Arlet® is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that contains two active components: a penicillin antibiotic of semi-synthetic origin (amoxicillin) and an inhibitor of bacterial beta-lactamase enzymes (clavulanic acid).
The antibiotic destroys the cell wall of bacteria, which leads to the death of bacteria, and clavulanate protects the antibiotic from destruction by beta-lactamases.
The drug is available in the form of tablets with different dosages of active ingredients, which makes it possible to regulate the intensity of therapy for different categories of patients.
Release form and composition
Dosage form – film-coated tablets: oblong, biconvex, white or almost white (in contour strip packs of 7 tablets, 2 packs in bags, 1 bag in a cardboard box; 14 tablets in dark glass jars, 1 jar in a cardboard box).
Composition of 1 tablet:
- active ingredients: amoxicillin – 250, 500 or 875 mg; clavulanic acid – 125 mg;
- auxiliary components: low molecular weight povidone, talc, pregelatinized starch, calcium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose;
- shell: hypromellose, propylene glycol, macrogol 4000, titanium dioxide.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- infectious mononucleosis or lymphocytic leukemia (there is a risk of exanthema);
- liver dysfunction (including jaundice) due to combined use of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid in the anamnesis;
- chronic renal failure with creatinine clearance (CC) less than 30 ml/min (only for tablets 875 mg + 125 mg);
- age up to 6 years (in the presence of chronic renal failure - up to 12 years);
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, as well as antibiotics of the cephalosporin and penicillin groups, and other beta-lactam antibiotics.
Relative:
- severe liver failure;
- chronic renal failure;
- diseases of the digestive system (including anamnestic data on colitis due to the use of penicillin);
- pregnancy period;
- breastfeeding period.
Analogues of the drug according to ATC codes:
AMOXICLAV AMOXICLAV AMOXICLAV AMOXICLAV KVIKTAB AMOXICILLIN+CLAVULANIC ACID AUGMENTIN AUGMENTIN PANCLAV RAPICLAV TRIFAMOX IBL FLEMOCLAVE SOLUTAB ECOCLAVE ECOCLAVE All
Before using ARLET, you should consult your doctor. These instructions for use are for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
Directions for use and dosage
Arlet is administered orally. In order to minimize undesirable reactions from the digestive system, the tablets are taken at the beginning of a meal: swallowed whole, without chewing.
The dosage regimen depends on the patient's age, weight, kidney condition, and the severity of the disease.
For children 6–12 years old (weight less than 40 kg), the following dosage regimen is recommended: 1 tablet 250 mg + 125 mg 2–3 times a day or 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg twice a day. For severe diseases, the dose may be doubled. The children's daily dose of amoxicillin is 20–30 mg/kg (maximum – 45 mg/kg), clavulanic acid – 5–7.5 mg/kg (maximum – 10 mg/kg).
It is important to understand that 2 tablets of 250 mg + 125 mg are not equivalent to 1 tablet of 500 mg + 125 mg. The content of clavulanic acid in them is twice as high.
Children 12 years old and adults (weight 40 kg or more):
- mild or moderate infections (except for diseases of the lower respiratory tract): 1 tablet 250 mg + 125 mg three times a day or 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg twice a day;
- severe infections (or lower respiratory tract infections): 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg three times a day or 1 tablet 875 mg + 125 mg twice a day;
- Oral infections: 1 tablet 250 mg + 125 mg three times a day or 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg twice a day for 5 days.
The maximum daily dose of amoxicillin is 6000 mg, clavulanic acid – 600 mg.
Treatment lasts at least 5 days. The duration of therapy is determined more precisely by the attending physician, but not more than 14 days without a second medical examination. Therapy for otitis media lasts 5–7 days.
Dosage regimen for special categories of patients:
- insufficiency of renal function with CC more than 10–30 ml/min: 1 tablet 250 mg + 125 mg twice a day for mild to moderate infections; 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg twice a day for severe infections and diseases of the lower respiratory tract;
- insufficiency of renal function with CC less than 10 ml/min: 1 tablet 250 mg + 125 mg once a day for mild to moderate infections; 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg once a day for severe infections and diseases of the lower respiratory tract;
- hemodialysis (adult patients): 1 tablet 500 mg + 125 mg or 2 tablets 250 mg + 125 mg every 24 hours. In addition, take an additional 1 dose during the dialysis session and at its end;
- hemodialysis (children): the dose is calculated based on the child’s weight - 15 mg/kg amoxicillin and 3.75 mg/kg clavulanic acid in one dose. In addition, take an additional 1 dose during the dialysis session and at its end.
For anuria, the interval between doses of Arleta should not be less than 48 hours.
Indications
Treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the drug:
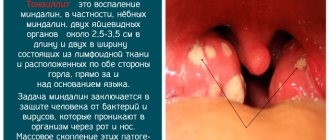
- infections of the upper respiratory tract and ENT organs (incl.
- acute and chronic sinusitis,
- acute and chronic otitis media,
- retropharyngeal abscess,
- tonsillitis,
- pharyngitis);
- lower respiratory tract infections (incl.
- acute bronchitis with bacterial superinfection,
- Chronical bronchitis,
- pneumonia);
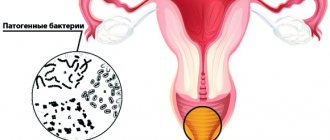
- urinary tract infections;
- gynecological infections;
- skin and soft tissue infections;
- infections of bone and connective tissue;
- biliary tract infections (cholecystitis,
- cholangitis);
- odontogenic infections.
Side effects
- digestive system: often - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, liver failure, increased activity of liver enzymes; rarely – hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis; very rarely - inflammation of the tongue, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, stomatitis, hemorrhagic/pseudomembranous colitis, enterocolitis, black “villous” tongue, darkening of tooth enamel;
- hematopoietic system: rarely - decreased number of leukocytes/neutrophils in the blood (reversible), decreased number of platelets, reversible agranulocytosis and hemolytic anemia; very rarely - increased duration of bleeding, anemia, increased number of eosinophils/platelet cells;
- central nervous system: often – dizziness, headache, increased activity, convulsions; very rarely - insomnia, agitation, anxiety, behavior change;
- urinary system: very rarely - the presence of blood in the urine;
- hypersensitivity reactions: infrequently - urticaria, erythema, itching; rarely – erythema multiforme; very rarely - Ritter dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis, Quincke's edema, symptoms arising from serum sickness, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, measles exanthema;
- other: often – superinfection (including candidiasis); rarely – increase in prothrombin time (reversible), crystallization of salts in the urine, interstitial nephritis, vasculitis.
special instructions
Before starting treatment, you need to make sure that the patient does not have hypersensitivity to penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics. If allergic reactions develop, taking Arleta should be discontinued. For severe hypersensitivity reactions, adrenaline (epinephrine) is administered. Oxygen therapy, intravenous corticosteroids, and intubation to ensure airway patency may also be required.
Cases of necrotizing colitis have been identified in newborns whose mothers took amoxicillin and clavulanic acid for prophylaxis during pregnancy with antepartum rupture of membranes.
During the treatment of diarrhea caused by the bacterium Clostridium difficile, it is not recommended to use drugs that reduce intestinal motility. It is permissible to take medications containing kaolin or attapulgite for diarrhea.
After the patient’s condition improves, it is recommended to take Arlet for another 48–72 hours.
The active ingredients of the drug can cause a false-positive reaction when performing an antiglobulin test, as well as a test for glucose in urine using copper sulfate (Benedict's reagent or Fehling's solution). When performing a urine glucose test, it is recommended to use enzymatic glucose oxidase methods.
Patients taking Arlet concomitantly with anticoagulants require constant monitoring, since the possibility of an increase in prothrombin time cannot be ruled out.
When taking large doses of amoxicillin, drink more fluids and maintain normal diuresis to minimize the risk of amoxicillin crystal formation.
Due to the growth of microflora insensitive to the active substances of the drug, the development of superinfection, which requires a change in antibacterial therapy, cannot be ruled out.
During the period of treatment, care must be taken when operating mechanisms that require increased concentration.
Pharmacokinetics
The main pharmacokinetic parameters of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid are similar.
Suction
After taking the drug orally, both components are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; food intake does not affect the degree of absorption. Cmax in blood plasma is achieved 1 hour after taking the drug and is (depending on the dose) for amoxicillin 3-12 mcg/ml, for clavulanic acid - about 2 mcg/ml.
Distribution
Both components are characterized by a good volume of distribution in body fluids and tissues (including lungs, middle ear, pleural and peritoneal fluids, uterus, ovaries). Amoxicillin also penetrates into the synovial fluid, liver, prostate gland, tonsils, muscle tissue, gall bladder, secretions of the paranasal sinuses, saliva, and bronchial secretions.
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid do not penetrate the BBB when the meninges are not inflamed.
The active substances penetrate the placental barrier and are excreted in breast milk in trace concentrations. The degree of binding to plasma proteins is low.
Metabolism
Amoxicillin is partially metabolized, clavulanic acid appears to be extensively metabolized.
Removal
Amoxicillin is excreted by the kidneys almost unchanged by tubular secretion and glomerular filtration. Clavulanic acid is excreted by glomerular filtration, partly in the form of metabolites. Small amounts may be excreted through the intestines and lungs.
T1/2 amoxicillin and clavulanic acid - 1-1.5 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In severe renal failure, T1/2 increases to 7.5 hours for amoxicillin and to 4.5 hours for clavulanic acid. Both components are removed by hemodialysis and minor amounts by peritoneal dialysis.
Drug interactions
- antacids, glucosamine, aminoglycosides, laxatives: slow down and reduce the absorption of Arleta;
- ascorbic acid: improves drug absorption;
- antibacterial agents (including cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, rifampicin, vancomycin, cycloserine): mutually enhance the effect;
- bacteriostatic drugs (chloramphenicol, tetracyclines, lincosamides, macrolides): mutually weaken the effect;
- indirect anticoagulants: their activity increases;
- allopurinol: increased incidence of exanthema;
- hormonal contraceptives, drugs that form para-aminobenzoic acid, ethinyl estradiol: their effectiveness decreases;
- allopurinol, diuretics, phenylbutazone, tubular secretion blockers: increase the concentration of amoxicillin;
- methotrexate: its toxicity increases.