do not help in any way with ARVI or influenza.
- Going to work, shopping, carrying illness on your feet. This increases the risk of infecting others and threatens to complicate the disease. During treatment, it is better to stay at home and follow the doctor's recommendations.
Treatment method
Treatment of viral tonsillitis is carried out by following the following recommendations:
- Medicines such as ibuprofen and paracetamol help relieve chills and pain. It is not recommended to use ibuprofen if you have ulcers, asthma, pregnancy, or kidney disease.
- Aspirin should not be used in treatment for children under 16 years of age.
- Special lozenges are used to soothe the throat.
- Gargling with saline solution and herbal infusions.
Tonsil removal
It is believed that a sore throat goes away after the tonsils are removed.
Removal of the tonsils is performed under general anesthesia. In this case, the mouth is open, and the surgeon uses special scissors for the operation. After the procedure, special sutures are applied, which dissolve over time.
Rehabilitation after tonsil removal consists of the following steps:
- Full recovery after removal occurs after two weeks.
- After surgery, you should take sick leave for two weeks and avoid visiting public places.
- After the procedure, you need to consume plenty of fluids, but you should avoid juices and dairy products.
- After having your tonsils removed, you should brush your teeth after eating to prevent infection.
- The painful sensations continue for about a week, and additional pain appears in the ear.
Types of sore throat
There are no significant differences in the classification of the disease in children and adults. The disease can be catarrhal, lacunar, follicular, necrotic. The mildest is catarrhal, and the most severe is necrotic. Let us consider in detail what kind of sore throat occurs in children and adults.
- Catarrhal tonsillitis - superficial damage to the tonsils and moderate signs of intoxication, temperature up to 38 degrees, changes in the blood are minor. When examining the throat, bright hyperemia is detected, covering the back wall of the pharynx, hard and soft palate. The tonsils enlarge mainly due to swelling and infiltration.
- Lacunar and follicular tonsillitis. These types of sore throat have similar symptoms and often develop simultaneously: accompanied by a temperature of up to 39-40 degrees, signs of intoxication are clearly expressed
- Fibrinous tonsillitis - characterized by the presence of a whitish-yellow fibrinous plaque on the tonsils, regional lymphadenitis is observed. It is necessary to note the following feature of this type of sore throat - it occurs more often in children with severely weakened immunity. This disease can be the result of lacunar tonsillitis or develop independently.
- Phlegmonous tonsillitis is a purulent melting of the tonsil area. People between the ages of 15 and 40 are mainly affected. The tonsil is hyperemic, enlarged, and painful on palpation. The throat hurts severely when talking and swallowing, and signs of intoxication are clearly visible. The patient's temperature rises to an alarming level of 39-40 degrees.
- Necrotizing tonsillitis. In this case, general and local symptoms are more pronounced than in the forms described above. The patient has a persistent fever, signs of confusion, and constant vomiting. A plaque with a pitted surface is found on the tonsils. Its color can be grayish or greenish-yellow. The affected areas are often saturated with fibrin, that is, they become dense.
Causes of sore throat
The main cause of sore throat is various viruses, sometimes it can be bacteria, of which hemolytic streptococcus occurs in 80% of cases. In the secondary form of angina, the causes may be infectious diseases and blood diseases: scarlet fever, measles, mononucleosis, diphtheria, syphilis, agranulocytosis and leukemia.
Sore throat is transmitted by airborne droplets, through food and water, as well as through communication and contact with a sick person. Most often, the disease occurs in damp and cold seasons, in autumn or winter. Sore throat in a child can be a consequence of hypothermia with weak immunity and other diseases. The causes of sore throat can be dental diseases, caries and infections in the oral cavity.
Sore throat in a baby
Sore throat in an infant is a rather dangerous phenomenon that can lead to serious consequences. To prescribe adequate treatment, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. This task is made more difficult by the fact that the baby cannot talk about his feelings. When making a diagnosis, the doctor relies on examination data and information received from parents.
The following signs give reason to suspect a sore throat in an infant:
- a rise in temperature to 39-40 degrees, against which convulsions sometimes occur;
- refusal to eat, vomiting, diarrhea;
- restlessness and constant crying.
During illness, you need to properly care for your baby. Rest and sleep will bring the moment of recovery closer. If a child does not cry, there is no point in holding him in your arms all the time - he will be better off in a crib. When your baby is sleeping, you should not wake him up unless you need to give him medicine.
If necessary, the baby is placed in a hospital. This will have to be done if he suffers from congenital diseases, a sore throat has caused complications, or there are signs of severe intoxication.
What should you do if you have a cold?
- Visit a doctor. Most likely, he will recommend bed rest and antiviral drugs - oseltamivir or zanamivir. Their effectiveness has been proven, but the medicine can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor - sometimes the side effects can be worse than the possible benefits.
- Check the effectiveness of medications. Before you buy a drug prescribed by a doctor, it is worth checking whether this drug has been found effective. Some drugs that can be bought in Russian pharmacies are “dummies”, although they position themselves as remedies for many diseases. For example, Arbidol is the best-selling medicine for flu and colds. At the same time, the drug has no proven effectiveness, WHO does not recommend its use, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) refused to register it for sale in the United States.
- Drink enough water. The liquid accelerates the removal of toxins from the body that are formed due to the activity of the virus.
- Rest, ventilate the room, wash your hands often. This will help you recover faster and support your immune system.
Prevention of sore throat
Prevention of angina is aimed at overall strengthening of the body and eliminating various infections that provoke the disease. It requires an integrated approach:
- Maintaining personal hygiene. During illness, the patient must use a separate towel, toiletries and utensils.
- If you have a sore throat, the patient must be isolated from other family members and people. The room should be cleaned regularly.
- Supporting proper nutrition. It should be healthy, nutritious, contain vitamins and minerals.
- Regular examination and treatment of helminth infections, as well as all sources of chronic infection: caries, pyelonephritis, sinusitis, chronic tonsillitis, various purulent skin diseases. Maintain oral hygiene and get examined by a dentist. If necessary, carry out partial or complete removal of adenoids or tonsils.
- Hardening a child from an early age. It is best to start hardening in childhood, but it can be done at any age. Among the methods of hardening are dousing, rubbing, contrast showers, swimming, walking barefoot on stones and sand. The process should be gradual so that the body gets used to the stress. Hardening can only be carried out in a healthy state.
- Increased immunity level. It is necessary to protect the mucous membranes from damage with dry and warm air. Do not frequently use local antiseptics in the form of sprays. Cold drinks and foods can be consumed only in small quantities so that the mucous membranes get used to low temperatures. It is necessary to increase the body's defenses. To do this, you can make an appointment with an immunologist who will prescribe medications that stimulate cellular and humoral immunity, immunomodulators of bacterial origin, and a complex of vitamins.
Prevention of complications
Taking into account what complications can occur after a sore throat, the need for thoughtful preventive measures becomes obvious. Following a few simple recommendations will prevent serious health consequences. So, how to avoid complications after a sore throat?
- It is necessary to maintain bed rest until the symptoms from the oropharynx finally go away, even if the temperature is within normal limits.
- Local treatment aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease should include lubrication of the affected tonsils and rinsing.
- After suffering from a sore throat, you should refrain from vigorous physical activity for some time and try not to get too cold.
It is very important to follow the diet and nutrition recommendations given by the doctor. He should explain what complications occur after a sore throat and how to avoid them.
How is angina transmitted?
Pathogenic microorganisms live in the tonsils of every person, including absolutely healthy ones, usually without manifesting themselves in any way. But if any provoking factors arise, the pathogenic microflora is activated, as a result of which the tonsils become inflamed and a sore throat develops.
Typically, the peak incidence occurs in the winter and off-season, when people cough and sneeze especially often. This is due to the fact that sore throat is transmitted by airborne droplets. You can become infected from a loved one through a kiss or sharing personal hygiene items.
Complications after a sore throat
For a disease such as tonsillitis, treatment in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations is a guarantee that the disease will not provoke the development of more serious pathologies. In practice, many people come to the doctor when it becomes impossible to turn away from the consequences of tonsillitis caused by viruses.
Any inflammatory process in the throat area is fraught with a potential threat, even if the course of the disease at first seems mild. The body weakened by the virus is not able to resist bacterial infections (staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus). As a result, pathogenic processes spread to organs that are located not only near the larynx, but also far from this area.
A child may develop a retropharyngeal abscess, characterized by severe pain in the throat that worsens when he opens his mouth. If an abscess ruptures, pus enters the posterior mediastinum. In this case, posterior mediastinitis develops, the consequences of which are neuropsychic disorders and cardiovascular failure.
Sore throat can cause inflammation in the middle ear and parotid gland. Getting into the lymph and blood, the infection in some cases affects the joints, liver or kidneys.