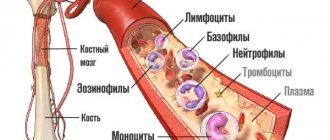
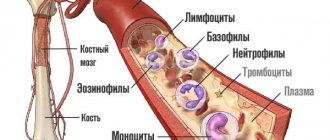
Blood is a functional system that ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissue cells and the removal of metabolic products from organs and intertissue spaces. It consists of plasma and formed elements: red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets.
Anisocytosis is a condition in which red blood cells of abnormal size are detected in the blood.
Red blood cells are biconcave disc-shaped cells without a nucleus that provide transport of respiratory gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide), amino acids, hormones, and also maintain blood pH levels.
Red blood cell distribution width by volume (RDW) is a calculated indicator reflecting the degree of heterogeneity of red blood cells by volume, an indicator of anisocytosis, which means the appearance of larger or smaller cells in a blood test, in contrast to the norm.
In human blood, red blood cells can have the following sizes:
- normocytes with an average diameter of 7.5 µm (7.2–7.7 µm): up to 75%;
- microcytes: ~12.5%;
- macrocytes: ~12.5%.
Under various physiological and pathological conditions, the composition of the blood and the percentage of cells in it change. In diagnosing changes in the qualitative and quantitative composition of blood, the morphological characteristics of red blood cells are used. They are assessed using an automatic analyzer (erythrocyte indices: MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW) or visually - in a blood smear under a microscope. To do this, a clinical (general) blood test is taken from a vein or finger.
To accurately determine the erythrocyte index, modern hematological analyzers must be used
Modern hematology analyzers maintain cell stability, which is difficult to achieve with manual counting. This is due to the smear drying out under the microscope and the diameter of the red blood cells decreasing by 10–20%. Therefore, assessing the degree of anisocytosis under a microscope may be erroneous.
What is RDW
Red blood cell distribution width (RDW) is the change in size (volume) of red blood cells (RBCs). Basically, this test tells you how equal or unequal your red blood cells are in size. The RDW is part of a complete blood count that also measures hemoglobin , hematocrit, and red and white blood cell counts. [, ]
LEFT – ALMOST THE SAME SIZES OF RED CELLS (RDW – NORMAL), RIGHT – SIZES OF RED CELLS VARY GREATLY (RDW – NOT NORMAL)
Low RDW values mean your red blood cells are about the same size, which is normal and desirable. But higher RDW values mean that your red blood cells are produced in different sizes. In other words, there are some problems with the production and survival of red blood cells. [, , ]
value is important , but not specific (not indicating a specific disease) value, therefore the width of the distribution of erythrocytes by volume is used in conjunction with other blood indicators.
Therefore, along with RDW, blood tests also measure such indicators as: MCV (average erythrocyte volume), MCHC (average hemoglobin concentration in an erythrocyte).
How the research works
In modern medicine, equipment plays an important role in treatment. the same can be said about a blood test. On an empty stomach, blood is drawn either from a vein in the elbow or from a finger (this method is especially often practiced in the case of children), and then all the work is transferred to a modern analyzer, which conducts research quickly and with high quality, giving an accurate result .
It counts the number of red blood cells of different sizes per microliter of blood, calculates the average cell size and determines the degree of deviation from the norm of this indicator. The largest and smallest cells are also measured and the difference between this spread and the possible norm is analyzed. This indicator is recorded in femtoliters.
Of course, the equipment may not always be accurate; maximum accuracy of results can only be obtained by manual counting, but this is a very long and labor-intensive process, which is practically not used in modern medicine.
If deviations in this indicator occur, the blood test is performed again to obtain a reliable result, because the diagnosis cannot be made as a result of a single blood sample.
RDW increased: association with diseases
Elevated RDW values may indicate, but do not diagnose or confirm, the following diseases: [, , , ]
- Lack of iron in the body or vitamin deficiency
- Lack of B vitamins, including B12 and folic acid
- Anemia (various types, including sickle cell anemia)
- Inflammation
- Insomnia
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Blood loss due to hemorrhage (including surgery)
- Thalassemia
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Cancer
- Alzheimer's disease
- Alcoholism
- and others.
However, RDW may still be at normal levels in people with leukemia , or with certain types of anemia (such as aplastic anemia ).
Therefore, it is important to look not only at the RDW value, but also at the relationship with other markers. []
Signs
In the event that deviations in the activity of the circulatory system become more than minor changes, the human body gives certain alarm signals.
In any case, adjusting your diet or starting to treat the pathological process at an early stage is easier than bringing the matter to a critical stage.
The following symptoms may indicate an increase in RDW in the body:
- a strong increase in temperature of a systematic nature;
- excessive sweating;
- decreased activity, general fatigue, drowsiness;
- sudden changes in mood for no apparent reason;
- in some cases, the skin acquires a yellow tint.
If the symptoms listed above are noted, then there is no need to self-medicate or think that everything will go away on its own. It’s not worth much effort to see a doctor and get tested at the nearest laboratory or clinic. It is impossible to allow the occurrence of such consequences that can manifest themselves with the development of anisocytosis to the second, third and fourth degrees.
It is very important to understand the significance of a general blood test. RDW is often elevated, but only a qualified specialist is able to make the correct diagnosis based on the information received. In this case, it will also help to add possible additional signs that may worry the patient. Naturally, it is much easier to prevent a disease or eliminate it at an early stage.
Normal RDW values
Normal RDW values are the same for men and women. The range of normal RDW in adults is 11.5 – 15.5% , but may vary slightly depending on the reagents used by different laboratories.
In newborn children, normal RDW values are increased to 14.9 – 18.7% due to stress at birth and adjustment to life outside the mother. But as children grow older, their normal RDW values gradually approach those of adults.
At the same time, with age, red blood cells become more varied in size (volume), which leads to an increase in RDW. []
Degrees of anisocytosis
Erythrocyte anisocytosis is divided into four stages:
- I degree. Diagnosed when 27% or 50% of red blood cells have a different volume.
- II degree. Occurs when 55% or 70% of red blood cells have a change in size.
- III degree. More than 75% of blood cells are modified and have different dimensions.
- IV degree. Almost 100% of blood cells are different from normal.
Clinical analysis reveals blood levels of rdw, ranging from a slight degree to a pronounced degree, when the highest percentage of deviation from the blood flow composition standards is detected. In ideal condition, the size of red blood cells should vary between 7-9 micrometers. According to the degree of change in the size of red blood cells in one direction or another, anisocytosis is classified into:
- Macroanacitosis - a larger number of red blood cells of increased volume.
- Microanacitosis is the predominant number of red blood cells of small diameter.
- Mixed type, combining macrocytes and microcytes.
There are also megalocytes, which have the maximum possible blood cell size of more than 12 microns. Macrocytes are red blood cells whose size is more than 8 microns. Their normal amount should be in the range of 12−15%. Microcytes include blood cells smaller than 6.9 microns. Mixed anisocytosis is characterized by the presence of both reduced and enlarged blood cells in the bloodstream. Combined studies are carried out using the calculation method using the Price-Jones curve.
RDW reduced
A low RDW value indicates that your red blood cells are uniform in size, which is desirable for health. [] However, it is worth remembering that there is still a possibility of having some kind of disease. []
For example, with reduced RDW values, one may suspect disturbances in the functioning of the spleen, where damaged red blood cells are recycled. In addition, if RDW is low, it is worth thinking about the following possible reasons:
- Recent surgery
- Blood donation
- Severe blood loss (including hidden in the stomach and intestines)
- Hormonal disorders during pregnancy, puberty, and when taking contraceptives
Treatment
If the erythrocyte distribution index is low or above normal, the first step should be to treat the underlying disease. In some situations, therapy is limited only to:
- changing your usual diet;
- refusal to consume alcohol;
- introducing foods fortified with iron and other micronutrients into the menu;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
In other circumstances, therapy will be purely individual:
- when cancerous tumors are detected, they turn to medical intervention, radiation treatment and chemotherapy;
- for gastrointestinal pathologies, drug tactics and diet therapy are used;
- myelodysplastic syndrome is eliminated through the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and other conservative methods.
Recovery is spoken of in such cases: improvement in well-being and complete absence of clinical signs, positive dynamics regarding changes in general blood test parameters.
RDW increased
A high RDW means your red blood cells (RBCs) are unequal in size. This condition is called anisocytosis. [, ] This happens when, for some reason, you have trouble producing red blood cells.
Anisocytosis is determined by RDW and is classified according to red blood cell size along with MCV (mean erythrocyte volume):
- Anisocytosis with microcytosis (small red blood cells). Possible causes: iron deficiency, sickle cell anemia.
- Anisocytosis with macrocytosis (large red blood cells). Possible causes: deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, cytotoxic chemotherapy, chronic liver disease, myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Anisocytosis with normal erythrocyte sizes. Possible causes: iron deficiency, vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency, dimorphic anemia, sickle cell anemia, chronic liver disease, myelodysplastic syndrome.
ABNORMAL SHAPE AND SIZE OF RED CYTES
What measures to take?
What to do when the red blood cell distribution index is low?
A highly qualified doctor during a consultation will most likely ask the patient to take the test again, because the RDW indicator is almost never underestimated. Because this suggests that all cells are ideal in their parameters, but this cannot happen in principle. If the indicator is confirmed by repeated analysis, then a full examination of the body’s condition is carried out, paying special attention to oncological examinations.
Reasons for increasing RDW
Nutrient deficiency
Deficiencies of various nutrients can cause an increase in RDW, for example:
- Iron deficiency [, , , ]
- Folic acid deficiency []
- Vitamin B12 deficiency [, ]
This is because your body needs these nutrients to produce healthy red blood cells. Any of these deficiencies can eventually lead to anemia.
Inflammation
Some studies suggest that higher RDW values are associated with inflammation and higher levels of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 , IL-8 and TNF-alpha . [, , , , , , ]
Inflammatory cytokines can interfere with red blood cell production and thereby increase RDW. Additionally, oxidative stress , which often accompanies chronic inflammation, can reduce red blood cell lifespan and further increase RDW values. [, ]
High RDW has been found in people with diseases associated with inflammation, such as inflammatory bowel disease , celiac disease, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and major depressive disorder (MDD). [, , , ]
REASONS FOR INCREASING RDW
Sleep disorders
In a study of 17,500 adults, those who slept less or more than 7-8 hours a night were more likely to have high RDW values. This was especially true for people who slept 10 hours a night - their chances of having increased RDW increased by almost 70%. []
RDW values are higher in people with sleep apnea . [, ]
RDW rates were also associated with shift work with circadian rhythm . In a study of 7,000 women, those who worked shift shifts were almost 50% more likely to experience an increase in RDW compared to women who worked day shifts. []
Bleeding
Severe and moderate injuries with heavy bleeding increase RDW. [] Bleeding may not be visible, as is the case with intestinal and gastric bleeding. [, ]
Blood transfusion
If a person undergoes multiple blood transfusions, their RDW may increase due to differences in blood composition between the donor and recipient. [, ]
Liver disease
Increases in RDW occur in a variety of liver diseases, including hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, biliary cirrhosis, and liver cancer. []
An observational study of 423 adults with liver disease found that their RDW was significantly higher than that of healthy controls. []
In another study of 446 hepatitis B patients, increasing RDW levels corresponded with increased liver size (hepatomegaly) and increased inflammation. []
Kidney disease
One of the kidney hormones, erythropoietin, is needed for the maturation of blood cells. Problems with the production of this hormone occur with kidney disease, leading to the development of RDW. [] People with reduced kidney function have higher levels of RDW. []
Alcoholism
Alcoholics can exhibit high RDW values without liver disease. This is because alcohol can have a toxic effect on red blood cells. []
Thalassemia
Thalassemia may cause increased RDW values. However, patients with thalassemia may also demonstrate normal RDW levels. [, , ]
Sickle cell anemia and hereditary spherocytosis
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease. People with this disease have higher RDW values because many of their red blood cells are misshapen. []
Hereditary spherocytosis (Minkowski-Choffard disease), another disease in which red blood cells become misshapen, also causes increased RDW levels. [, ]
DISEASES IN WHICH RDW LEVELS INCREASE (https://medcraveonline.com)
Cancer
RDW rates are often higher in various types of cancer, including stomach cancer , liver cancer , colon cancer , and kidney cancer . [, , , ]
There are many factors in cancer that can interfere with the normal production of blood cells, including chronic inflammation and poor nutrition.
In cancer, RDW often increases with disease severity and metastasis . []
In a study of 25,000 people, the risk of cancer was 30% higher in those people who showed the highest RDW values compared to people with the lowest values. Postmenopausal women with the highest RDW values had a 22% increased risk of developing cancer. But no association was found between RDW values and cancer in premenopausal women. []
Cardiovascular diseases
According to a meta-analysis, an increase in RDW levels accompanies various cardiovascular diseases: acute coronary syndrome (including myocardial infarction ), coronary heart disease , peripheral arterial disease, arterial hypertension , as well as atrial fibrillation . Higher RDW values predict more negative outcomes for these diseases. []
Increased RDW has been associated with various types of cardiovascular disease in studies. [, , ]
In a study of 25,500 adults, each 1% increase in RDW resulted in a 13% increase in heart attack risk . Those people who showed low RDW values had a 71% reduced risk of having a heart attack (myocardial infarction) compared to people with the highest RDW levels. []
Elevated levels of RDW are associated with a high risk of cholesterol plaque building up in the arteries ( atherosclerosis ) in patients with hypertension . []
RWD is associated with autoimmune diseases
There is an association between high RDW levels and increased disease activity in autoimmune problems such as rheumatoid arthritis , lupus, psoriasis, Crohn's disease , Sjögren's syndrome, systemic scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis ( ankylosing spondylitis ). [, , , , , , ]
INCREASING RDW WITH INCREASING CROHN'S DISEASE/ULCERATIVE COLITIS ACTIVITY (https://www.wjgnet.com)
RWD and metabolic syndrome
People with higher levels of RDW show more advanced degrees of metabolic syndrome. This was found in studies involving more than 217,000 people. [, ]
RWD and diabetes risk
In a study that monitored more than 2,600 people with normal blood glucose levels over 4 years, high RDW values increased the risk of developing diabetes compared to people with low RDW. []
RWD and risk of dementia (dementia)
In a study of approximately 2,500 older adults, higher RDW values had an increased risk of dementia. This risk was significant in those people who were not anemic. []
RWD is associated with mortality
High RDW values increase inflammation and oxidative stress, which contribute to the risk of mortality. In various studies, adult (45+) hospital patients with elevated RDW levels demonstrated a higher risk of cardiovascular mortality, infection, and all-cause mortality . [, , ]
Additionally, in a review of 13 studies (involving 10,410 patients), low RDW was associated with a lower risk of mortality. []
RDW and depression
The study, which followed 43,226 patients with depression for 5.3 years, measured RDW values at the time of diagnosis and in subsequent contacts with doctors. It was found that patients with cardiovascular disease had more advanced depressive syndromes with increasing RDW . []
Types of analysis and when it is prescribed
To begin with, it is worth saying that the research method itself is heterogeneous.
Several modifications are used:
- RDW-CV. Characterized as a deviation of red blood cells from the average norm. It is used especially widely and shows the degree of violation. But it does not indicate the type of condition in a particular patient.
- RDW-SD. One more indicator. It is calculated as the difference between the smallest red blood cell in the population and the largest. Used to clarify the condition or pathological process.
The study is prescribed in most cases when there is a suspicion of diseases of the hematopoietic system.
Specific indications for diagnosis include:
- Inflammatory processes. Regardless of type and character. Infectious and autoimmune. Doesn't matter. The indicator will clarify the situation in both cases.
- Liver disorders. Including suspicions of hepatitis, cirrhosis and other abnormal conditions.
- Kidney disorders. Disturbances that relate to excretory function and filtration. There are quite a lot of options here. Subjectively, thoughts about the need for research may be prompted by lower back pain, urinary problems and other symptoms.
- Chest discomfort, blood pressure instability. Potentially, these signs indicate diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Headaches, disorders of cognitive activity, memory, quality and productivity of thinking.
It can be said that the level is examined in most suspicious cases. Because it is nonspecific and very often indicates inflammatory and all kinds of degenerative, destructive processes, regardless of type.
Ways to reduce RWD
First of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease - the cause of increased RDW values. Below are additional options that can help you improve your health and reduce your RDW.
Balanced diet
Eating a healthy and balanced diet helps prevent nutritional deficiencies. It is especially important that the diet contains the recommended amounts of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. [, , ] Correcting nutritional deficiencies can improve blood cell production and lower RDW values.
Reduce alcohol consumption
Reducing alcohol consumption may help reduce damage to red blood cells. [, ] Additionally, alcohol also reduces the absorption of nutrients such as vitamin B12 and folic acid, which are essential for the production of red blood cells. [, ]
More physical activity
People who do little or no physical activity show higher levels of RDW. [, ]
Exercise, including light intensity exercise, has been shown in research to improve RDW scores. [, , ]
In a study of more than 8,000 people, as the amount of exercise time per week increased, the risk of showing increased levels of RDW decreased by 11%. []
Quit smoking
Smoking increases oxidative stress. Higher RDWs are identified in smokers and are associated with the number of cigarettes smoked per day as well as the duration of smoking. []
Preparation for the procedure
Since taking blood for a general analysis does not imply anything unusual, and the study itself is carried out regularly for almost all people, preparation does not require a person to take any special measures, but no one has canceled the standard recommendations before taking tests so that the results are reliable and correctly reflect the clinical picture:
- The RDW test is taken in the morning and on an empty stomach. Dinner in the evening of the previous day before donating blood should be light and at least 8 hours should pass between the last meal and the test, and preferably 12
- It is highly not recommended to drink alcohol 2 days before the test, as it can significantly distort the results
- It is advisable to give up fatty and fried foods, which have a negative effect on the body, 2 days in advance.
- You should not take a blood test after physiological and x-ray procedures
- It is recommended to refrain from smoking one hour before blood collection.
- It is advisable to exclude any physical and emotional stress; before the analysis, a 15-minute break and complete calm are required.
- Particular attention must be paid to the medications you are taking. Almost any medicine can distort the results of a blood test, so before donating blood you need to consult with a specialist: you may have to stop taking the medicine for a while to get an accurate clinical picture, or simply take the drug after the test.
If a repeat blood test is prescribed, it must be taken at the same time (since the composition of the blood may depend on the body’s circadian rhythms) and in the same laboratory. This is due to the fact that units and methods of measurement may vary between laboratories. Only if all recommended measures are followed will the result of the study be correct.