Chronic rheumatic disorders include deforming osteoarthritis (DOA), in which dystrophic abnormalities occur in the bone joints. Injury to the joints of the upper and lower extremities is predominantly observed, as a result of which bone growths appear on the arms and legs. The development of grade 1 DOA is extremely difficult to notice on your own, since the main clinical picture appears in the later stages. A timely visit to a doctor is required, who will diagnose deformational osteoarthritis and select individual treatment.
If the causes of the disease are not identified in time and therapeutic measures are not taken, then multiple damage to the joints with subsequent disability is possible.
Description of the disease
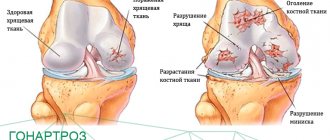
Deforming osteoarthritis is a degenerative-dystrophic pathology that most often affects large joints - ankle, hip, knee, shoulder. First, the cartilage lining the surfaces of the bones is damaged. Due to malnutrition, they cannot retain the moisture necessary for their restoration. The cartilaginous layers become thin, dense, and covered with cracks. When bending and straightening the joint, they “cling” to each other, which further injures them.
Now the cartilage does not properly perform its shock-absorbing functions, so the bone surfaces are gradually destroyed. They grow with the formation of growths - osteophytes. These sharp thorns injure soft tissues, pinching nerve endings and blood vessels, further aggravating the course of the disease.
Causes of deforming osteoarthritis
Primary deforming osteoarthritis is a pathology that develops without any reason. Secondary disease is often triggered by increased stress on the joint. Because of them, microtraumatized tissues do not have time to recover, which becomes the impetus for the destruction of the cartilage layer. Researchers also identify the following reasons for the development of osteochondrosis:
- previous injuries - fractures, dislocations, muscle ruptures, damage to the ligamentous-tendon apparatus;
- endocrine diseases, for example, diabetes, hypothyroidism;
- circulatory disorders in the joint area;
- systemic inflammatory pathologies - scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, gout, rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis occurs against the background of natural aging of the body, including as a result of weakening of ligaments and tendons. Factors that provoke it include low physical activity, obesity, smoking, and deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body.
Risk factors
- hereditary predisposition to increased traumatism,
- weight gain,
- age-related changes,
- belonging to specific professions that require additional physical stress on the skeleton,
- infectious diseases,
- hormonal imbalance,
- joint injuries,
- process of breakdown in connective tissue.
Fact. Composition of human bone tissue: 52% - water 22% - inorganic compounds 12% - organic compounds 14% - fatty compounds
Bone tissue is regenerated every 7 years.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
Deforming osteoarthritis is characterized by an asymptomatic course at the initial stage of development. As the joint deteriorates, the first pain appears. They are mild and usually occur after physical exertion. The intensity of pain slowly but steadily increases. They are accompanied by other symptoms of pathology:
- swelling of the joint in the morning;
- stiffness of movement within 30 minutes after waking up;
- crunching, clicking when bending and straightening the joint.
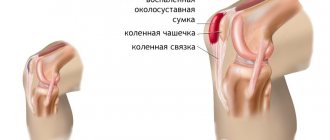
The course of osteoarthritis is often accompanied by synovitis - inflammation of the synovial membrane. In such cases, the patient’s general well-being worsens, up to the appearance of chills and fever.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of the pathological process consists of avoiding overload of the joints, complete treatment of injuries and certain diseases: flat feet, dysplasia, scoliosis. The patient is recommended to increase the frequency of sports activities - to the extent of the body’s strength and capabilities, and to control his own body weight.
The progression of deforming osteoarthritis depends on the form of the disease, location, age and general condition of the body. Damage to the joints can lead to loss of ability to work and disability. The therapy allows you to eliminate pain and partially restore the functions of the organ, but it is almost impossible to achieve complete recovery without installing an implant. Only timely treatment will allow you to catch the problem in the early stages, prevent its development and possible complications.
Diagnostic principles
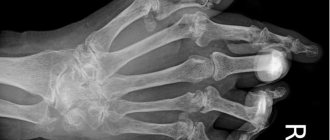
Symptoms of deforming osteoarthritis can mask bursitis, tendinitis, and arthritis. Therefore, it is difficult to make a diagnosis based on the results of an external examination and anamnestic data. The most informative is radiography, which helps not only to identify osteoarthritis, but also to establish its stage and the nature of its course. All radiographic signs of the disease are visualized on the images obtained in two projections:
- narrowing of the joint space;
- formation of single or multiple osteophytes;
- deformation of bone surfaces with the formation of cysts;
- subchondral osteosclerosis.
The results of other instrumental studies - ultrasound, CT, MRI - will allow a more detailed assessment of the condition of the cartilage. If necessary, joint puncture is performed with biopsy samples taken for further morphological study.
Treatment prices
Pricing for the provision of qualified medical care depends on:
- The nature and number of diagnostic studies.
- Qualifications of medical personnel.
- The chosen treatment regimen (cost of medications, endoprostheses, aids).
- Territorial affiliation of the medical institution.
- Conditions for providing medical care (outpatient or inpatient).
- Accreditation of an institution providing medical care.
How to cure deforming osteoarthritis
The main goals of treatment for deforming osteoarthritis are to eliminate all symptoms and prevent the spread of the destructive-degenerative process to healthy cartilage, bones, and ligaments. An integrated approach to therapy is practiced. Patients are prescribed medications, massage, electrophoresis with anesthetics, and exercise therapy. For orthopedic correction, they are recommended to wear soft, semi-rigid, and in some cases, rigid orthoses.
Drug therapy
For acute pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - Meloxicam, Voltaren, Ketorolac - are administered intramuscularly. If the use of injection solutions turns out to be ineffective, patients are prescribed drug blockades with glucocorticosteroids (Diprospan, Triamcinolone, Methylprednisolone) and anesthetics (Novocaine, Lidocaine). Moderate pain is relieved by taking NSAID tablets. These are Celecoxib, Nise, Etoricoxib, Ketorol, Ibuprofen. The following drugs are also used in the treatment of deforming osteoarthritis:
- muscle relaxants - Sirdalud, Mydocalm, Baklosan, Tolperisone;
- means to improve blood circulation - Pentoxifylline, Eufillin, Xanthinol Nicotinate;
- preparations with B vitamins - Combilipen, Milgamma, Neuromultivit.
Treatment regimens include chondroprotectors Artra, Teraflex, Structum, Chondroxide, Alflutop. In case of grade 1 osteoarthritis, they partially restore cartilage tissue, in other cases they slow down degenerative changes in all articular structures.
Local
Ointments, gels, balms, including dietary supplements, are used to eliminate mild pain. They usually occur during a period of remission after hypothermia, increased physical activity, during influenza or ARVI. External painkillers can also be prescribed in the subacute period to reduce doses of systemic drugs, which often have a toxic effect on internal organs.
| Ointments for the treatment of deforming osteoarthritis | Names of medicines | Therapeutic effect |
| NSAIDs | Voltaren, Ortofen, Fastum, Bystrumgel, Dolgit, Diclofenac, Artrosilene, Indomethacin | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory |
| Products with a warming effect | Capsicam, Viprosal, Capsicam, Nayatox, Apizartron, Turpentine ointment, Efkamon | Improves blood circulation, analgesic |
| Chondroprotectors | Chondroitin-Acos, Chondroxide, Theraflex | Stimulating partial restoration of cartilage |
| dietary supplement | Balms Dikulya and Sofya, Arthrocin, Arthro-Active, Shark oil, Honda | Improves overall joint health |
Physiotherapy
In the acute and subacute period of deforming osteoarthritis, electrophoresis and ultraphonophoresis with glucocorticosteroids, anesthetics, and B vitamins are used. After relief of acute pain, patients are prescribed up to 10 sessions of the following physiotherapeutic procedures:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- shock wave therapy;
- applications with paraffin;
- ozokerite treatment.
After a course of physiotherapy, the blood supply to the damaged joint with nutrients improves. The regeneration of soft tissue structures is accelerated, destructive processes are slowed down or completely stopped.
Diet
Nutritionists recommend that patients reduce the amount of salt or completely abandon it. It is also necessary to drink about 2.5 liters of liquid daily - clean water, lightly salted mineral waters (Slavyanovskaya, Smirnovskaya, Essentuki No. 2), berry fruit drinks, vegetable juices, fruit jelly and compotes.
Diet as a treatment method is indicated for patients with excess body weight. They need to lose weight to reduce the load on the joints affected by osteoarthritis. To do this, you should avoid fatty, fried foods, sausages and confectionery products. Instead, your diet should include fermented milk products, fresh vegetables, fruits, and herbs.
Surgical method of treatment
For grade 3 deforming osteoarthritis, orthopedists immediately offer patients surgical intervention. Indications for surgery include pain that cannot be eliminated with medication, and rapid progression of the pathology. The most popular and therapeutically effective is unipolar or bipolar endoprosthetics. This is the name given to replacing a damaged joint with an artificial implant. The average service life of an endoprosthesis is 15 years. After endoprosthetics and rehabilitation, the patient can lead an active lifestyle and perform professional duties.
If there are contraindications to joint replacement, then arthrodesis is performed. The joint structures are fixed in a functionally advantageous position so that the patient can move with crutches and perform simple movements.
Therapeutic gymnastics and its role
Pharmacological drugs often only eliminate the symptoms of osteoarthritis, and daily exercise therapy prevents their occurrence. This becomes possible due to the multifaceted effects of dosed loads on damaged joints:
- improve blood circulation, eliminate nutritional deficiencies;
- strengthening the muscle corset, stabilizing cartilaginous and bone structures;
- improving the condition of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus.
Regular training helps to get rid of stiffness in movements and increase their amplitude. Posture improves and loads are distributed correctly when walking. Physical therapy is the most effective way to treat and prevent deforming osteoarthritis.
Traditional methods
In the treatment of osteoarthritis of any localization, homemade ointments, alcohol and oil rubbing, compresses, and applications are used. Particularly in demand are teas made from medicinal plants, which have a mild calming effect and improve a person’s psycho-emotional state. Tinctures with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties are also useful. Here are the most therapeutically effective folk remedies for osteoarthritis:
- put 0.5 teaspoon of dry leaves of lemon balm, mint, oregano into a ceramic teapot, pour in a glass of boiling water. After an hour, strain, add a little flower honey, take 100 ml 2 times a day;
- Fill a dark glass container 1/3 with fresh horseradish leaves and roots, add a couple of pods of red hot pepper. Pour vodka up to the neck and leave for 1-2 months. Rub in for pain.
Folk remedies are used only during the remission stage, after the main treatment. Their use in the acute and subacute period of osteoarthritis can distort the effect of pharmacological drugs.
Preventive measures
Prevention of deforming osteoarthritis also involves weight control, moderate physical activity and good nutrition. For this purpose, the diet of not only sick, but also healthy people should include:
- All types of dairy products;
- Chicken and quail eggs;
- Jelly and jellied meats - they contain collagen, which is necessary for cartilage tissue;
- Various cereals;
- Fruits and vegetables;
- River and sea fish;
- Various types of vegetable oils;
- Nuts, raisins, whole grain and bran bread.
All this will help to avoid the development of a serious disease that requires constant systematic treatment.
It is possible to cure osteoarthrosis deformans only in the initial stage, but doctors rarely manage to catch the disease during this period, since patients do not perceive mild symptoms as something threatening. They seek medical help at the second or third stage, when only relative stabilization of the situation is possible, allowing them to achieve a more or less long-term remission.
Possible consequences
Muscle wasting gradually develops, contractures occur (limitation of passive movements in the joint). When the joints of the legs are affected, this leads to functional shortening of the limb, a noticeable limp when walking, and in the absence of medical intervention, to complete immobility (ankylosis).
Complications of deforming osteoarthritis also include spontaneous hemarthrosis (bleeding into the joint cavity), secondary reactive synovitis.